Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Урок-викторина по страноведению для 7 классов "Britain for you"
Содержание
- 1. Урок-викторина по страноведению для 7 классов "Britain for you"
- 2. 1. The UK of Great Britain and
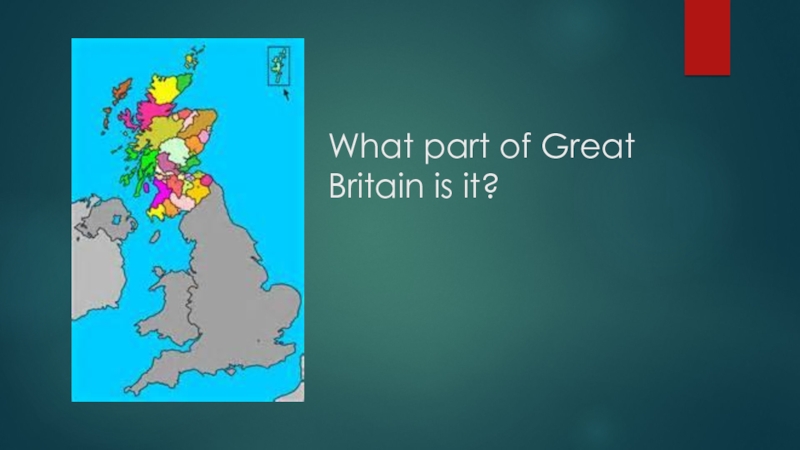
- 3. What part of Great Britain is it?
- 4. What part of Great Britain is it?
- 5. What part of Great Britain is it?
- 6. What part of Great Britain is it?
- 7. Match the parts of the Britain with
- 8. Choose the suitable words
- 9. It is the national emblem of …
- 10. It is the national emblem of …
- 11. These are the national emblems of …
- 12. SOLVE THE CROSSWORD “Vegetation and Wildlife”
- 13. Cross:1. мак 2. черный дрозд 3. выдра
- 14. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
- 15. Industry of Great BritainThe history of manufacturing
- 16. Silk weaving – ткацкое производство шёлка;Pottery – гончарное производство;Cutlery – ножевые изделия;
- 17. In the 18th century a number of
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Many towns throughout Britain became manufacturing centers
- 20. Britain now manufactures 40 percent of Europe’s
- 21. Scotland and Northern Ireland are still noted
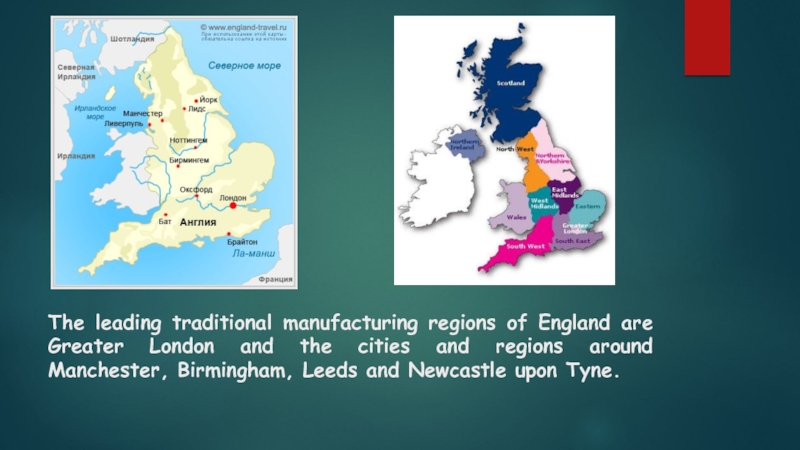
- 22. The leading traditional manufacturing regions of England
- 23. Скачать презентанцию
1. The UK of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is situated on … 2. Great Britain consists of four parts: … 3. The coasts of Great Britain are washed by
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 7Match the parts of the Britain with their mountains:
1. The
Cheviot Hills a. England
2. Snowdon
3. The Pennines
b. Scotland4. Ben Nevis
5. The Pennines c. Wales
6. The Cumbrian
Слайд 8
Choose the suitable words for each sentences.
The climate of England
is rather … 2. The climate of Britain is usually
… as cool … and humid. 3. Snow never … on the ground for long. 4. The climate of the UK is generally … and temperate. 5. Even on a bright sunny day one cannot … it is not going to rain in a few hours. 6. The famous London fogs are … to everyone. 7. It soon … 8. The weather is never … two days running. 9. The average temperature in January is 3-7 … 10. The cold air which comes to England from the continent to Britain … many clouds. 11. The trees and flowers begin … early in … 12. The … and mild climate is good for … 13. Sometimes it brings … or … 14. … are rare. 15. They never leave house without … or …(an umbrella, soft, to blossom, a raincoat, melts, described, the same, degrees, temperate, well-known, spring, lies, above zero, whirlwinds, brings, hurricanes, mild, be sure, plants, humid, droughts)
Слайд 13Cross:
1. мак 2. черный дрозд 3. выдра 4. сосна 5.
чайка
6. болотистая местность 7. вяз
Down:
8. дуб 9. береза 10.
ёжик 11. млекопитающее 12. чертополох 13. олень
Слайд 15Industry of Great Britain
The history of manufacturing in Britain is
unique because of Britain’s role as the birthplace of the
Industrial Revolution. During the Middle Ages the production of woolen textiles was a key industry in Britain. In the 16th and 17th centuries, new industries developed. These included silk weaving, garment making, and the manufacturing of hats, pottery and cutlery. All of these operations were generally conducted in small craft shops and were labor-intensive.Слайд 16Silk weaving – ткацкое производство шёлка;
Pottery – гончарное производство;
Cutlery –
ножевые изделия;
Слайд 17In the 18th century a number of changes in British
society prepared the way for the Industrial Revolution. Colonial and
commercial expansion created markets in North America, Africa and parts of Asia. An agricultural revolution in the 18th century introduced new crops and crop rotation techniques, better breeding methods, and mechanical devices for cultivation.Expansion – распространение
Market – рынок, базар
Crop – урожай
Rotation – оборот
Breeding – разведение скота
Devices - устройства
Слайд 19Many towns throughout Britain became manufacturing centers during the Industrial
Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries. Newcastle upon Tyne
in northern eastern England, became important for steel production and shipbuilding. In the 1990s it was still a transportation hub.The structure of industry changes in the last half of the 20th century. The coal mining and cotton textile industries declined. As coal production declined, oil production replaced it as a major industry. Motor-vehicle production became a significant part of the industrial base.