Слайд 2Insulin - první gen biotech 1982
Слайд 3
Recombinant proteins for human use
~2003
Approved in US or EU
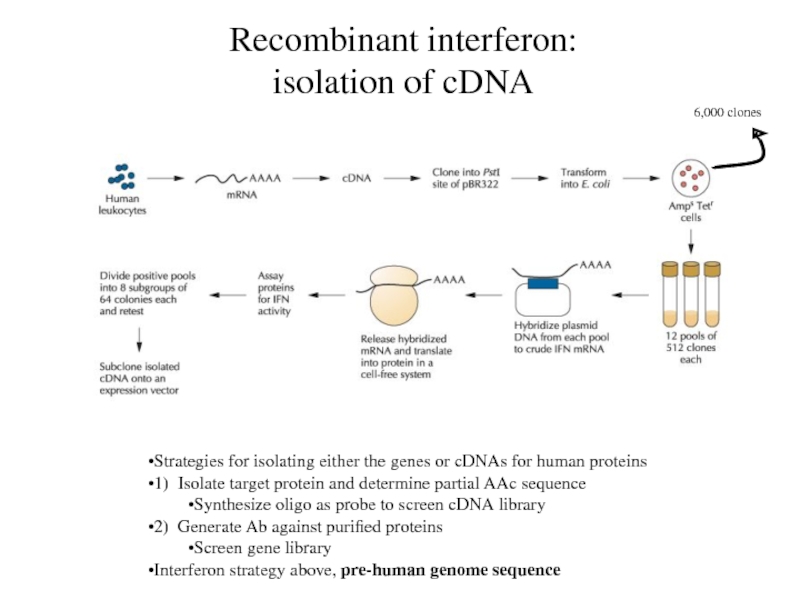
Слайд 4Recombinant interferon: isolation of cDNA
Strategies for isolating either the genes
or cDNAs for human proteins
1) Isolate target protein and determine
partial AAc sequence
Synthesize oligo as probe to screen cDNA library
2) Generate Ab against purified proteins
Screen gene library
Interferon strategy above, pre-human genome sequence
6,000 clones
Слайд 5
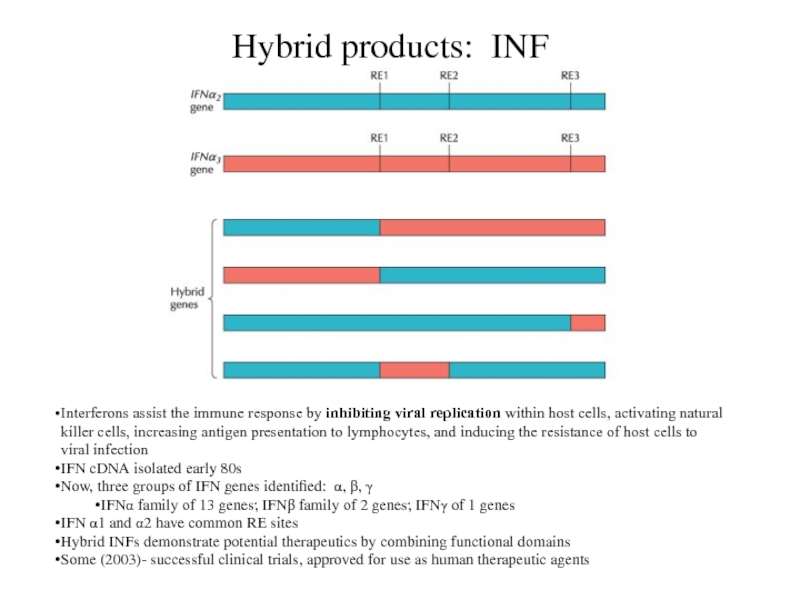
Hybrid products: INF
Interferons assist the immune response by inhibiting
viral replication within host cells, activating natural
killer cells, increasing
antigen presentation to lymphocytes, and inducing the resistance of host cells to
viral infection
IFN cDNA isolated early 80s
Now, three groups of IFN genes identified: , ,
IFN family of 13 genes; IFN family of 2 genes; IFN of 1 genes
IFN 1 and 2 have common RE sites
Hybrid INFs demonstrate potential therapeutics by combining functional domains
Some (2003)- successful clinical trials, approved for use as human therapeutic agents
Слайд 6
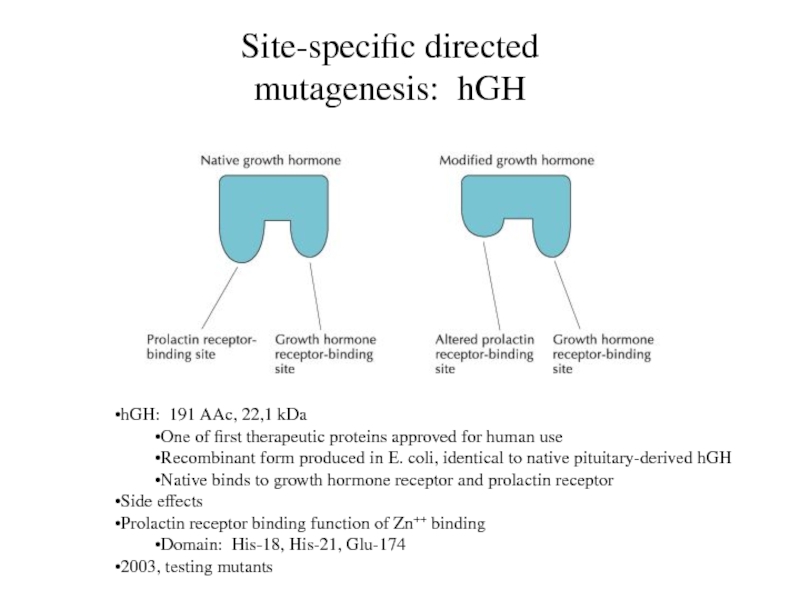
Site-specific directed mutagenesis: hGH
hGH: 191 AAc, 22,1 kDa
One of
first therapeutic proteins approved for human use
Recombinant form produced in
E. coli, identical to native pituitary-derived hGH
Native binds to growth hormone receptor and prolactin receptor
Side effects
Prolactin receptor binding function of Zn++ binding
Domain: His-18, His-21, Glu-174
2003, testing mutants
Слайд 7
Optimizing gene expression
Multistep process:
Design a protein, construct a recombinant
molecule, express and characterize
Need to optimize expression
First, either prokaryote or
eukaryote host
Comparative analysis of host and expression
ex., interleukin-3 expression
Best in Bacillus licheniformis
Balance with glycosylation in eukaryotic hosts
But, glycosylation is not essential for interleukin-3 activity
Слайд 8
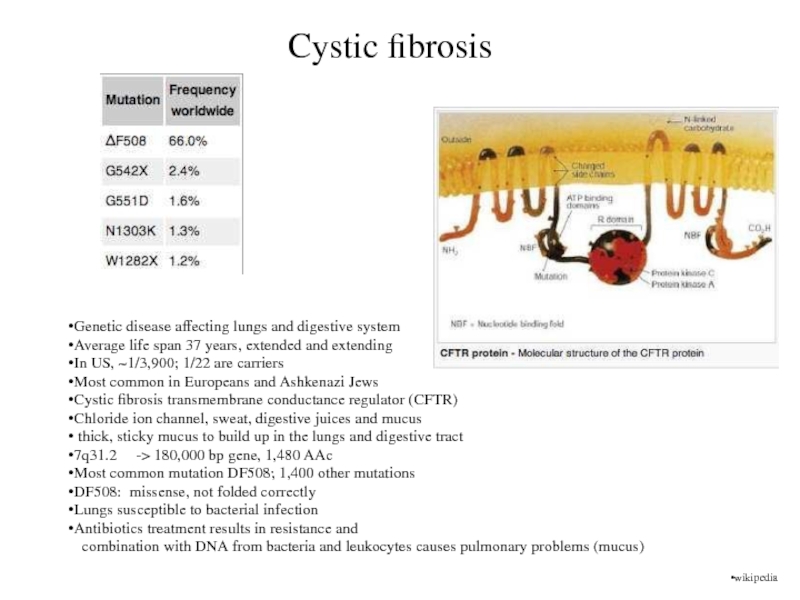
Cystic fibrosis
Genetic disease affecting lungs and digestive system
Average life
span 37 years, extended and extending
In US, ~1/3,900; 1/22 are
carriers
Most common in Europeans and Ashkenazi Jews
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)
Chloride ion channel, sweat, digestive juices and mucus
thick, sticky mucus to build up in the lungs and digestive tract
7q31.2 -> 180,000 bp gene, 1,480 AAc
Most common mutation DF508; 1,400 other mutations
DF508: missense, not folded correctly
Lungs susceptible to bacterial infection
Antibiotics treatment results in resistance and
combination with DNA from bacteria and leukocytes causes pulmonary problems (mucus)
wikipedia
Слайд 9
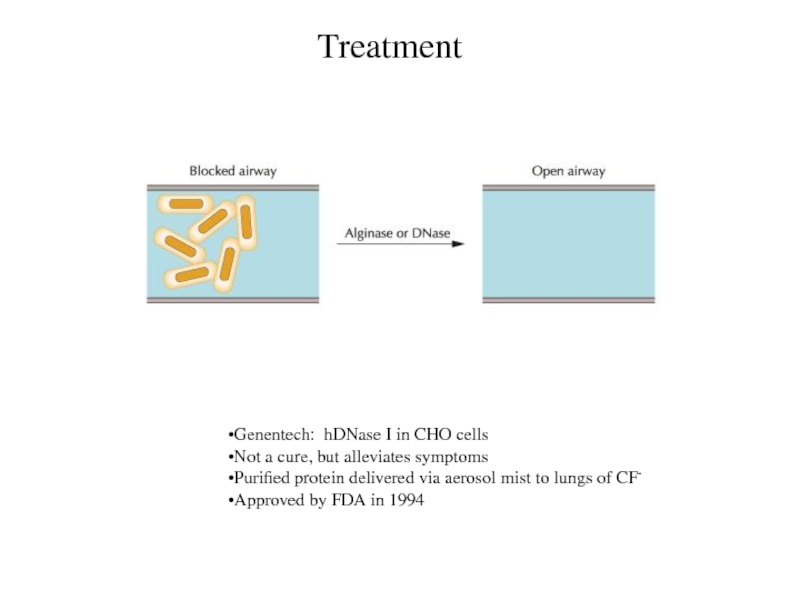
Treatment
Genentech: hDNase I in CHO cells
Not a cure, but
alleviates symptoms
Purified protein delivered via aerosol mist to lungs of
CF-
Approved by FDA in 1994
Слайд 10
Optimizing treatment
Another symptom,
In response to bacteria in lungs,
leukocytes
cluster and lyse bacteria (and leukocytes)
Lysed leukocytes release actin
Monomeric actin
binds DNase I very tightly and inhibits
Limits effectiveness
X-ray structure data suggested Ala-144 required for binding
or Tyr-65
Changing either to Arg decreases actin binding by 10,000x
Clinical efficacy of mutants to be determined (2003)
Слайд 11
Clearing the lungs 2 with alginate lyase
http://www.lsbu.ac.uk/water/hyalg.html
Alginate produced by
seaweeds, soil and marine bacteria
P. aeruginosa excretion in lungs contributes
to viscosity of mucus
In addition to DNase I treatment, alginate lysate can be used as therapeutic agent
Слайд 12
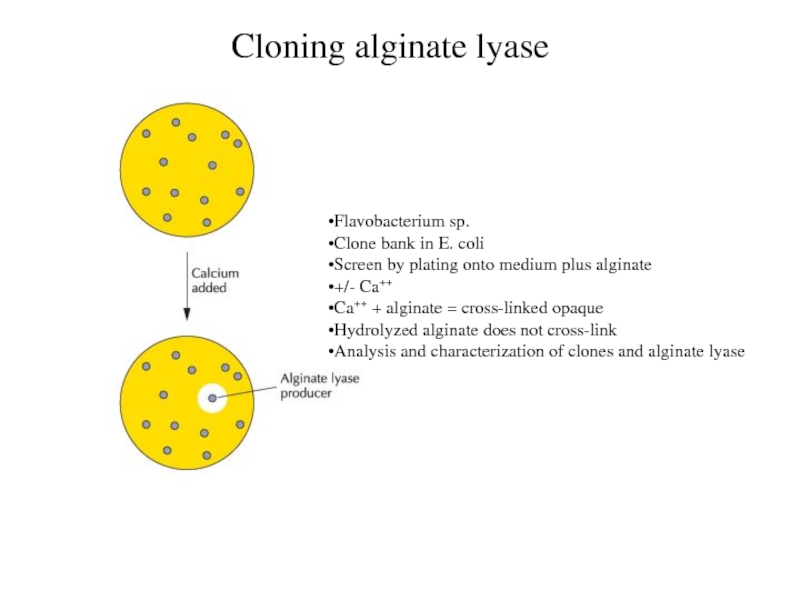
Cloning alginate lyase
Flavobacterium sp.
Clone bank in E. coli
Screen by
plating onto medium plus alginate
+/- Ca++
Ca++ + alginate = cross-linked
opaque
Hydrolyzed alginate does not cross-link
Analysis and characterization of clones and alginate lyase
Слайд 13
Alginate lyase[s]
ORF 69,000 Da
Precursor of three alginate lyases
-> 3,000
Da + 63,000 Da
63,000 Da lyses both bacterial and seaweed
alginates
63,000 Da -> 23,000 Da seaweed effective+ 40,000 Da bacterial effective
Clone bacterial activity portion
Слайд 14
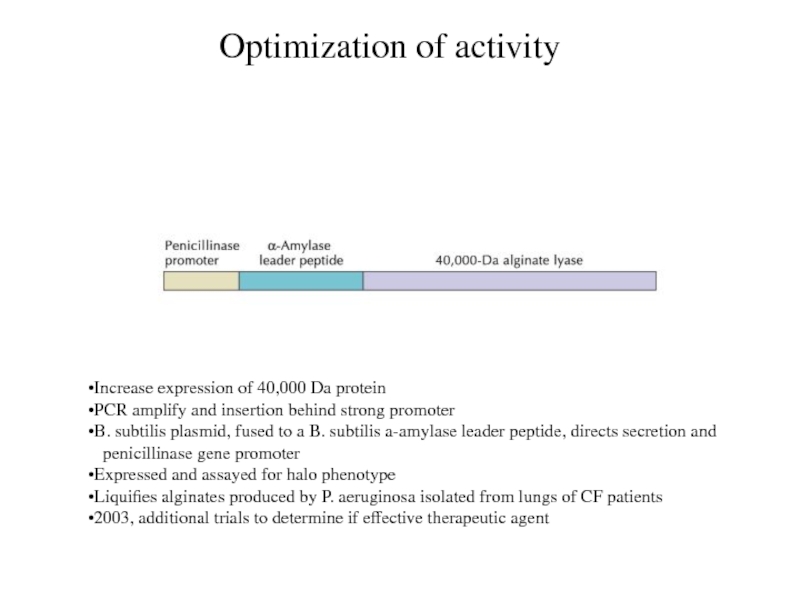
Optimization of activity
Increase expression of 40,000 Da protein
PCR amplify
and insertion behind strong promoter
B. subtilis plasmid, fused to a
B. subtilis a-amylase leader peptide, directs secretion and
penicillinase gene promoter
Expressed and assayed for halo phenotype
Liquifies alginates produced by P. aeruginosa isolated from lungs of CF patients
2003, additional trials to determine if effective therapeutic agent
Слайд 15
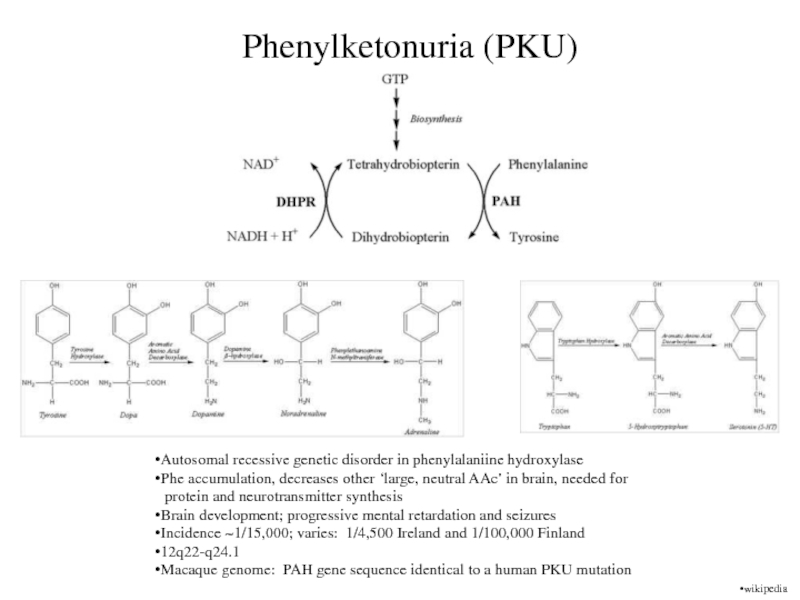
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Autosomal recessive genetic disorder in phenylalaniine hydroxylase
Phe accumulation,
decreases other ‘large, neutral AAc’ in brain, needed for
protein and neurotransmitter synthesis
Brain development; progressive mental retardation and seizures
Incidence ~1/15,000; varies: 1/4,500 Ireland and 1/100,000 Finland
12q22-q24.1
Macaque genome: PAH gene sequence identical to a human PKU mutation
wikipedia
Слайд 16
Phenylketonuria treatment[s]
Traditional treatment: diagnosis at birth or prenatal
Controlled semi-synthetic
diet with low levels of Phe
Possible treatment: metabolism of Phe
PAH
multienzyme complex, requiring cofactor
Phe ammonia lyase (PAL) converts Phe as well
Stable and does not require cofactor
To test concept, yPAL cloned and overexpressed in E. coli
Preclinical studies (2003) with mice deficient in PAL
See lower plasma levels of Phe when PAL injected or
administered as oral encapsulated enzyme
Слайд 17
Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) as therapeutic agents
Mouse mAb OKT3 first
to be approved by FDA
Immunosuppressive agent after organ transplant in
humans
Слайд 18
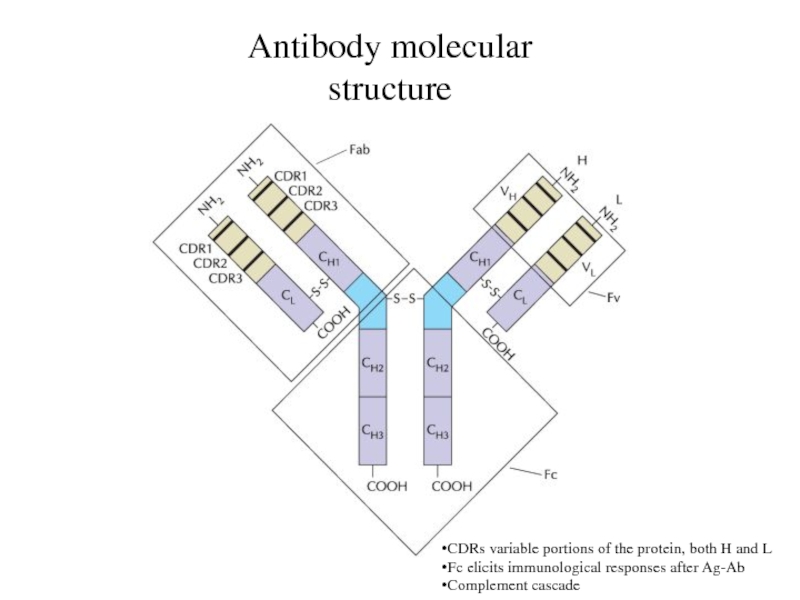
Antibody molecular structure
CDRs variable portions of the protein, both
H and L
Fc elicits immunological responses after Ag-Ab
Complement cascade
Слайд 19
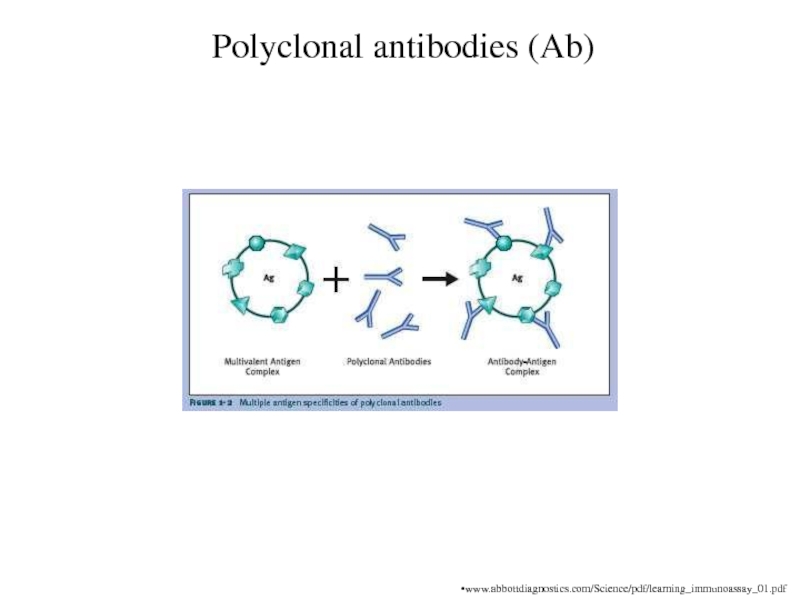
Polyclonal antibodies (Ab)
www.abbottdiagnostics.com/Science/pdf/learning_immunoassay_01.pdf
Слайд 20
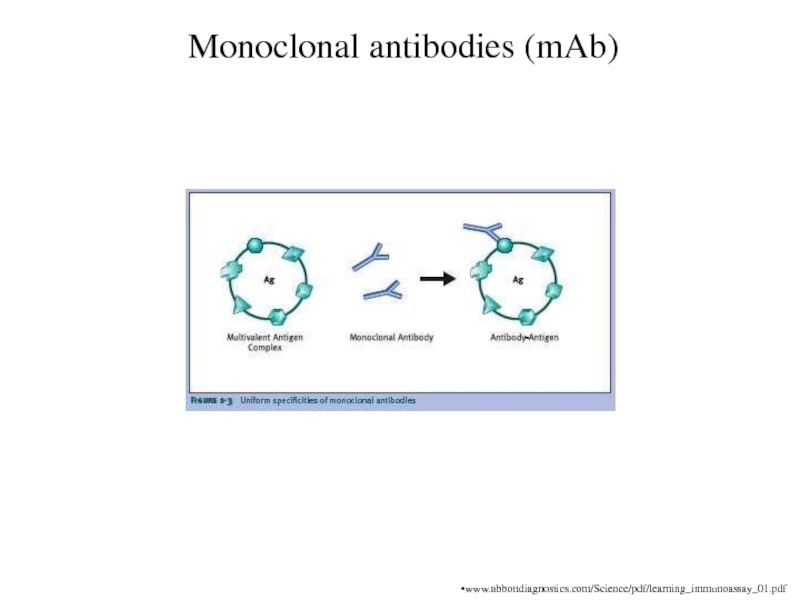
Monoclonal antibodies (mAb)
www.abbottdiagnostics.com/Science/pdf/learning_immunoassay_01.pdf
Слайд 21
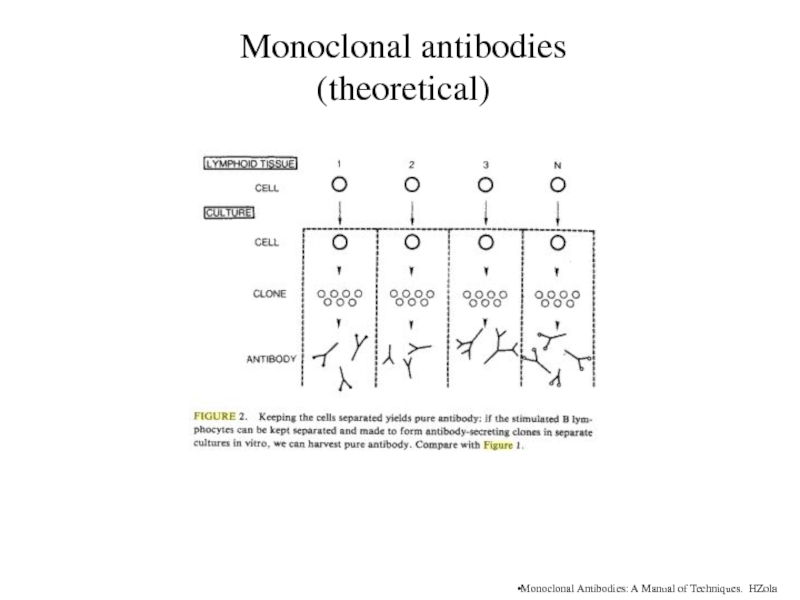
Monoclonal antibodies (theoretical)
Monoclonal Antibodies: A Manual of Techniques. HZola
Слайд 22
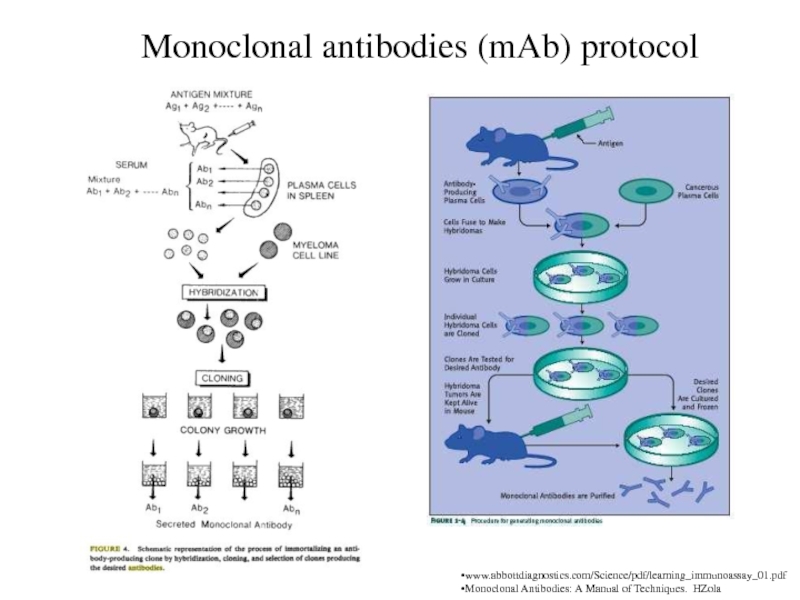
Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) protocol
www.abbottdiagnostics.com/Science/pdf/learning_immunoassay_01.pdf
Monoclonal Antibodies: A Manual of Techniques.
HZola
Слайд 23
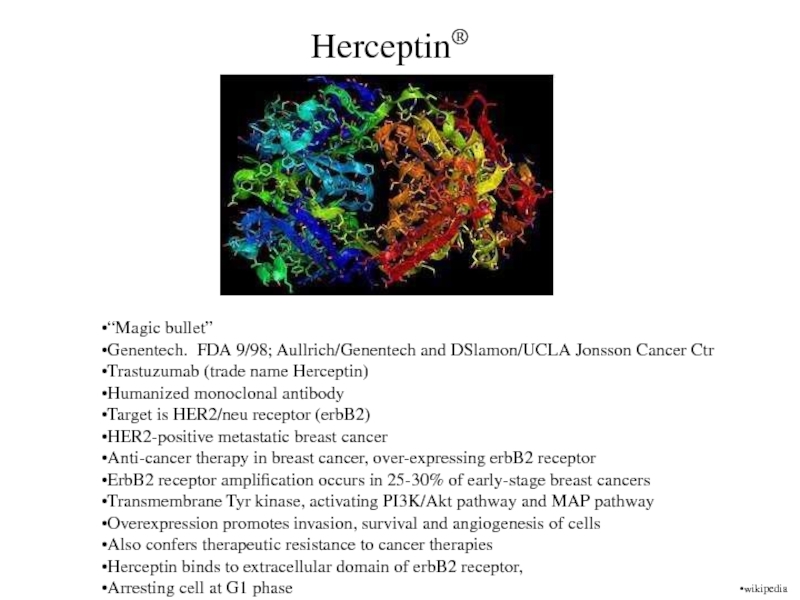
Herceptin®
“Magic bullet”
Genentech. FDA 9/98; Aullrich/Genentech and DSlamon/UCLA Jonsson Cancer
Ctr
Trastuzumab (trade name Herceptin)
Humanized monoclonal antibody
Target is HER2/neu receptor (erbB2)
HER2-positive
metastatic breast cancer
Anti-cancer therapy in breast cancer, over-expressing erbB2 receptor
ErbB2 receptor amplification occurs in 25-30% of early-stage breast cancers
Transmembrane Tyr kinase, activating PI3K/Akt pathway and MAP pathway
Overexpression promotes invasion, survival and angiogenesis of cells
Also confers therapeutic resistance to cancer therapies
Herceptin binds to extracellular domain of erbB2 receptor,
Arresting cell at G1 phase
wikipedia
Слайд 24
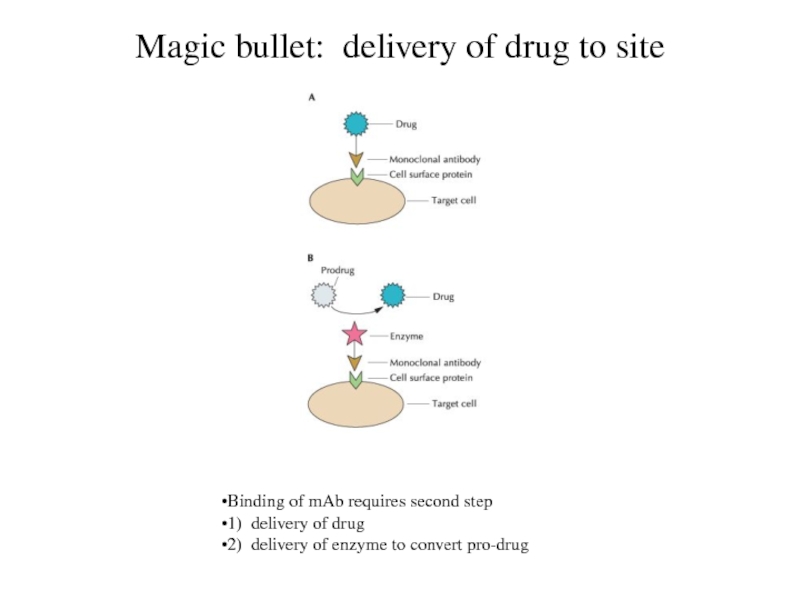
Magic bullet: delivery of drug to site
Binding of mAb
requires second step
1) delivery of drug
2) delivery of enzyme to
convert pro-drug
Слайд 25
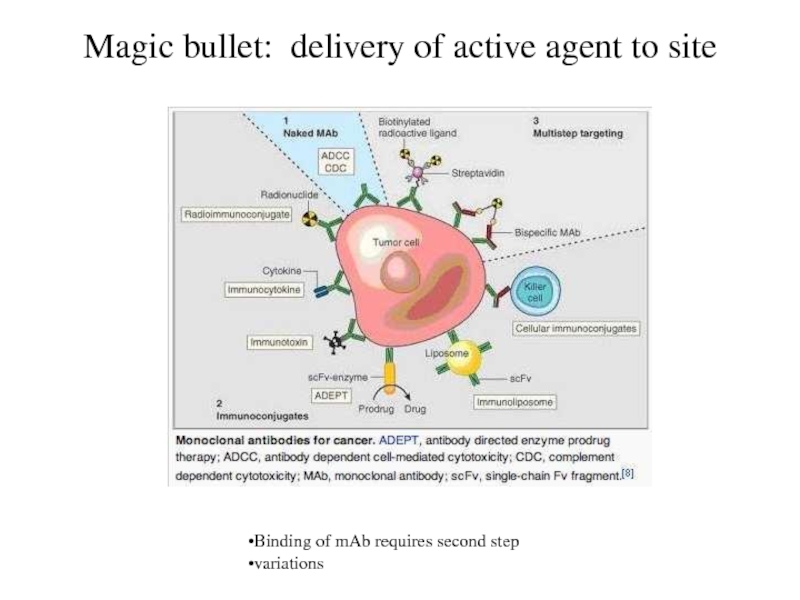
Magic bullet: delivery of active agent to site
Binding of
mAb requires second step
variations
Слайд 27
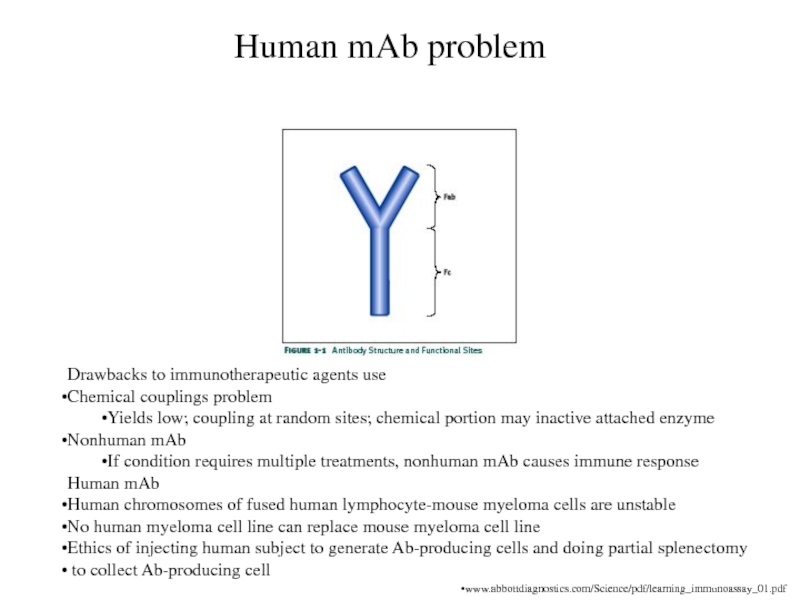
Human mAb problem
Drawbacks to immunotherapeutic agents use
Chemical couplings problem
Yields
low; coupling at random sites; chemical portion may inactive attached
enzyme
Nonhuman mAb
If condition requires multiple treatments, nonhuman mAb causes immune response
Human mAb
Human chromosomes of fused human lymphocyte-mouse myeloma cells are unstable
No human myeloma cell line can replace mouse myeloma cell line
Ethics of injecting human subject to generate Ab-producing cells and doing partial splenectomy
to collect Ab-producing cell
www.abbottdiagnostics.com/Science/pdf/learning_immunoassay_01.pdf
Слайд 28
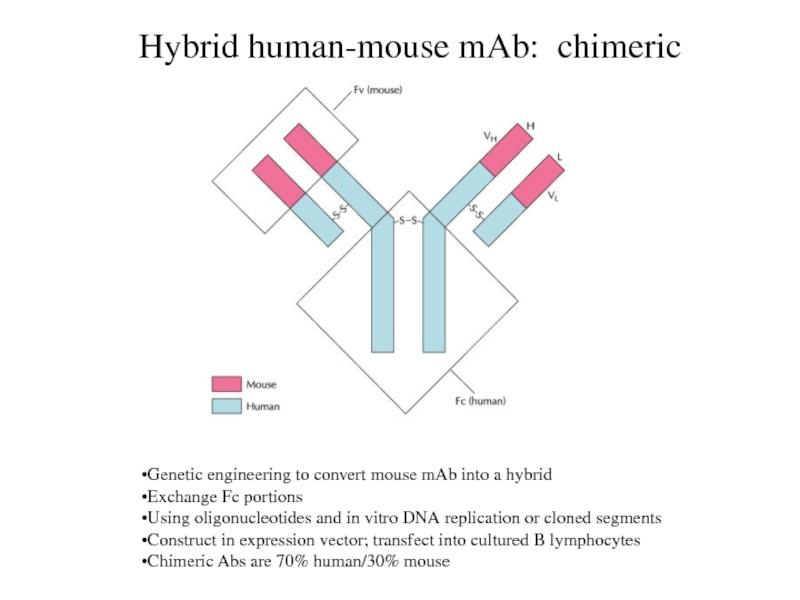
Hybrid human-mouse mAb: chimeric
Genetic engineering to convert mouse mAb
into a hybrid
Exchange Fc portions
Using oligonucleotides and in vitro DNA
replication or cloned segments
Construct in expression vector; transfect into cultured B lymphocytes
Chimeric Abs are 70% human/30% mouse
Слайд 29
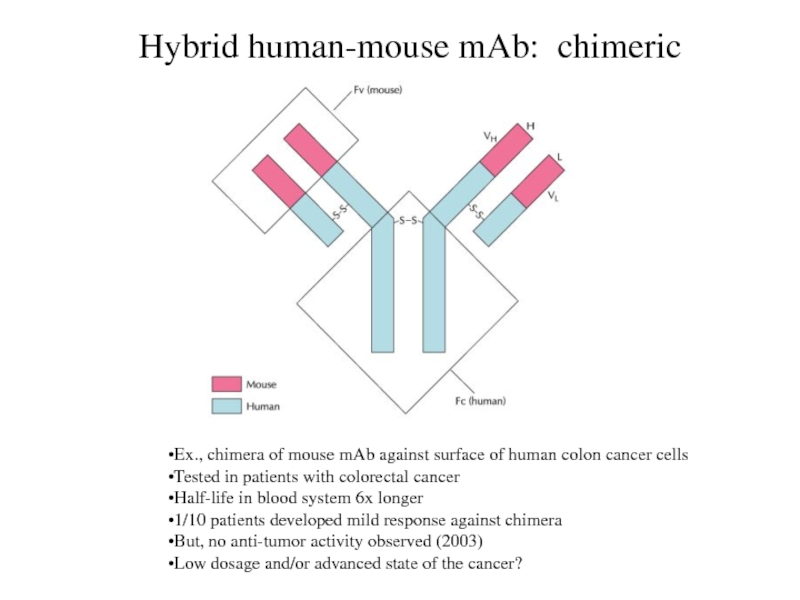
Hybrid human-mouse mAb: chimeric
Ex., chimera of mouse mAb against
surface of human colon cancer cells
Tested in patients with colorectal
cancer
Half-life in blood system 6x longer
1/10 patients developed mild response against chimera
But, no anti-tumor activity observed (2003)
Low dosage and/or advanced state of the cancer?
Слайд 31
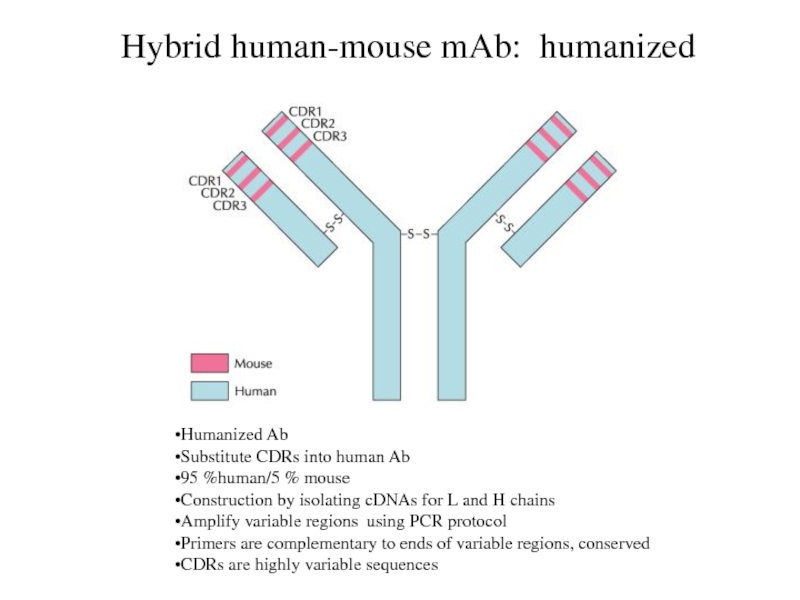
Hybrid human-mouse mAb: humanized
Humanized Ab
Substitute CDRs into human Ab
95
%human/5 % mouse
Construction by isolating cDNAs for L and H
chains
Amplify variable regions using PCR protocol
Primers are complementary to ends of variable regions, conserved
CDRs are highly variable sequences
Слайд 32
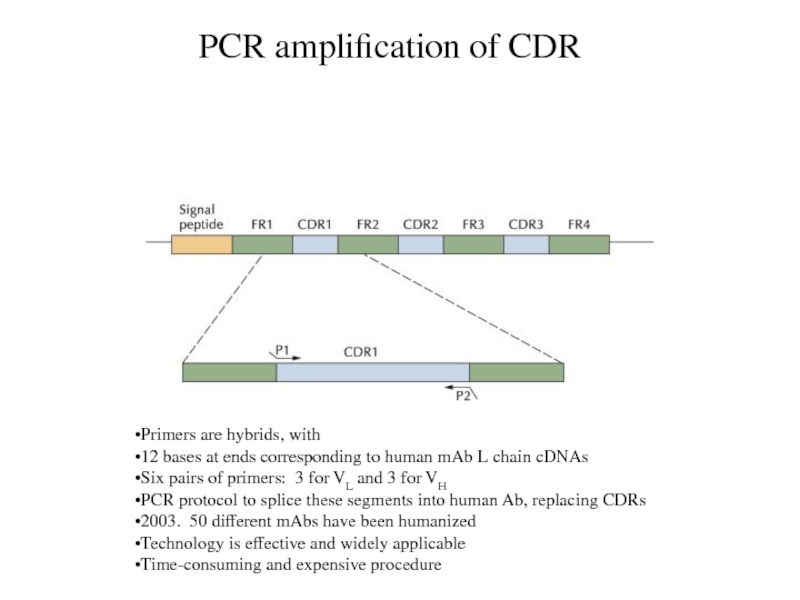
PCR amplification of CDR
Primers are hybrids, with
12 bases at
ends corresponding to human mAb L chain cDNAs
Six pairs of
primers: 3 for VL and 3 for VH
PCR protocol to splice these segments into human Ab, replacing CDRs
2003. 50 different mAbs have been humanized
Technology is effective and widely applicable
Time-consuming and expensive procedure
Слайд 33
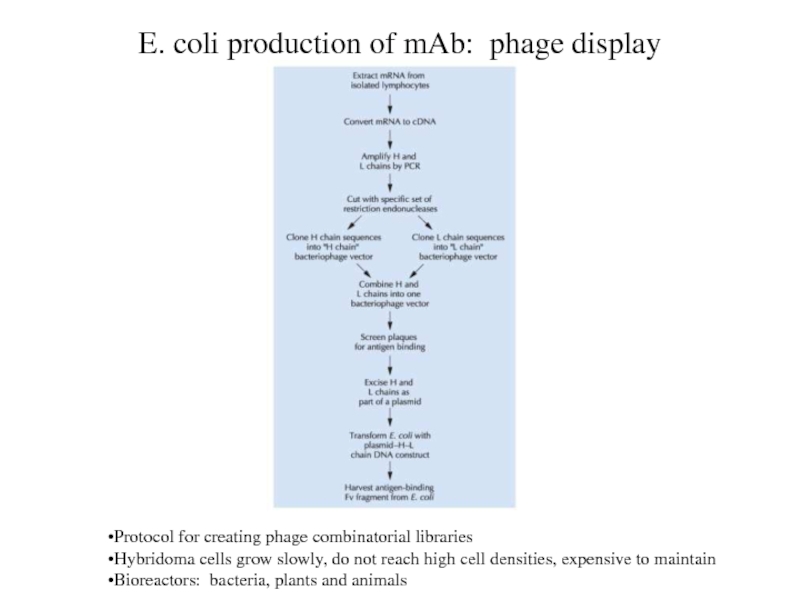
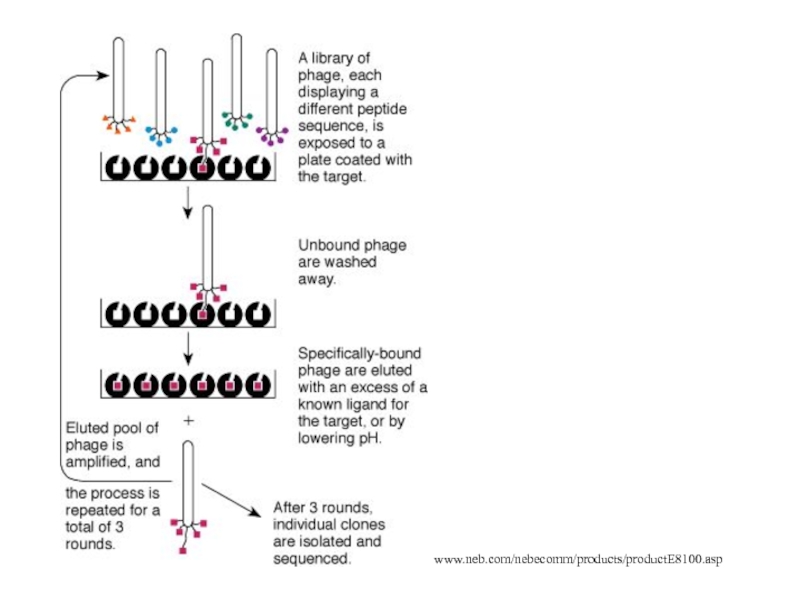
E. coli production of mAb: phage display
Protocol for creating
phage combinatorial libraries
Hybridoma cells grow slowly, do not reach high
cell densities, expensive to maintain
Bioreactors: bacteria, plants and animals
Слайд 34
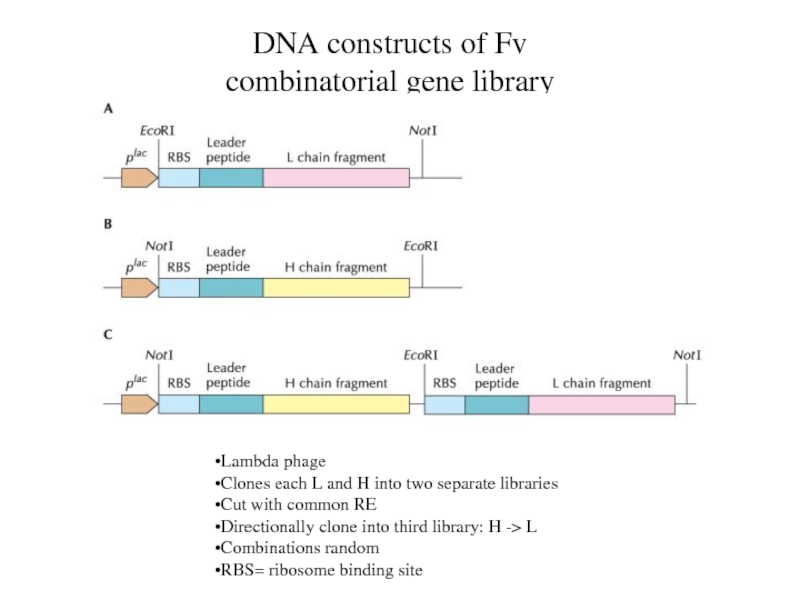
DNA constructs of Fv combinatorial gene library
Lambda phage
Clones each
L and H into two separate libraries
Cut with common RE
Directionally
clone into third library: H -> L
Combinations random
RBS= ribosome binding site
Слайд 35
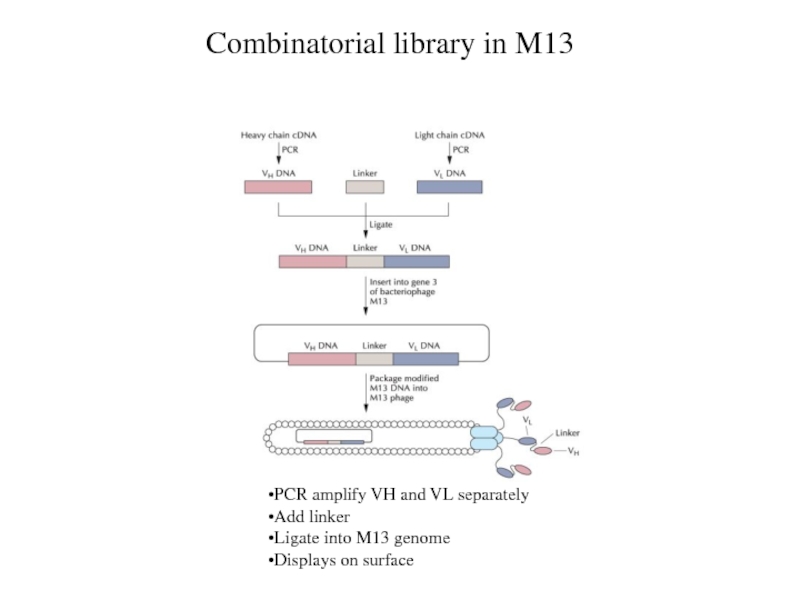
Combinatorial library in M13
PCR amplify VH and VL separately
Add
linker
Ligate into M13 genome
Displays on surface
Слайд 36Phage Display
Display peptide or protein on surface of bacterial virus
(in principle can use other viruses but phage viruses easiest
to prepare etc.)
Some proteins on viral coats can accommodate peptides or proteins and
will present them on the surface.
The phage genome (or alternatively phagemid) contains the sequence for the protein or peptide so isolation of the phage with desired phenotype will also provide the genotype.
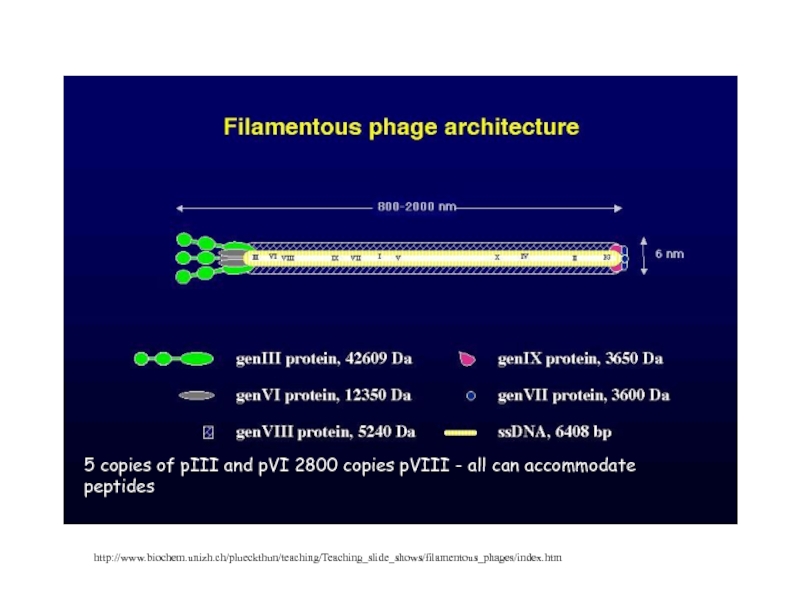
Most popular is filamentous phage f1 or M13.
pIII on the end or pVIII along the length of the rod-like virion
for pVIII ~10% can be loaded with alternate peptide
Advantage of phage display: easy to screen over 109 sequences
Can either clone library directly into phage genome
or use a phagemid (plasmid that contains f1 ori) with replication
deficient helper phage
Слайд 37http://www.biochem.unizh.ch/plueckthun/teaching/Teaching_slide_shows/filamentous_phages/index.htm
5 copies of pIII and pVI 2800 copies pVIII -
all can accommodate
peptides
Слайд 38www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productE8100.asp
Слайд 39
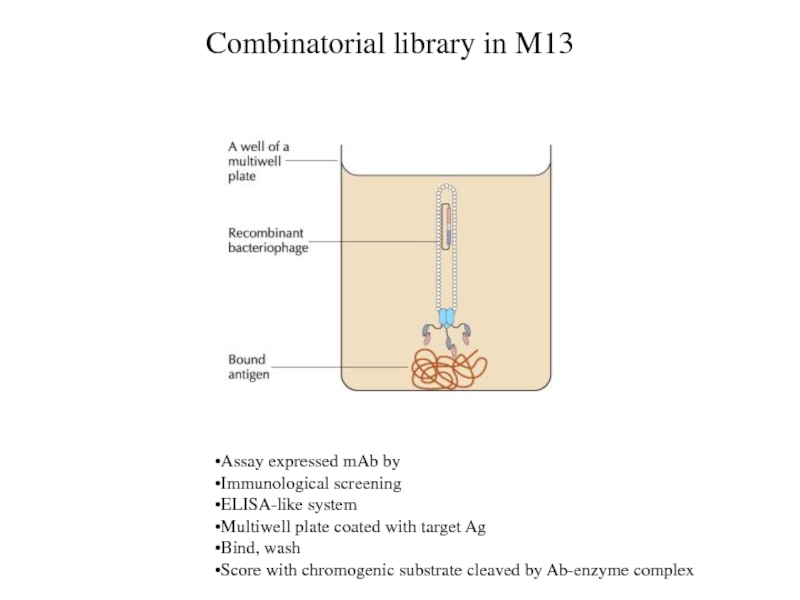
Combinatorial library in M13
Assay expressed mAb by
Immunological screening
ELISA-like system
Multiwell
plate coated with target Ag
Bind, wash
Score with chromogenic substrate cleaved
by Ab-enzyme complex
Слайд 40
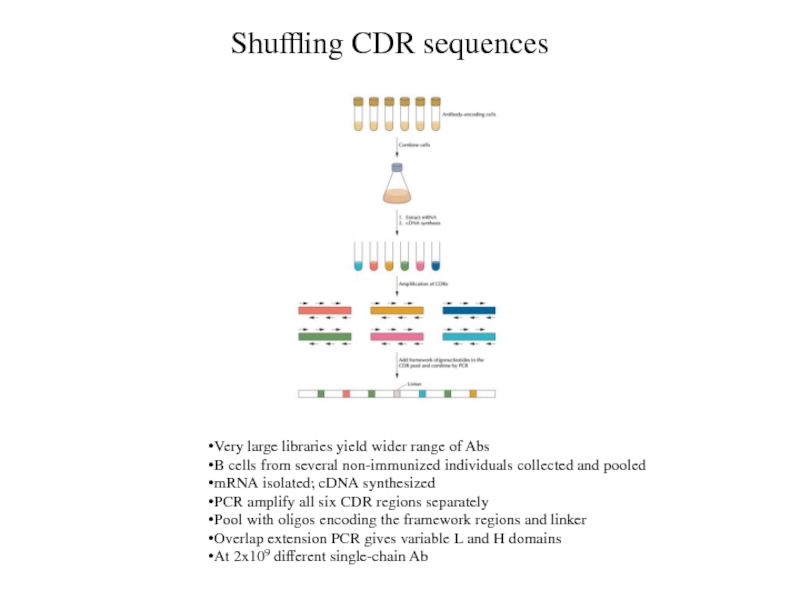
Shuffling CDR sequences
Very large libraries yield wider range of
Abs
B cells from several non-immunized individuals collected and pooled
mRNA isolated;
cDNA synthesized
PCR amplify all six CDR regions separately
Pool with oligos encoding the framework regions and linker
Overlap extension PCR gives variable L and H domains
At 2x109 different single-chain Ab
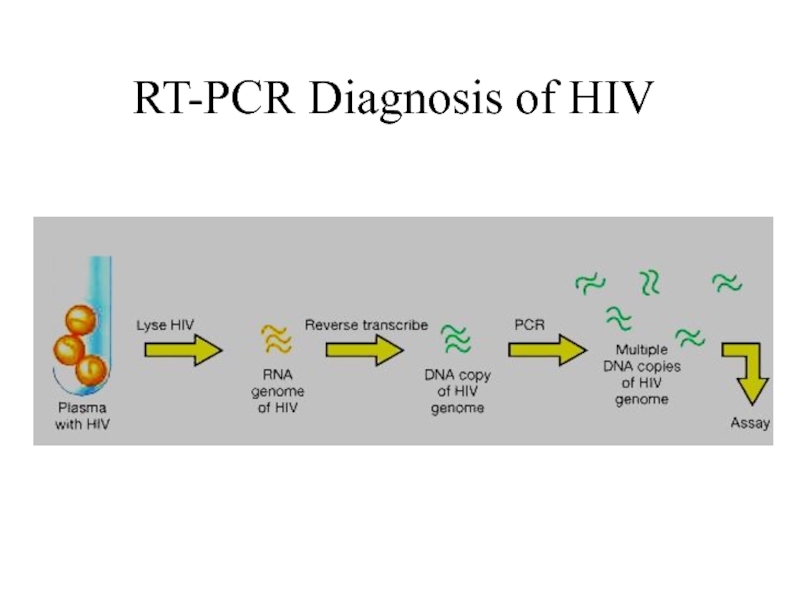
Слайд 41Using PCR to Detect for HIV
RT-PCR (reverse transcriptase PCR).
HIV has
a ssRNA genome.
Lyse plasma cells from the potentially infected person
to release HIV RNA genome.
The RNA is precipitated using isopropanol.
Reverse transciptase is used to make a cDNA copy of the RNA of the virus.
This cDNA is used as a template to make dsDNA.
Diagnostics
Слайд 43Using PCR to Detect for HIV
Specific primers are used to
amplify a 156 bp portion of the HIV gag gene.
Using
standards the amount of PCR product can be used to determine the viral load.
PCR can also be used as a prognostic tool to determine viral load.
This method can also be used to determine the effectiveness antiviral therapy.
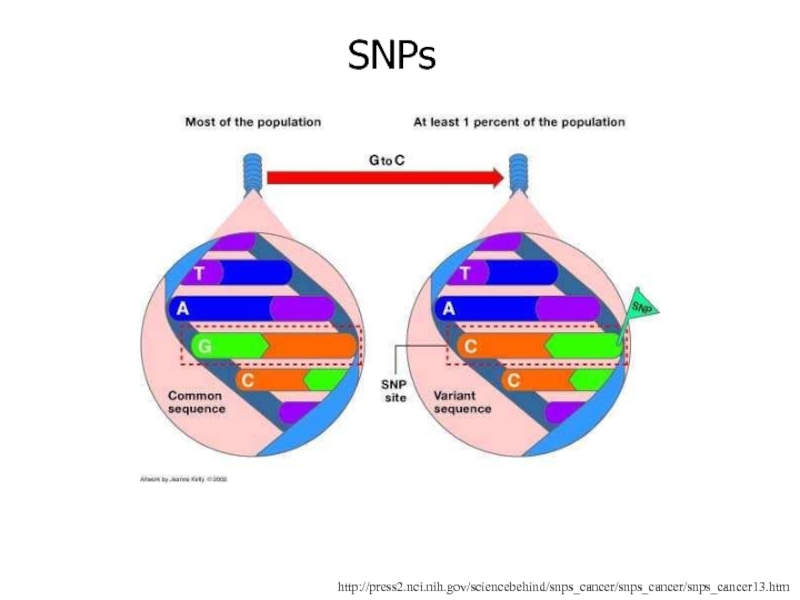
Слайд 44Polymorphic refers to the existence of two or more forms
of the same gene, or genetic marker
Each form must be
too common in a population to be merely attributable to a new mutation
One type of polymorphism, Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs), can be used as a diagnostic tool
Gene polymorphism
Слайд 45SNPs are the 3.2 million single nucleotide changes that differ
between genomes
Most SNPs occur outside of genes, but some occur
in gene promoters & a few occur in genes themselves
For SNPs to be useful, a person's DNA must be examined for the presence of specific SNPs
Слайд 46http://press2.nci.nih.gov/sciencebehind/snps_cancer/snps_cancer/snps_cancer13.htm
SNPs
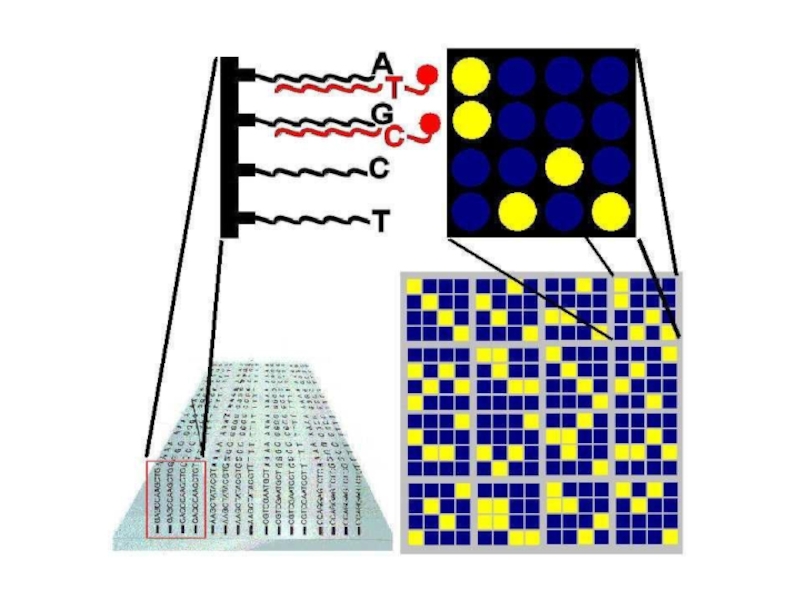
Слайд 47How do we identify SNPs?
DNA microarrays (DNA chips) make it
possible to examine person for the presence of specific SNPs
quickly and affordably
A single microarray can now be used to screen 100,000 SNPs found in a patient's genome in a matter of hours
Слайд 48How Are Microarrays Made?
Short fragments of DNA (oligonucleotides) corresponding to
each version of all known SNPs are spotted onto a
glass slide in a known order
A patients DNA is fragmented and each fragment is linked to a fluorescent dye
This pool of fragments is allowed to hybridize to its corresponding oligonucleotide on the chip
The pattern of fluorescence determines which SNPs are found in the patient
Слайд 50Whole Human Genome Microarray by Agilent Technologies
1” x 3” glass
slide with 44,000 genes dotted
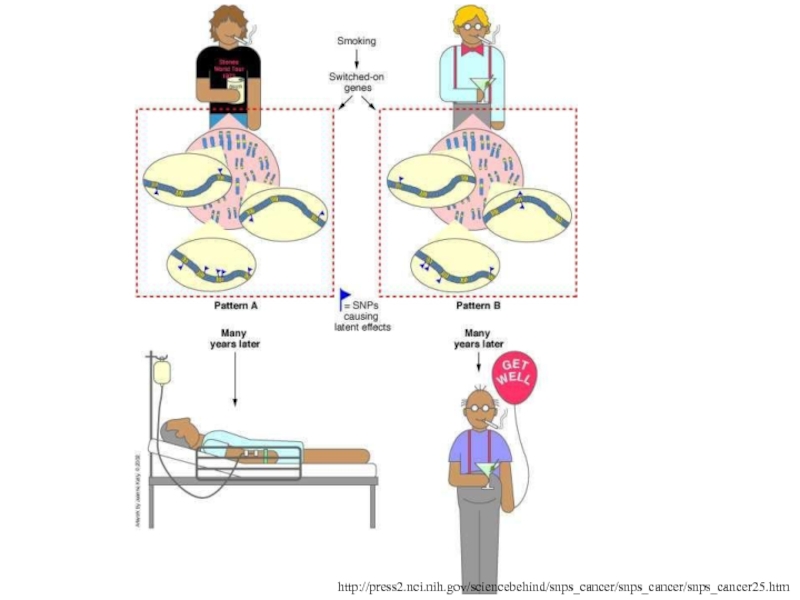
Слайд 51What Can SNPs Be Used to Predict?
Слайд 52A person’s susceptibility to disease is linked to which alleles
they carry as well as how those alleles interact with
the environment
SNPs can be used to build a profile of a person’s susceptibility to various diseases
Example:
Craig Venter (Celera genomics) has an increased risk of heart attack based on a SNP in the promoter of the MMP-3 gene
Слайд 53http://press2.nci.nih.gov/sciencebehind/snps_cancer/snps_cancer/snps_cancer25.htm
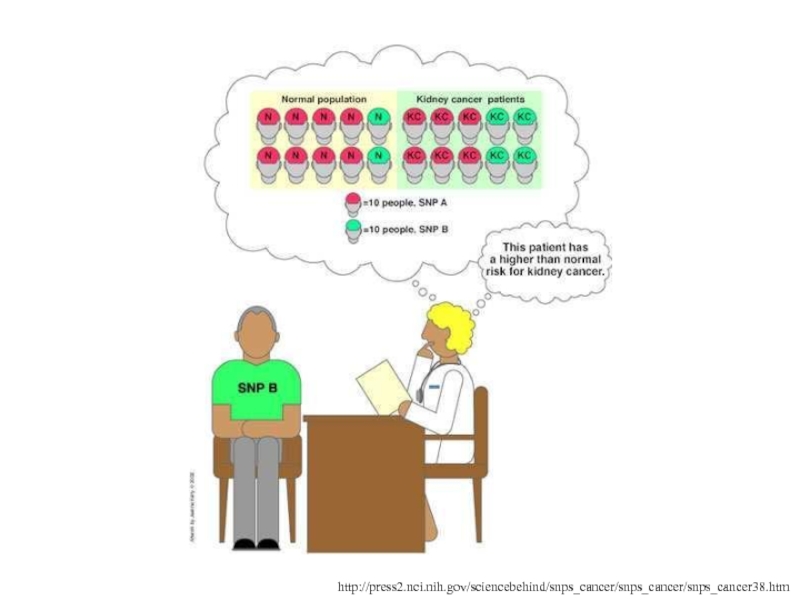
Слайд 54http://press2.nci.nih.gov/sciencebehind/snps_cancer/snps_cancer/snps_cancer38.htm
Слайд 56Average patient
There is no simple way to determine how particular
patient will respond to a medication
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs)
one of the important causes of hospitalization and death in the United States
Medical drugs are developed using a ”average” patient
Pharmacogenomics examines the DNA variations that is correlated to drug response
Can be used to predict if a patient will have a good response to a drug, a bad response to a drug, or no response at all
1http://www.fda.gov/CDER/drug/drugReactions/default.htm
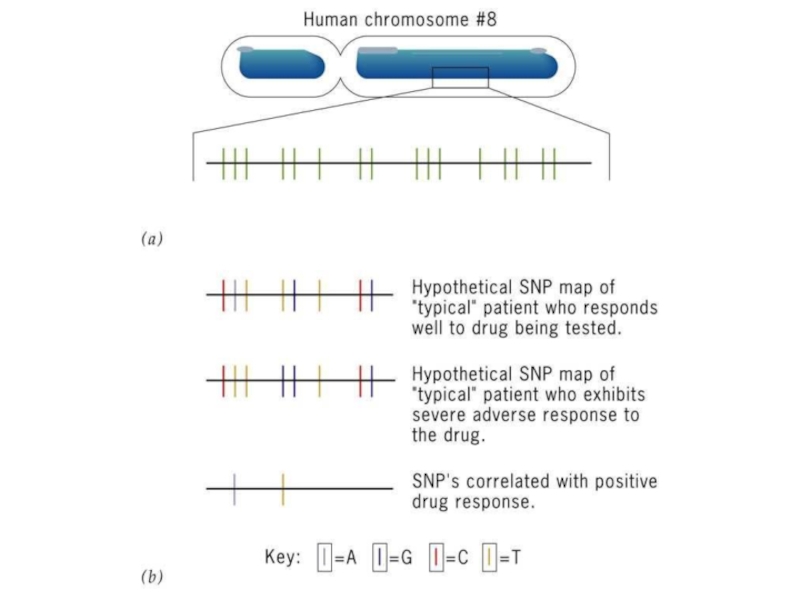
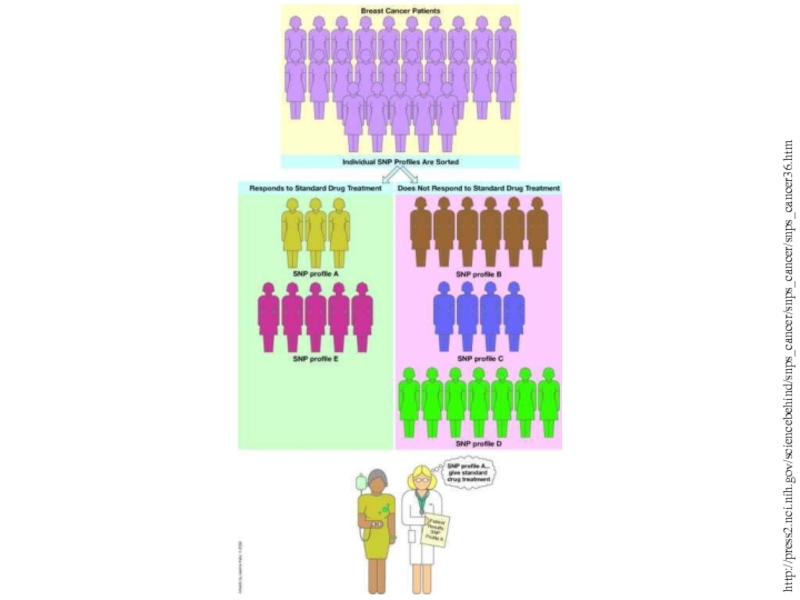
Слайд 58http://press2.nci.nih.gov/sciencebehind/snps_cancer/snps_cancer/snps_cancer36.htm
Слайд 59Testing for Variation
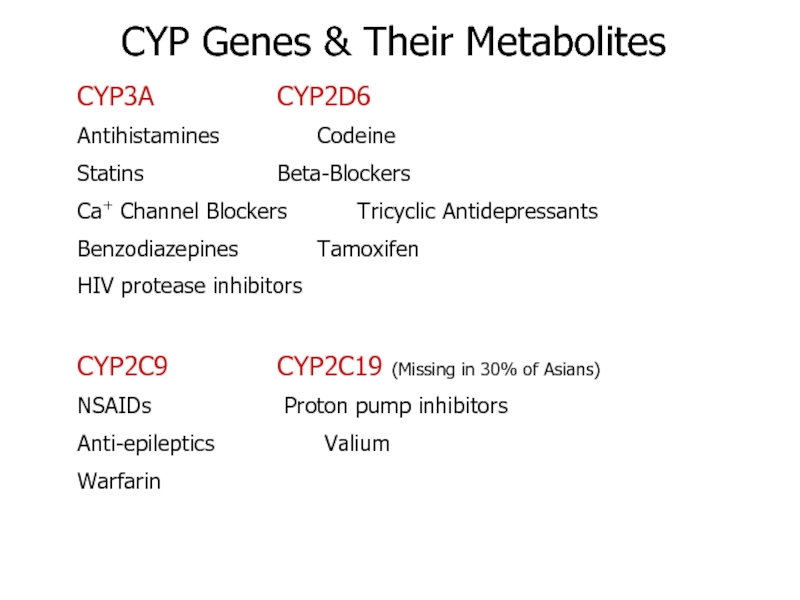
Cytochrome p450 (CYP450) involved in drug metabolism Four
major types; CYP3A, CYP2C9, CYP2D6 & CYP2C19
Variations in at
least 3 genes regulate drug metabolism
By looking at the alleles a person has of these genes it is possible to predict how a patient will react to a drug
Dosing can be regulated so that a patient gets the maximum benefit without possible toxic side effects
Слайд 60CYP3A CYP2D6
Antihistamines Codeine
Statins Beta-Blockers
Ca+ Channel Blockers Tricyclic Antidepressants
Benzodiazepines Tamoxifen
HIV protease inhibitors
CYP2C9 CYP2C19 (Missing in 30%
of Asians)
NSAIDs Proton pump inhibitors
Anti-epileptics Valium
Warfarin
CYP Genes &
Their Metabolites
Слайд 61Herceptin targets HER2 & is effective in stopping breast cancer
growth
Only 25 to 30% of breast cancers overexpress HER2
Erbitux effective
in colorectal cancers by stopping signaling through EGFR
Not all colorectal cancers overepress EGFR
Diagnostic tests are used to detect which tumors will benefit from treatment allowing better use of treatment time & money
Слайд 621733 Genes
84 breast tumor samples
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=stryer.figgrp.832
Red =gene induction
Green = gene
repression
Tumors Are Not Identical So Why Should Every Patient be
Treated the Same?
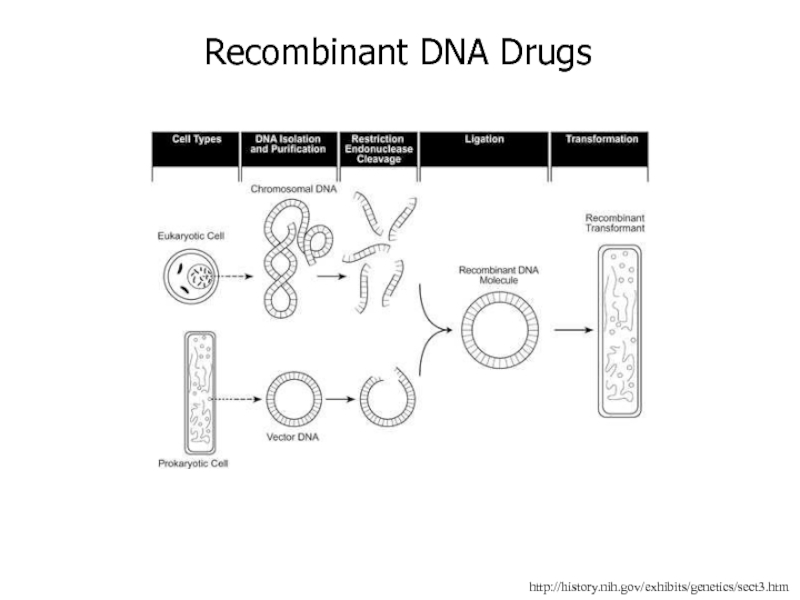
Слайд 63http://history.nih.gov/exhibits/genetics/sect3.htm
Recombinant DNA Drugs
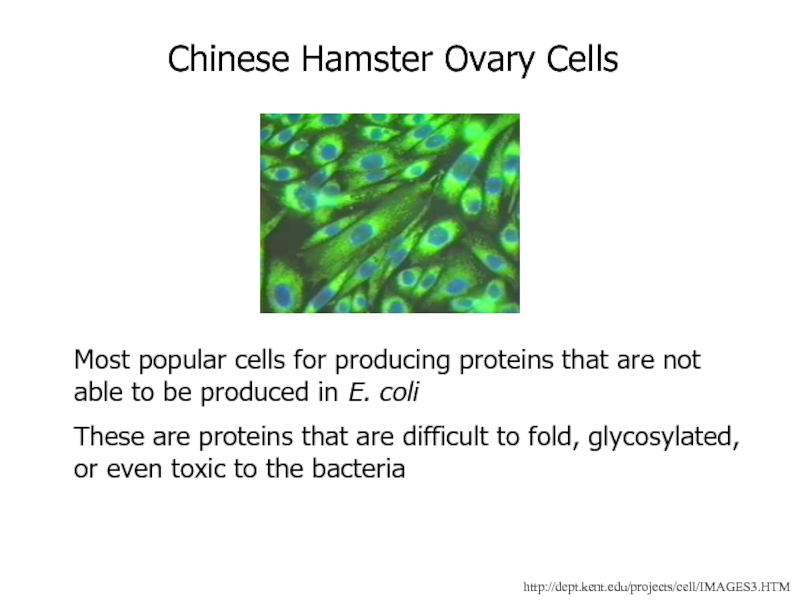
Слайд 64http://dept.kent.edu/projects/cell/IMAGES3.HTM
Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells
Most popular cells for producing proteins that
are not able to be produced in E. coli
These are
proteins that are difficult to fold, glycosylated, or even toxic to the bacteria
Слайд 65http://www.nbsc.com/ferm_eq/bf6000.asp
Mammalian Cell Bioreactor
Слайд 66Protein Drugs Made in CHO Cells
Avonex (Interferon Beta-1a) Multiple Sclerosis
- Biogen
Herceptin (Trastuzumab) Breast Cancer - Genentech
Humira (Adalimumab) Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Abbott Labs
Remicade (Infliximab) Crohn’s Disease - Centocor
Embrel (Etanercept) Rheumatoid Arthritis - Amgen
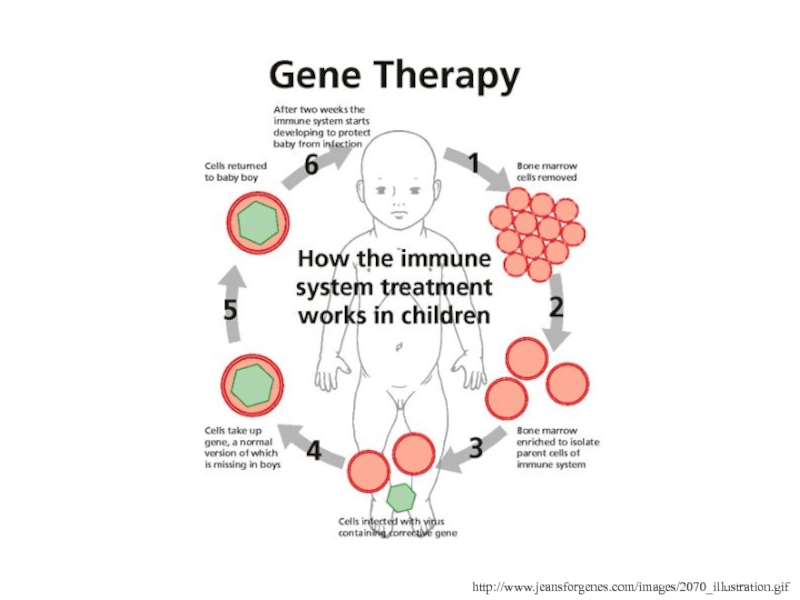
Слайд 68Gene Therapy
Cells are removed from a patient and modified either
by having a working copy of a defective gene inserted
or a therapeutic gene added
Once the cells are expressing the new gene correctly, they are inserted back into the patient (ex vivo)
The gene is usually delivered using a defective virus
Sometimes the virus is delivered directly into the patient (in vivo)
Слайд 69Jak je to delano,
priklady, doplnit
Слайд 70http://www.jeansforgenes.com/images/2070_illustration.gif
Слайд 71Gene-Therapy and SCIDs
Severe Combined Immune Defiency (SCID): no T cells
Two types: ADA-SCID & SCID-X1
>20 SCID patients have been successfully
treated
The FDA has not approved any human gene therapy
Слайд 72Current State of Gene Therapy
Little progress has been made since
the first gene therapy clinical trials begun in 1990
In 1999,
gene therapy suffered a major setback with the death of 18-year-old Jesse Gelsinger
Part of a gene therapy trial for ornithine transcarboxylase deficiency (OTCD)
Died from multiple organ failures 4 days post-treatment
Death was caused by a severe immune response
Слайд 73In 2003, the FDA placed a temporary halt on all
gene therapy trials using retroviral vectors in blood stem cells
FDA
took this action after it learned that two childern treated in a French gene therapy trial had developed a leukemia-like condition
These children in August 2002 had been successfully treated by gene therapy (SCID-X1)
Слайд 75Stem cells are unspecialized cells that renew themselves for long
periods through cell division.
Under certain physiologic or experimental conditions,
they can be induced to become cells with special functions such as the beating cells of the heart muscle or the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas
These cells could then be used to repair or replace damaged organs or tissues
Слайд 76Three Types of Stem Cells
Embryonic
Adult/Somatic
Induced Pluripotent
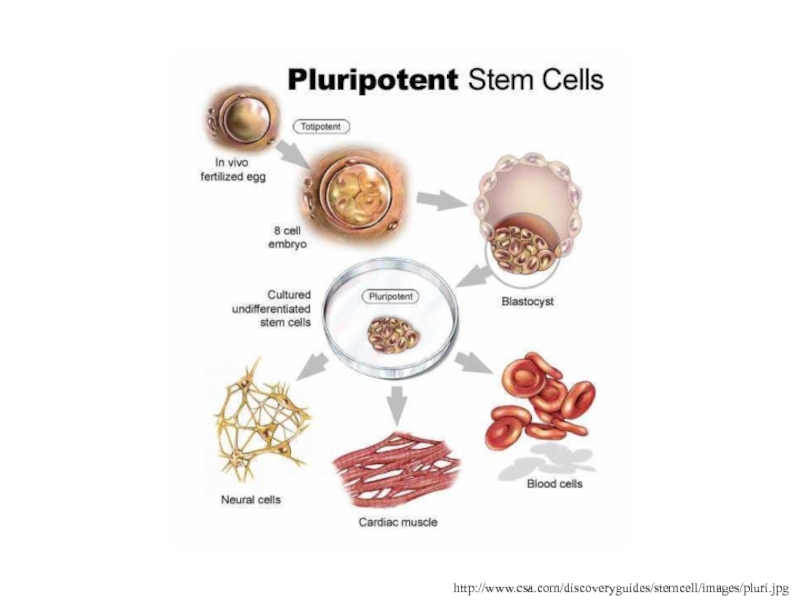
Слайд 77In 1998, human embryonic stem cells (hES) were isolated and
grown in the laboratory
hES cells are derived from the ICM
of human blastocysts
These cells are pluripotent just like mouse ES cells
The embryos used in these studies were created for infertility purposes through in vitro fertilization
They were donated for research with the informed consent of the donor
Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Слайд 78http://www.csa.com/discoveryguides/stemcell/images/pluri.jpg
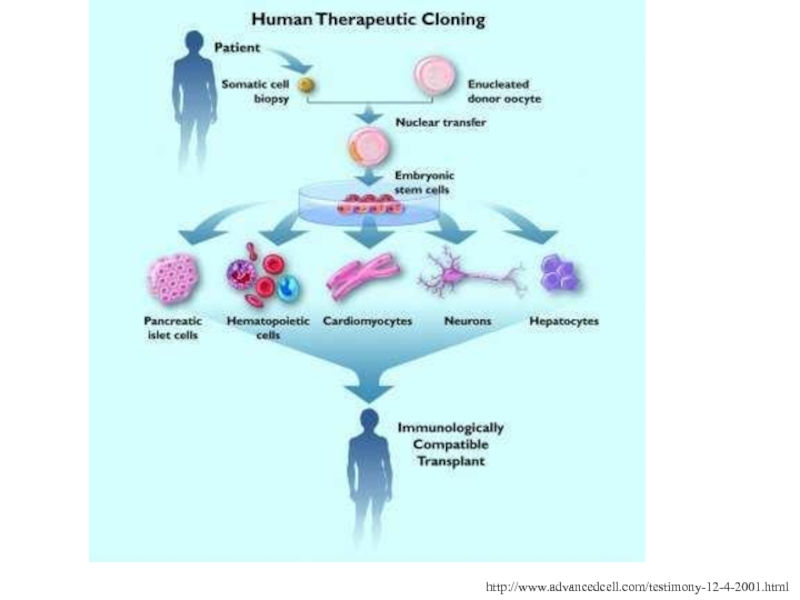
Слайд 79Therapeutic Cloning
Isolation of cloned cells/tissue for curing disease or injury
The
nucleus from an adult cell is placed in an enucleated
egg
Instead of implanting the egg and letting it grow into a fetus, it is cultured until the blastocyst stage where ES cells are removed and cultured
These ES cells are coaxed down a specific developmental pathway such that they differentiate into a specific tissue
This allows for the creation of cells identical to the donor thus preventing rejection
Слайд 80http://www.advancedcell.com/testimony-12-4-2001.html
Слайд 81An adult or somatic stem cell is an undifferentiated cell
found among differentiated cells in a tissue or organ
It can
renew itself, and can differentiate to yield the major specialized cell types of the tissue or organ
The primary roles of adult stem cells are to maintain and repair the tissue in which they are found
These cells are more restricted as to what cell types they can become & are thus said to be multipotent
Adult Stem Cells
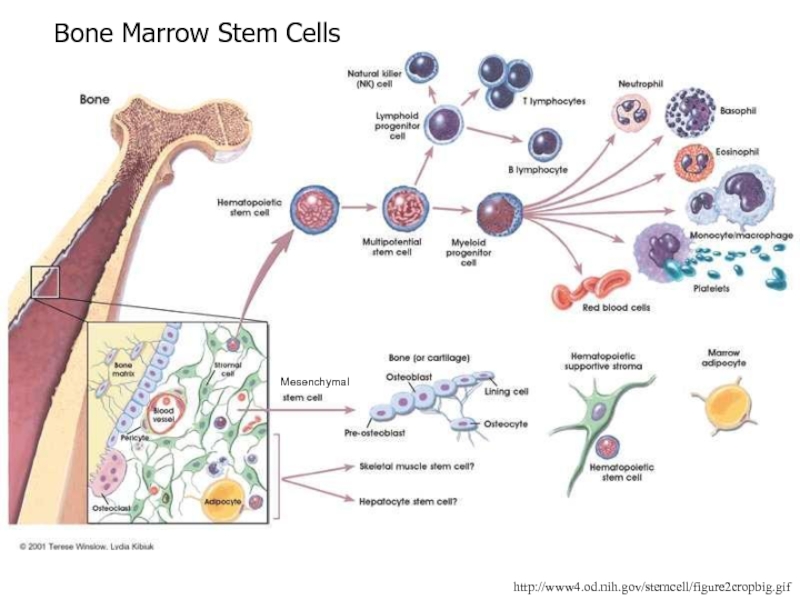
Слайд 821960s, two stem cell populations identified in bone marrow
One population,
called hematopoietic stem cells, forms all the types of blood
cells in the body
The second, called mesenchymal stem cells generate bone, cartilage, fat, & connective tissue
Hematopoietic stem cells have also been isolated from umbilical cord blood
Mesenchymal stem cells have now been isolated from amniotic fluid, umbilical cord blood, and adipose tissue
Слайд 83http://www4.od.nih.gov/stemcell/figure2cropbig.gif
Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Mesenchymal
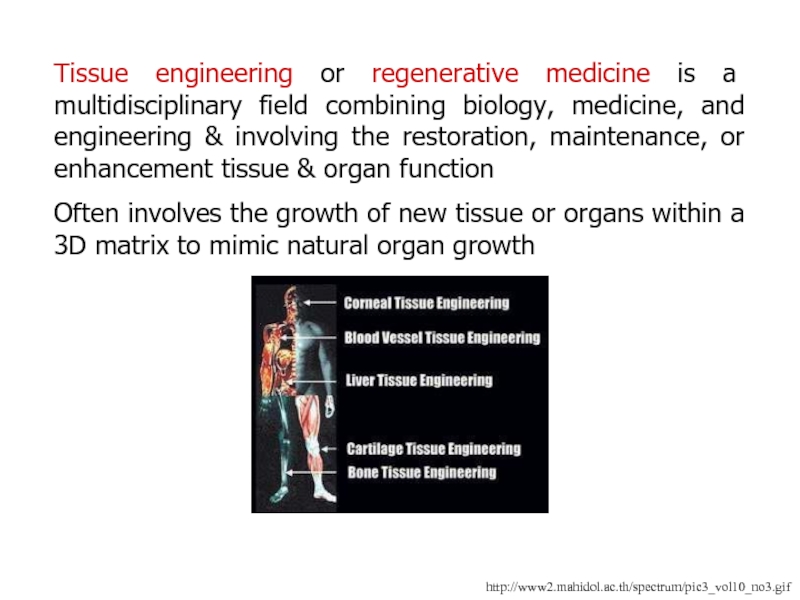
Слайд 85Tissue engineering or regenerative medicine is a multidisciplinary field combining
biology, medicine, and engineering & involving the restoration, maintenance, or
enhancement tissue & organ function
Often involves the growth of new tissue or organs within a 3D matrix to mimic natural organ growth
http://www2.mahidol.ac.th/spectrum/pic3_vol10_no3.gif
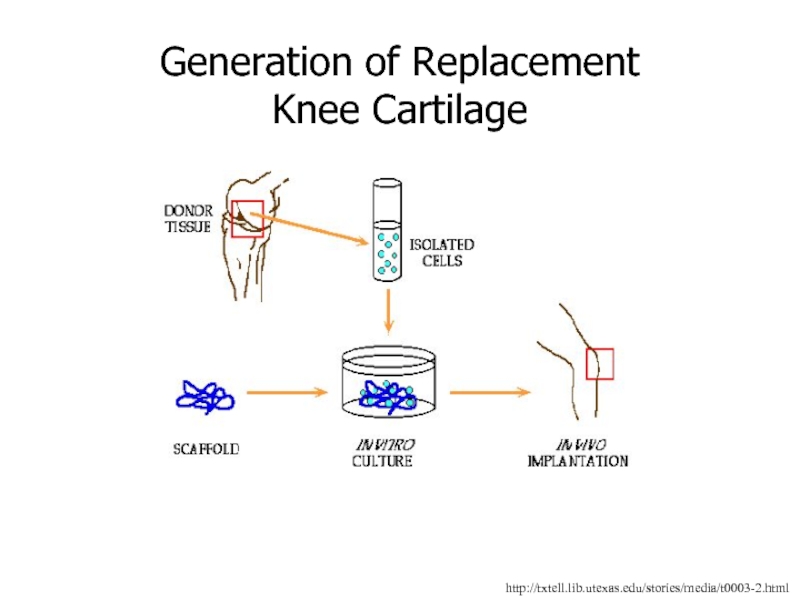
Слайд 86http://txtell.lib.utexas.edu/stories/media/t0003-2.html
Generation of Replacement Knee Cartilage
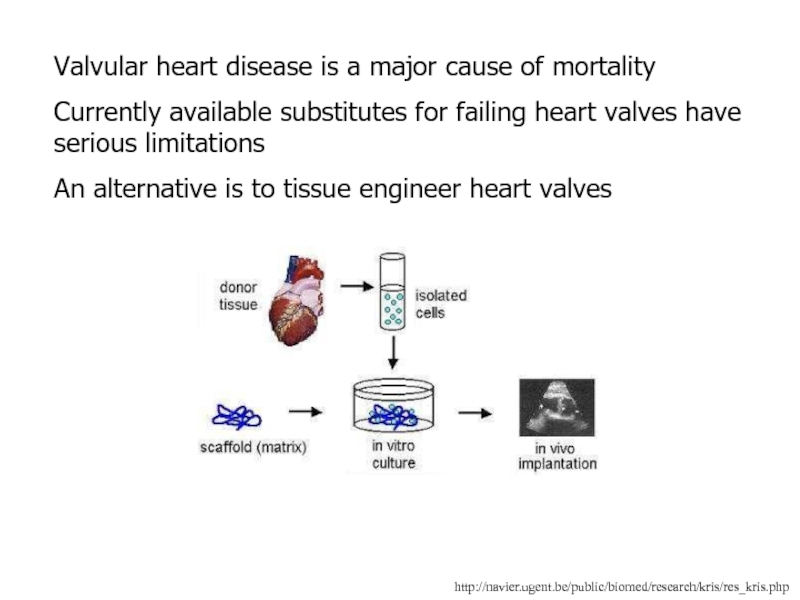
Слайд 87http://navier.ugent.be/public/biomed/research/kris/res_kris.php
Valvular heart disease is a major cause of mortality
Currently available
substitutes for failing heart valves have serious limitations
An alternative is
to tissue engineer heart valves
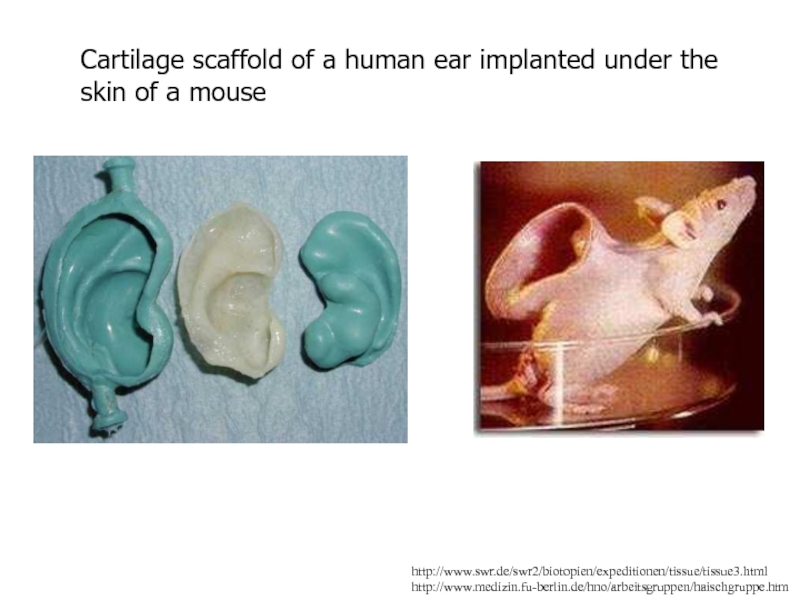
Слайд 89http://www.swr.de/swr2/biotopien/expeditionen/tissue/tissue3.html
http://www.medizin.fu-berlin.de/hno/arbeitsgruppen/haischgruppe.htm
Cartilage scaffold of a human ear implanted under the skin
of a mouse





![Medical biotechnology Alginate lyase[s]ORF 69,000 DaPrecursor of three alginate lyases-> 3,000 Da Alginate lyase[s]ORF 69,000 DaPrecursor of three alginate lyases-> 3,000 Da + 63,000 Da63,000 Da lyses both](/img/thumbs/3d933c470f81428a653860c47135257e-800x.jpg)
![Medical biotechnology Phenylketonuria treatment[s]Traditional treatment: diagnosis at birth or prenatalControlled semi-synthetic diet Phenylketonuria treatment[s]Traditional treatment: diagnosis at birth or prenatalControlled semi-synthetic diet with low levels of PhePossible treatment:](/img/thumbs/73e624c3a1a93857f98a93591a486de3-800x.jpg)