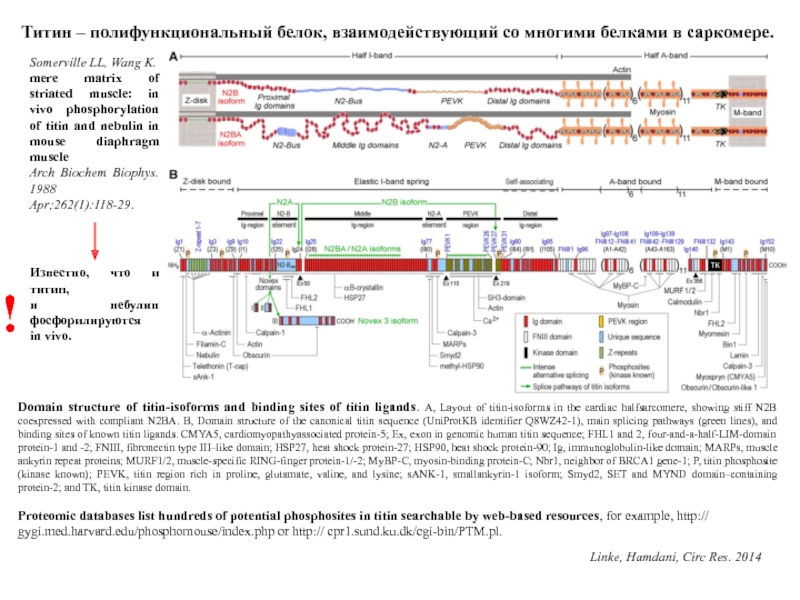
A, Layout of titin-isoforms in the cardiac halfsarcomere, showing stiff
N2B coexpressed with compliant N2BA. B, Domain structure of the canonical titin sequence (UniProtKB identifier Q8WZ42-1), main splicing pathways (green lines), and binding sites of known titin ligands. CMYA5, cardiomyopathyassociated protein-5; Ex, exon in genomic human titin sequence; FHL1 and 2, four-and-a-half-LIM-domain protein-1 and -2; FNIII, fibronectin type III–like domain; HSP27, heat shock protein-27; HSP90, heat shock protein-90; Ig, immunoglobulin-like domain; MARPs, muscle ankyrin repeat proteins; MURF1/2, muscle-specific RING-finger protein-1/-2; MyBP-C, myosin-binding protein-C; Nbr1, neighbor of BRCA1 gene-1; P, titin phosphosite (kinase known); PEVK, titin region rich in proline, glutamate, valine, and lysine; sANK-1, smallankyrin-1 isoform; Smyd2, SET and MYND domain–containing protein-2; and TK, titin kinase domain.
Proteomic databases list hundreds of potential phosphosites in titin searchable by web-based resources, for example, http://
gygi.med.harvard.edu/phosphomouse/index.php or http:// cpr1.sund.ku.dk/cgi-bin/PTM.pl.
Linke, Hamdani, Circ Res. 2014
Somerville LL, Wang K.
mere matrix of striated muscle: in vivo phosphorylation of titin and nebulin in mouse diaphragm muscle
Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Apr;262(1):118-29.
Известно, что и титин,
и небулин фосфорилируются
in vivo.
!
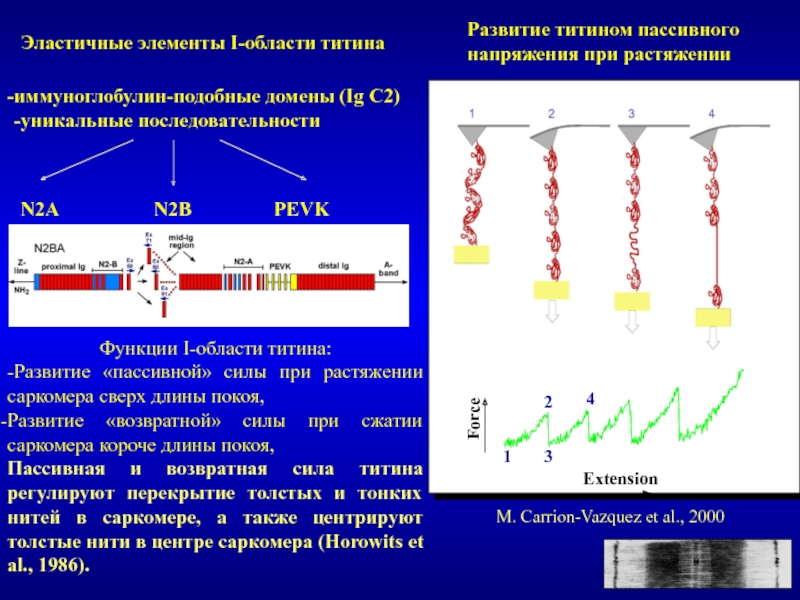
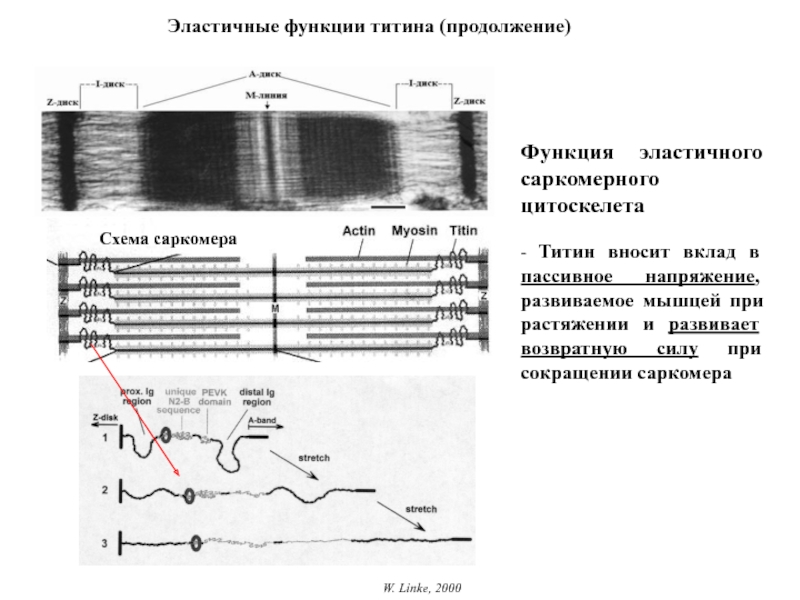
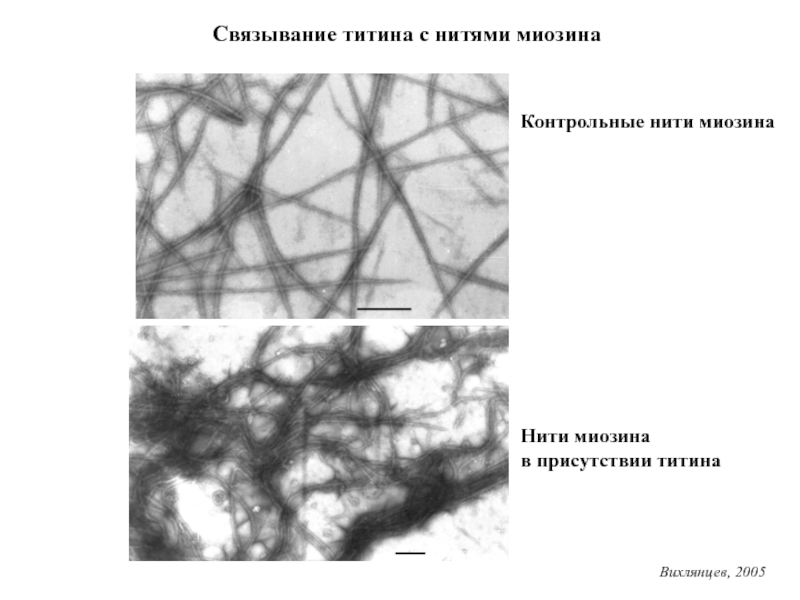
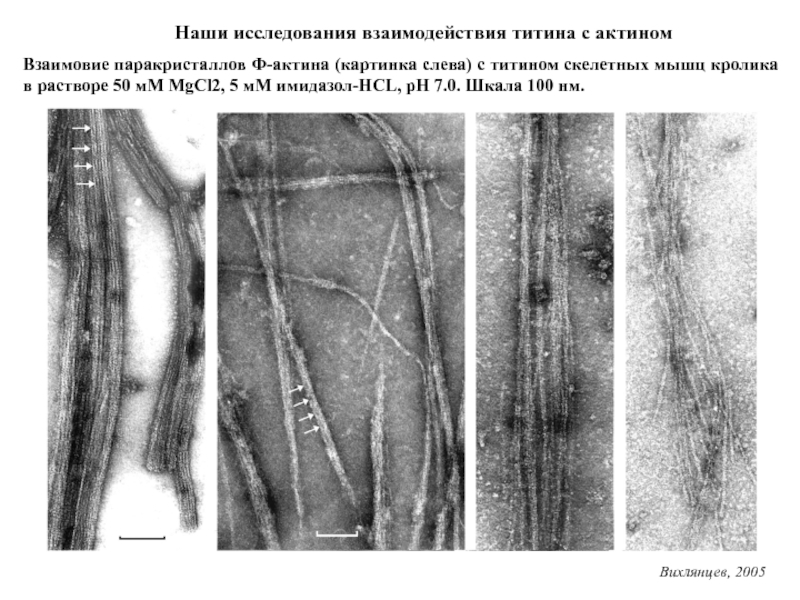
Титин – полифункциональный белок, взаимодействующий со многими белками в саркомере.