Слайд 1Accessibility in Information and Communication
Henna karhapää (culture open –project coordinator)
Слайд 2What is accessible communication?
Accessible communication makes information clear, direct and
easy to understand
Continuous
To the point
Clear
Understandable
Accessible communication is written, spoken, presented,
heard and seen.
Always consider providing alternative ways to communicate
Слайд 3Concise and clear information
Provide alternative communication methods
Use assistive technologies
Слайд 4Communication that is continuous
Up to date:
Plan what to communicate
beforehand
Be timely: give time for your audience to receive the
information
Keep your audience updated on any changes to the information
Describe the progress towards your desired outcome: seminar, speech, roundtable, performance, etc.
After outcome is completed: use communication to reflect -> successess, improvements, feedback
Слайд 5”We are planning to conduct accessibility mappings”
”We have begun conduncting
accessibility mappings”
”We have completed our accessibility mappings”
”The results of our
accessibility mappings are disseminated”
”We have feedback regarding our accessibility mappings”
Слайд 6Communication that is to the point
Tailored to be reachable for
the intended audience
Reachability is realized by using the most suitable
communication channels
Ask your audience which communication channels they prefer to use: Print media? social media? Websites? event calendar?
Use language that puts the person before the label
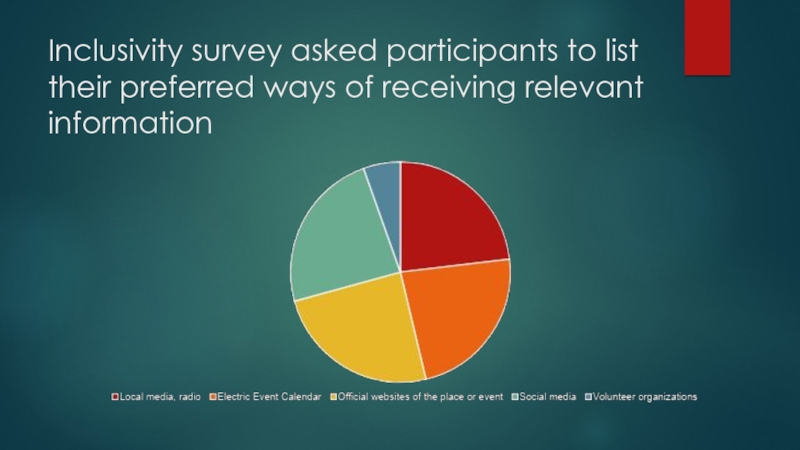
Слайд 7Inclusivity survey asked participants to list their preferred ways of
receiving relevant information
Слайд 8DO NOT USE
LABEL:
”Disabled”
”Able-bodied”
”Mental handicap”
”Visually impaired”
”Hearing impaired”
”Autistic”
”Learning disabled”
”Down”
”Invalid”
DO USE
PERSON FIRST:
”Person with
a disability”
”Other people”
”Person with intellectual disabilities”
”Person with a visual impairment”
”Person
with a hearing impairment”
”Person with autism”
”Person with a learning disability”
”Person with Down Syndrome”
”Person with a physical disability”
Слайд 9Communication that is clear
Language and presentation is accessible
Use a variety
of formats; visual, audio
Utilize symbols for visual shorthand
Tell your audience
HOW the information you provide is accessible
Be concise and specific when giving instructions
Divide information into manageable chunks: use titles, subheadings and images to deliver information
Слайд 10Title
Subheading 1
This is an example text. This text shows how
to divide written information into manageable portions for increased readability.
Subheading
2
By dividing your text, you also enable assistive technology, such as screen readers, to work in a more concise manner.
Слайд 11Communication that is understandable
Readable to the intended audience:
Use assistive technology,
such as alt text, colour contrast, readable font, large font
Can
be read with a screen reader
Presentations:
Describe verbally any images you show
When answering questions, repeat the question in your answer
Allow more time for communication
Слайд 12Example text
Example text
Contrast:
Readable font:
Describe visually and verbally what you are
talking about
Example text
Example text
Слайд 13How to plan accessible events (1/2)
Ask participants beforehand if they
have any special requirements
Ensure, that the event location is accessible
AND that getting there is easy
Make sure the location has an Internet access, a decent sound- and amplifying system, and preferably an induction loop -> always make sure you have enough people to man the events, as well as people who have technical expertise
Give the interpreters a visible spot
Take accessibility needs into consideration when timetabling the event
Give the presenters/ speakers the accessibility guidelines for the event and ask them to provide you with a copy of their presentation beforehand.
Слайд 14How to plan accessible events (2/2)
Give the participants accessible information
on the location and the timetable of the event. Make
sure these materials are available also after the event.
If the event has co-creative activities, make sure these are accessible as well
Utilize various communication channels, such as social media, and communication styles (visual, audio), ask participants to participate in event communication.
Organize accessible seating near the entryways and the stage area
Evaluate the success of the events afterwards, identify issues for improvement and ask feedback from the participants
Слайд 15Make sure there is plenty of help available at the
event
Make sure the venue is accessible
Place interpreters in a visible
place
Give participants the opportunity to provide event communication
Слайд 17Useful links:
Bridging the Gap: Inclusive and Accessible Communication Guideline
https://bridgingthegap-project.eu/wp-content/uploads/BtG_Inclusive-and-accessible-Communication-Guidelines.pdf
Culture for
All: Accessibility guidelines
http://www.kulttuuriakaikille.fi/accessibility
Accessible Presentations
http://www.w3.org/WAI/teach-advocate/accessible-presentations/
Accessible Conference Guide
http://www.sigaccess.org/welcome-to-sigaccess/resources/accessible-conference-guide/
Topics for Web-Accessibility Training
http://www.w3.org/WAI/teach-advocate/accessibility-training/topics/