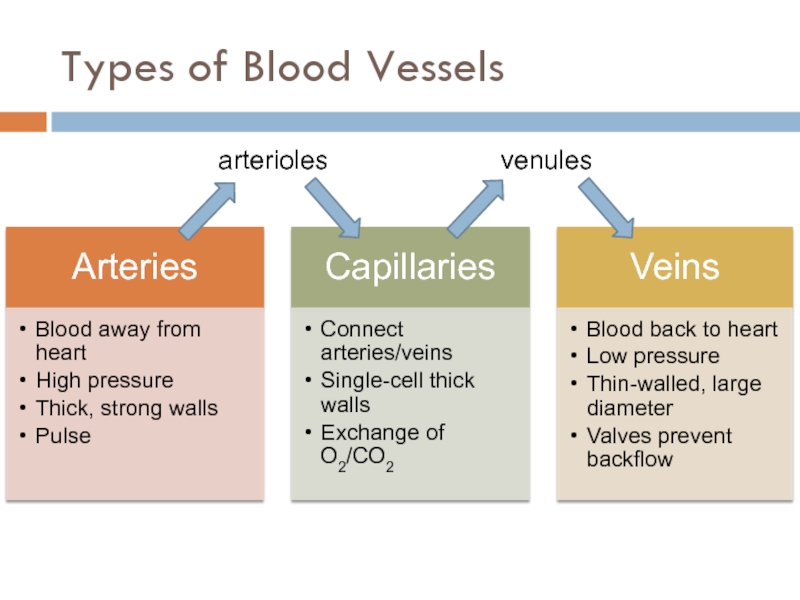
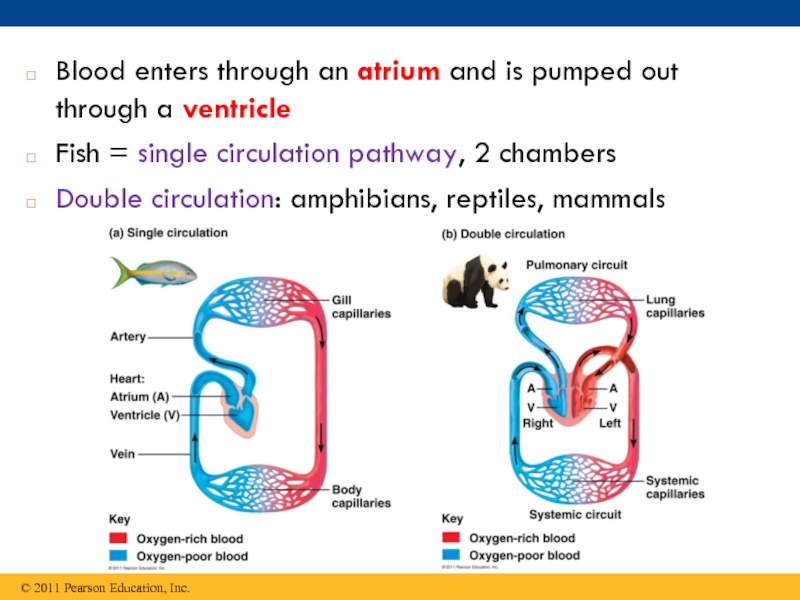
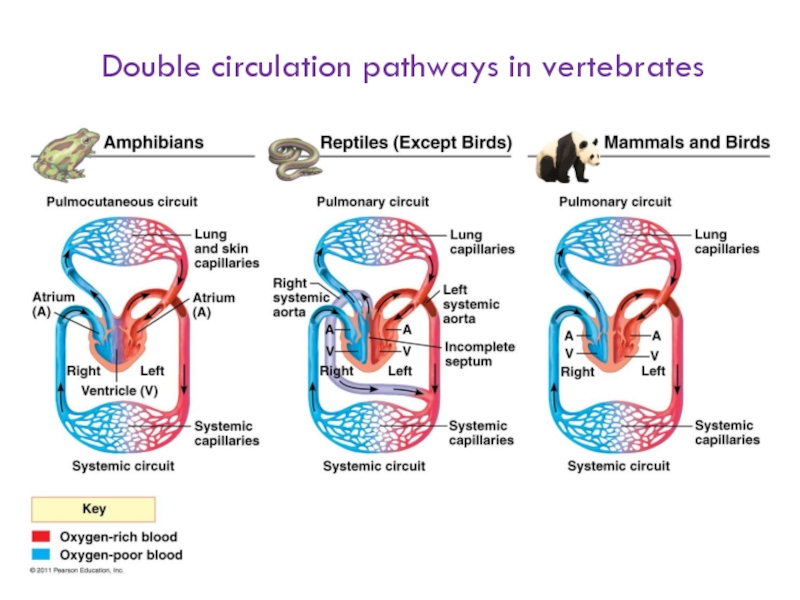
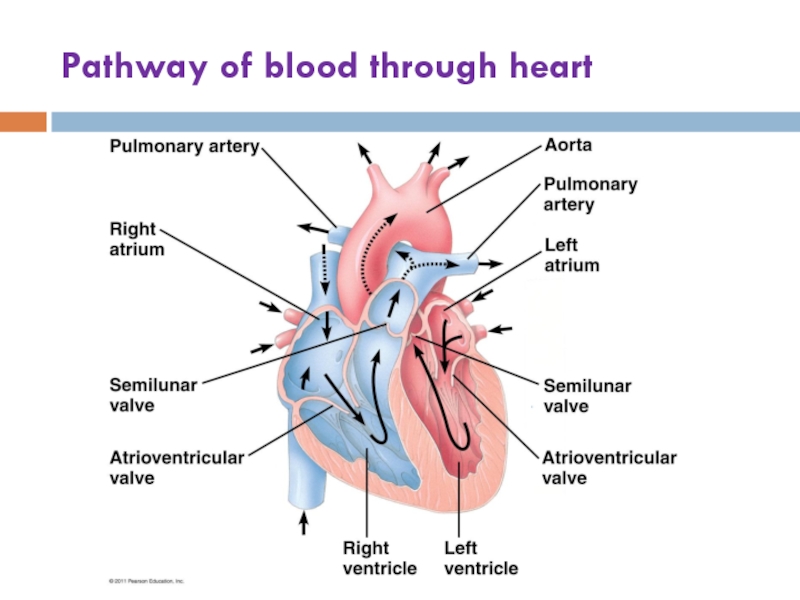
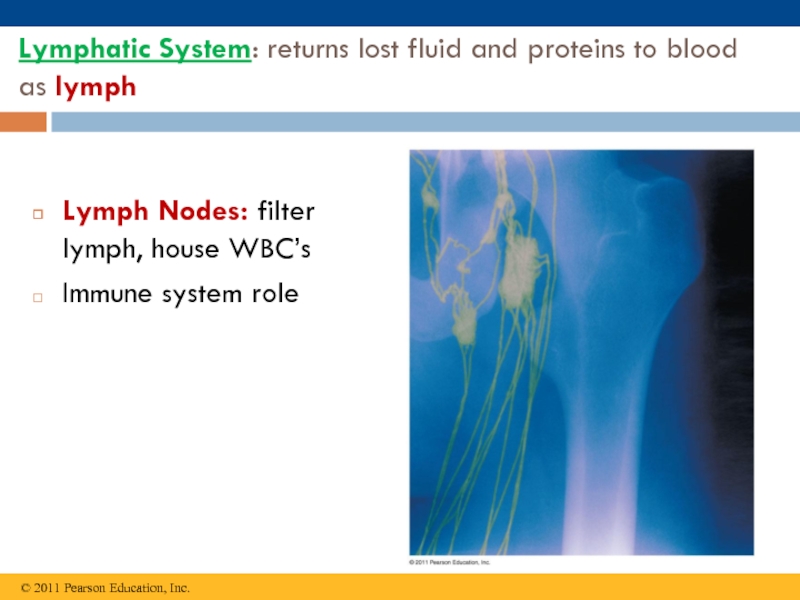
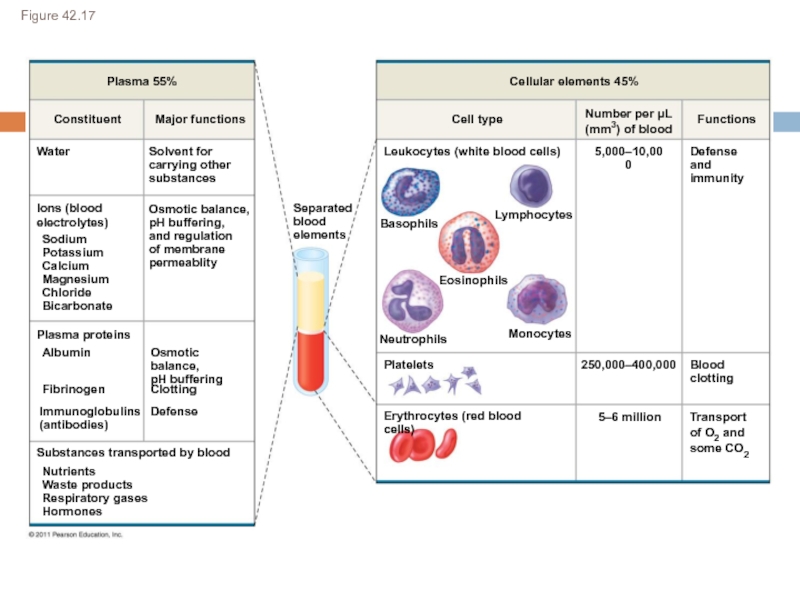
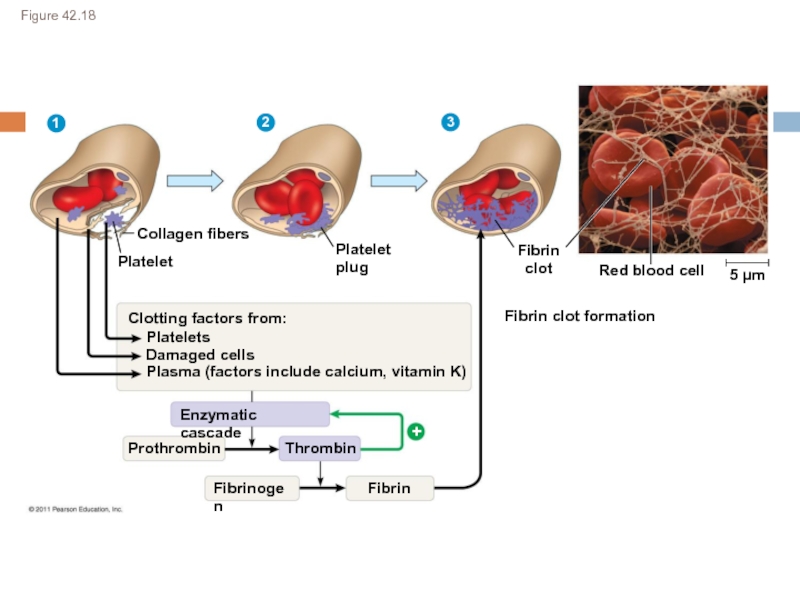
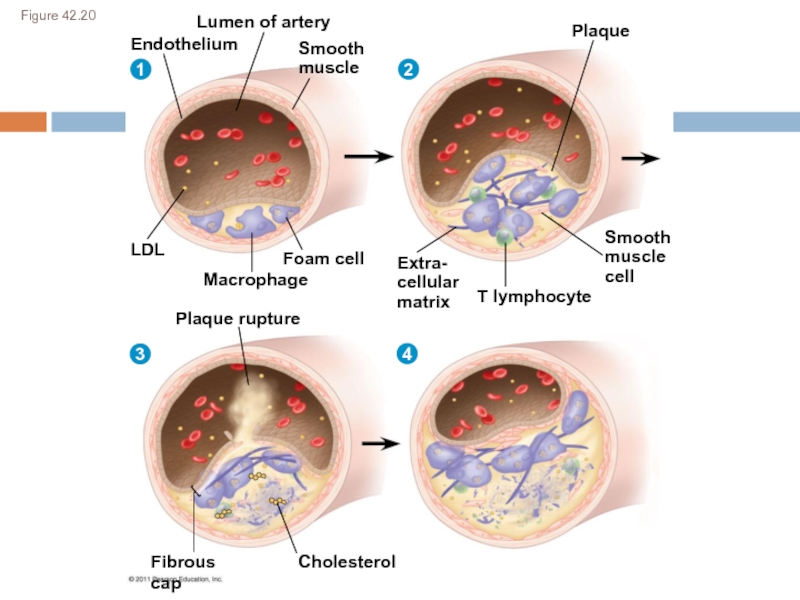
macromolecules are chemically digested.
(Ch. 41) Where do vertebrates store excess
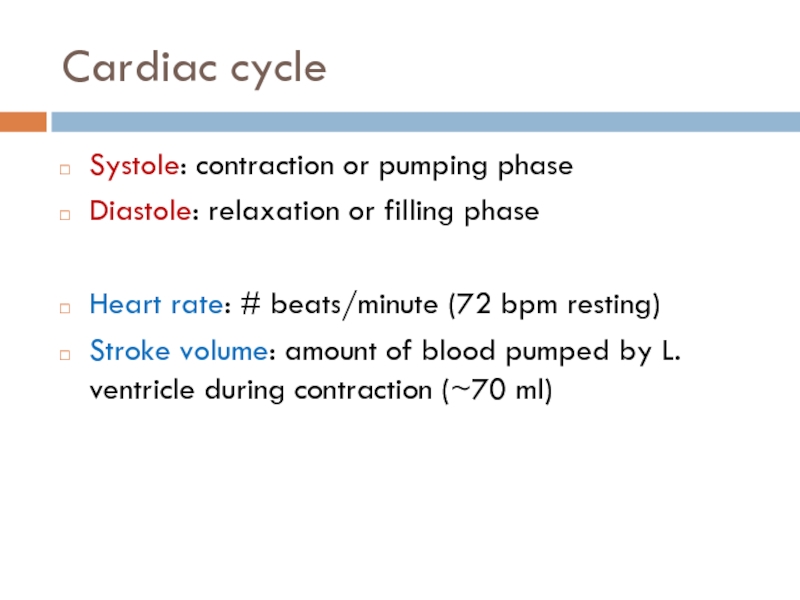
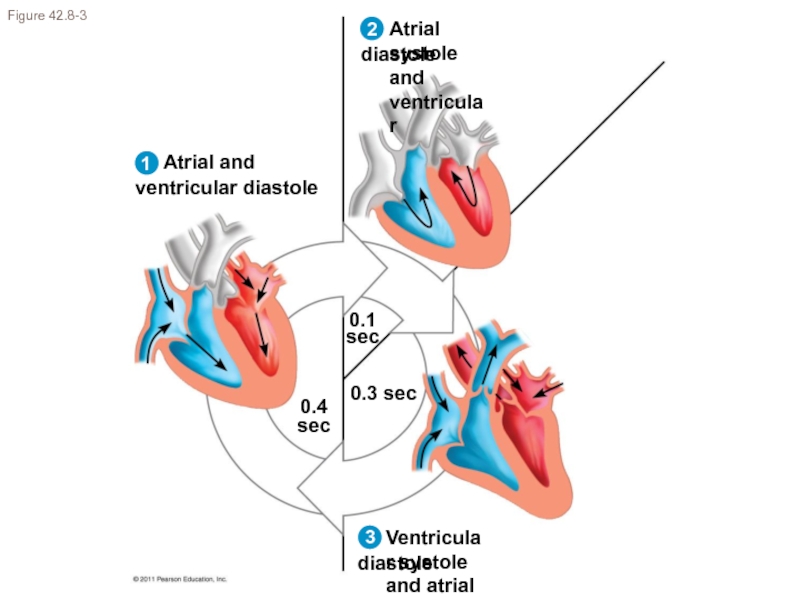
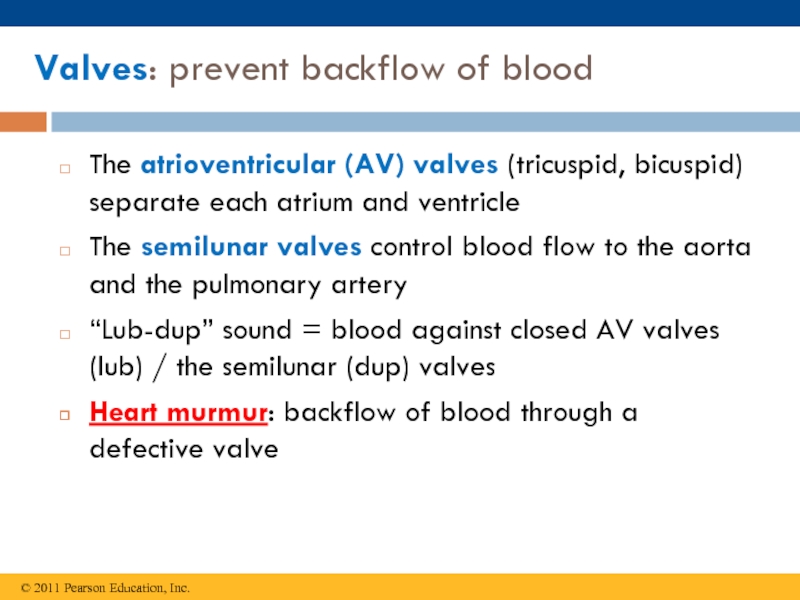
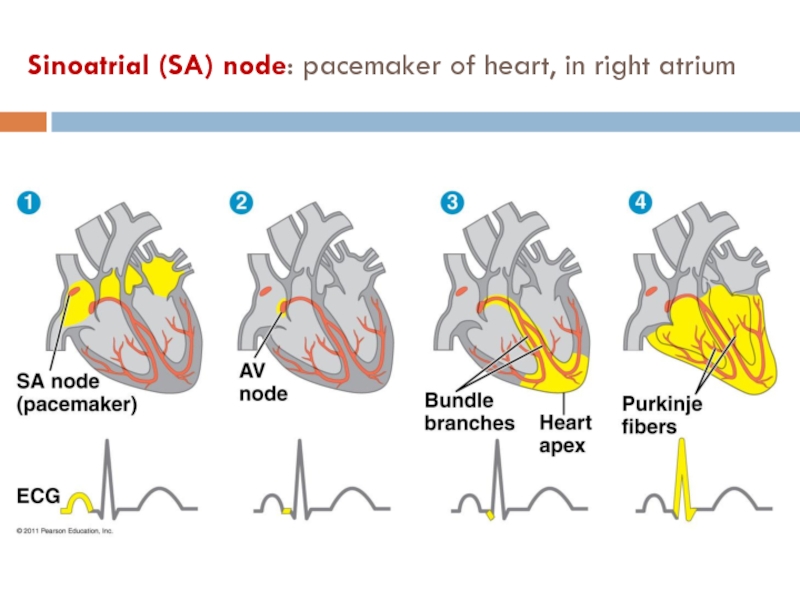
calories?(Ch. 42) Draw and label the structure of a human heart.
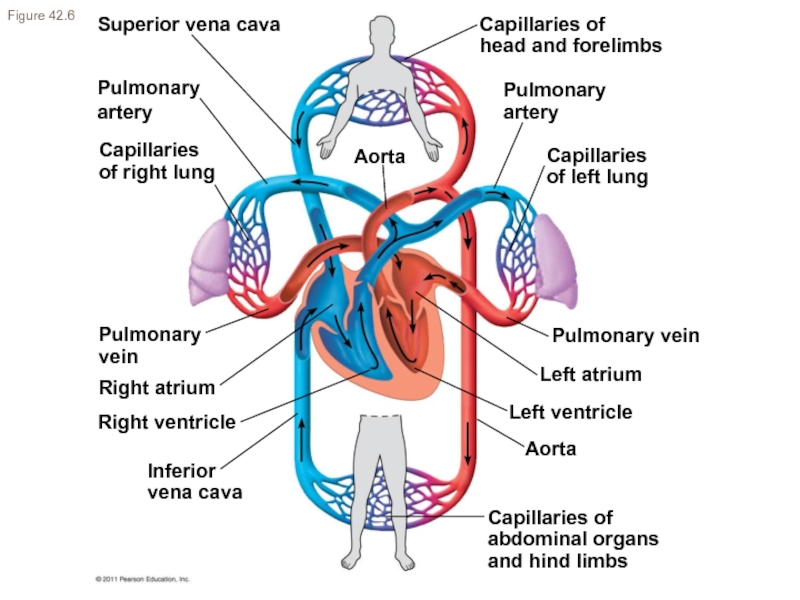
(Ch. 42) List the pathway of a single red blood cell through the heart.