Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Ancient Indian and Chinese philosophy
Содержание
- 1. Ancient Indian and Chinese philosophy
- 2. In the West, the term Eastern (Oriental)
- 3. One must take into account that this
- 4. Ancient eastern philosophy developed mainly in India
- 5. Ancient Indian philosophy
- 6. Ancient Indian civilization has some special features. These are:* Rigid (жесткий) caste social structure.
- 7. * Intellectual and religious passivity of people.* The priority of the irrational over the rational.
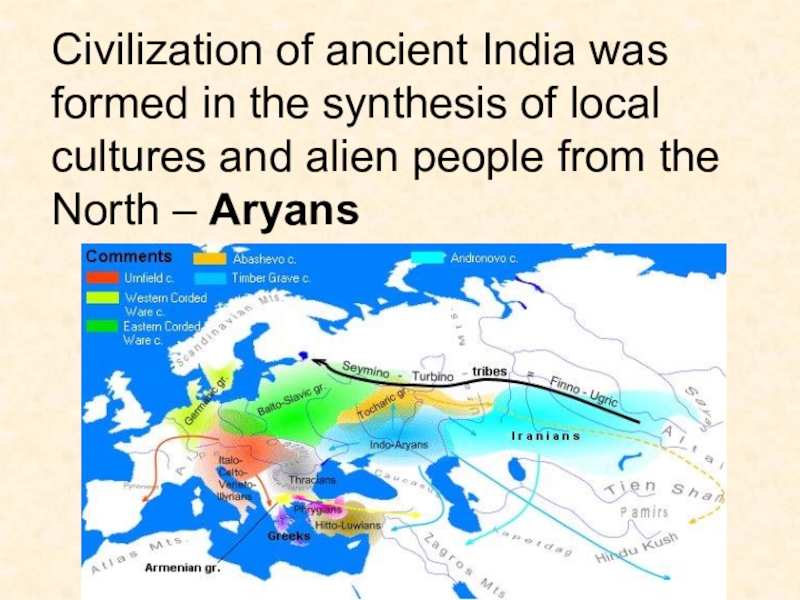
- 8. Civilization of ancient India was formed in
- 9. The development of ancient Indian philosophy consists of two periods: the Vedic and Classical.
- 10. Rig-Veda (Sanskrit ऋग्वेद, «Veda hymns») is a
- 11. The word «veda» means «knowledge» and comes
- 12. Rig-Veda contains an extreme pluralism: the gods,
- 13. At the heart of cosmos there is
- 14. The world and its phenomena are considered
- 15. Head corresponds to the caste of Brahmins
- 16. Feet – Vaisya caste (merchants, artisans). Footsteps
- 17. Universal law, which operates in the past,
- 18. If a person adheres to a strict
- 19. According to a traditional principle of classification,
- 20. These are regarded as orthodox, not because
- 21. To the first group belong the six chief philosophical systems (popularly known as sad-darsana):
- 22. Mimamsa (Prabhakara), the tradition of Vedic exegesis
- 23. Samkhya (Kapila), the school of enumeration or
- 24. Yoga (Patanjali), practice of contemplation, theoretical basis
- 25. Vaisesika (Kanada), the atomistic school, looking for
- 26. During next classical period, there appears an
- 27. Buddhism (Pali बुद्ध धम्म, Buddha Dhamma, “Teaching
- 28. At the core of Buddhism is the
- 29. In Buddhism it’s proposed median (срединный), or
- 30. Eightfold PathRighteous faith. The true determination (решимость). Righteous speech. Righteous deeds (дела).
- 31. 5. Saintliness (Праведная жизнь). 6. Righteous thoughts. 7. Righteous intentions (помыслы). 8. True contemplation.
- 32. Jainism preaches non-violence to all living beings
- 33. Lokayata (also Charvaq, Skt. चार्वाक) is a
- 34. Ancient Chinese philosophy
- 35. The main features of ancient Chinese philosophy
- 36. Considering all things as a unity of
- 37. Yin and yang is a Chinese symbol
- 38. Basically, this symbol represents the Positive and
- 39. In Chinese mythology, it is allocated the
- 40. During this period, freely and creatively there were six major philosophical schools.
- 41. 1) School of Confucians;2) School of yin
- 42. Confucianism is the philosophy based on the
- 43. Confucianism focuses on the ethical rules, social
- 44. Confucianism was made to stop the fall
- 45. People slowly started to believe in it,
- 46. The teachings of Confucius focus largely on the respect of one’s parents, elders, and ancestors.
- 47. Also, he taught that humans 'can never
- 48. Confucianism can be considered as the oldest school of philosophy in China.
- 49. Ethics of Confucius explaned human in connection
- 50. The social order (Li) Confucius had established
- 51. Another important feature of the social order
- 52. Ren (仁) – humanity, love for people
- 53. Слайд 53
- 54. Moists school was named after the founder
- 55. The whole meaning was to the ideas
- 56. School of Names examined the relations of
- 57. Legism (Bu Hei Shen, Han Feng-tzu) is
- 58. It is political philosophy which say that
- 59. One of the most important contributors to
- 60. 2. Shu (method, tactic or art): These are methods
- 61. One of the major directions in China,
- 62. The world is in constant motion and
- 63. Lao Tzu (old teacher) is a senior
- 64. Скачать презентанцию
In the West, the term Eastern (Oriental) philosophy refers very broadly to the various philosophies of “the East”, namely Asia, including China, India, Japan, Persia and other areas.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3One must take into account that this term ignores that
these countries do not belong to a single culture.
Слайд 4Ancient eastern philosophy developed mainly in India and China. The
Indian or Hindu schools of philosophy can be considered the
oldest schools of philosophy.Слайд 6Ancient Indian civilization has some special features.
These are:
* Rigid
(жесткий) caste social structure.
Слайд 7* Intellectual and religious passivity of people.
* The priority of
the irrational over the rational.
Слайд 8Civilization of ancient India was formed in the synthesis of
local cultures and alien people from the North – Aryans
Слайд 9The development of ancient Indian philosophy consists of two periods:
the Vedic and Classical.
Слайд 10Rig-Veda (Sanskrit ऋग्वेद, «Veda hymns») is a collection of religious
hymns, the first known monument of Indian literature.
Слайд 11The word «veda» means «knowledge» and comes from the root
«vid-», (Sanskrit «know»), that reconstructed from Proto-Indo-European root «weid», meaning
«to see» or «to know». «Weid-» is source of English word «wit», as well as the Latin «vision».Слайд 12Rig-Veda contains an extreme pluralism: the gods, people, animals, plants,
elements, seasons, countries, qualities of body, spiritual abilities, etc. are
animate (одушевленные) substances, which are connected with each other and can transform into one another.Слайд 13At the heart of cosmos there is an eternal substance
– Brahman. It is identical to the eternal inner core
(ядро) of the individual Atman.Слайд 14The world and its phenomena are considered as the improvement
of the primary entity (Purusha). Purusha is also understood to
be the first person, which consists of castes.Слайд 15Head corresponds to the caste of Brahmins (priests).
Hands –
to the caste of the Kshatriyas (the military or ruling
class).Слайд 16Feet – Vaisya caste (merchants, artisans).
Footsteps –Sudras caste (servants).
There were also untouchables, that is, most lower of the
castes.Слайд 17Universal law, which operates in the past, present and future
called karma.
Samsara is a cycle of repeated rebirth.
Слайд 18If a person adheres to a strict asceticism, his samsara
ceases (прекращается), and he reaches a state of nirvana, that
means fading. Ce’ssation (прекращение) of rebirth is called moksha.Слайд 19According to a traditional principle of classification, the schools or
systems of Indian philosophy are divided into two broad classes,
namely, orthodox (astika) & heterodox (nastika).Слайд 20These are regarded as orthodox, not because they believe in
god, but because they accept the authority of the Vedas.
Слайд 21To the first group belong the six chief philosophical systems
(popularly known as sad-darsana):
Слайд 22Mimamsa (Prabhakara), the tradition of Vedic exegesis (толкование) of sacrifice
(жертвоприношения)
Vedanta (Badarayana), teaching about the origin of the world from
BrahmanСлайд 23Samkhya (Kapila), the school of enumeration or “reasonable deliberation” (разумное
взвешивание, обдумывание): atheistic pluralism – the first substance is not
connected with the spiritСлайд 24Yoga (Patanjali), practice of contemplation, theoretical basis is the Samkhya,
but it acknowledged (признавать) a personal God.
Nyaya (Akshapada Gotama), the
school of logicСлайд 25Vaisesika (Kanada), the atomistic school, looking for identify the differences
among all that is opposed in the outer and inner
worlds. It saw the emancipation of a human soul in the separation of soul from all material.Слайд 26During next classical period, there appears an interest in ethical
issues. Agnostics, materialists and fatalists oppose the Brahmins and the
reformists.Слайд 27Buddhism (Pali बुद्ध धम्म, Buddha Dhamma, “Teaching of Awakening (Пробужденный)”)
is a religious-philosophical doctrine (dharma) of spiritual awakening (bodhi), which
arose about in the VI century B.C. and based on the ideas of Buddha ShakyamuniСлайд 28At the core of Buddhism is the doctrine of the
Four high-minded (благородный) Truths:
- suffering,
- the origin and
causes of suffering, - a true cessation of suffering,
- the true ways to stop suffering.
Слайд 29In Buddhism it’s proposed median (срединный), or the Eightfold Path
(Восьмеричный Путь) of achieving Nirvana. This path is directly related
to the cultivation of three varieties of virtues: morality, concentration and wisdom.Слайд 30Eightfold Path
Righteous faith.
The true determination (решимость).
Righteous speech.
Righteous
deeds (дела).
Слайд 315. Saintliness (Праведная жизнь).
6. Righteous thoughts.
7. Righteous intentions
(помыслы).
8. True contemplation.
Слайд 32Jainism preaches non-violence to all living beings in this world.
Philosophy and practice of Jainism is based primarily on the
cultivation of soul to attain om’niscience (всеведение), om’nipotence (всесилие) and eternal bliss (блаженство).Слайд 33Lokayata (also Charvaq, Skt. चार्वाक) is a materialist doctrine of
ancient India.
Lokayata is a belief in the real world (loka)
and disbelief in the existence of the underworld.Слайд 35The main features of ancient Chinese philosophy are:
Practical orientation
of philosophical constructions.
Absence of strict categorical framework.
The domination of the ethical issues.Слайд 36Considering all things as a unity of opposites (Yang –
Yin), Chinese thinkers have explained the endless process of moving
through their dialectical interaction.Слайд 37Yin and yang is a Chinese symbol of balance and
harmony, and the opposite forces of nature.
The symbol has two
colours, White and Black which symbolize nature's balance of forces such as Good and Evil, Up and Down, Light and Dark, Male and Female, Life and Death, etc.Слайд 38Basically, this symbol represents the Positive and Negative forces in
the Universe. This symbol has been used in Asia for
a long time, and has become popular in the rest of the world, too.Слайд 39In Chinese mythology, it is allocated the highest principle, which
rules the world, the existence of things. This principle is
sometimes understood as the highest personified ruler (Shang-di), but more often as the word “the heaven” (Tian).Слайд 411) School of Confucians;
2) School of yin and yang;
3) School
of moism (Mo-jia);
4) School of names (Ming-jia);
5) School of lawyers,
legists (Fa jia); 6) School of Taoism (Tao Jia).
Слайд 42Confucianism is the philosophy based on the teachings of Confucius,
who was an important Chinese philosopher. Confucianism has a complex
system of moral, social, political, and religious thought, and has had a large influence on the history of Chinese civilization.Слайд 43Confucianism focuses on the ethical rules, social norms and regulation
control.
Confucius (551-479 BC), his name is Latinized version of
the name Kung Fu Tzu (teacher Kun). He is one of the first Chinese thinkers, philosophers.Слайд 44Confucianism was made to stop the fall of Chinese society.
After the Zhou Dynasty fell, people cared only for themselves
and did not have any respect for others. Confucianism became a social order for China, teaching that social relationships are the most important.Слайд 45People slowly started to believe in it, because they wanted
to have peace, but they had to care for themselves,
too. As a result, Confucianism brought the people love, harmony, and respect for one another.Слайд 46The teachings of Confucius focus largely on the respect of
one’s parents, elders, and ancestors.
Слайд 47 Also, he taught that humans 'can never stop learning'; meaning
that knowledge is infinite, therefore we will always learn, never
stopping. For example, he once asked a seven-year-old child to be his teacher, because the child knew something that he did not.Слайд 49Ethics of Confucius explaned human in connection with his social
functions, and education is to bring people to the execution
(исполнение) of these functions.Слайд 50The social order (Li) Confucius had established through the ideal
of universality, respect to nature and, especially, relations between people.
This
realization of functions and order based on the order leads to the manifestation of humanity (Ren).Слайд 51Another important feature of the social order is strong obedience
(повиновение) to elders, respect to them.
State is a big
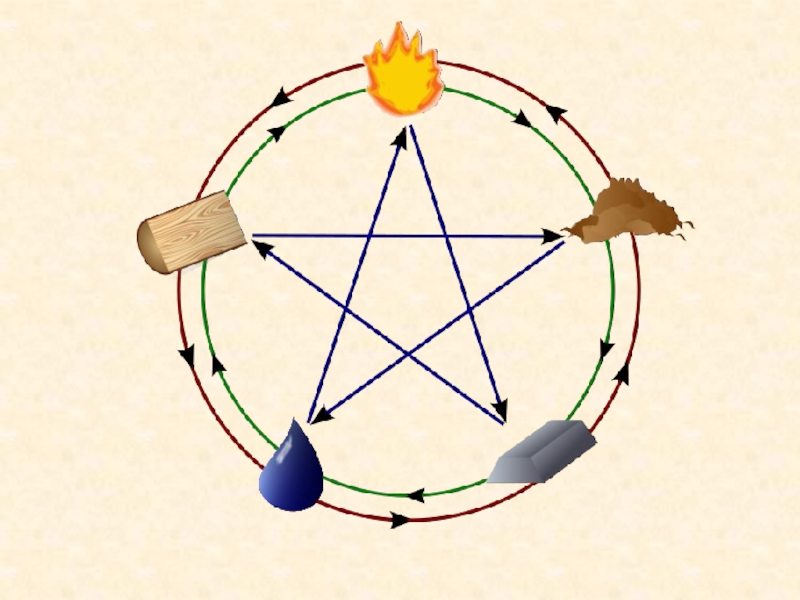
family, and family is a small state.Слайд 52Ren (仁) – humanity, love for people (tree)
I (义) –
the truth, justice (metal)
Li (礼) – custom, ceremony, ritual (fire)
Zhi
(智) – common sense, wisdom (water)Xin (信) – sincerity (искренность), good intentions (ground)