Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Assessing of reading
Содержание
- 1. Assessing of reading
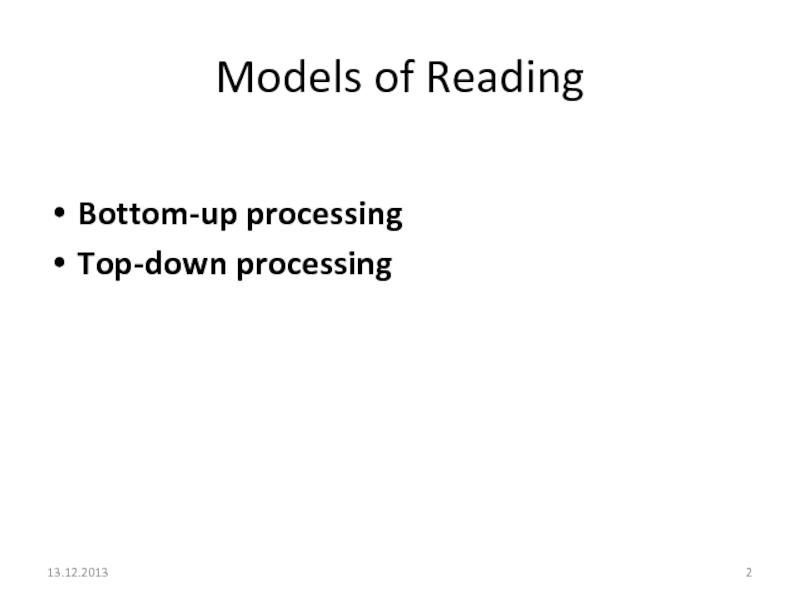
- 2. Models of ReadingBottom-up processingTop-down processing
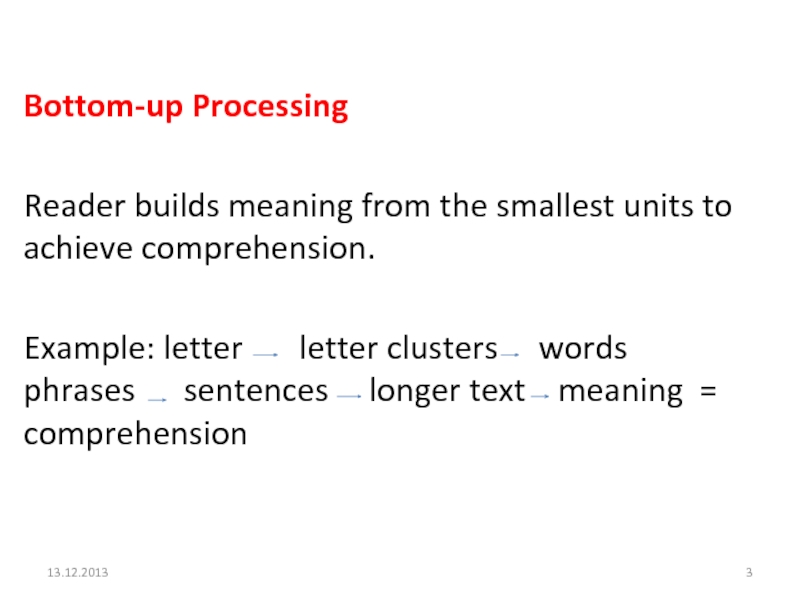
- 3. Bottom-up ProcessingReader builds meaning from the smallest
- 4. Top-down ProcessingReader generates meaning by employing background
- 5. The assessment of reading ability does not
- 6. Genres of readingAcademic Reading (i.e. articles, thesis,
- 7. MicroskillsDiscriminate among the distinctive graphemes and orthographic
- 8. MacroskillsRecognize the rhetorical forms of written discourse
- 9. DESIGNING ASSESSMENT TASKSPerceptive reading SelectiveInteractiveExtensive
- 10. Perceptive Reading- involve attending to the components
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Selective Reading- brief responses are intended
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. Слайд 15
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Interactive Reading - tasks at this level
- 23. Interactive Reading Two approaches to
- 24. Interactive Reading Cloze procedure,
- 25. Interactive Reading Cloze procedure,
- 26. Interactive Reading Variations on
- 27. Interactive Reading IMPROMPTU READING PLUS
- 28. Interactive ReadingEDITING (LONGER TEXTS)-authenticity is increased. the
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. Sсanninga one to two page news
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. Extensive Reading - it involves somewhat longer
- 33. Tasks that can be applied in extensive
- 34. Слайд 34
- 35. Слайд 35
- 36. Слайд 36
- 37. Responding - it asks the
- 38. Thank you
- 39. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3
Bottom-up Processing
Reader builds meaning from the smallest units to achieve
comprehension.
words phrases sentences longer text meaning = comprehensionСлайд 4Top-down Processing
Reader generates meaning by employing background knowledge, expectations, assumptions,
and questions, and reads to confirm these expectations.
Example: Pre-reading activities
+ background knowledge (cultural, linguistic, syntactic, and historical) = comprehensionСлайд 5
The assessment of reading ability does not end with the
measurement of comprehension. Strategic pathways to full understanding are often
important factors to include in assessing learners, especially in the case of most classroom assessments that are formative in nature.All assessment of reading must be carried out by inference.
Слайд 6Genres of reading
Academic Reading (i.e. articles, thesis, textbooks, essays ect.)
Job-related
Reading (i.e. letter/emails, manuals, applications, project repots ect.)
Personal Reading (i.e.
newspapers/magazines, novels, messages, poetry, recipes, menus, maps ect.Слайд 7Microskills
Discriminate among the distinctive graphemes and orthographic patterns of English.
Retain
chunks of language of different lengths in short term memory.
Recognize
a core of words, and interpret word order patterns and their significance.Recognize grammatical word classes (nouns, verbs), systems (tense, agreement, pluralization), patterns, rules and elliptical forms.
Recognize that a particular meaning may be expressed in different grammatical forms.
Recognize cohesive devices in written discourse and their role in signaling the relationship between and among clauses.
Слайд 8Macroskills
Recognize the rhetorical forms of written discourse and their significance
for interpretation.
Recognize the communication functions of written texts, according to
form and purpose.Infer context that is not explicit by using background knowledge.
Distinguish between literal and implied meanings.
Detect culturally specific references and interpret them in a context of the appropriate cultural schemata.
Develop and use reading strategies, such as scanning and skimming, detecting discourse markers, guessing the meaning of words from context, and activating for the interpretation of texts.
Слайд 10Perceptive Reading
- involve attending to the components of larger stretches
discourse: letters, words, punctuation and other graphemic symbols.
- bottom-up processing
is implied.1) Reading aloud
2) Written response
3) Multiple-Choice
4) Picture-Cued Items
Слайд 11
Perceptive Reading
Multiple ChoiceMinimal pair distinction
Test takers read: Circle “S” for same or “D” for different.
1. led let S D
2. bit bit S D
3. seat set S D
4. too to S D
Слайд 12
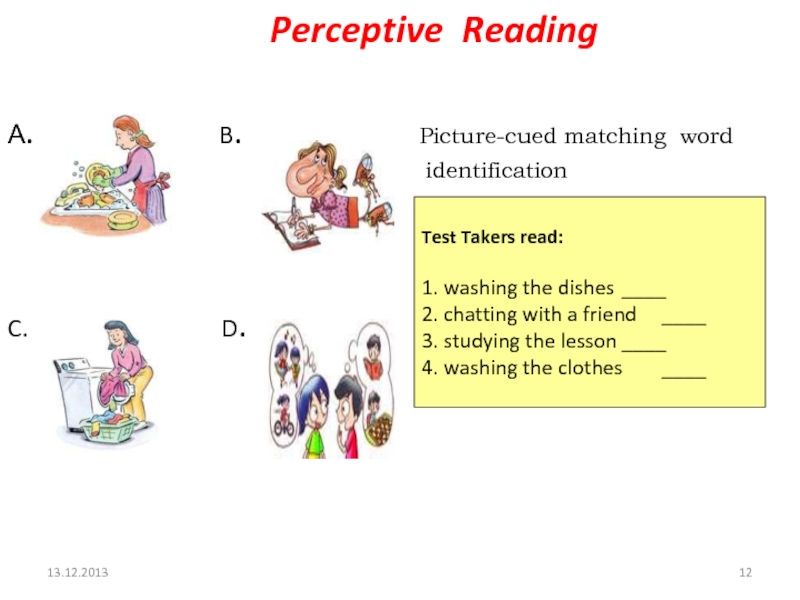
Perceptive Reading
A.
B. Picture-cued matching word identification
C. D.
Test Takers read:
1. washing the dishes ____
2. chatting with a friend ____
3. studying the lesson ____
4. washing the clothes ____
Слайд 13Selective Reading
- brief responses are intended and a combination
of bottom-up and top-down processing may be used.
stimuli include sentences,
brief paragraphs and simple charts and graphs.Multiple-Choice
2) Matching Tasks
3) Editing Tasks
4) Gap-Filling Tasks
Слайд 14
Selective Reading
Multiple-choice vocabulary/grammar tasks1. He’s not married. He’s __________.
A. young
B. single
C. first
D. a husband
2. If there’s no doorbell, please __________ on the door.
A. kneel
B. type
C. knock
D. shout
Слайд 15
Selective Reading
3. The mouse is __________
the bed.A. under
B. around
C. between
4. The bank robbery occurred __________ I was in the
restroom.
A. that
B. during
C. while
D. which
Слайд 16
Selective Reading
Contextualized multiple-choice vocabulary/grammar tasks
1. Oscar:
Do you like champagne?Lucy: No. I can’t __________.
A. stand
B. prefer
C. hate
2. Manager: Do you like to work by yourself?
Employee: Yes, I like to work __________.
A. independently
B. definitely
C. impatiently
Слайд 17
Selective Reading
Multiple-choice cloze vocabulary/grammar tasksI’ve lived in the United States (21) _____ three years. I (22) _____
live in Costa Rica. I (23) _____ speak any English. I used to (24)_____
homesick, but now I enjoy (25) _____ here. I never (26) _____ back
home (27) _____ I came to the United States, but I might (28) _____
to visit my family soon.
21. A. since 23. A. couldn’t 25. A. Live 27. A. when
B. for B. could B. to live B. while
C. during C. can C. living C. since
22. A. used to 24. A. been 26. A. be 28. A. go
B. use to B. be B. been B. will go
C. was C. being C. was C. going
Слайд 18
Selective Reading
Matching Tasks
Vocabulary matching task
Write in the letter of the definition on the right that matches
the word on the left.
____1. exhausted a. unhappy
____2. disappointed b. understanding of others
____3. enthusiastic c. tired
____4. empathetic d. excited
Слайд 19
Selective Reading
Editing Tasks
- Editing for grammatical or rhetorical errors is a widely used test method for assessing linguistic competence in reading.
Слайд 20
Selective Reading
Multiple-choice grammar editing
taskChoose the letter of the underlined word that is not correct.
1. The abrasively action of the wind wears away softer layers of rock.
A B C D
2. There are two way of making a gas condense: cooling it or putting it
A B C D
under pressure.
3. Researchers have discovered that the application of bright light can
A B
sometimes be uses to overcome jet lag.
C D
Слайд 21
Selective Reading
Gap-Filling Tasks
-the response is to write a word or phrase.
Oscar: Doctor, what should I do if I get sick?
Doctor: It is best to stay home and ________________.
If you have a fever, ______________________.
You should drink as much _________________.
The worst thing you can do is _______________.
You should also __________________________.
Слайд 22Interactive Reading - tasks at this level have a combination
of form-focused and meaning-focused objectives but with more emphasis on
meaning.- it implies a little more focus on top-down processing than on bottom-up.
Cloze Tasks - the ability to fill in gaps in an incomplete image (visual, auditory or cognitive) and supply (from background schemata) omitted details.
cloze tests are usually a minimum of two paragraphs in length in order to account for discourse expectancies.
-typically, every seventh word (plus or minus two) is deleted (known as fixed-ratio deletion) but many cloze test designers instead use a rational deletion procedure of choosing deletions according to the grammatical or discourse functions of the words.
Слайд 23
Interactive Reading
Two approaches to the scoring of cloze test
Exact word
method- gives credit to test-takers only if they insert the
exact word that was originally deleted.Appropriate word method- gives credit to the test-taker for supplying any word that is grammatically correct and that makes good sense in the context.
Слайд 24
Interactive Reading
Cloze procedure, fixed ratio deletion (every seventh word)
The recognition
that one’s feelings of (1) ____ and unhappiness
can coexist
much like (2) ____ and hate in a close relationship(3) ____ offer valuable clues on how to (4) ____ a happier life. It
suggests, for (5) ____ that changing or avoiding things that (6)
____ you miserable may well make you (7) ____ miserable but
probably no happier.
Слайд 25
Interactive Reading
Cloze procedure, rational deletion (prepositions and conjunctions)
The recognition that
one’s feelings (1) ____ happiness (2) ____
unhappiness can coexist much
like love and hate (3) ____ a close relationship may offer valuable clues (4) ____ how to lead
a happier life. It suggests, (5) ____ example, that changing (6)
____ avoiding things that make you miserable may well make
you less miserable (7) ____ probably no happier.
Слайд 26
Interactive Reading
Variations on Standard Cloze Testing
C-test- the second half (according
to the number of letters) of every other word is
obliterated and the test-taker must restore each word.Cloze-elide procedure- it inserts words into a text that do not belong. The test-taker’s task is to detect and cross out the “intrusive” words.
Слайд 27
Interactive Reading
IMPROMPTU READING PLUS COMPREHENSION QUESTIONS
-the traditional “Read a passage
and answer some questions” technique which is the oldest and
the most common.SHORT-ANSWER TASKS
-a reading passage is presented and the test-taker reads questions that must be answered in a sentence or two.
Open-ended reading comprehension questions
1. What do you think is the main idea of this passage?
2. What would you infer from the passage about the future of air
travel?
3. In line 6, the word sensation is used. From the context, what
do you think this word means?
4. Why do you think the airlines have recently experienced a
decline?
Слайд 28Interactive Reading
EDITING (LONGER TEXTS)
-authenticity is increased.
the task simulates proofreading
one’s own essay, where it is imperative to find and
correct errors.if the test is connected to a specific curriculum, the test designer can draw up specifications for a number of grammatical and rhetorical categories that match the content of the courses.
Слайд 29
Interactive reading
Scanning
-it is a strategy used by all readers to find relevant information in a text.
Слайд 30 Sсanning
a one to two page news article
an essay
a chapter
in a textbook
a technical report
a table or chart depicting some
research findingsСлайд 31
Interactive reading
Ordering Taskssometimes called the “strip story” technique.
Sentence ordering tasks
Put the scrambled sentences into the correct order that they happened.
(…..) A. It was called “The Last Waltz”.
(…..) B. The street was in total darkness.
(…..) C. Because it was one he and Richard had learnt at school.
(…..) D. Peter looked outside.
(…..) E. he recognised the tune.
(…..) F. And it seemed deserted
(…..) G. he thought he heard someone whistling
Слайд 32Extensive Reading
- it involves somewhat longer texts. Journal articles, technical
reports, longer essays, short stories and books fall into this
category.- reading of this type of discourse almost always involves a focus on meaning using mostly top-down processing, with only occasional use of targeted bottom-up strategy.
Слайд 33Tasks that can be applied in extensive reading:
-impromptu reading
plus comprehension questions
-short answer tasks
-editing
-scanning
-ordering
-information
transfer and-interpretation (discussed under graphics)
Слайд 34
Skimming Tasks
- it is the process of rapid coverage of reading matter to determine its gist or main idea.
Слайд 35
Skimming
Task
The test-taker skims the text and answer the following questions.
What is the main idea of this text?
What is the author’s purpose in writing the text?
What kind of writing is this (newspaper, article, manual, novel, etc.)?
What type of writing is this (expository, technical, narrative, etc.)?
How easy or difficult do you think this text will be?
What do you think you will learn from the text?
How useful will the text be for your (profession, academic needs, interests)?
Слайд 36
Extensive Reading
Summarizing and RespondingSummarizing- requires a synopsis or overview of the text.
Criteria for assessing a summary
1. Expresses accurately the main idea and supporting ideas.
2. Is written in the student’s own words; occasional vocabulary from the original text is acceptable.
3. Is logically organized.