Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Содержание
- 1. ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
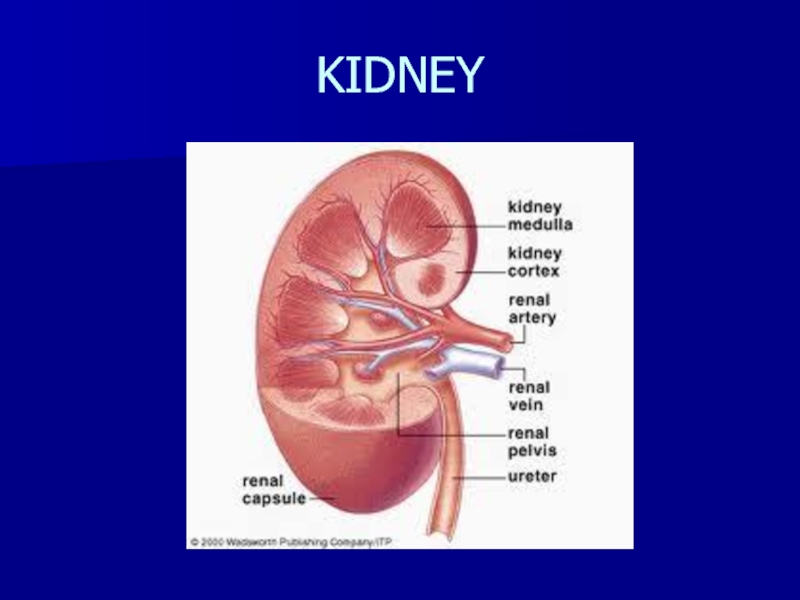
- 2. KIDNEY
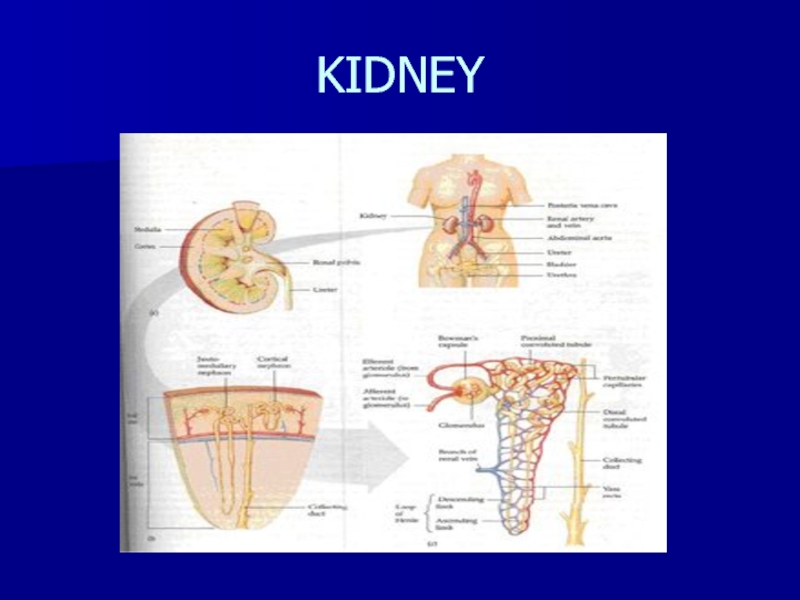
- 3. KIDNEY
- 4. URINE95% water, 5% soluteVolume is 1% of
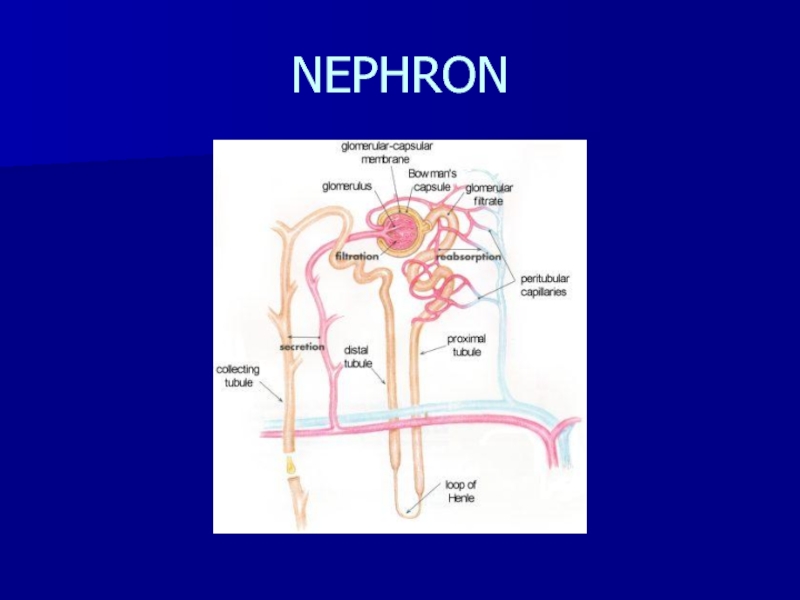
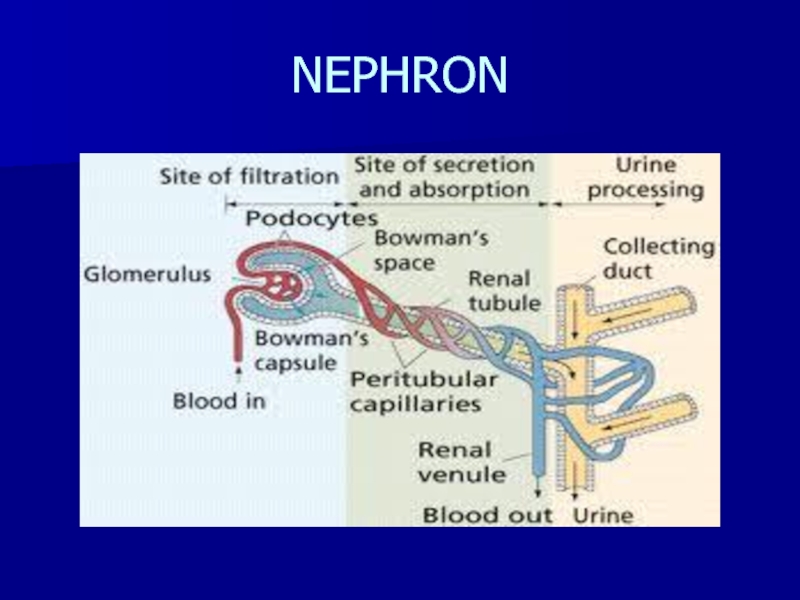
- 5. NEPHRONPrimary renal functional unitAbout 1 million nephronsglomerulus- filtering systemTubule- the filtered liquid passes through this
- 6. NEPHRON
- 7. GLOMERULUSCapillary network surrounded by a membrane (Bowman’s
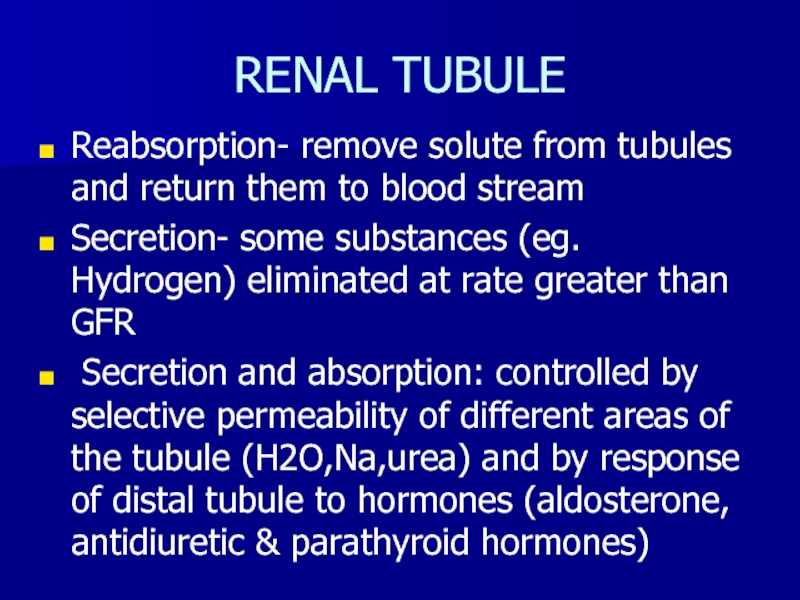
- 8. RENAL TUBULEReabsorption- remove solute from tubules and
- 9. NEPHRON
- 10. URINE VOLUMEBowman’s capsule- 100% filtrate producedProximal tubule-
- 11. CREATININEBy-product of muscle metabolismProduced at a fixed
- 12. RENAL FAILURELoss of renal functionUremia- retention of nitrogenous waste
- 13. ACUTE RENAL FAILURERapid onsetOften reversiblePre-renal, renal, post-renal
- 14. AZOTEMIARetention of nitrogenous waste reflected by an
- 15. AZOTEMIAFactors related to decreased Urea Nitrogen Excretion: Renal
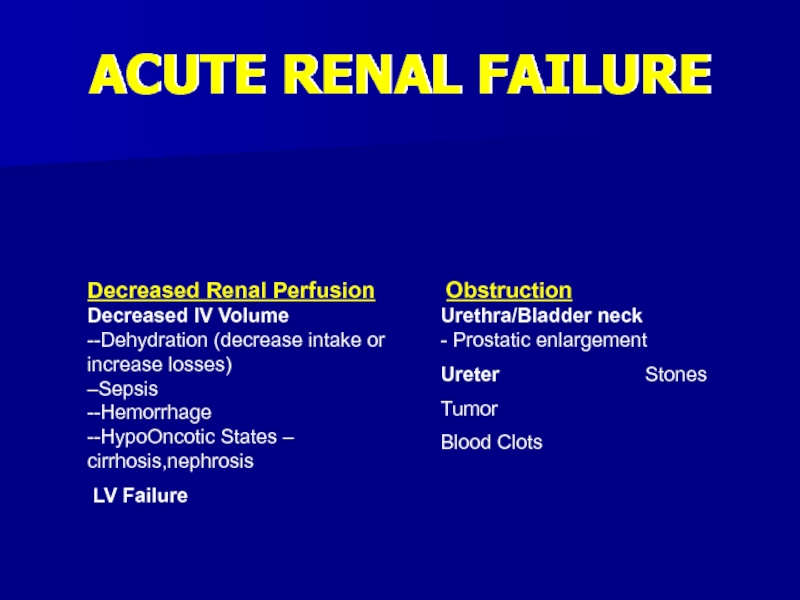
- 16. ACUTE RENAL FAILUREDecreased Renal Perfusion
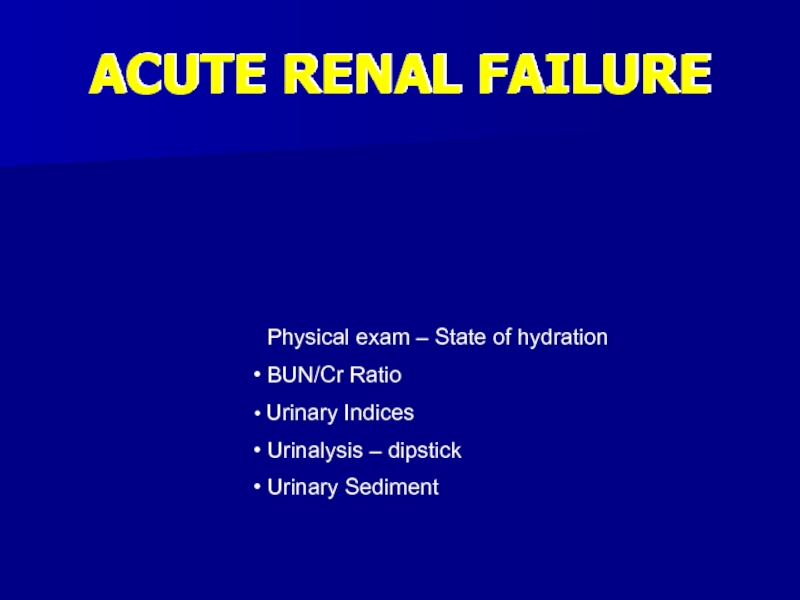
- 17. ACUTE RENAL FAILURE Physical Exam – State
- 18. Post-Renal FailureObstruction to flow of urineBilateralUnilateralLevelsBladder InletOutletUreters
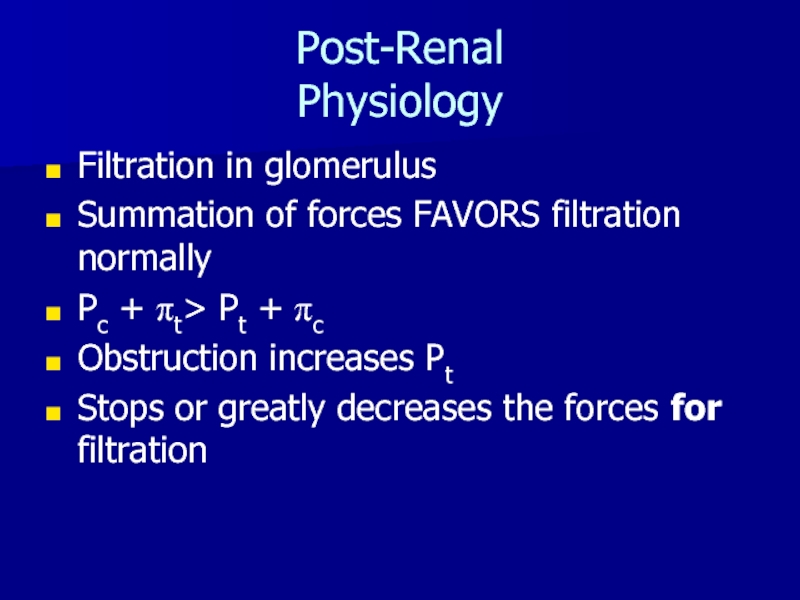
- 19. Post-Renal PhysiologyFiltration in glomerulusSummation of forces FAVORS
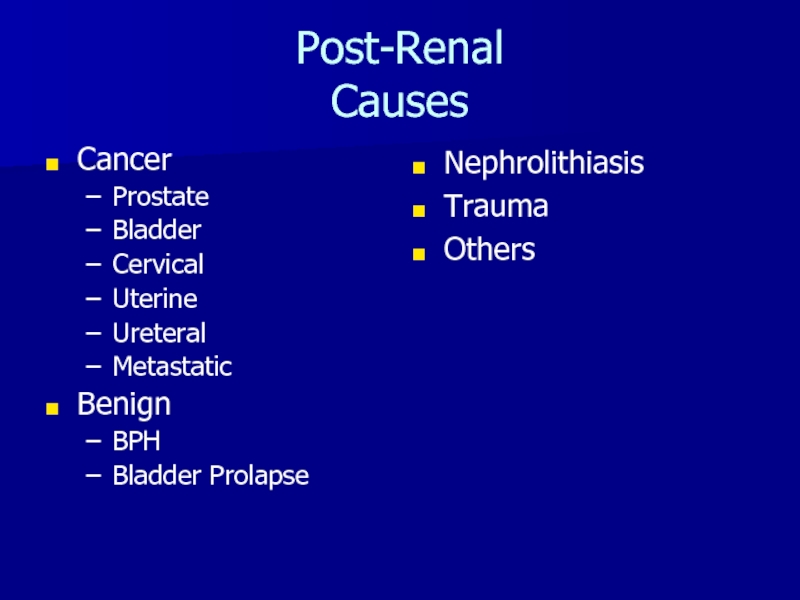
- 20. Post-Renal CausesCancerProstateBladderCervicalUterineUreteralMetastaticBenignBPHBladder ProlapseNephrolithiasisTraumaOthers
- 21. Pre-Renal FailureMost commonDecrease in perfusion of the nephronsOften iatrogenicEssentially decrease in Pc
- 22. Pre-Renal Failure CausesVolume depletionDiureticsGI lossesBleedingVomitingDiarrheaFree Water lossesHeat strokeInability to get to waterDecrease intravascular perfusionCirrhosis“Nephrosis”DrugsNSAID’s
- 23. ACUTE RENAL FAILURE Physical exam – State
- 24. ACUTE RENAL FAILURE Acute GN ATN AIN Arterial emboli Vasculitis
- 25. Intrinsic Renal FailureVesselsGlomerulusTubulo-interstitial
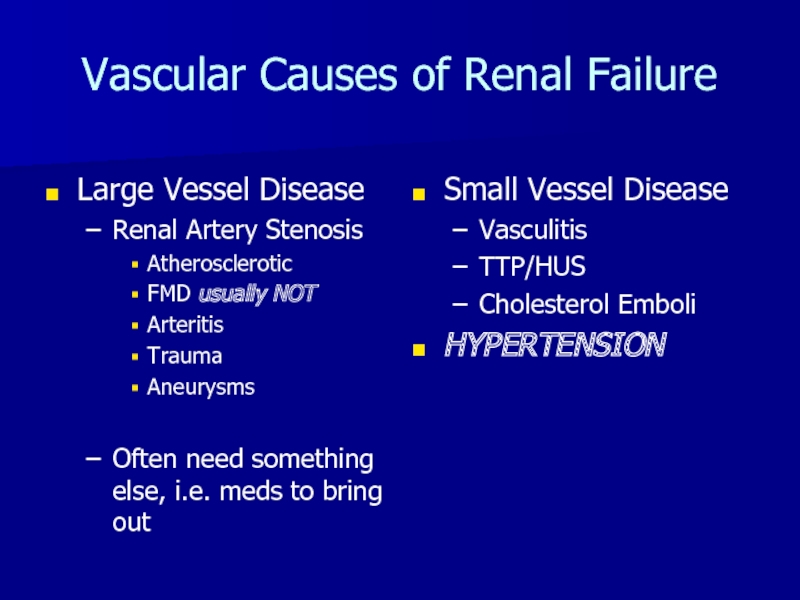
- 26. Vascular Causes of Renal FailureLarge Vessel DiseaseRenal
- 27. Glomerular GlomerulonephritisAcuteChronicPrimarySecondary
- 28. Secondary GNMost commonDiabeticHIV associated nephropathy (HIVAN)SLESystemic vasculitidesOthersCan be acute or chronic
- 29. Primary GNNil diseaseMinimal change diseaseFocal Segmental GlomerulonephritisMembranous nephropathyIgA (Berger’s Disease)Henoch-Schoenlein PurpuraMesangial GNMesangiocapillary GNCrescentic GN
- 30. Tubulo-Interstitial Renal DiseaseAcute INDrugsInfectiousIdiopathicChronic IN Balkan nephropathyAllergic Interstitial nephritis
- 31. ACUTE RENAL FAILURELABORATORYThe laboratory findings are used to confirm your clinical suspicion.
- 32. BASIC METABOLIC PROFILEBUNCreatinineSerum glucoseSodiumPotassiumChlorideCO2 = HCO3-
- 33. ACUTE RENAL FAILUREBUN/Cr Ratio> 20:1 10:1 VariablePotassiumTCO2Laboratory
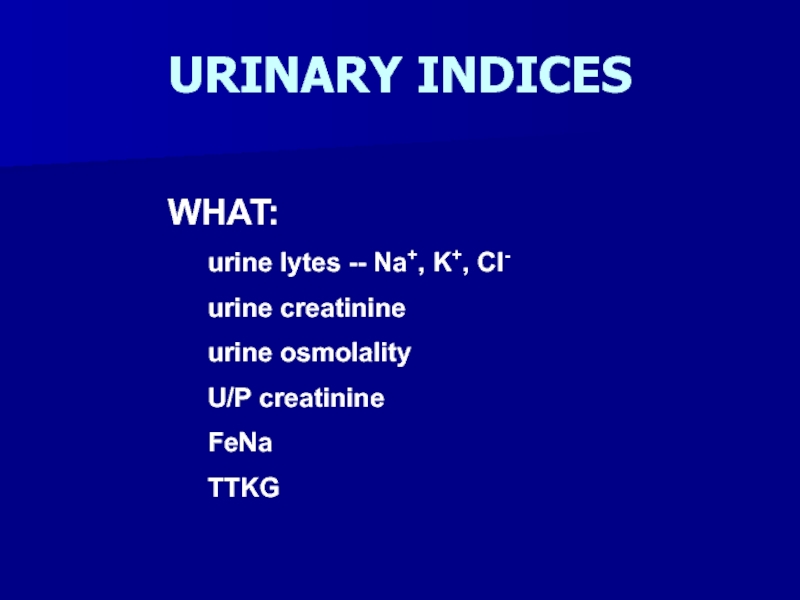
- 34. URINARY INDICES WHAT: urine lytes -- Na+, K+, Cl- urine creatinine urine osmolality U/P creatinine FeNa TTKG
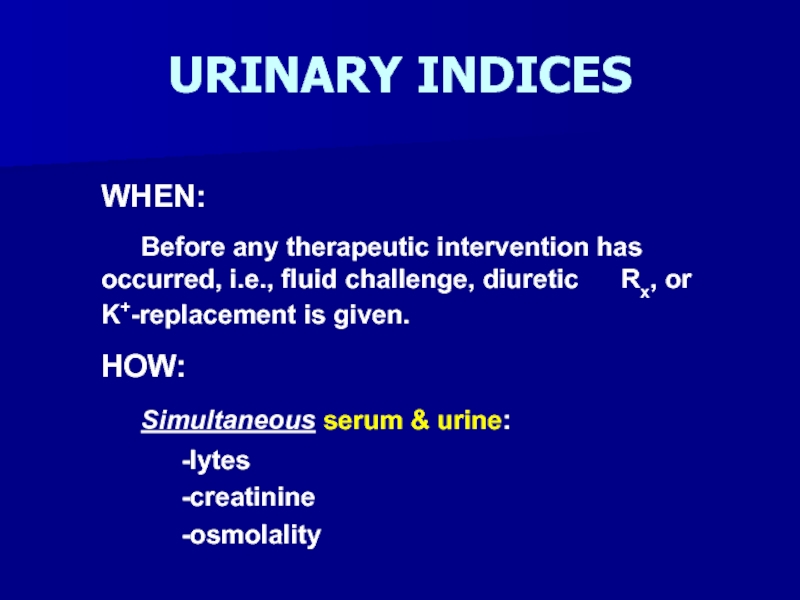
- 35. URINARY INDICESWHEN: Before any therapeutic intervention has occurred,
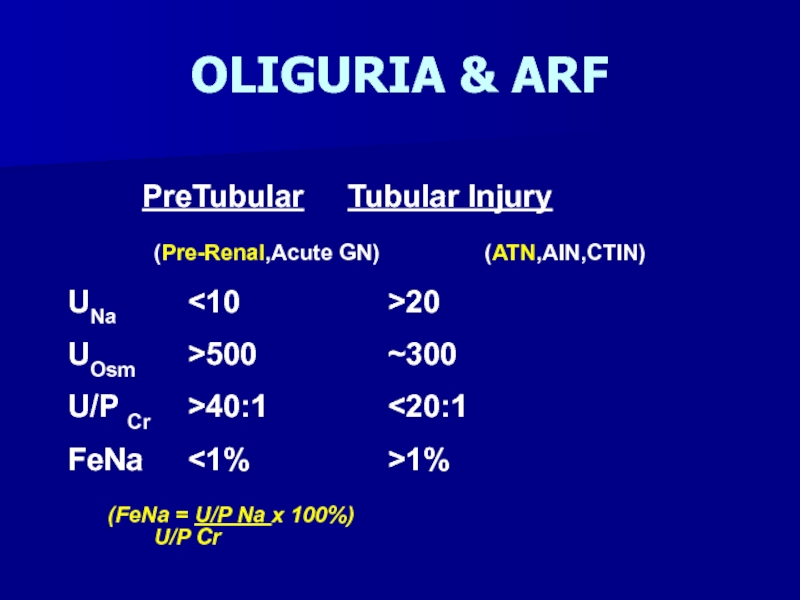
- 36. OLIGURIA & ARF PreTubular Tubular Injury
- 37. ACUTE TUBULAR NECROSISIschemic ATN – prolonged hypotension
- 38. Klahr, S. et al. N Engl J
- 39. RADIOCONTRAST NEPHROPATHY3rd leading cause of ARF in
- 40. MANAGEMENT OF OLIGURIADehydrated – IV NSS -fluid challenge -continuous
- 41. POTENTIAL OUTCOMES OF INTERVENTIONSuccessful Reversal of oliguriaPulmonary artery catheterization (Swan-Ganz Catheter)Dialysis
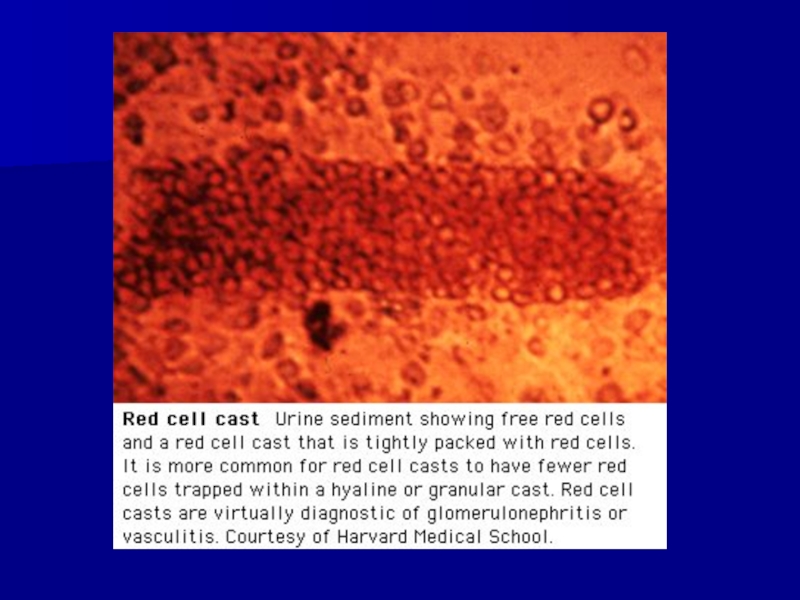
- 42. ARF DUE TO ACUTE GNHematuria (RBC’s +/- RBC casts)Proteinuria (albuminuria)HypertensionEdemaAzotemia
- 43. Слайд 43
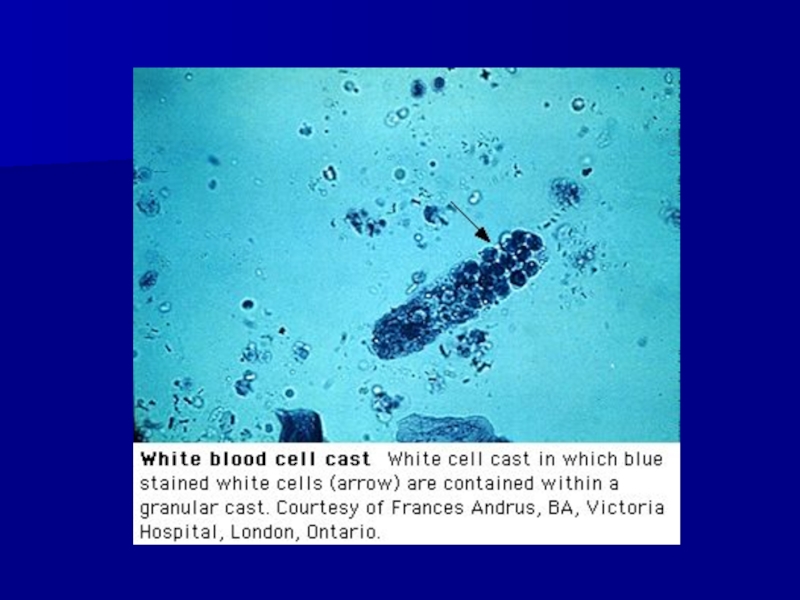
- 44. ARF DUE TO AINPyuria (WBC’s +/- WBC Casts) Tubular proteinuriaHypertensionEdemaAzotemia
- 45. Слайд 45
- 46. Acute vs. Chronic Renal FailureClinical determinationOnly really
- 47. Minimum Work-upU/A, C&SUrine eosinophilsRenal UltrasoundRenal Flow scan24
- 48. Full Work-up“Minimum” plus:ANA, C3, C4, ANCA, ASO
- 49. SummaryApproach renal failure patients as you would
- 50. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4URINE
95% water, 5% solute
Volume is 1% of total filtrate volume
About
25% of cardiac output is received (1200 ml/minute)
liters of urine excreted per dayСлайд 5NEPHRON
Primary renal functional unit
About 1 million nephrons
glomerulus- filtering system
Tubule- the
filtered liquid passes through this
Слайд 7GLOMERULUS
Capillary network surrounded by a membrane (Bowman’s capsule)
Afferent arteriole- blood
from renal artery
Efferent arteriole- formed from capillaries rejoining at the
distal glomerulusUrine formation begins in the glomerular capillaries with dissolved substances passing into the proximal tubule from the force of blood pressure in afferent arteriole and in Bowman’s capsule
Слайд 8RENAL TUBULE
Reabsorption- remove solute from tubules and return them to
blood stream
Secretion- some substances (eg. Hydrogen) eliminated at rate greater
than GFRSecretion and absorption: controlled by selective permeability of different areas of the tubule (H2O,Na,urea) and by response of distal tubule to hormones (aldosterone, antidiuretic & parathyroid hormones)
Слайд 10URINE VOLUME
Bowman’s capsule- 100% filtrate produced
Proximal tubule- 80% filtrate reabsorbed-
active and passive
Distal tubule- 9% filtrate reabsorbed- variable reabsorption and
secretionCollecting tubule- 4% filtrate reabsorbed- variable salt and water reabsorption
Слайд 11CREATININE
By-product of muscle metabolism
Produced at a fixed (constant) rate except
in situations of muscle diseases, abnormal muscle metabolism, or muscle
injury; e.g., rhabdomyolysis, crush injuryUseful for measuring GFR: -freely filtered -not reabsorbed -minimal proximal tubule secretion
Males – 20-25 mg/kg/d
Females -- 15-20 mg/kg/d
Слайд 14AZOTEMIA
Retention of nitrogenous waste reflected by an increase in BUN
(Normal = 10-15 mg%)
Factors that increase Urea Nitrogen Generation:
Dietary protein
intake (TPN/ETN) Hemolysis Hypercatabolic states Resorption of extravascular –fever blood collections –sepsis -GI Bleed –malignancy -Hematomas Catabolic drugs –steroids –tetracyclines
Слайд 15AZOTEMIA
Factors related to decreased Urea Nitrogen Excretion:
Renal Failure
Pre-Renal – increased
reabsorption
Renal Parenchymal – decreased filtration
Post-Renal – obstruction to elimination
Слайд 16ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Decreased Renal Perfusion Decreased IV Volume
--Dehydration (decrease intake
or increase losses) –Sepsis --Hemorrhage --HypoOncotic States – cirrhosis,nephrosisLV Failure
Obstruction Urethra/Bladder neck - Prostatic enlargement
Ureter Stones
Tumor
Blood Clots
Слайд 17ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Physical Exam – State of Hydration
BUN/Cr
Ratio
Urinary Indices
Urine analysis – dipstick
Urinary Sediment
Outlet
Renal
UltrasoundСлайд 18Post-Renal Failure
Obstruction to flow of urine
Bilateral
Unilateral
Levels
Bladder
Inlet
Outlet
Ureters
Слайд 19Post-Renal
Physiology
Filtration in glomerulus
Summation of forces FAVORS filtration normally
Pc + pt>
Pt + pc
Obstruction increases Pt
Stops or greatly decreases the forces
for filtrationСлайд 20Post-Renal
Causes
Cancer
Prostate
Bladder
Cervical
Uterine
Ureteral
Metastatic
Benign
BPH
Bladder Prolapse
Nephrolithiasis
Trauma
Others
Слайд 21Pre-Renal Failure
Most common
Decrease in perfusion of the nephrons
Often iatrogenic
Essentially decrease
in Pc
Слайд 22Pre-Renal Failure
Causes
Volume depletion
Diuretics
GI losses
Bleeding
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Free Water losses
Heat stroke
Inability to get to
water
Decrease intravascular perfusion
Cirrhosis
“Nephrosis”
Drugs
NSAID’s
Слайд 23ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Physical exam – State of hydration
BUN/Cr
Ratio
Urinary Indices
Urinalysis – dipstick
Urinary Sediment
Слайд 26Vascular Causes of Renal Failure
Large Vessel Disease
Renal Artery Stenosis
Atherosclerotic
FMD usually
NOT
Arteritis
Trauma
Aneurysms
Often need something else, i.e. meds to bring
outSmall Vessel Disease
Vasculitis
TTP/HUS
Cholesterol Emboli
HYPERTENSION
Слайд 28Secondary GN
Most common
Diabetic
HIV associated nephropathy (HIVAN)
SLE
Systemic vasculitides
Others
Can be acute or
chronic
Слайд 29Primary GN
Nil disease
Minimal change disease
Focal Segmental Glomerulonephritis
Membranous nephropathy
IgA (Berger’s Disease)
Henoch-Schoenlein
Purpura
Mesangial GN
Mesangiocapillary GN
Crescentic GN
Слайд 30Tubulo-Interstitial Renal Disease
Acute IN
Drugs
Infectious
Idiopathic
Chronic IN
Balkan nephropathy
Allergic Interstitial nephritis
Слайд 31ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
LABORATORY
The laboratory findings are used to confirm your
clinical suspicion.
Слайд 32BASIC METABOLIC PROFILE
BUN
Creatinine
Serum glucose
Sodium
Potassium
Chloride
CO2 = HCO3-
Na+ Cl-
BUN
K+ CO2
CrsGlu
Слайд 34URINARY INDICES
WHAT:
urine lytes -- Na+, K+, Cl-
urine creatinine
urine osmolality
U/P creatinine
FeNa
TTKG
Слайд 35URINARY INDICES
WHEN:
Before any therapeutic intervention has occurred, i.e., fluid challenge,
diuretic Rx, or K+-replacement is given.
HOW:
Simultaneous serum & urine:
-lytes
-creatinine
-osmolality
Слайд 36OLIGURIA & ARF
PreTubular Tubular Injury
(Pre-Renal,Acute GN)
(ATN,AIN,CTIN)UNa <10 >20
UOsm >500 ~300
U/P Cr >40:1 <20:1
FeNa <1% >1%
(FeNa = U/P Na x 100%)
U/P Cr
Слайд 37ACUTE TUBULAR NECROSIS
Ischemic ATN – prolonged hypotension & shock
-precipitous
-oliguria
-muddy
brown casts
Nephrotoxic ATN – aminoglycosides -gradual onset -non-oliguric -RTE’s & RTE casts
Слайд 38Klahr, S. et al. N Engl J Med 1998;338:671-675
Photomicrograph of
Urinary Sediment Obtained from a Patient with Acute Tubular Necrosis
(x200)Слайд 39RADIOCONTRAST NEPHROPATHY
3rd leading cause of ARF in hospital
Combination of medullary
ischemia and direct tubulo-toxicity
At risk: CKD, DM, CHF, dehydration, and
hi volume contrast media (>250cc)Prevention: IV NSS prior to, during and post procedure; Sodium Bicarbonate; Acetylcysteine
Слайд 40MANAGEMENT OF OLIGURIA
Dehydrated – IV NSS -fluid challenge -continuous -re-assess state of
hydration -pressors
Volume Overloaded – diuretic -IV loop blocking agent -inotropic support
Euhydrated – Assume
“dry unless wet”Non-Oliguric ARF always is easier to manage and has better overall prognosis than Oliguric ARF
Слайд 41POTENTIAL OUTCOMES OF INTERVENTION
Successful Reversal of oliguria
Pulmonary artery catheterization (Swan-Ganz
Catheter)
Dialysis
Слайд 42ARF DUE TO ACUTE GN
Hematuria (RBC’s +/- RBC casts)
Proteinuria (albuminuria)
Hypertension
Edema
Azotemia
Слайд 46Acute vs. Chronic Renal Failure
Clinical determination
Only really an educated guess
Renal
biopsy
CLUES
History
Physical exam
Kidney size
Anemia, PO4, Ca++, U/A, acid-base very little help
in determining chronicity of GNСлайд 47Minimum Work-up
U/A, C&S
Urine eosinophils
Renal Ultrasound
Renal Flow scan
24 hr urine collection
for protein, creatinine and protein electrophoresis
CBC with diff
Слайд 48Full Work-up
“Minimum” plus:
ANA, C3, C4, ANCA, ASO titer, Hepatitis profile,
SPEP, UPEP, HIV
?Renal biopsy
?Doppler US renal arteries
?MRA
?Renal arteriogram
Other tests,
guided by H&PСлайд 49Summary
Approach renal failure patients as you would ANY OTHER PATIENT
Try
to make differential diagnosis based on H&P
Order tests compatible with
proving or disproving the diff dxGo from there