Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
QUALITATIVE & QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH Editor: Stephen Murray
Содержание
- 1. QUALITATIVE & QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH Editor: Stephen Murray
- 2. OVERALL FRAMEWORK
- 3. KEEP IN MIND THAT …Qualitative research generally
- 4. QUALITATIVE RESEARCHResearch used in range of activities
- 5. QUALITATIVE RESEARCHPOPULARITY COMES FROM:*ECONOMICAL *FLEXIBLE*OPENS A DOOR TO “WHY, HOW”*RICHNESS OF DATA*BEST TO START WITH...
- 6. QUALITATIVE RESEARCHIdentification of a given question; opportunity
- 7. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH FOCUS GROUPSCharacteristics:6-12 peopleLead by a
- 8. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH FOCUS GROUPS
- 9. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH FOCUS GROUPS
- 10. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGN Qualitative Research: ExamplesCase
- 11. Characteristics of Case Studies: It gives very
- 12. Procedure for Historical Research: Define the problem
- 13. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH IN-DEPTH INTERVIEWCharacteristics:A well trained interviewer+intervieweeInterviewee
- 14. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH IN-DEPTH INTERVIEWApplications:-Interviews with professionals-Interviews
- 15. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH IN-DEPTH INTERVIEW
- 16. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECHNIQUEDefinition:*These are unstructured
- 17. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECHNIQUES
- 18. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECHNIQUESTypes:Word Association
- 19. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECHNIQUES *Source: http://www.nielsenbuzzmetrics.com/images/uploaded/NikeBAM.gif
- 20. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECH.2. Sentence Completion
- 21. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECH.3. Cartoon Tests
- 22. QUALITATIVE MARKETING - PROJECTIVE TECH.HthHntfyfhngfhnLet’s see if we can pick up some house wares at WalmartWALMART
- 23. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECH.4. Role PlayingRespondents
- 24. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECH.5. Third PersonWay
- 25. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECH.6.Picture InterpretationA technique
- 26. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PROJECTIVE TECH.
- 27. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH 1. Degree of Structure2. Probing
- 28. QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH SURVEYSURVEY METHOD:STRUCTURED QUESTIONNAIRE GIVEN TO
- 29. QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH - SURVEY
- 30. QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH - EXPERIMENTATIONEXPERIMENTATION METHOD:Scientific investigation in
- 31. QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
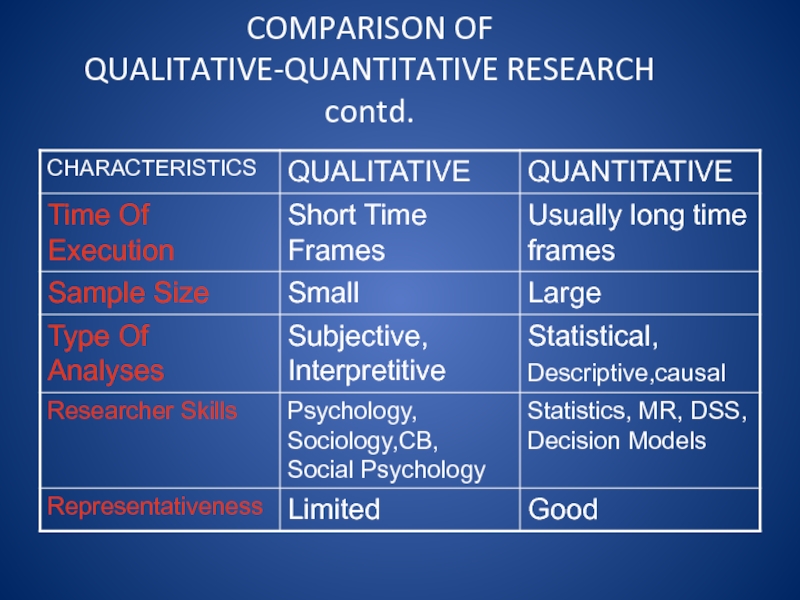
- 32. COMPARISON OF QUALITATIVE-QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
- 33. COMPARISON OF QUALITATIVE-QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH contd.
- 34. SUMMARYQualitative methods focus on generating exploratory initial/progressive
- 35. SUMMARYQuantitative Research is interested in using formalised,
- 36. OVERALL FRAMEWORKSource: http://www.informedbusinessdecisions.com/RoadMapt400c.jpg
- 37. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3KEEP IN MIND THAT …
Qualitative research generally deals in words,
images and the subjective
Quantitative research generally deals in numbers,
logic and the objectiveСлайд 4QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Research used in range of activities from exploratory designs
to means of completing explanations
Qualitative research assumes that people have
meaningful actions or experiences
that can be interpreted
Слайд 5QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
POPULARITY COMES FROM:
*ECONOMICAL
*FLEXIBLE
*OPENS A DOOR TO “WHY, HOW”
*RICHNESS
OF DATA
*BEST TO START WITH...
Слайд 6QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Identification of a given question; opportunity or information requirements
Interest
in obtaining insights for
motivational /social (group) or emotional and
attitudinal (individual) factors
In IR: primary data of events or personalities supporting explanations and argument
(Cf. In marketing: for new product launch, new service development or repositioning current product
Слайд 7QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
FOCUS GROUPS
Characteristics:
6-12 people
Lead by a trained moderator
in-depth discussion on
1 particular topic or concept
Relaxed, informal atmosphere
1-3 hour duration
Goal:
Learn and
understand what people say and why?Слайд 10QUALITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGN
Qualitative Research:
Examples
Case studies on effect of
vocational training in Papua
Ethnographic studies on indigenous populations in
Oaxaca, Mexico Qualitative Research Types:
Case studies
Developmental research
Historical research
Ethnograph studies
Case Studies:
Purpose: to do an in depth study
In brief: Background, current status and/or environmental factors that interact for each group (individual, institution or community)
Слайд 11Characteristics of Case Studies:
It gives very detailed information about
individuals / group / community
It may give a detailed explanation
of a complete life cycle or part of itNumber of cases studied may be small but the number of variables studied are usually more in-depth (e.g. if compared to a survey)
Developmental Research:
Conducted to research on the development of individuals / group / institution / community
TWO TYPES: Cross-sectional and Longitudinal
Historical Research:
Used to gain information on an event, development and/or previous educational experience
Process may involve studying previous situation, checking on current situation, and to predict if the same situation will occur again
Conclusion on previous event is done based on collected facts and evidences to answer why and how the event and repercussions occurred
Useful to solve questions that involve sensitive issues
Important for systematically & objectively collecting and defining facts and evidences
Слайд 12Procedure for Historical Research:
Define the problem
Specify source of
evidence
Collect evidence / reference materials
Primary source / original
(observation or witnesses of events or authentic objects – e.g. artifacts, speech text, records etc.) Secondary source (materials or information collected from primary sources – e.g. paintings, films, news reports, documents
Critique of evidences
External critique: confirming if collected sources are genuine and reliable (authenticity of paintings, signatures, chemical analysis etc.)
Internal critique: conducted after authenticity of source of information is confirmed – involves evaluation of collected evidences– is it important? Required?
Able to explain the researched phenomenon?
Prepare the report
Ethnographic Research:
In-depth study of natural behaviours in a culture or social group
Purpose – to understand relationships between behaviour and culture
Example: In education – to understand schooling process (e.g., immigrant children) Involves widespread observations (participant & nonparticipant)
Here often starts research without hypothesis – hypothesis is developed in the process of observations, and the researcher explores and test his hypothesis
Слайд 13QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
IN-DEPTH INTERVIEW
Characteristics:
A well trained interviewer+interviewee
Interviewee is exposed to set
of probing questions
Usually face to face
Interviewer encourages the interviewee to
talk moreGoal:
To collect as much as memory, attitudinal and
behavioral data from the subject
Слайд 14QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
IN-DEPTH INTERVIEW
Applications:
-Interviews with professionals
-Interviews with witnesses
-When detailed probing
is needed
-Discussion of sensitive, confidential issues
-When strong, social norms exist
-Interviews
with competitorsСлайд 16QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
PROJECTIVE TECHNIQUE
Definition:*
These are unstructured prompts or stimulus that
encourage the respondent to project their underlying motivations, beliefs, attitudes,
or feelings onto an ambiguous situationThey are all indirect techniques that attempt to disguise the purpose of the research
*Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Qualitative_marketing_research
Слайд 18QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
PROJECTIVE TECHNIQUES
Types:
Word Association
Customers are required
to show response to the concept they are told within
2-3 sec.Слайд 19QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
PROJECTIVE TECHNIQUES
*Source: http://www.nielsenbuzzmetrics.com/images/uploaded/NikeBAM.gif
Слайд 20QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
PROJECTIVE TECH.
2. Sentence Completion
Customers are
required to complete sentences or stories in their own words
People
who are concerned about ecology …When I think of a city …
I drink a Coca-Cola, usually when .
Starbucks reminds me of…
Слайд 22QUALITATIVE MARKETING - PROJECTIVE TECH.
Hth
Hntfyf
hngfhn
Let’s see if we can pick
up some house wares at Walmart
WALMART
Слайд 23QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
PROJECTIVE TECH.
4. Role Playing
Respondents are asked to assume
the behavior of someone else
Useful for emphatic approaches for conflict
resolutionSales Supervisors are asked to become Sales Represantatives, and vice versa.
Слайд 24QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
PROJECTIVE TECH.
5. Third Person
Way of learning respondents feelings
or opinions by asking them to answer for a third
party :“your neighbour”
“most people”
“typical person”
Слайд 25QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
PROJECTIVE TECH.
6.Picture Interpretation
A technique whereby respondents are shown
a picture and are asked to tell a story describing
itСлайд 27QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
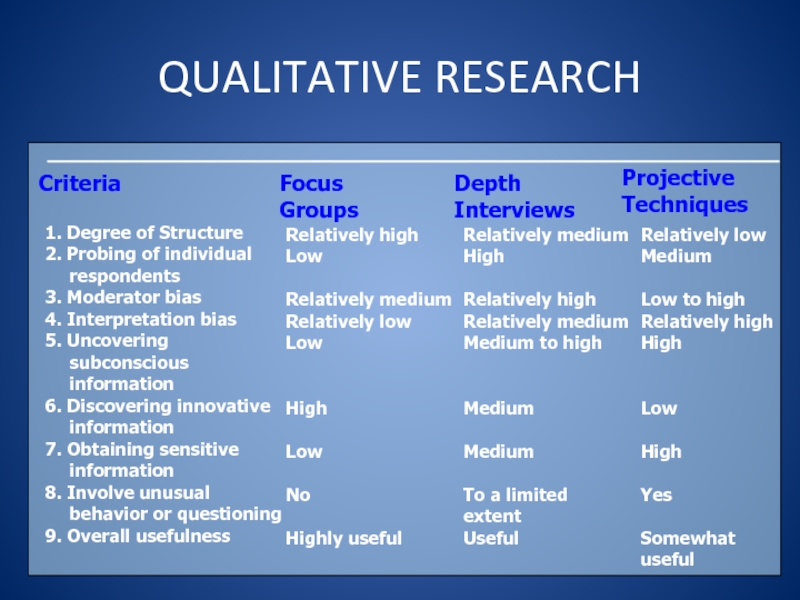
1. Degree of Structure
2. Probing of individual respondents
3.
Moderator bias
4. Interpretation bias
5. Uncovering subconscious information
6. Discovering innovative information
7.
Obtaining sensitive information8. Involve unusual behavior or questioning
9. Overall usefulness
Relatively high
Low
Relatively medium
Relatively low
Low
High
Low
No
Highly useful
Relatively medium
High
Relatively high Relatively medium Medium to high
Medium
Medium
To a limited extent
Useful
Relatively low
Medium
Low to high
Relatively high
High
Low
High
Yes
Somewhat useful
Focus Groups
Depth Interviews
Projective Techniques
Criteria
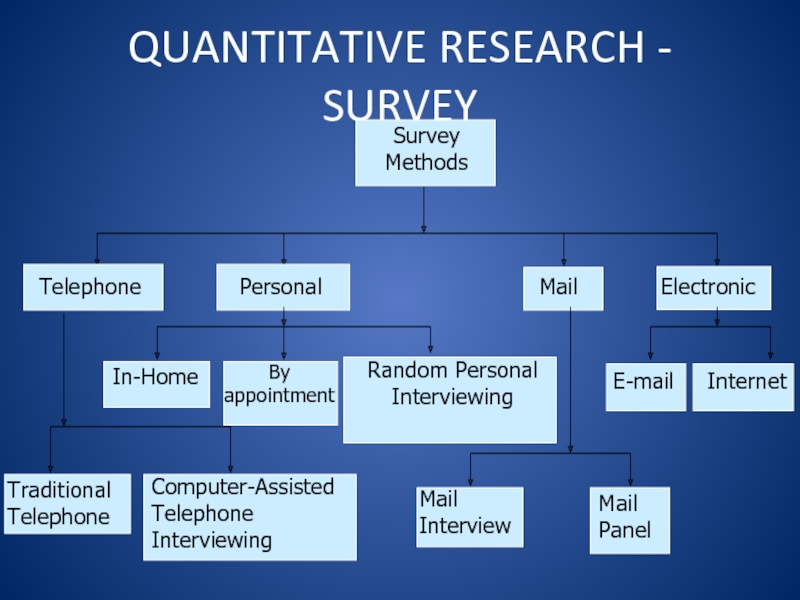
Слайд 28QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH SURVEY
SURVEY METHOD:
STRUCTURED QUESTIONNAIRE
GIVEN TO A SAMPLE OF
A POPULATION
DESIGNED TO GAIN SPECIFIC INFORMATION
Слайд 30QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH - EXPERIMENTATION
EXPERIMENTATION METHOD:
Scientific investigation in which
an investigator
manipulates and controls one or more independent variables and
observes
the dependent variable for variation concomitant to the manipulation of the independent variables.*Слайд 34SUMMARY
Qualitative methods focus on generating exploratory initial/progressive insights into questions
and problems
Depth probing of hidden attitudes, feelings or behaviour
Focus Groups
In depth Interviews
Projective Techniques
Слайд 35SUMMARY
Quantitative Research is interested in using formalised, standard structured questioning,
whereby response options are pre-determined
Usually to be administered to significantly
large numbers of people.Descriptive Causal
(Surveys) (Experimentation)