Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Managing Teams
Содержание
- 1. Managing Teams
- 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 4. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 5. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 6. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 7. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 8. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall11–Exhibit 11–2 Stages of Group Development
- 9. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall11–Exhibit 11–3 Group Performance Satisfaction Model
- 10. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 11. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 12. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 13. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 14. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 15. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 16. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 17. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 18. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 19. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall11–Exhibit 11–7 Conflict and Group Performance
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 27. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 28. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 29. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 30. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall11–Exhibit 11–9 Groups versus Teams
- 31. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall11–Exhibit 11–9 Groups Versus Teams
- 32. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 33. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 34. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall11–Exhibit 11–10 Characteristics of Effective Teams
- 35. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 36. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 37. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 38. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 39. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 40. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 41. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 42. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Learning
Outcomes Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this
chapter.11.1 Groups and Group Development
Define the different types of groups.
Describe the five stages of group development.
11.2 Work Group Performance and Satisfaction
List the major components that determine group performance and satisfaction.
Describe how external conditions and group member resources affect group performance and satisfaction.
Discuss how group structure influences group performance and satisfaction.
Describe how group processes and group tasks influence group performance and satisfaction.
Слайд 3Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Learning
Outcomes
11.3 Turning Groups Into Effective Teams
Compare groups and teams.
Describe the
four most common types of teams.List the characteristics of effective teams.
11.4 Current Challenges In Managing Teams
Discuss the challenges of managing global teams
Explain the role of informal (social) networks in managing teams
Слайд 4Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Groups
and Group Development
Group
Two or more interacting and interdependent individuals
who come together to achieve specific goals.Formal groups
Work groups defined by the organization’s structure that have designated work assignments and tasks.
Appropriate behaviors are defined by and directed toward organizational goals.
Informal groups
Groups that are independently formed to meet the social needs of their members.
Слайд 5Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–1 Examples of Formal Groups
Command Groups
Groups that are determined by the
organization chart and composed of individuals who report directly to a given manager.Task Groups
Groups composed of individuals brought together to complete a specific job task; their existence is often temporary because once the task is completed, the group disbands.
Слайд 6Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–1 Examples of Formal Groups (cont’d)
Cross-Functional Teams
Groups that bring together the
knowledge and skills of individuals from various work areas or groups whose members have been trained to do each others’ jobs.Self-Managed Teams
Groups that are essentially independent and in addition to their own tasks, take on traditional responsibilities such as hiring, planning and scheduling, and performance evaluations.
Слайд 7Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Stages
in Group Development
Forming
Members join and begin the process of defining
the group’s purpose, structure, and leadership.Storming
Intragroup conflict occurs as individuals resist control by the group and disagree over leadership.
Norming
Close relationships develop as the group becomes cohesive and establishes its norms for acceptable behavior.
Performing
A fully functional group structure allows the group to focus on performing the task at hand.
Adjourning
The group prepares to disband and is no longer concerned with high levels of performance.
Слайд 8Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–2 Stages of Group Development
Слайд 9Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–3 Group Performance Satisfaction Model
Слайд 10Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
External
Conditions Imposed on the Group
Organization’s strategy
Authority relationships
Formal regulations
Available organizational resources
Employee
selection criteriaPerformance management (appraisal) system
Organizational culture
General physical layout of work space
Слайд 11Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Member Resources
Knowledge
Skills
Interpersonal skills such as conflict management and
resolution, collaborative problem solving, and communication determine how effectively members perform in a groupAbilities
Determine what members can do
Personality traits
Positive traits tend to be positively related to group productivity and morale
Слайд 12Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Structure
Role
The set of expected behavior patterns attributed to someone who
occupies a given position in a social unit that assists the group in task accomplishment or maintaining group member satisfaction.Role conflict: experiencing differing role expectations
Role ambiguity: uncertainty about role expectations
Слайд 13Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Structure (cont’d)
Norms
Acceptable standards or expectations that are shared by the
group’s members.Common types of norms
Effort and performance
Output levels, absenteeism, promptness, socializing
Dress
Loyalty
Слайд 14Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Structure (cont’d)
Conformity
Individuals conform in order to be accepted by groups.
Group
pressures can have an effect on an individual member’s judgment and attitudes.The effect of conformity is not as strong as it once was, although still a powerful force.
Groupthink
The extensive pressure of others in a strongly cohesive or threatened group that causes individual members to change their opinions to conform to that of the group.
Слайд 15Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–4 Examples of Cards Used in the Asch
StudyСлайд 16Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Structure (cont’d)
Status System
The formal or informal prestige grading, position, or
ranking system for members of a group that serves as recognition for individual contributions to the group and as a behavioral motivator.Formal status systems are effective when the perceived ranking of an individual and the status symbols accorded that individual are congruent.
Слайд 17Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Structure: Group Size
Small groups
Complete tasks faster than larger groups.
Make more
effective use of facts.Large groups
Solve problems better than small groups.
Are good for getting diverse input.
Are more effective in fact-finding.
Social Loafing
The tendency for individuals to expend less effort when working collectively than when working individually.
Слайд 18Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Structure (cont’d)
Group Cohesiveness
The degree to which members are attracted to
a group and share the group’s goals.Highly cohesive groups are more effective and productive than less cohesive groups when their goals aligned with organizational goals.
Слайд 19Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–5 The Relationship Between Cohesiveness
and ProductivityСлайд 20Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Processes: Group Decision Making
Advantages
Generates more complete information and knowledge.
Generates more
diverse alternatives.Increases acceptance of a solution.
Increases legitimacy of decision.
Disadvantages
Time consuming
Minority domination
Pressures to conform
Ambiguous responsibility
Слайд 21Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–6 Techniques for Making More Creative
Group DecisionsСлайд 22Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Processes: Conflict Management
Conflict
The perceived incompatible differences in a group resulting
in some form of interference with or opposition to its assigned tasks.Traditional view: conflict must be avoided.
Human relations view: conflict is a natural and inevitable outcome in any group.
Interactionist view: conflict can be a positive force and is absolutely necessary for effective group performance.
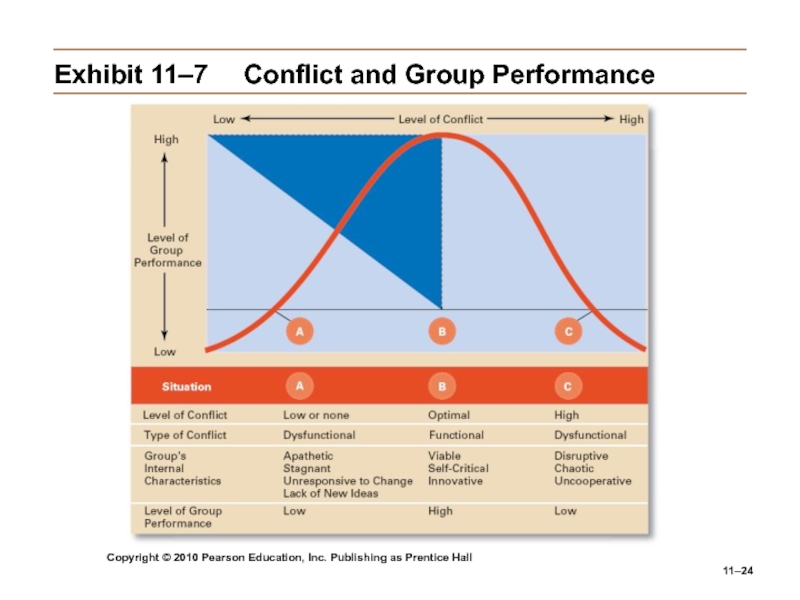
Слайд 23Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Processes: Conflict Management (cont’d)
Categories of Conflict
Functional conflicts are constructive.
Dysfunctional conflicts
are destructive.Types of Conflict
Task conflict: content and goals of the work
Relationship conflict: interpersonal relationships
Process conflict: how the work gets done
Слайд 24Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–7 Conflict and Group Performance
Слайд 25Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
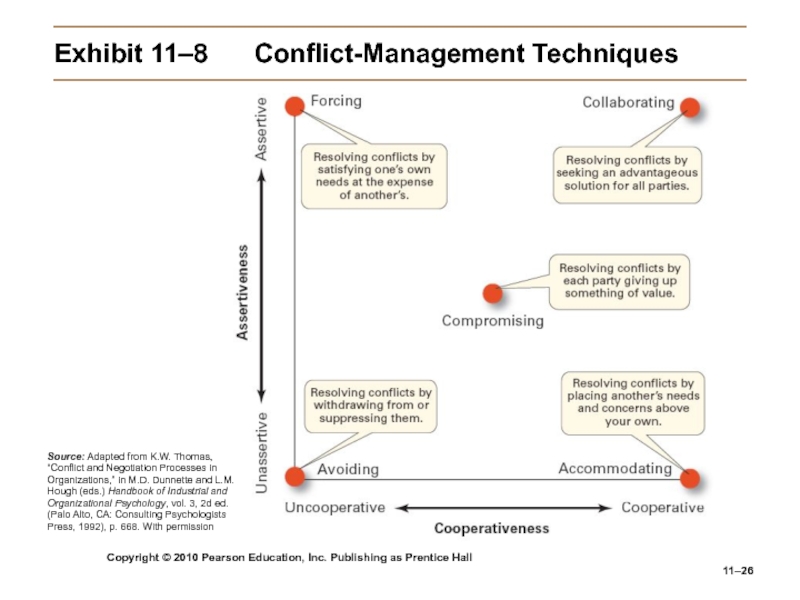
Processes: Conflict Management (cont’d)
Techniques to Manage Conflict:
Avoidance
Accommodation
Forcing
Compromise
Collaboration
Слайд 26Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–8 Conflict-Management Techniques
Source: Adapted from K.W. Thomas, “Conflict and Negotiation
Processes in Organizations,” in M.D. Dunnette and L.M. Hough (eds.) Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, vol. 3, 2d ed. (Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press, 1992), p. 668. With permissionСлайд 27Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Group
Tasks and Group Effectiveness
Highly complex and interdependent tasks require:
Effective communications:
discussion among group members.Controlled conflict: More interaction among group members.
Слайд 28Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Advantages
of Using Teams
Teams outperform individuals.
Teams provide a way to better
use employee talents.Teams are more flexible and responsive.
Teams can be quickly assembled, deployed, refocused, and disbanded.
Слайд 29Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
What
Is a Work Team?
Work Team
A group whose members work intensely
on a specific common goal using their positive synergy, individual and mutual accountability, and complementary skills.Types of Teams
Problem-solving teams
Self-managed work teams
Cross-functional teams
Virtual teams
Слайд 30Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–9 Groups versus Teams
Слайд 31Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–9 Groups Versus Teams
Слайд 32Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Types
of Teams
Problem-Solving Teams
Employees from the same department and functional area
who are involved in efforts to improve work activities or to solve specific problems.Self-Managed Work Teams
A formal group of employees who operate without a manager and responsible for a complete work process or segment.
Слайд 33Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Types
of Teams (cont’d)
Cross-Functional Teams
A hybrid grouping of individuals who are
experts in various specialties and who work together on various tasks.Virtual Teams
Teams that use computer technology to link physically dispersed members in order to achieve a common goal.
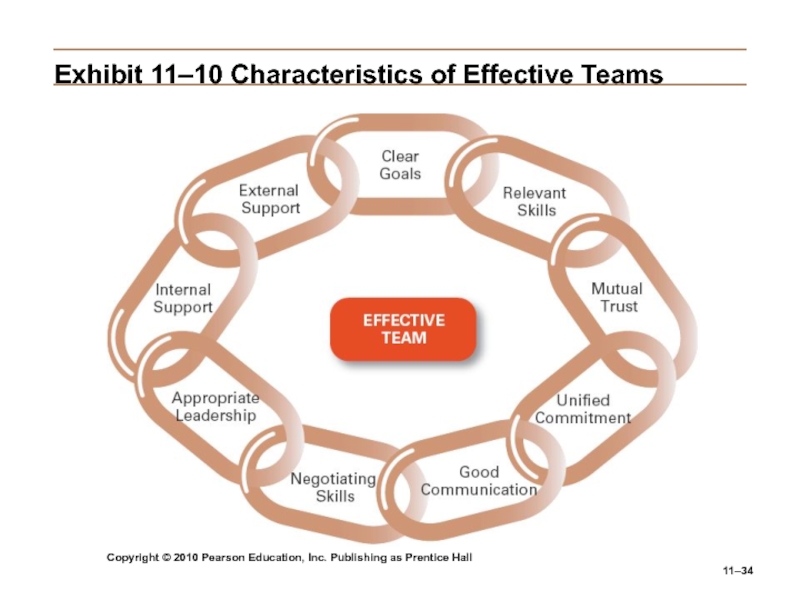
Слайд 34Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–10 Characteristics of Effective Teams
Слайд 35Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Characteristics
of Effective Teams
Have a clear understanding of their goals.
Have competent
members with relevant technical and interpersonal skills.Exhibit high mutual trust in the character and integrity of their members.
Are unified in their commitment to team goals.
Have good communication systems.
Possess effective negotiating skills.
Have appropriate leadership.
Have both internally and externally supportive environments.
Слайд 36Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Current
Challenges in Managing Teams
Getting employees to:
Cooperate with others
Share information
Confront differences
Sublimate
personal interest for the greater good of the teamСлайд 37Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Managing
Global Teams
Group Member Resources
Unique cultural characteristics of team members
Avoiding stereotyping
Group
StructureConformity—less groupthink
Status—varies in importance among cultures
Social loafing—predominately a Western bias
Cohesiveness—more difficult to achieve
Group processes—capitalize on diverse ideas.
Manager’s role—a communicator sensitive to the type of global team to use.
Слайд 38Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Exhibit
11–11 Drawbacks and Benefits of Global
TeamsSource: Based on N. Adler, International Dimensions in Organizational Behavior, 4th ed. (Cincinnati, OH: South-western
Publishing, 2002), pp. 141–147
Слайд 39Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Understanding
Social Networks
Social Network
The patterns of informal connections among individuals within
groups.The Importance of Social Networks
Relationships can help or hinder team effectiveness.
Relationships improve team goal attainment and increase member commitment to the team.
Слайд 40Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
11–
Terms
to Know
group
forming stage
storming stage
norming stage
performing stage
adjourning stage
role
norms
groupthink
status
social loafing
group cohesiveness
conflict
traditional view
of conflicthuman relations view of conflict
interactionist view of conflict
functional conflicts
dysfunctional conflicts
task conflict
relationship conflict
process conflict
work teams
problem-solving team
self-managed work team
cross-functional team
virtual team
social network structure