Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Climate and Weather
Содержание
- 1. Climate and Weather
- 2. Polar regionsCool temperate latitudesSubtropicsTropical and monsoon regionsDesertsRainforestsMountains Content
- 3. Polar Regions Regions with a polar climate
- 4. Polar climate results in treeless tundra, glaciers, or a permanent or semi-permanent layer of ice.
- 5. Solar radiation has a lower intensity in
- 6. Temperate climate In geography, temperate latitudes
- 7. Within these borders there are many
- 8. The cool temperate type of
- 9. Cool temperate climate This climate is found
- 10. Deciduous trees (which lose their leaves
- 11. Changeable weather is characteristic of these
- 12. In subtropical climates the winters
- 13. TROPICAL A tropical climate is a
- 14. Geographic DistributionCoastal areas of southwest India, Sri
- 15. Слайд 15
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. DESERTS
- 18. A desert is a landscape
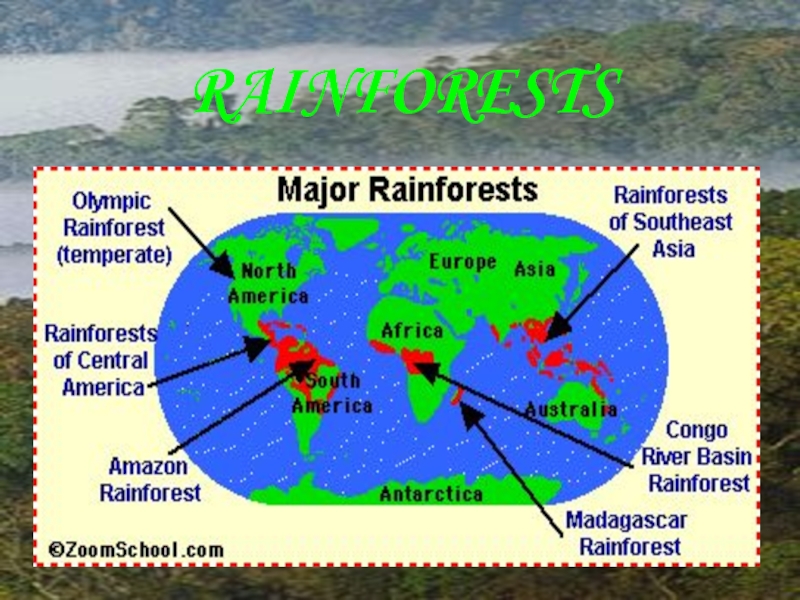
- 19. RAINFORESTS
- 20. Rainforests are forests characterized by
- 21. The largest tropical rainforests exist
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. MOUNTAINS Mountains cover 54% of Asia,
- 24. The highest mountains of each continent (the
- 25. Слайд 25
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. Скачать презентанцию
Polar regionsCool temperate latitudesSubtropicsTropical and monsoon regionsDesertsRainforestsMountains Content
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1CLIMATE AND WEATHER
Маслова Нина Александровна
Учитель английского языка ЦО 1828 «Сабурово»
г. Москва
Слайд 2Polar regions
Cool temperate latitudes
Subtropics
Tropical and monsoon regions
Deserts
Rainforests
Mountains
Content
Слайд 3Polar Regions
Regions with a polar climate are characterized by
a lack of warm summers. No month has an average
temperature of 10 °C or higher.The tundra covers over 20% of the earth. The sun shines 24 hours in the summer, and barely ever shines at all in the winter.
Слайд 4Polar climate results in treeless tundra, glaciers, or a permanent
or semi-permanent layer of ice.
Слайд 5Solar radiation has a lower intensity in polar regions because
it travels a longer distance through the atmosphere, and is
spread across a larger surface area.Слайд 6Temperate climate
In geography, temperate latitudes of the globe
lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes
in these regions between summer and winter are generally subtle, warm or cool, rather than extreme, burning hot or freezing cold. However, a temperate climate can have very unpredictable weather.Слайд 7
Within these borders there are many climate types, which
are generally grouped into six categories: oceanic, mediterranean, humid subtropical,
continental, arid and semi-arid.Слайд 9Cool temperate climate
This climate is found in much of
northwest Europe, New Zealand and coastal North America.
Слайд 10
Deciduous trees (which lose their leaves in winter) are
found in the warmer areas, and coniferous trees (with needle-type
leaves) are found everywhere.Слайд 11
Changeable weather is characteristic of these areas and they
are strongly influenced by large moving weather systems called depressions
or 'lows', and anticyclones or 'highs'.Слайд 12
In subtropical climates the winters are relatively warm,
but not as hot as the summer season. These climates
rarely—if ever—see frost or snow, and you can adore plants such as palm, citrus and many broadleaf evergreens flourish.Слайд 13TROPICAL
A tropical climate is a type of climate
typical in the tropics. Climate classification defines it as a
non-arid climate in which all twelve months have mean temperatures above 18°C (64.4 °F).Слайд 14Geographic Distribution
Coastal areas of southwest India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Mynamar
(Burma), Southwestern Africa, French Guiana, northeast and southeast Brazil.
Слайд 18
A desert is a landscape or region that
receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough
to support growth of most plants. Deserts are defined as areas with an average annual precipitation of less than 250 millimetres per year.Слайд 20
Rainforests are forests characterized by high rainfall. The
monsoon trough, alternately known as the intertropical convergence zone, plays
a significant role in creating Earth's tropical rain forests.Слайд 21 The largest tropical rainforests exist in the Amazon
Basin, in Nicaragua, the southern Yucatán Peninsula, in much of
equatorial Africa, in much of southeastern Asia, northern and eastern Australia.Слайд 23MOUNTAINS
Mountains cover 54% of Asia, 36% of North
America, 25% of Europe, 22% of South America, 17% of
Australia, and 3% of Africa. As a whole, 24% of the Earth's land mass is mountainous.Слайд 24The highest mountains of each continent (the Seven Summits):
Mountain
Peak Continent
HeightMount Everest Asia 8,850 m
Aconcagua South America 6,959 m
Mount McKinley North America 6,194 m
Kilimanjaro Africa 5,895 m
Mount Elbrus Europe 5,642 m
Vinson Massif Antarctica 4,897 m
Mount Kosciuszko Australia – Oceania 4,884 m
Теги