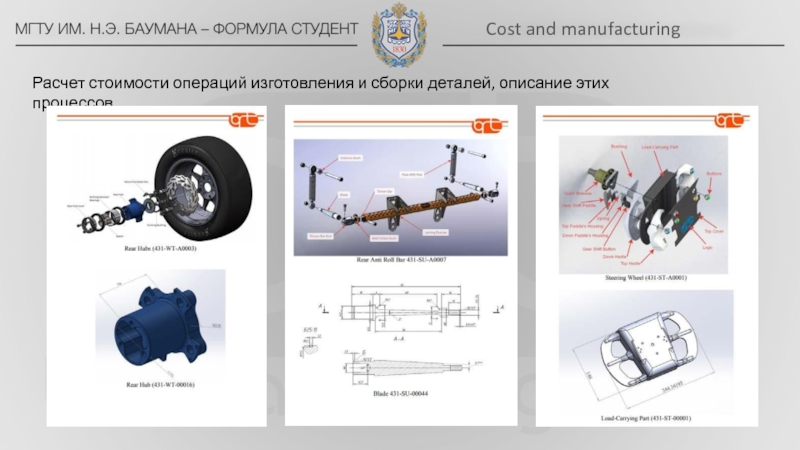
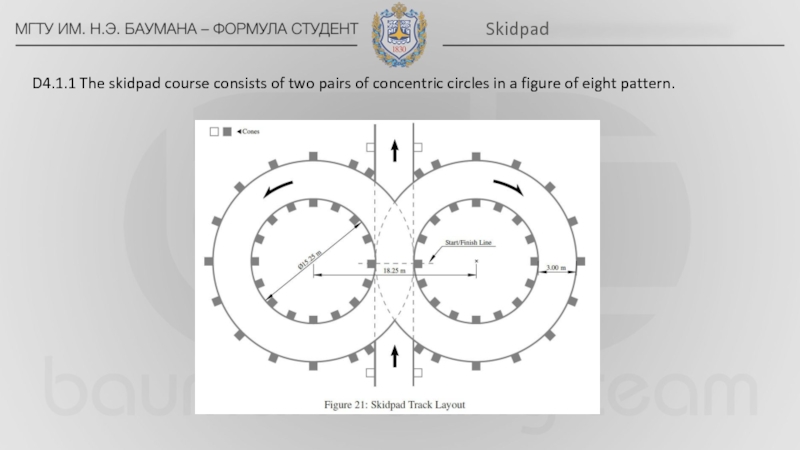
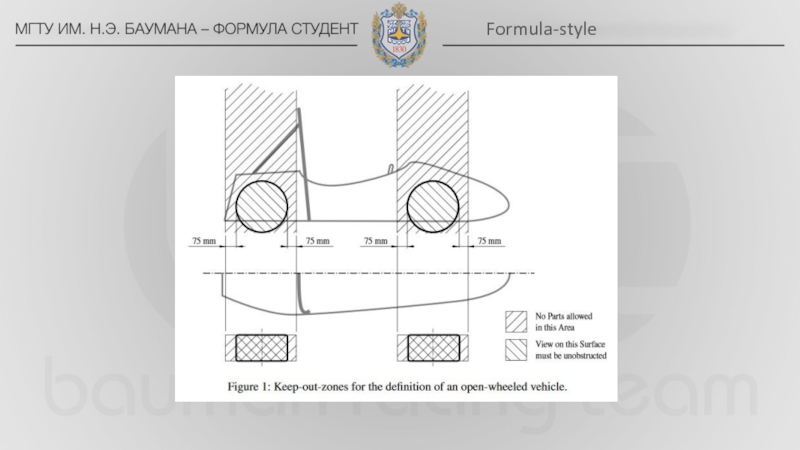
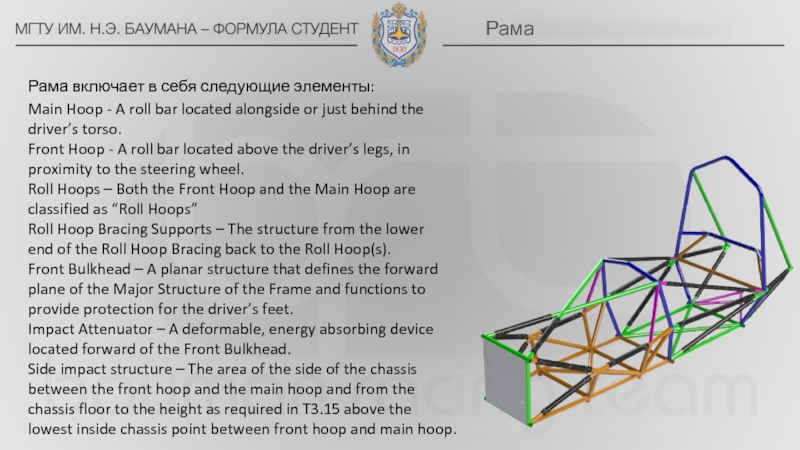
bar located alongside or just behind the
driver’s torso.
Front Hoop -
A roll bar located above the driver’s legs, in
proximity to the steering wheel.
Roll Hoops – Both the Front Hoop and the Main Hoop are classified as “Roll Hoops”
Roll Hoop Bracing Supports – The structure from the lower end of the Roll Hoop Bracing back to the Roll Hoop(s).
Front Bulkhead – A planar structure that defines the forward plane of the Major Structure of the Frame and functions to provide protection for the driver’s feet.
Impact Attenuator – A deformable, energy absorbing device
located forward of the Front Bulkhead.
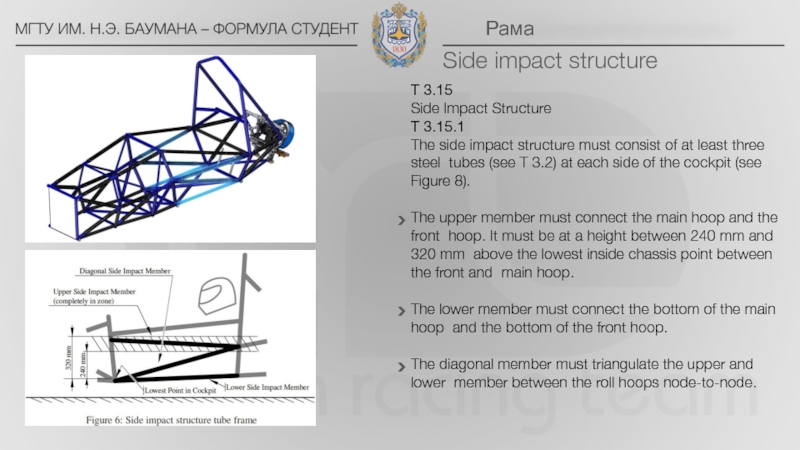
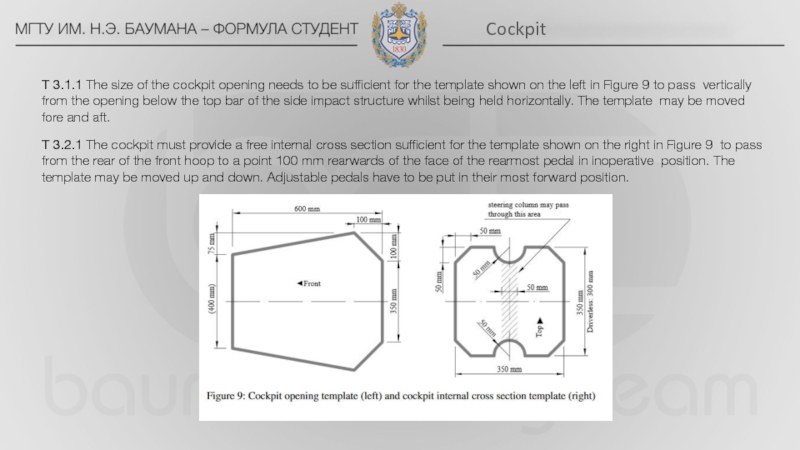
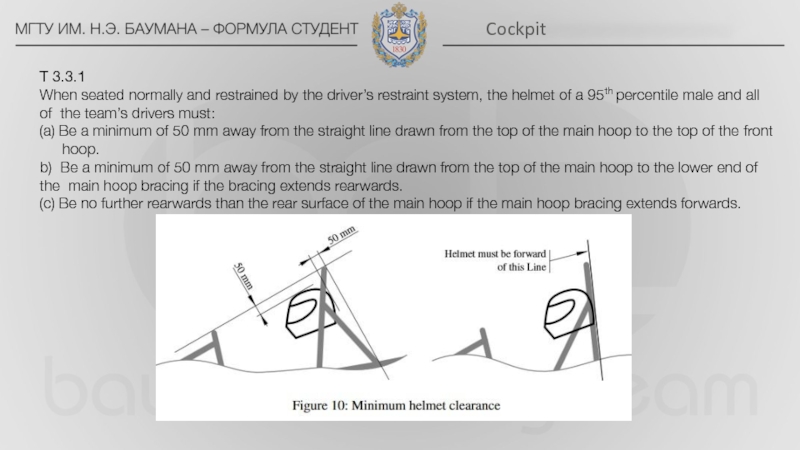
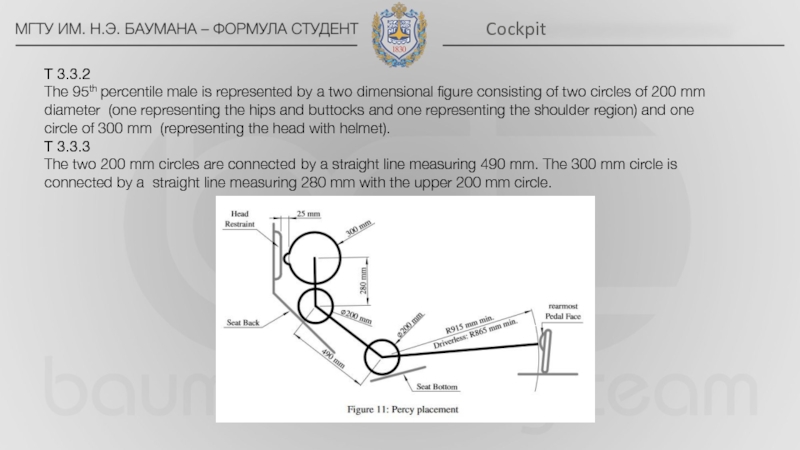
Side impact structure – The area of the side of the chassis between the front hoop and the main hoop and from the chassis floor to the height as required in T3.15 above the lowest inside chassis point between front hoop and main hoop.
Рама




![Лекция_по_регламенту Техническая инспекцияIN1.1.1 The technical inspection is divided into the following parts:• Техническая инспекцияIN1.1.1 The technical inspection is divided into the following parts:• Pre-Inspection• [EV ONLY] Accumulator Inspection• [EV](/img/thumbs/480493d82d344375529c1ed9da630338-800x.jpg)