Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Global Economic Crisis and Belarus
Содержание
- 1. Global Economic Crisis and Belarus
- 2. CONTENTSIntroductionMacroeconomic and market situationCrisis’s consequences a) Devaluation of Belarusian ruble b) Social issuesWays off
- 3. INTRODUCTION At first glance, it seems that Belarus’
- 4. Macroeconomic and market situation The rapid decrease of
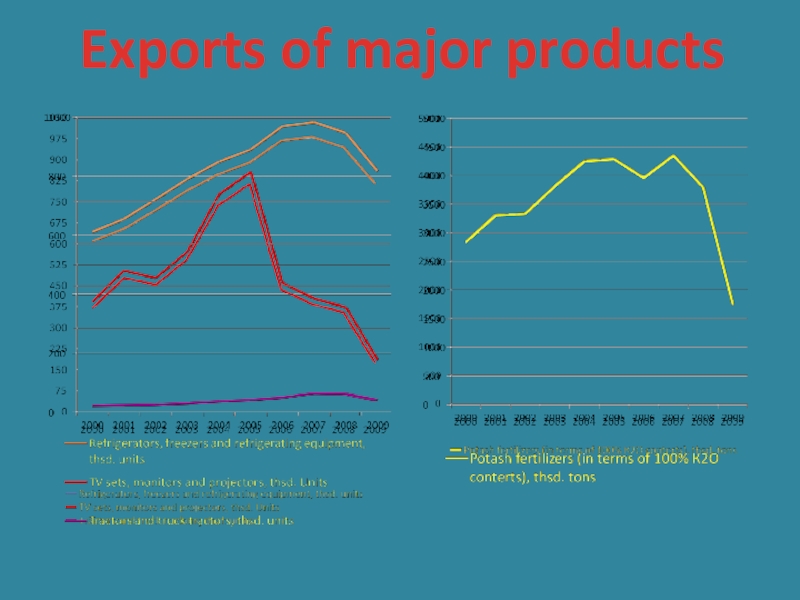
- 5. Exports of major products
- 6. Macroeconomic and market situation Taking into account the
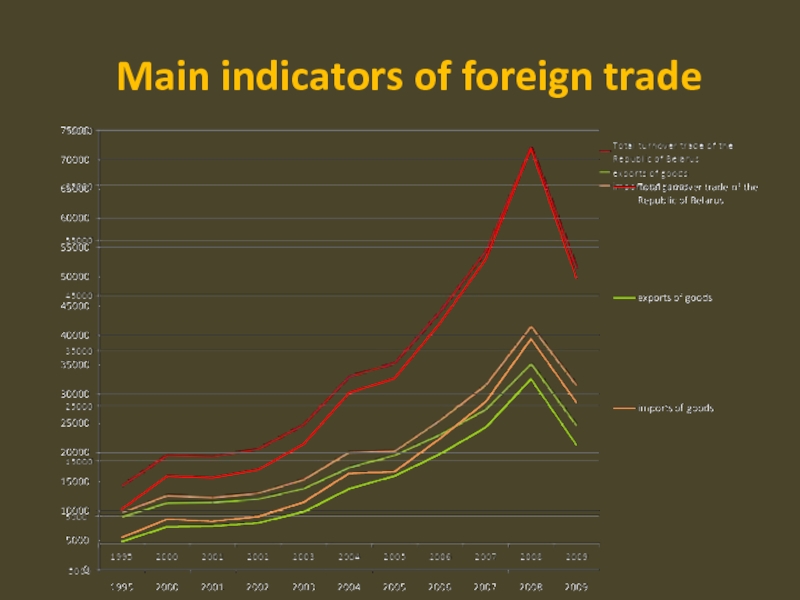
- 7. Main indicators of foreign trade
- 8. CRISIS’S CONSEQUENCES. DEVALUATION OF BELARUSIAN RUBLE Growing
- 9. CRISIS’S CONSEQUENCES. DEVALUATION OF BELARUSIAN RUBLE Thus
- 10. Crisis’s consequences and Social issues The potential increase
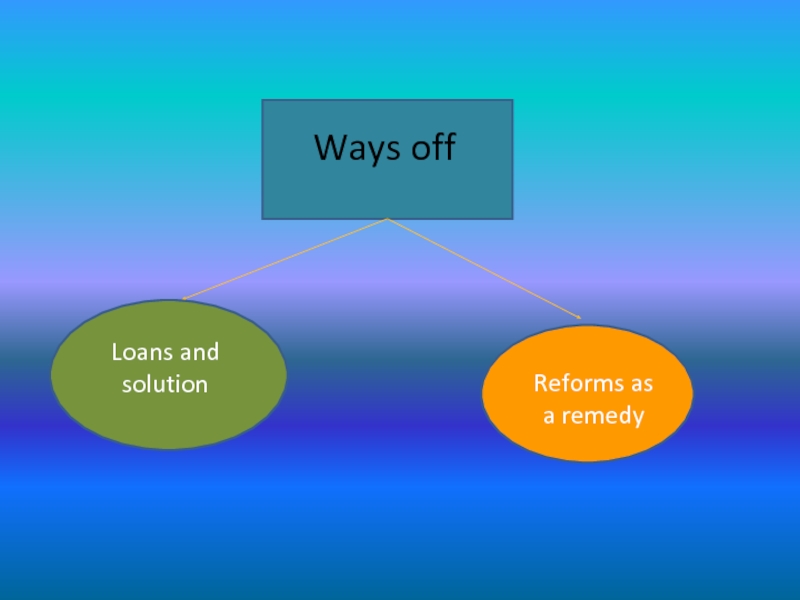
- 11. Ways offLoans and solutionReforms as a remedy
- 12. Ways offLoans and solution. Belarus was among
- 13. Ways offReforms as a remedy
- 14. Thanks for attention!
- 15. Скачать презентанцию
CONTENTSIntroductionMacroeconomic and market situationCrisis’s consequences a) Devaluation of Belarusian ruble b) Social issuesWays off
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2CONTENTS
Introduction
Macroeconomic and market situation
Crisis’s consequences
a) Devaluation of Belarusian ruble
b) Social
issues
Слайд 3INTRODUCTION
At first glance, it seems that Belarus’ recent economic performance
surprised most outside observers. According to official statistics, economic growth
in Belarus between January and June 2009 amounted to a 0.3% increase year-on-year, while Russia’s economy – a major market for Belarusian industrial exports – dropped by 10.1% year-by-year. Comparison of the country’s previous economic performance illustrates the negative impact of the crisis. A decrease of external demand hit Belarusian industry and increased external imbalances, while the fall of energy prices and deterioration of enterprises deteriorated government revenues. All of these factors unveiled structural problems that required appropriate action. Instead, the government has chosen to delay “radical” reforms by borrowing abroad.Слайд 4Macroeconomic
and market situation
The rapid decrease of external demand in Belarus
is a major consequence of the global economic crisis. The
decline in industrial demand resulted in increased inventories (finished good and stock). As a result, between January and May of 2009, Belarusian merchandise exports dropped by 48% year-on-year.Слайд 6Macroeconomic
and market situation
Taking into account the existing relationship between export
and import volumes (1% to 0.64%), the contraction of Belarusian
exports should result in a growing trade deficit (see diagram).Слайд 8CRISIS’S CONSEQUENCES.
DEVALUATION OF BELARUSIAN RUBLE
Growing external imbalances forced the
government to revise exchange rate policy. The devaluation was required
by the IMF. Despite the measure, this devaluation has not been followed by a restriction in domestic demand,Слайд 9CRISIS’S CONSEQUENCES.
DEVALUATION OF BELARUSIAN RUBLE
Thus the current account deficit
persists. The main reason for exchange rate instability – the
current account deficit. Here you can see the basic measures accepted by the Belarus authorities. They are:Слайд 10Crisis’s consequences and
Social issues
The potential increase of poverty creates challenges
for social policy, due to a drastic of government revenues
and poor identification of vulnerable groups, especially unemployed and low-paid workers. The main “social” choice for the government is between hidden and open unemployment. Efficient privatization is another possible solution, although it would require firing excess labor. It would create new work places and generate revenues for social support.Слайд 12Ways off
Loans and solution.
Belarus was among the first transition economies
to ask for an International Monetary Fund (IMF) stand-by loan.
As a great part of the loan agreement the Fund expects the Belarusian government to promote father liberalization efforts which includes preparing the economy for privatization, as well as implementing some structural changes deemed “essential to improve prospects for long-run growth and external stability”.Слайд 13Ways off
Reforms as a remedy
At the moment, the
shape of this “revised” economic program is not clear. However,
the previous version, approved at the end of 2008, included several measures which can be viewed as improving liberalization efforts – including prices, wages, and doing business. After recent discussions with the IMF and World Bank it seems that Belarusian authorities are ready to launch large scale all of for privatization efforts. Evidently, these measures are good for growth in the medium to long- term, but the question remains:will they solve the country’s short-term economic problems?
Теги