Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Temperature curves
Содержание
- 1. Temperature curves
- 2. Fever is an elevation of body temperature
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. Слайд 4
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Temperature curves - graphic representation of the
- 12. 1. At constant fever (febris continua) body
- 13. 2. Laxative, or relapsing fever (febris remittens)
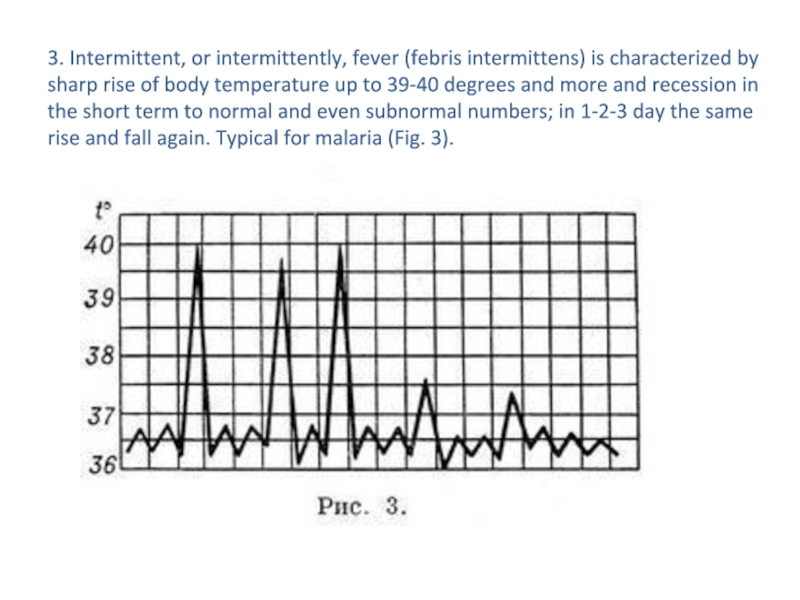
- 14. 3. Intermittent, or intermittently, fever (febris intermittens)
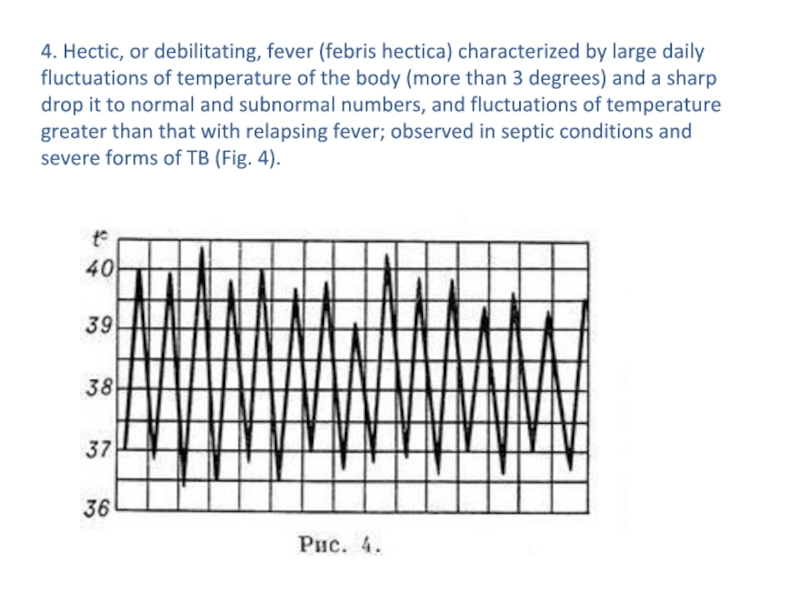
- 15. 4. Hectic, or debilitating, fever (febris hectica)
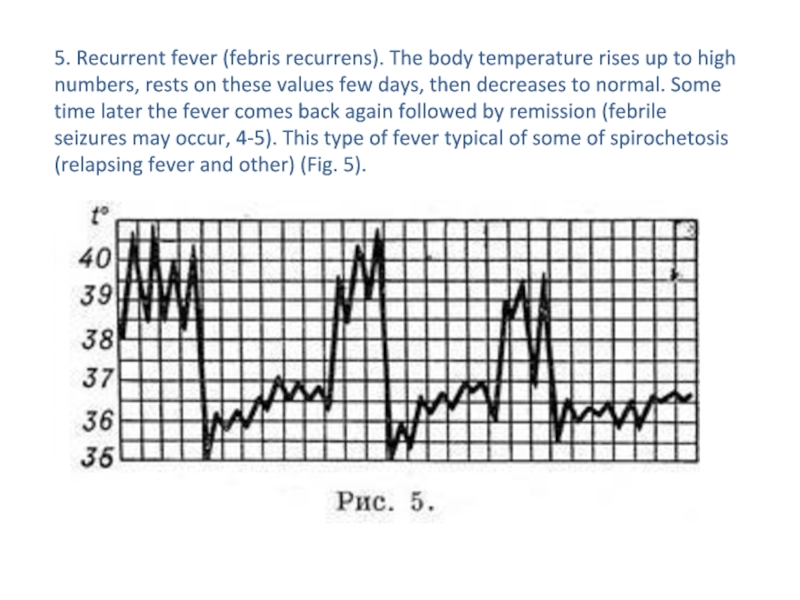
- 16. 5. Recurrent fever (febris recurrens). The body
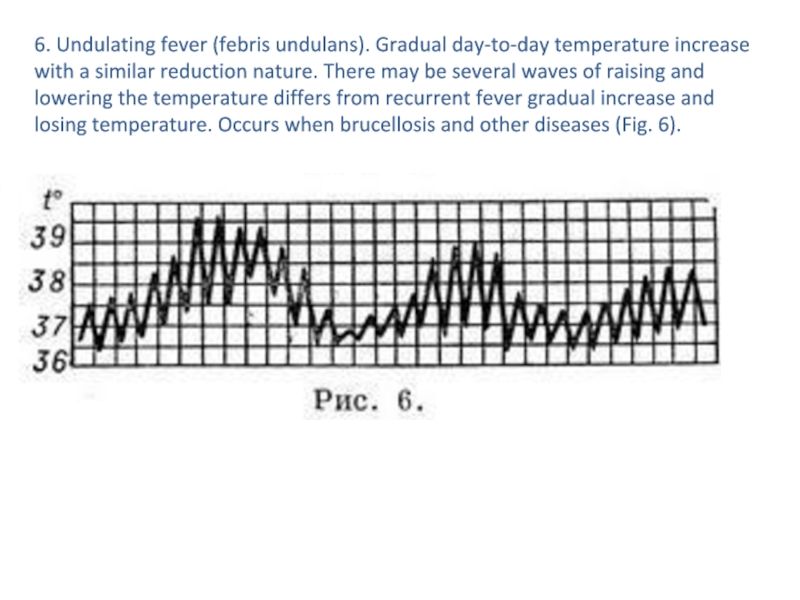
- 17. 6. Undulating fever (febris undulans). Gradual day-to-day
- 18. 7. Twisted fever (febris in versa). Morning
- 19. 8. Febris irregularis (irregular fever) is one
- 20. There are 3 periods of fever. 1.
- 21. 3. Stage of temperature reduction. The rapid
- 22. Temperature sheet is a medical document, intended
- 23. In addition to body temperature, the temperature
- 24. On a standard temperature of the page
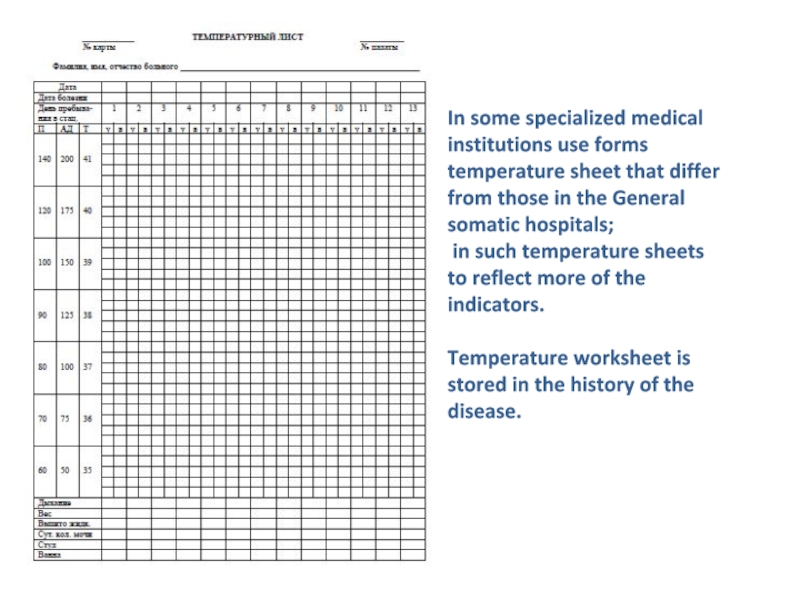
- 25. In some specialized medical institutions use forms
- 26. Скачать презентанцию
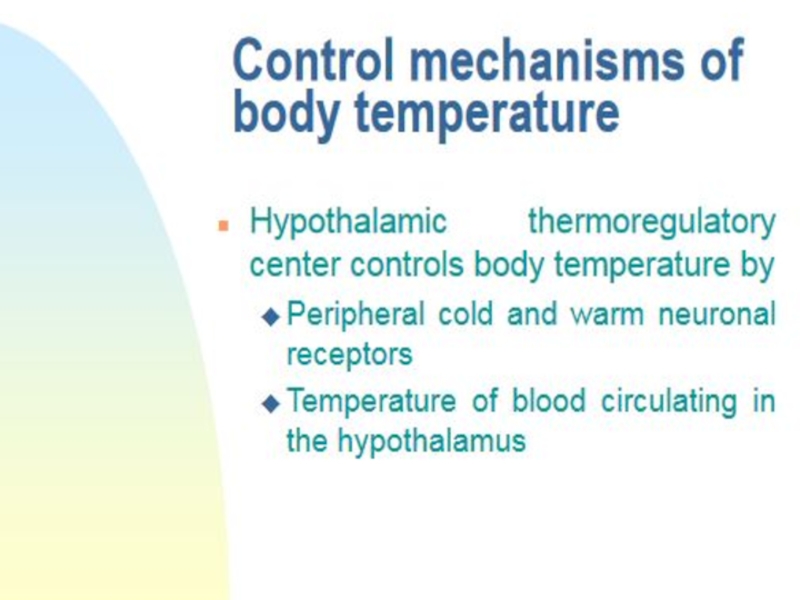
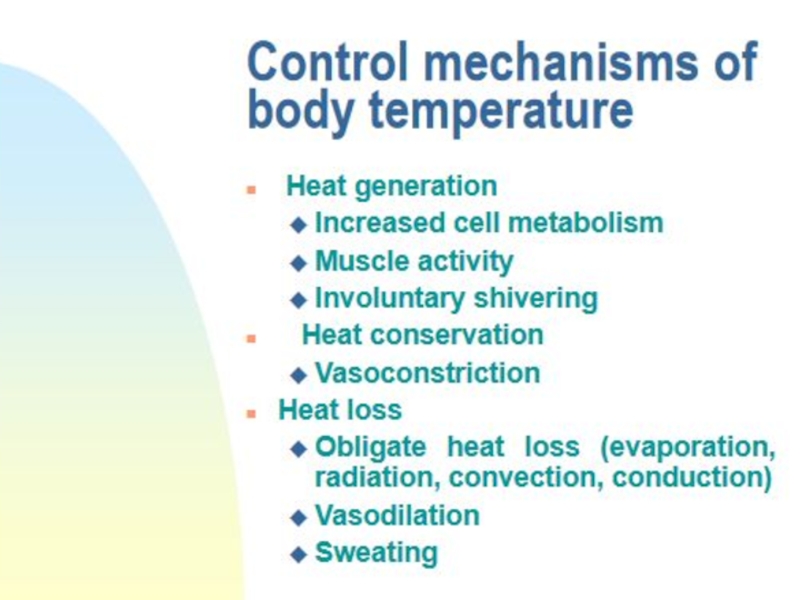
Fever is an elevation of body temperature mediated by an increase of the hypothalamic heat regulatory set-point.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Fever is an elevation of body temperature mediated by an
increase of the hypothalamic heat regulatory set-point.
Слайд 11Temperature curves - graphic representation of the temperature fluctuations during
the daily measurement.
Temperature curves give a clear picture of
the nature of fever (see)have often significant diagnostic and prognostic value.Слайд 121. At constant fever (febris continua) body temperature is usually
high, within 39C, held for a few days or weeks
with fluctuations within 1 degree. Occurs in acute infectious diseases: typhoid fever, lobar pneumonia, and other (Fig. 1).Слайд 132. Laxative, or relapsing fever (febris remittens) is characterized by
significant daily fluctuations in body temperature (up to 2 degrees
or more), found at purulent diseases (Fig. 2).Слайд 143. Intermittent, or intermittently, fever (febris intermittens) is characterized by
sharp rise of body temperature up to 39-40 degrees and
more and recession in the short term to normal and even subnormal numbers; in 1-2-3 day the same rise and fall again. Typical for malaria (Fig. 3).Слайд 154. Hectic, or debilitating, fever (febris hectica) characterized by large
daily fluctuations of temperature of the body (more than 3
degrees) and a sharp drop it to normal and subnormal numbers, and fluctuations of temperature greater than that with relapsing fever; observed in septic conditions and severe forms of TB (Fig. 4).Слайд 165. Recurrent fever (febris recurrens). The body temperature rises up
to high numbers, rests on these values few days, then
decreases to normal. Some time later the fever comes back again followed by remission (febrile seizures may occur, 4-5). This type of fever typical of some of spirochetosis (relapsing fever and other) (Fig. 5).Слайд 176. Undulating fever (febris undulans). Gradual day-to-day temperature increase with
a similar reduction nature. There may be several waves of
raising and lowering the temperature differs from recurrent fever gradual increase and losing temperature. Occurs when brucellosis and other diseases (Fig. 6).Слайд 187. Twisted fever (febris in versa). Morning temperatures above the
evening, meets with tuberculosis, protracted sepsis, prognostically unfavorable. 8. Irregular fever
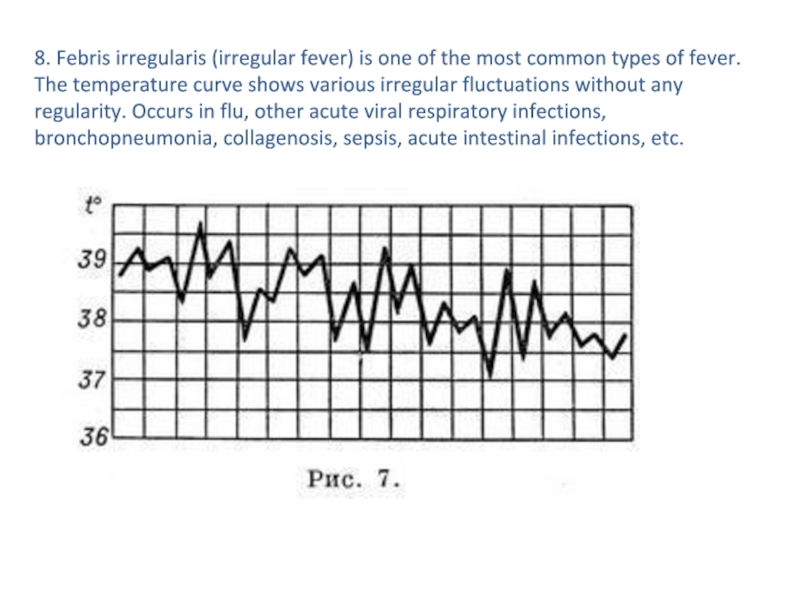
occurs most often. Daily fluctuations of body temperature varied, the duration is not determined. Observed at rheumatism, pneumonia, dysentery, influenza (Fig. 7).Слайд 198. Febris irregularis (irregular fever) is one of the most
common types of fever. The temperature curve shows various irregular
fluctuations without any regularity. Occurs in flu, other acute viral respiratory infections, bronchopneumonia, collagenosis, sepsis, acute intestinal infections, etc.Слайд 20There are 3 periods of fever.
1. The initial period, or
a stage of rise of temperature (stadium incrementi). Depending on
the nature of the disease, this period may be very short and measured in hours, usually accompanied by fever (for example, malaria, lobar pneumonia), or stretch out on a long term of up to several days (for example, typhoid fever).2. Stage height of fever (fastigium or acme). Lasts from several hours to several days.
Слайд 213. Stage of temperature reduction. The rapid drop in temperature
is called the crisis (malaria, lobar pneumonia, typhus; Fig. 8);
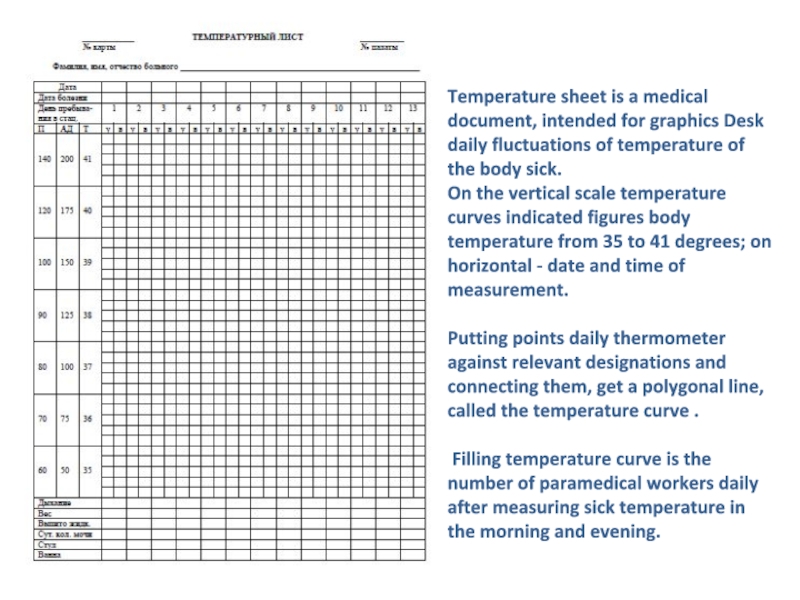
gradual decrease called lysis (typhoid and others; Fig. 9).Слайд 22Temperature sheet is a medical document, intended for graphics Desk
daily fluctuations of temperature of the body sick. On the vertical
scale temperature curves indicated figures body temperature from 35 to 41 degrees; on horizontal - date and time of measurement.Putting points daily thermometer against relevant designations and connecting them, get a polygonal line, called the temperature curve .
Filling temperature curve is the number of paramedical workers daily after measuring sick temperature in the morning and evening.
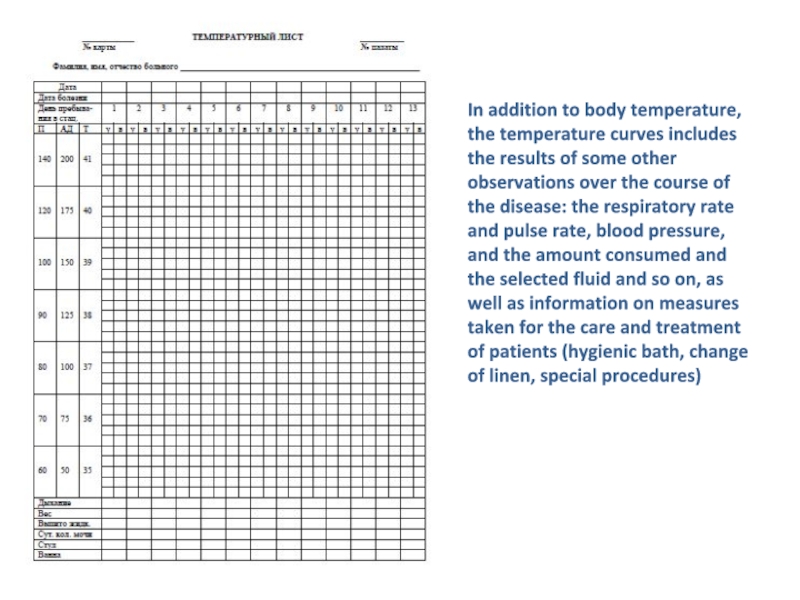
Слайд 23In addition to body temperature, the temperature curves includes the
results of some other observations over the course of the
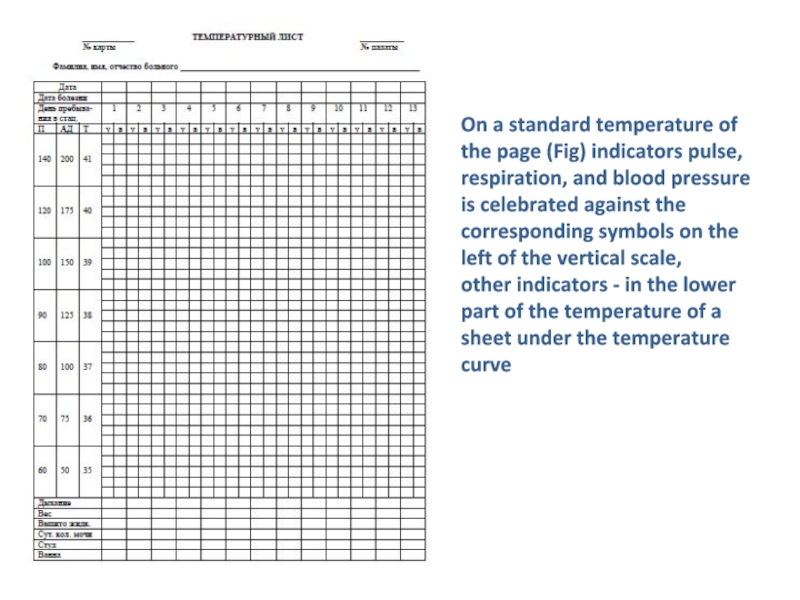
disease: the respiratory rate and pulse rate, blood pressure, and the amount consumed and the selected fluid and so on, as well as information on measures taken for the care and treatment of patients (hygienic bath, change of linen, special procedures)Слайд 24On a standard temperature of the page (Fig) indicators pulse,
respiration, and blood pressure is celebrated against the corresponding symbols
on the left of the vertical scale,other indicators - in the lower part of the temperature of a sheet under the temperature curve
Слайд 25In some specialized medical institutions use forms temperature sheet that
differ from those in the General somatic hospitals;
in such
temperature sheets to reflect more of the indicators.Temperature worksheet is stored in the history of the disease.