Слайд 2Forms of business organization
Sole (Single) Proprietorship
Partnership
Corporation
Co-operative
Слайд 3Sole Proprietorships
One Owner
ALL THE ASSETS AND Profits are
attributed directly to the owner.
No special legal requirements.
Owner’s
Equity consists primarily of the owner’s capital account.
responsibility for running the business, its liabilities or debts
Слайд 4SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
ADVANTAGES
Easiest and least expensive form of ownership to organize
Ease
of formation
Sole proprietors are in complete control, and within
the parameters of the law, may make decisions as they see fit
Слайд 5SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
ADVANTAGES
Sole proprietors receive all income generated by the business
to keep or reinvest.
Profits from the business flow-through directly to
the owner's personal tax return
Слайд 6SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
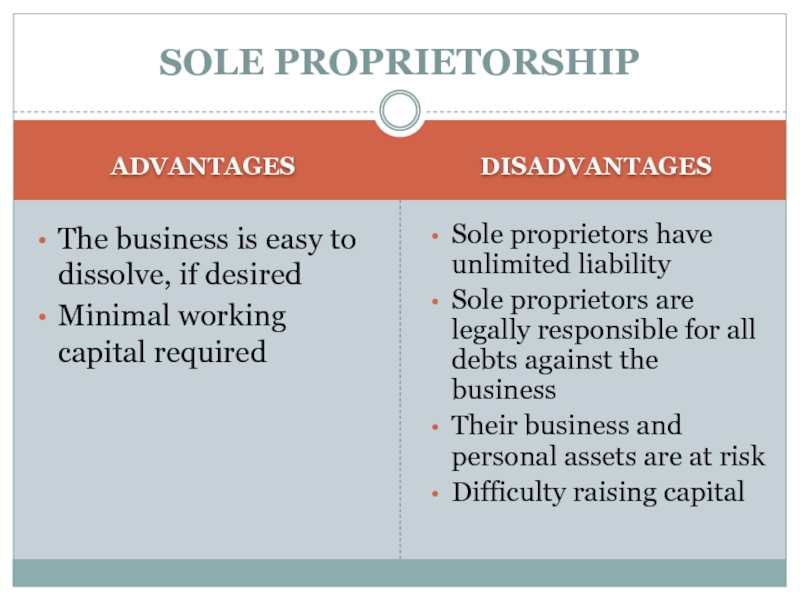
ADVANTAGES
The business is easy to dissolve, if desired
Minimal working
capital required
DISADVANTAGES
Sole proprietors have unlimited liability
Sole proprietors are legally responsible
for all debts against the business
Their business and personal assets are at risk
Difficulty raising capital
Слайд 7SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
ADVANTAGES
The business is easy to dissolve, if desired
DISADVANTAGES
Some employee
benefits such as owner's medical insurance premiums are not directly
deductible from business income (only partially deductible as an adjustment to income).
Lack of continuity in business organization in the absence of the owner
Слайд 8Partnerships
Two or more owners
Partnership agreement may be oral or
written.
Profits are attributed directly to the partners.
Owners’ Equity
consists primarily of the partners’ capital accounts.
The Partners should have a legal agreement that sets forth how decisions will be made, profits will be shared, disputes will be resolved, how future partners will be admitted to the partnership, how partners can be bought out, or what steps will be taken to dissolve the partnership when needed
Слайд 9Partnerships
the partners must decide up front how much time
and capital each will contribute
Слайд 10Partnerships
ADVANTAGES
Partnerships are relatively easy to establish; however time should be
invested in developing the partnership agreement
With more than one owner,
the ability to raise funds may be increased
Слайд 11Partnerships
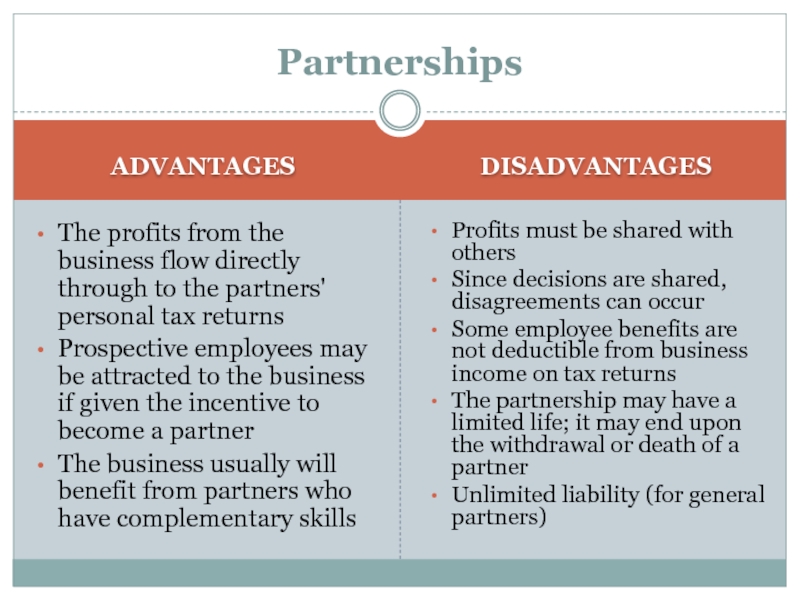
ADVANTAGES
The profits from the business flow directly through to the
partners' personal tax returns
Prospective employees may be attracted to the
business if given the incentive to become a partner
The business usually will benefit from partners who have complementary skills
DISADVANTAGES
Profits must be shared with others
Since decisions are shared, disagreements can occur
Some employee benefits are not deductible from business income on tax returns
The partnership may have a limited life; it may end upon the withdrawal or death of a partner
Unlimited liability (for general partners)
Слайд 12TYPES OF PARTNERSHIPS
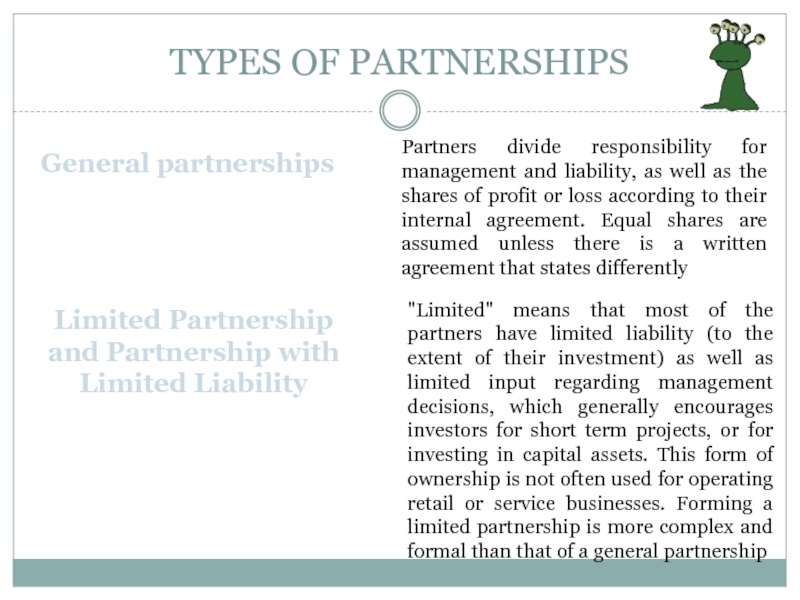
General partnerships
Partners divide responsibility for management and liability,
as well as the shares of profit or loss according
to their internal agreement. Equal shares are assumed unless there is a written agreement that states differently
Limited Partnership and Partnership with Limited Liability
"Limited" means that most of the partners have limited liability (to the extent of their investment) as well as limited input regarding management decisions, which generally encourages investors for short term projects, or for investing in capital assets. This form of ownership is not often used for operating retail or service businesses. Forming a limited partnership is more complex and formal than that of a general partnership
Слайд 13TYPES OF PARTNERSHIPS
Joint Venture
Acts like a general partnership, but is
clearly for a limited period of time or a single
project. If the partners in a joint venture repeat the activity, they will be recognized as an ongoing partnership and will have to file as such, and distribute accumulated partnership assets upon dissolution of the entity
Слайд 14Corporations
A corporation is identified by the terms "Limited", "Ltd.", "Incorporated",
"Inc.", "Corporation", or "Corp.".
Whatever the term, it must appear with
the corporate name on all documents, stationery, and so on, as it appears on the incorporation document
Слайд 15Corporations
Usually there are many owners.
Owners are referred to as shareholders.
The
owners have limited liability for the debts of the corporation.
No shareholder of a corporation is personally liable for the debts, obligations or acts of the corporation.
The shareholders elect a board of directors to oversee the major policies and decisions.
The corporation has a life of its own and does not dissolve when ownership changes.
Слайд 16Corporations
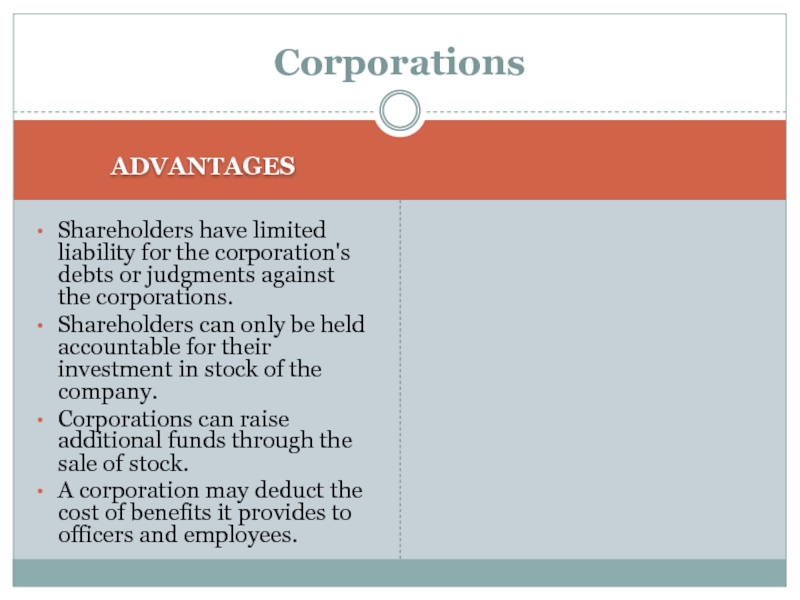
ADVANTAGES
Shareholders have limited liability for the corporation's debts or judgments
against the corporations.
Shareholders can only be held accountable for
their investment in stock of the company.
Corporations can raise additional funds through the sale of stock.
A corporation may deduct the cost of benefits it provides to officers and employees.
Слайд 17Corporations
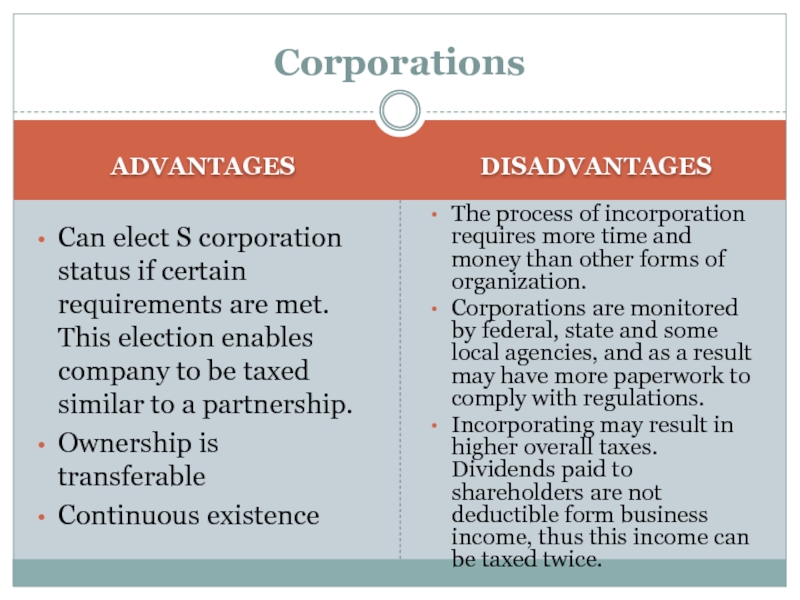
ADVANTAGES
Can elect S corporation status if certain requirements are met.
This election enables company to be taxed similar to a
partnership.
Ownership is transferable
Continuous existence
DISADVANTAGES
The process of incorporation requires more time and money than other forms of organization.
Corporations are monitored by federal, state and some local agencies, and as a result may have more paperwork to comply with regulations.
Incorporating may result in higher overall taxes. Dividends paid to shareholders are not deductible form business income, thus this income can be taxed twice.
Слайд 18TYPES OF CORPORATIONS
Subchapter S Corporations
A tax election only; this election
enables the shareholder to treat the earnings and profits as
distributions, and have them pass through directly to their personal tax return. The shareholder, if working for the company, and if there is a profit, must pay herself wages, and it must meet standards of "reasonable compensation". The basic rule is to pay yourself what you would have to pay someone to do your job, as long as there is enough profit. If you do not do this, the IRS (Internal Revenue Service) can reclassify all of the earnings and profit as wages, and you will be liable for all of the payroll taxes on the total amount
Слайд 19TYPES OF CORPORATIONS
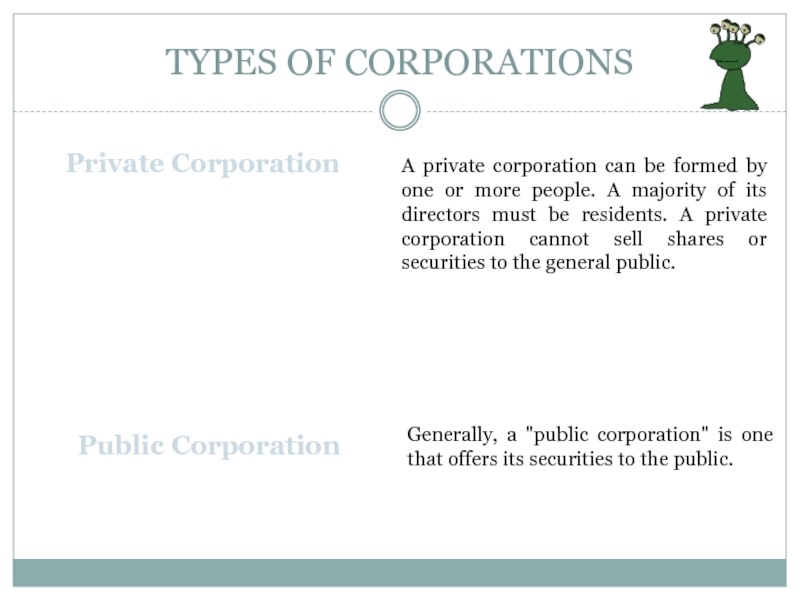
Private Corporation
A private corporation can be formed by
one or more people. A majority of its directors must
be residents. A private corporation cannot sell shares or securities to the general public.
Public Corporation
Generally, a "public corporation" is one that offers its securities to the public.
Слайд 20LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY (LLC)
The LLC is a relatively new type
of hybrid business structure. It is designed to provide the
limited liability features of a corporation and the tax efficiencies and operational flexibility of a partnership. Formation is more complex and formal than that of a general partnership.
The owners are members, and the duration of the LLC is usually determined when the organization papers are filed. The time limit can be continued if desired by a vote of the members at the time of expiration. LLC's must not have more than two of the four characteristics that define corporations:
Limited liability to the extent of assets;
Continuity of life;
Centralization of management;
Free transferability of ownership interests.