Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Brain Death Anatomy and Physiology
Содержание
- 1. Brain Death Anatomy and Physiology
- 2. Historical Perspective Prior to the advent of
- 3. Historical Perspective1959 Coma de’passe’ Mollaret and Goulon1968
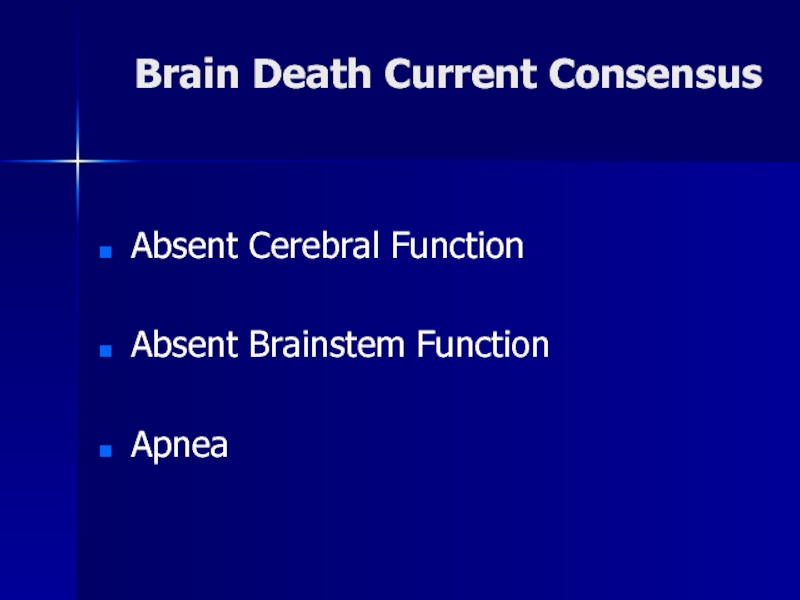
- 4. Brain Death Current ConsensusAbsent Cerebral Function Absent Brainstem Function Apnea
- 5. Normal Brain Anatomy
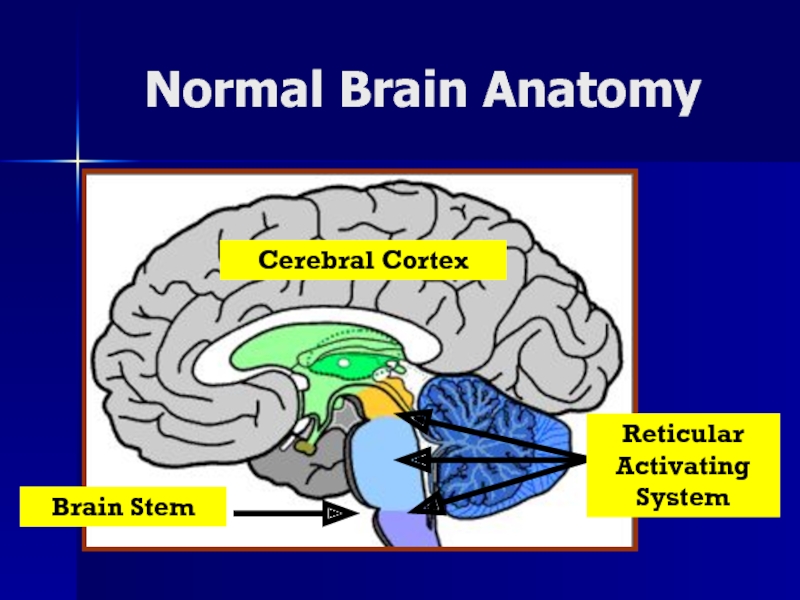
- 6. Normal Brain AnatomyCerebral CortexBrain StemReticular Activating System
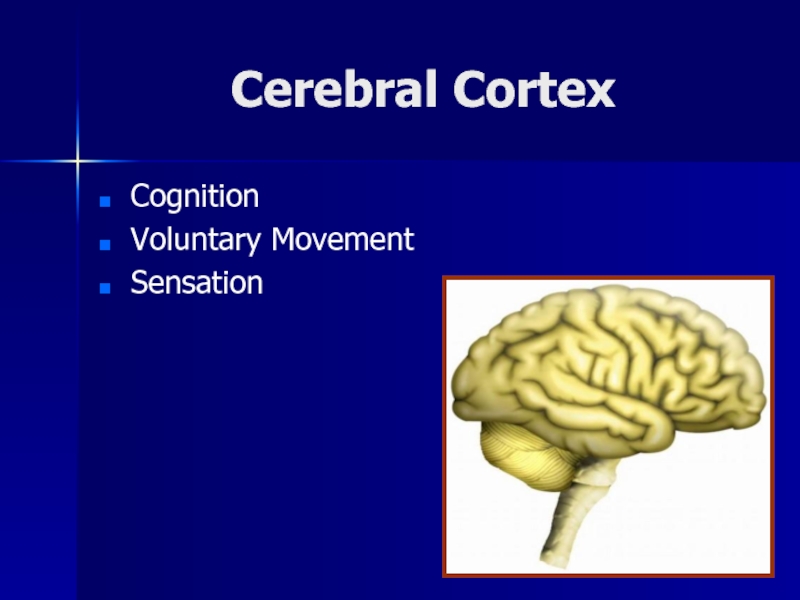
- 7. Cerebral CortexCognitionVoluntary MovementSensation
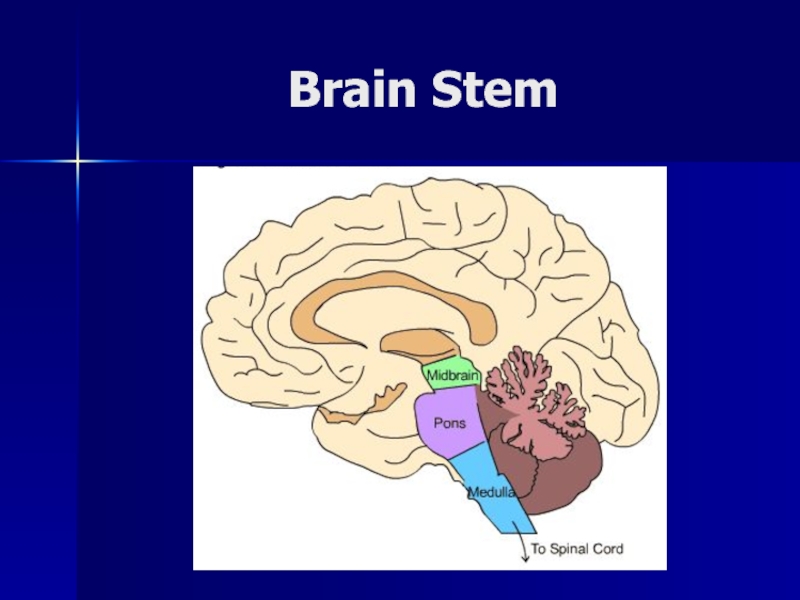
- 8. Brain Stem
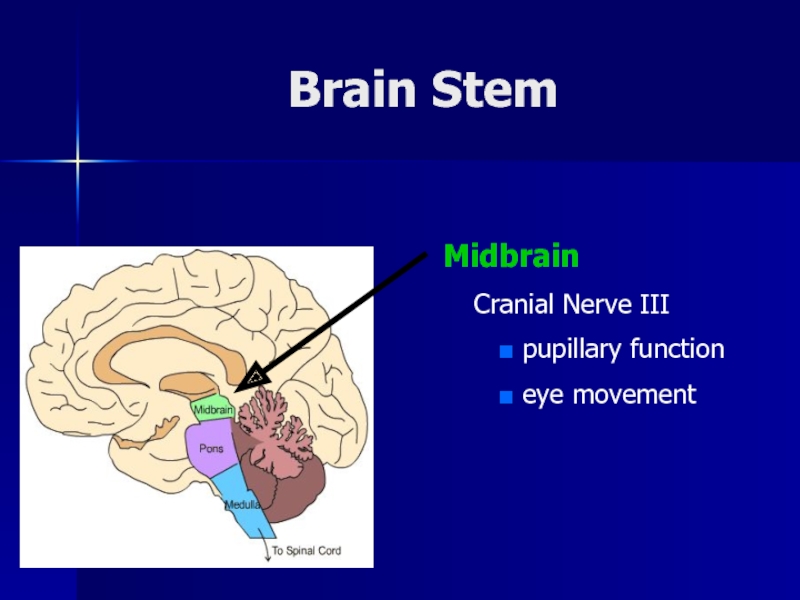
- 9. Brain Stem MidbrainCranial Nerve III pupillary function eye movement
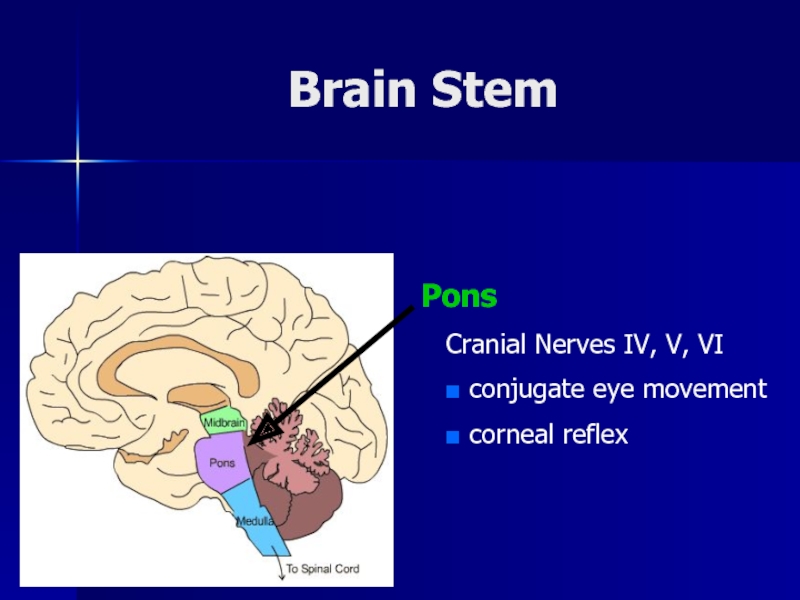
- 10. Brain StemPons Cranial Nerves IV, V, VI conjugate eye movement corneal reflex
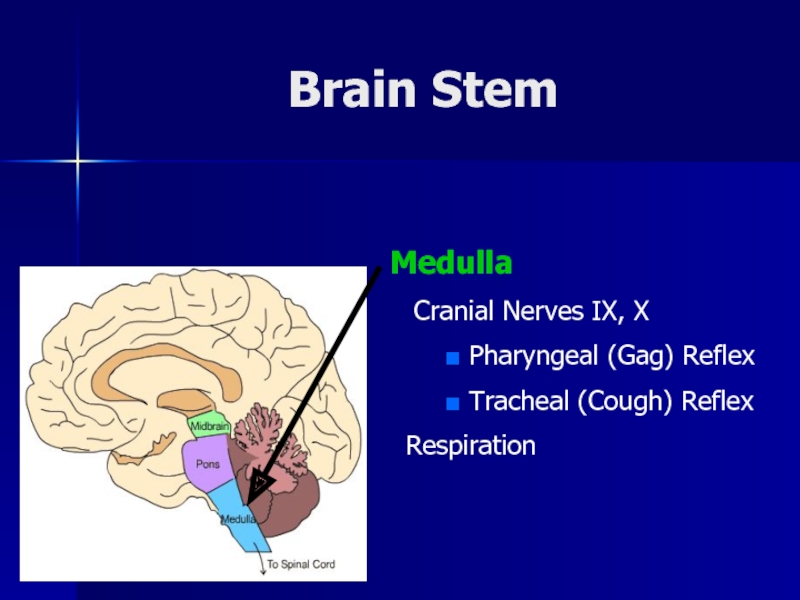
- 11. Brain Stem Medulla Cranial Nerves IX,
- 12. Reticular Activating System Receives multiple sensory inputsMediates wakefulness
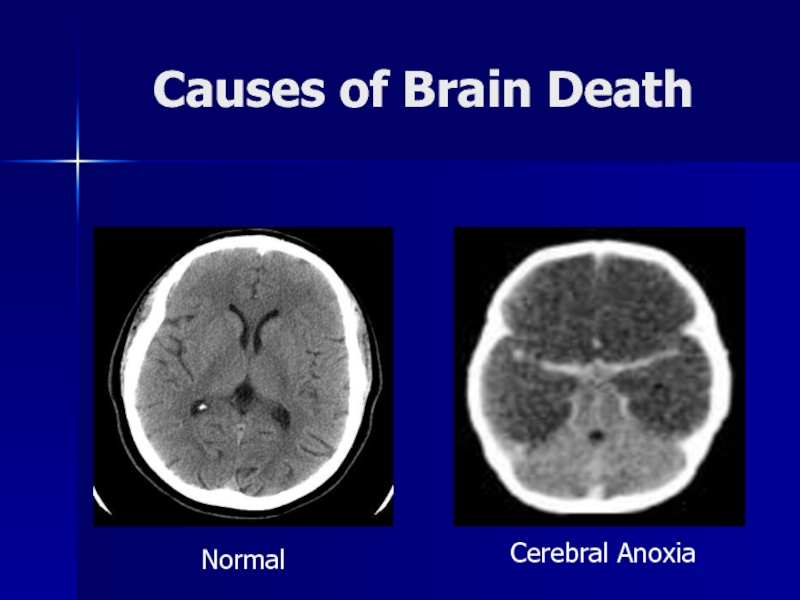
- 13. Causes of Brain DeathNormalCerebral Anoxia
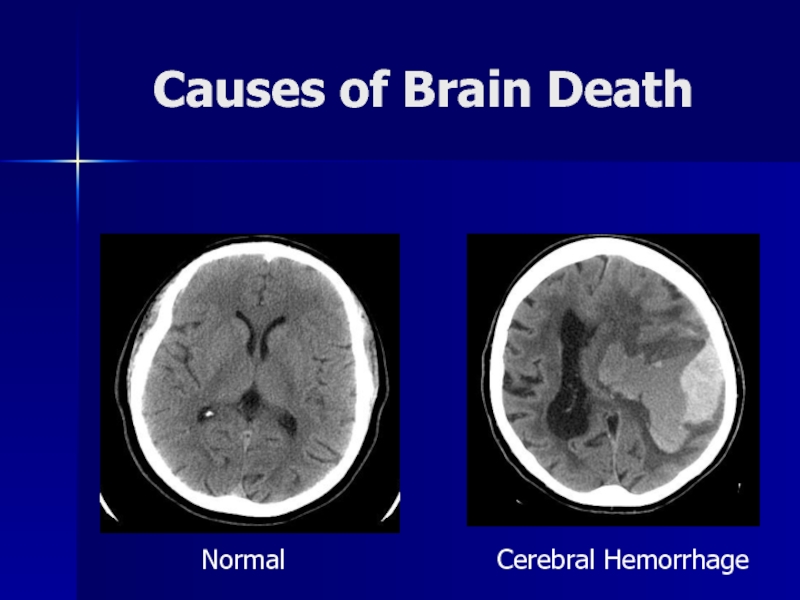
- 14. Causes of Brain DeathNormalCerebral Hemorrhage
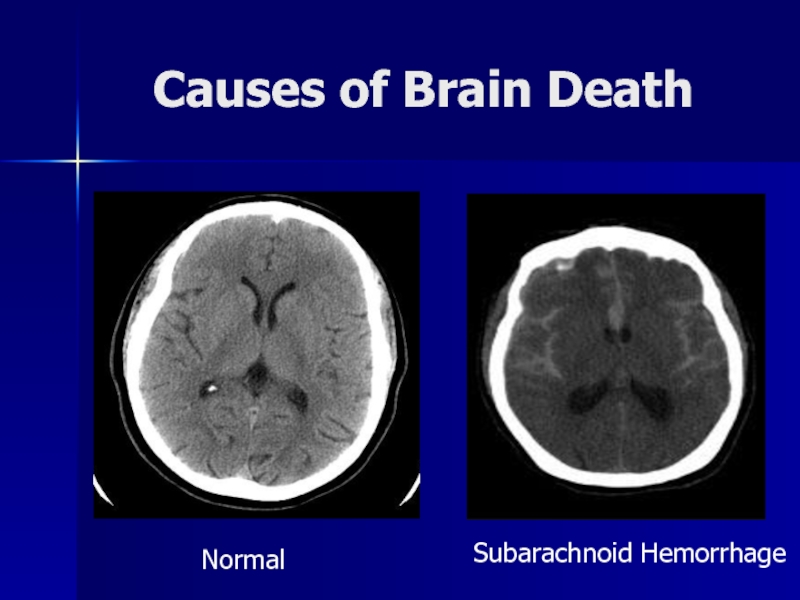
- 15. Causes of Brain DeathNormalSubarachnoid Hemorrhage
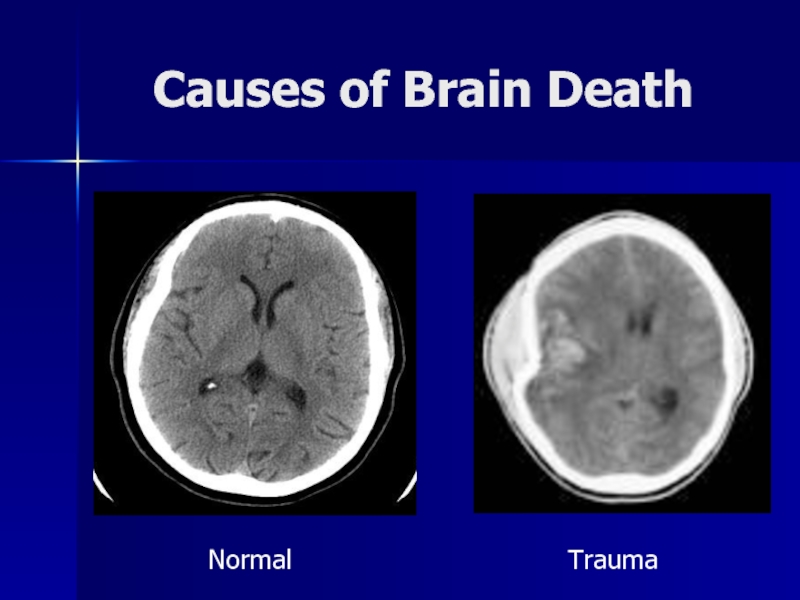
- 16. Causes of Brain DeathNormalTrauma
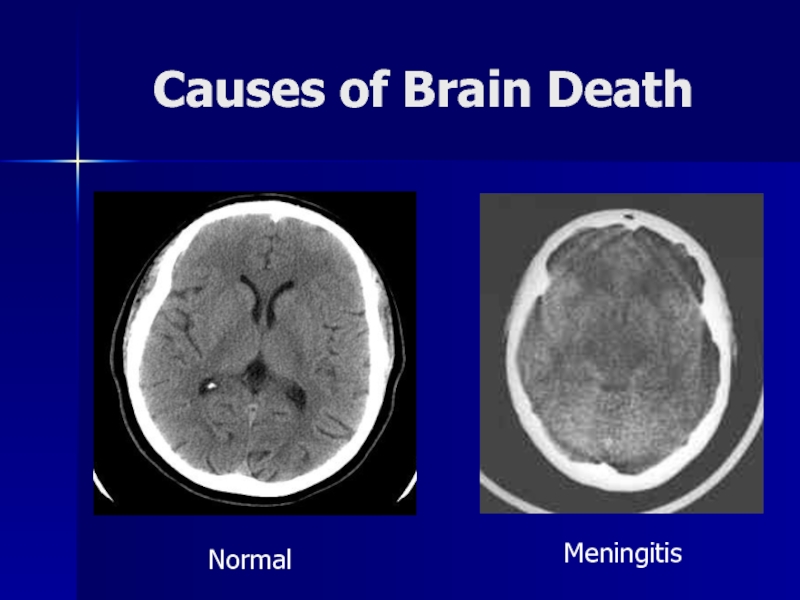
- 17. Causes of Brain DeathNormalMeningitis
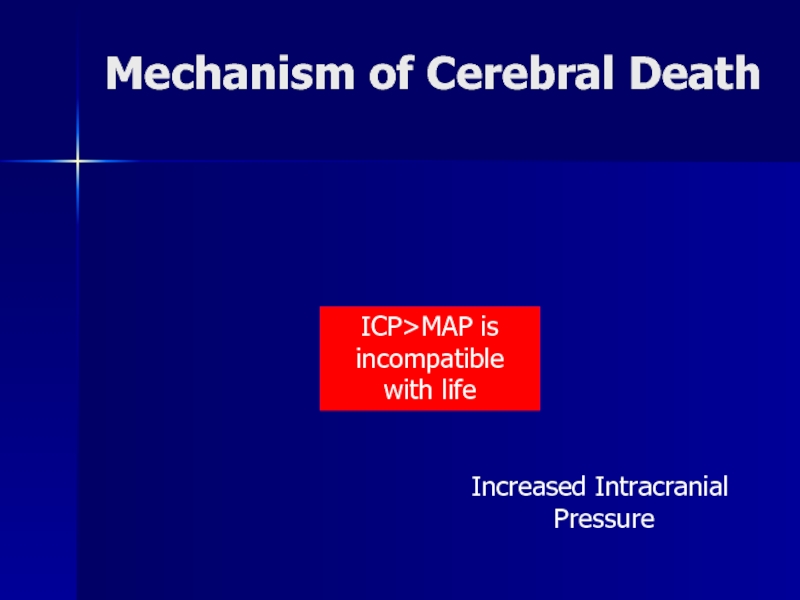
- 18. Mechanism of Cerebral DeathIncreased Intracranial PressureICP>MAP is incompatible with life
- 19. Conditions Distinct From Brain DeathPersistent Vegetative StateLocked-in SyndromeMinimally Responsive State
- 20. Persistent Vegetative StateNormal Sleep-Wake Cycles No Response
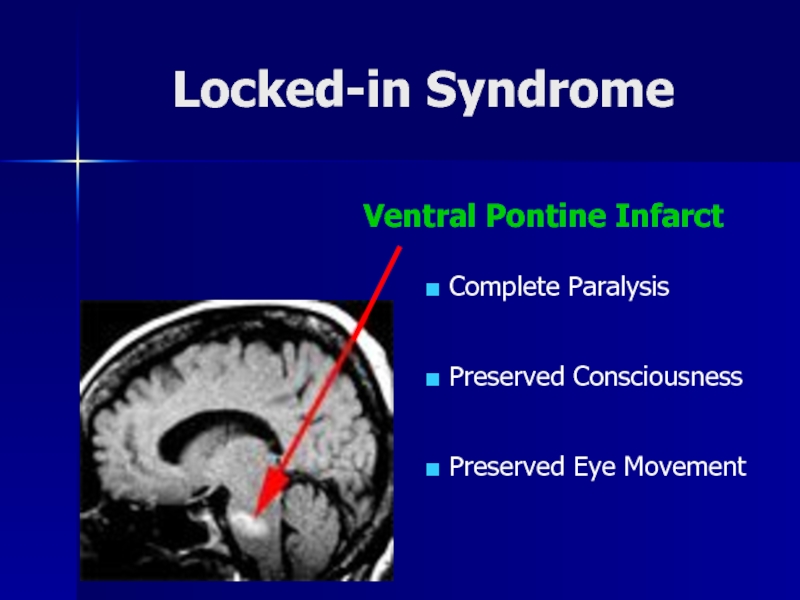
- 21. Locked-in SyndromeVentral Pontine Infarct Complete Paralysis Preserved Consciousness Preserved Eye Movement
- 22. Minimally Responsive StateDiffuse or Multi-Focal Brain InjuryPreserved Brain Stem FunctionVariable Interaction with Environmental StimuliStatic Encephalopathy
- 23. Brain Death Neurological ExaminationClinical Prerequisites:Known Irreversible CauseExclusion
- 24. Brain Death Neurological ExaminationComaAbsent Brain Stem ReflexesApnea
- 25. ComaNo Response to Noxious StimuliNail Bed PressureSternal RubSupra-Orbital Ridge Pressure
- 26. Absence of Brain Stem ReflexesPupillary ReflexEye MovementsFacial Sensation and Motor ResponsePharyngeal (Gag) ReflexTracheal (Cough) Reflex
- 27. Pupillary ReflexPupils dilated with no constriction to bright light
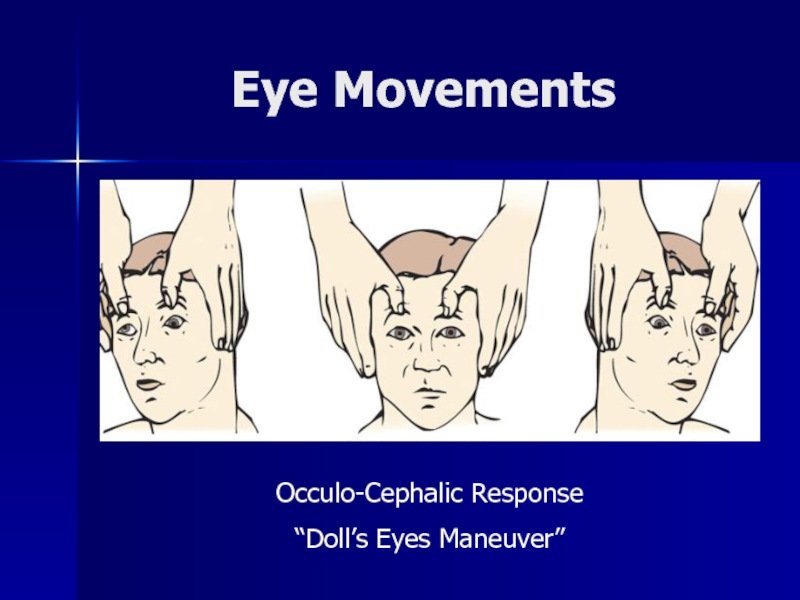
- 28. Eye Movements Occulo-Cephalic Response“Doll’s Eyes Maneuver”
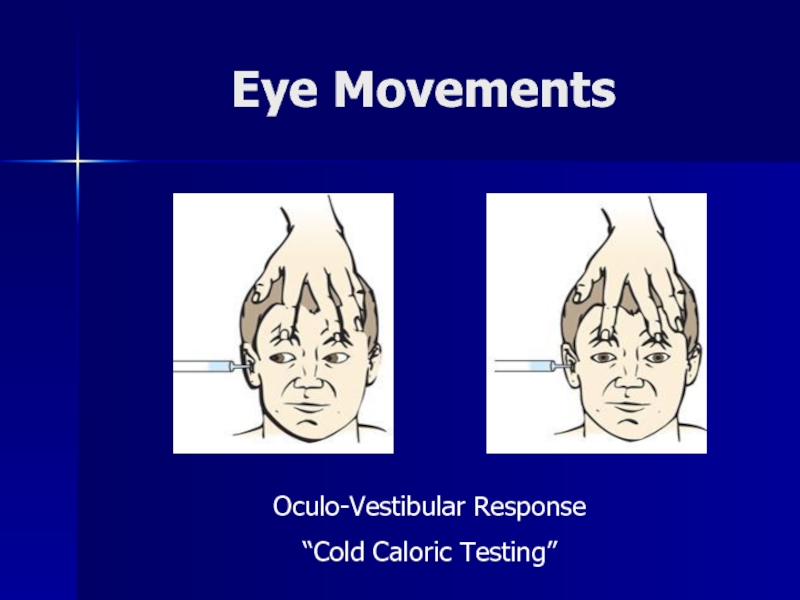
- 29. Eye MovementsOculo-Vestibular Response“Cold Caloric Testing”
- 30. Facial Sensation and Motor ResponseCorneal ReflexJaw ReflexGrimace to Supraorbital or Temporo-Mandibular Pressure
- 31. Apnea TestingPrerequisitesCore Body Temperature > 32° CSystolic Blood Pressure ≥ 90 mm HgNormal ElectrolytesNormal PCO2
- 32. Apnea Testing1. Pre-Oxygenation100% Oxygen via Tracheal Cannula
- 33. Confounding Clinical ConditionsFacial TraumaPupillary AbnormalitiesCNS Sedatives or Neuromuscular BlockersHepatic FailurePulmonary Disease
- 34. Observations Compatible with Brain DeathSweating, BlushingDeep Tendon ReflexesSpontaneous Spinal Reflexes- Triple FlexionBabinski Sign
- 35. Confirmatory Testing Recommended when the proximate
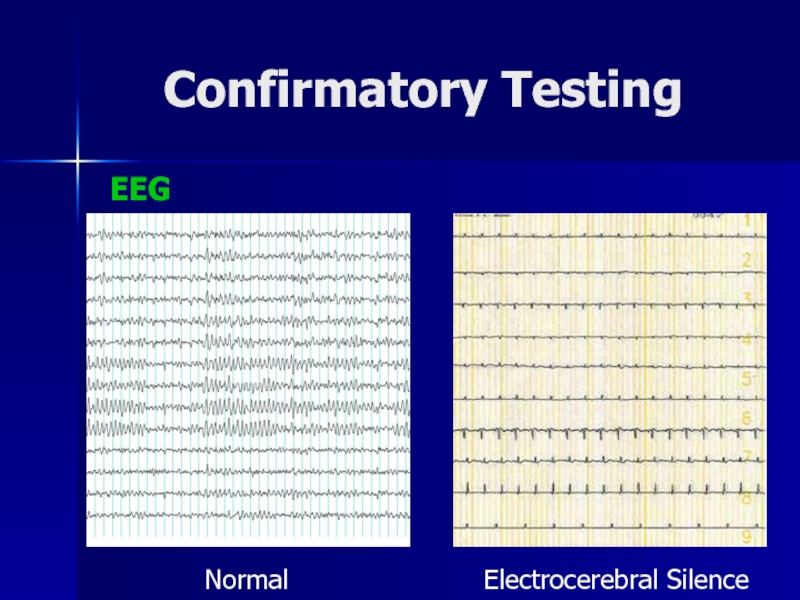
- 36. Confirmatory TestingEEGNormalElectrocerebral Silence
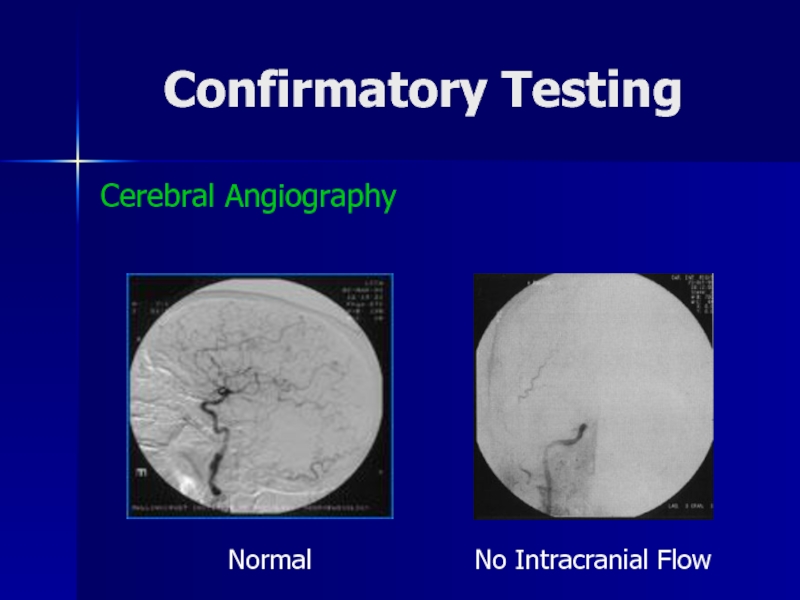
- 37. Confirmatory TestingCerebral AngiographyNormalNo Intracranial Flow
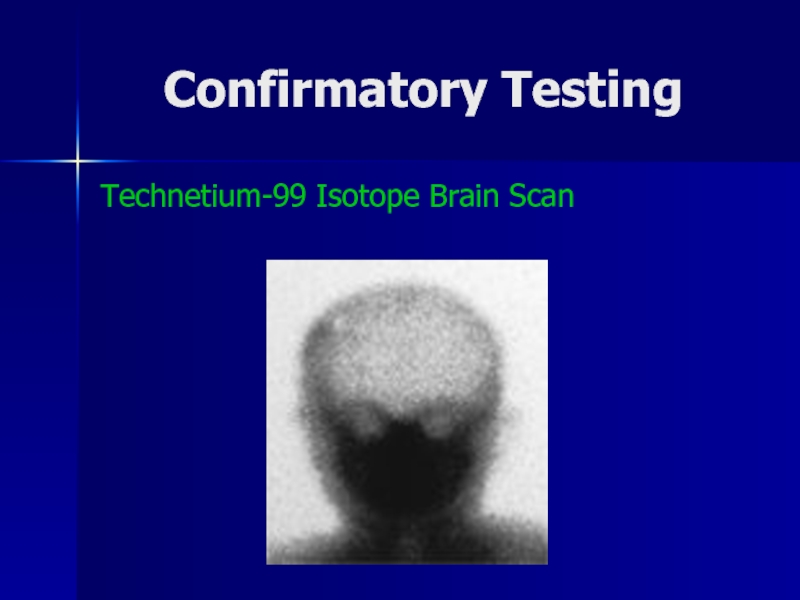
- 38. Confirmatory TestingTechnetium-99 Isotope Brain Scan
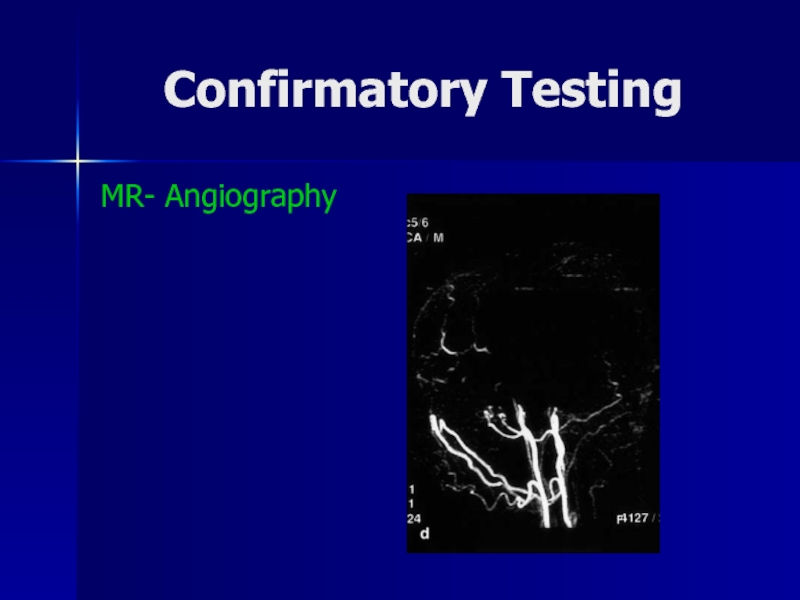
- 39. Confirmatory TestingMR- Angiography
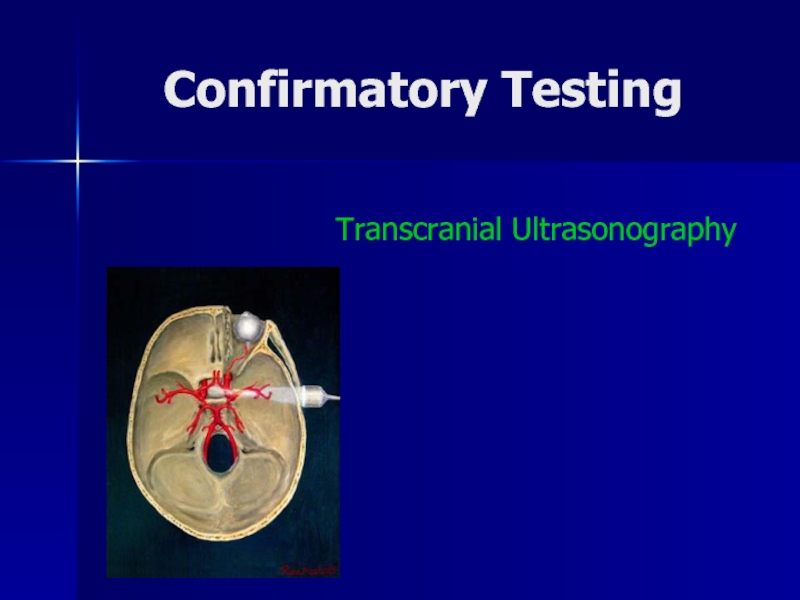
- 40. Confirmatory TestingTranscranial Ultrasonography
- 41. Confirmatory TestingSomatosensory Evoked Potentials
- 42. Concern for man and his fate
- 43. Скачать презентанцию
Historical Perspective Prior to the advent of mechanical respiration, death was defined as the cessation of circulation and breathing
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Brain Death
Anatomy and Physiology
Joel S. Cohen, M.D.
Associate
Professor of Clinical Neurology
Слайд 2Historical Perspective
Prior to the advent of mechanical respiration, death
was defined as the cessation of circulation and breathing
Слайд 3Historical Perspective
1959 Coma de’passe’ Mollaret and Goulon
1968 Irreversible Coma/Brain Death
Harvard Medical School Ad Hoc Committee
1981 Uniform Determination of
Death Act - President’s Commission for the Study of Ethical Problems in Medicine1994 American Academy of Neurology Guidelines for the determination of Brain Death
2005 NYS Guidelines for Determining Brain Death
Слайд 11Brain Stem
Medulla
Cranial Nerves IX, X
Pharyngeal
(Gag) Reflex
Tracheal (Cough) Reflex
Respiration
Слайд 19Conditions Distinct From Brain Death
Persistent Vegetative State
Locked-in Syndrome
Minimally Responsive State
Слайд 20Persistent Vegetative State
Normal Sleep-Wake Cycles
No Response to Environmental Stimuli
Diffuse
Brain Injury with Preservation of Brain Stem Function
Слайд 21Locked-in Syndrome
Ventral Pontine Infarct
Complete Paralysis
Preserved Consciousness
Preserved Eye
Movement
Слайд 22Minimally Responsive State
Diffuse or Multi-Focal Brain Injury
Preserved Brain Stem Function
Variable
Interaction with Environmental Stimuli
Static Encephalopathy
Слайд 23Brain Death Neurological Examination
Clinical Prerequisites:
Known Irreversible Cause
Exclusion of Potentially Reversible
Conditions
Drug Intoxication or Poisoning
Electrolyte or Acid-Base Imbalance
Endocrine Disturbances
Core Body temperature
> 32° CСлайд 26Absence of Brain Stem Reflexes
Pupillary Reflex
Eye Movements
Facial Sensation and Motor
Response
Pharyngeal (Gag) Reflex
Tracheal (Cough) Reflex
Слайд 30Facial Sensation and Motor Response
Corneal Reflex
Jaw Reflex
Grimace to Supraorbital or
Temporo-Mandibular Pressure
Слайд 31Apnea Testing
Prerequisites
Core Body Temperature > 32° C
Systolic Blood Pressure ≥
90 mm Hg
Normal Electrolytes
Normal PCO2
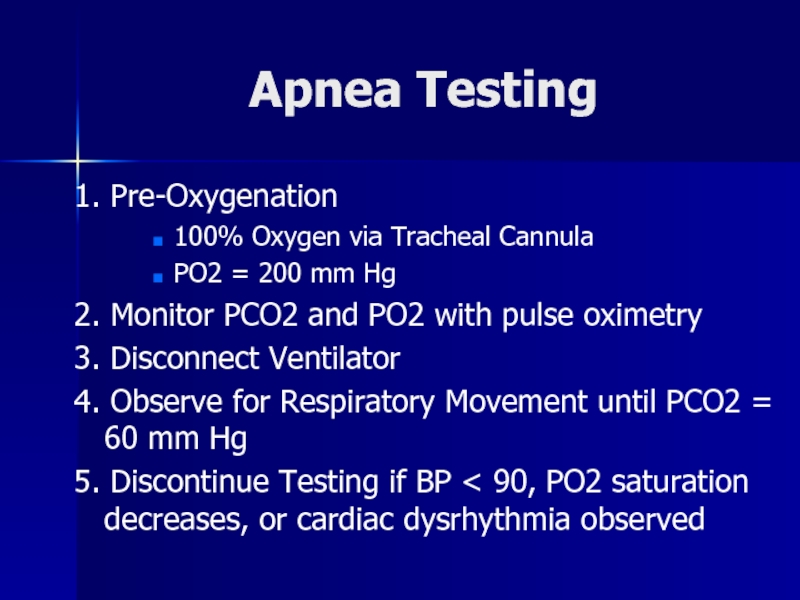
Слайд 32Apnea Testing
1. Pre-Oxygenation
100% Oxygen via Tracheal Cannula
PO2 = 200
mm Hg
2. Monitor PCO2 and PO2 with pulse oximetry
3. Disconnect
Ventilator4. Observe for Respiratory Movement until PCO2 = 60 mm Hg
5. Discontinue Testing if BP < 90, PO2 saturation decreases, or cardiac dysrhythmia observed
Слайд 33Confounding Clinical Conditions
Facial Trauma
Pupillary Abnormalities
CNS Sedatives or Neuromuscular Blockers
Hepatic Failure
Pulmonary
Disease
Слайд 34Observations Compatible with Brain Death
Sweating, Blushing
Deep Tendon Reflexes
Spontaneous Spinal Reflexes-
Triple Flexion
Babinski Sign
Слайд 35Confirmatory Testing
Recommended when the proximate cause of coma
is not known or when confounding clinical conditions limit the
clinical examinationСлайд 42 Concern for man and his fate must always form
the chief interest of all technical endeavors. Never forget this
in the midst of your diagrams and equations.Albert Einstein