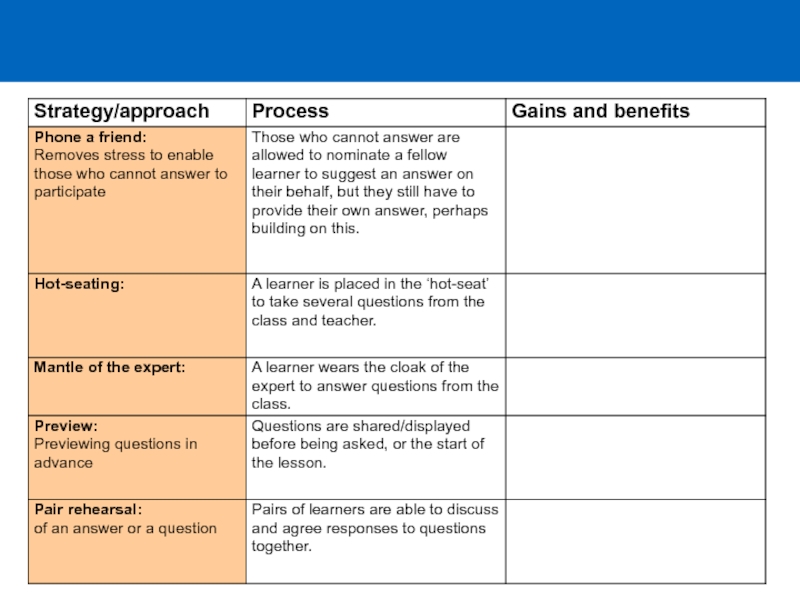
Слайд 1
Day 8
Features of primary language classroom management
Слайд 2
Session 1: Types of language classroom question and correction techniques
Слайд 3Questions relating to issues in this session?
Why are questions crucial
in all learning ? What specific extra purpose do they
serve in language classrooms?
How can we categorise types of classroom question?
What are crucial features in differentiating questions?
How can Ts vary question interaction patterns?
How and when do teachers correct answers?
Слайд 4Teachers typically ask between 300-400 questions per day
Questioning is
crucial in:
managing the class
engaging students with content
encouraging participation
increasing understanding.
promoting formative assessment.
The quantity of questions asked needs to be considered in relation to:
general time constraints
keep teacher talking time to a minimum
their effectiveness in maximising learner contributions.
Слайд 6Language teacher questions
convergent question
hypothetical question
probing question
procedural question
display question
divergent question
concept checking
question
referential question
to move lesson stages/activities along
to elicit a range
of learner language
to check learners have understood
to explore learner answers further
to focus on language meaning and forms
to promote learner speculation
to elicit a simple correct answer
to elicit something the teacher does not know answer to.
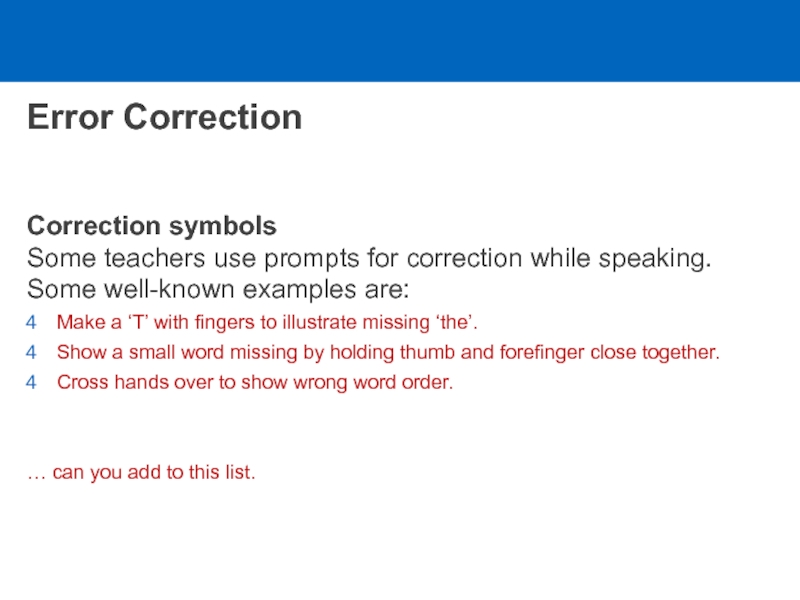
Слайд 10Error Correction
Correction symbols
Some teachers use prompts for correction while speaking.
Some well-known examples are:
Make a ‘T’ with fingers to illustrate
missing ‘the’.
Show a small word missing by holding thumb and forefinger close together.
Cross hands over to show wrong word order.
… can you add to this list.
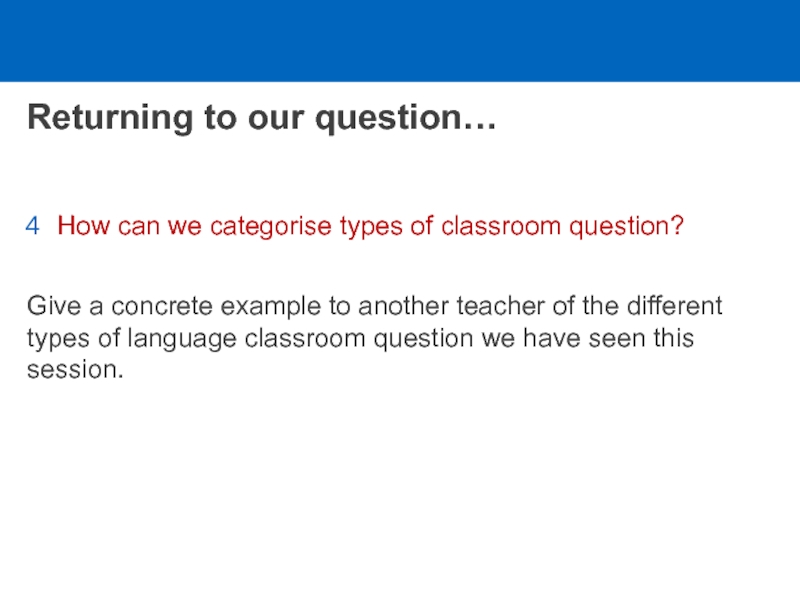
Слайд 11Returning to our question…
How can we categorise types of classroom
question?
Give a concrete example to another teacher of the different
types of language classroom question we have seen this session.
Слайд 13Questions relating to issues in this session
Why do young learners
find stories so engaging?
How can features of stories be exploited
pre-,while- and post-listening/reading?
How can Ts modify language when storytelling?
What’s the impact of accompanying story listening with viewing?
Слайд 14Tiddler ‘story’
[W] Listening to an animal story with
illustrations e.g. ‘Tiddler’. Teacher reads the story modified to class
language level.
[I] Listening to instructions for drawing, making and decorating different fish.
[P] Writing captions (bubbles) of things learners remember from the story or fish might say.
Слайд 15Key class phases in story activity
Pre:
pre-teaching/eliciting vocabulary
introducing characters
story-telling setting:
mat, props, hats, puppets, signs, etc.
While:
images, animation, reinforcing language
listening and
reading along
audience participation/pantomime
Post:
character empathy/voice consolidation
consolidating language
drama, craft, display
Слайд 16Bike stories: Curious George and other bikes
[W] Learners turn illustrations
of a bike story ‘My new bike’ and suggest language
for each picture.
www.myonlinereading.com/my-new-bike.php
[D] Teacher introduces some key words from the story: curious surprise animal show newspaper www.youtube.com/watch?v=eX7Jv_1YsuE
[W] Whole class watches animation ‘Curious George rides his bike’ and listen to teacher tell story.
[P] Learners work in pairs and make up and write captions for different sequences in the story.
[W] Teacher tells the story with animation again and learners shout out captions i.e. what ‘Curious George’ says/is thinking.
[W] Learners write out a selection of captions for a class story display.
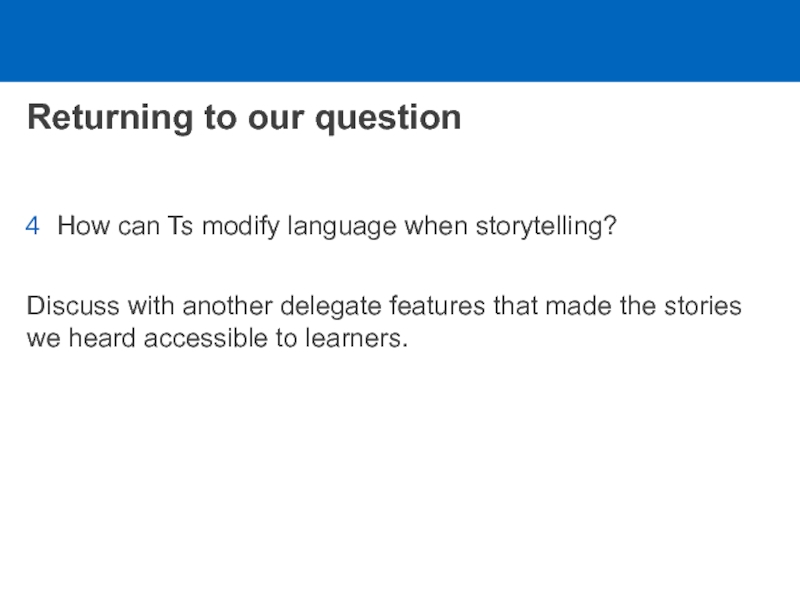
Слайд 17Returning to our question
How can Ts modify language when storytelling?
Discuss
with another delegate features that made the stories we heard
accessible to learners.
Слайд 18
Session 3: Craft activities and display
Слайд 19Questions related to issues in the session
What are the different
learning style/mode preferences typically exhibited by learners?
How can teachers effectively
address these in activities?
What type of language does performing craft activities particularly involve.
What purposes can organised classroom display serve?
Слайд 20Audio, visual and kinaesthetic learners
Learning styles are simply different preferences
in the ways of learning.
If teachers develop their teaching
styles and provide a variety of tasks in these different styles, learning will become more effective and efficient.
Слайд 21Audio learners like teachers that:
use role plays as part of
their teaching
encourage classroom discussions
encourage learners to work in groups
give time
for learners to ask questions
include reading passages aloud in their teaching
makes learners recall facts by reciting things – rhymes, mnemonics, etc.
do not need absolute silence in the classroom.
Audio, visual and kinaesthetic learners
Слайд 22Visual learners like teachers that:
use pictures and videos
draw on the
board
ask learners to visualise a scene, or successful outcome
gives
learners time to sketch out ideas or to take notes
encourages use of coloured pens
likes to have a colourful classroom.
Audio, visual and kinaesthetic learners
Слайд 23Kinaesthetic learners like teachers that:
encourage good note-taking (when watching videos,
listening to explanations or going through examples)
use activities that include
moving around the classroom
use sticky-notes and flash cards for noting and sorting ideas
encourage learning by doing, not just sitting.
Audio, visual and kinaesthetic learners
Слайд 24What’s in a task?
visual learners
auditory learners
kinaesthetic learners
Look at
the activities. Sort them according to which ones would appeal
more to:
Слайд 25Making finger/potato/hand puppets
a simple hand [bag] puppet
www.youtube.com/watch?v=BnFdE7lbaBE
Слайд 26Making a traditional hat
www.youtube.com/watch?v=nzmAf5xjQBo
Слайд 27Display
Display as stimulus - designed to arouse interest in a
particular concept or theme; cross-curricular links, develop aesthetic sense
Display as
information - designed to inform; provide reinforcement; act as resource, prompt
Display as celebration - designed to present children's work to a wider audience. validate work, sense of community, achievement and respect
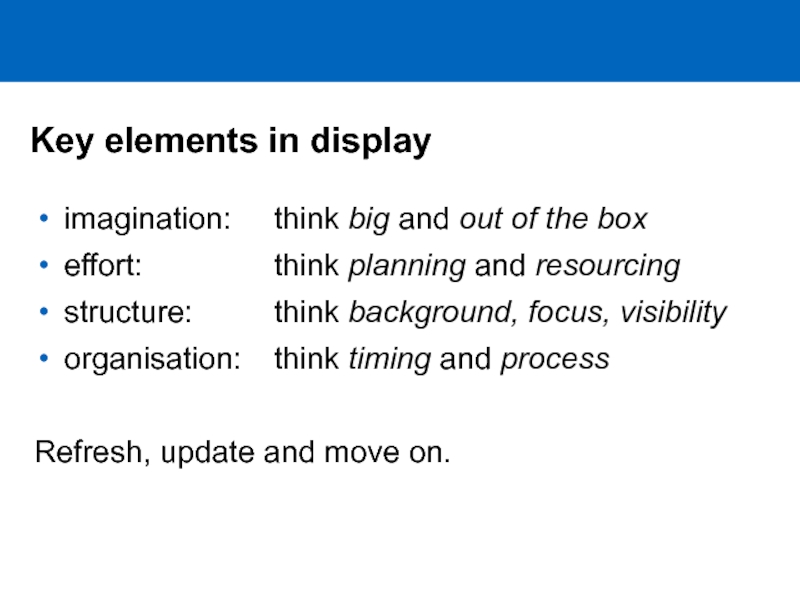
Слайд 28Key elements in display
imagination: think big and out of
the box
effort: think planning and
resourcing
structure: think background, focus, visibility
organisation: think timing and process
Refresh, update and move on.
Слайд 29Primary Display Internet inspiration
Find ‘display’ images from real classrooms that
might be used to inspire teachers related to these actual
displays in the curriculum
Spring in Kazakhstan
Underwater ocean scene
Puppet/mobile displays
Classroom rules/signs display
Слайд 30Returning to our earlier questions
What was the main motivational ‘purpose’
behind each display found on the internet ?
What type of
language did our craft activities typically involve.
Слайд 31
Session 4: Cross-curricular learning
Слайд 32Questions related to this session
Why use content/activities from other subjects
?
Can curricular concepts be taught in English?
What are some ways
in which we can teach collaboratively?
What additional steps are involved in cross-curricular lessons?
Слайд 33Collaborative teaching
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o0u16p4wyoE
Слайд 34Science
[P] Listening to instructions for cutting out, vehicle outlines, making
body of vehicle and showing how many people are inside.
[P] Visiting teacher’s moving parts shop and requesting the things needed to make rest of vehicle.
[P] Writing out labels in the form of flags for to put on learner vehicles, e.g. Tom and Tina’s tractor.
[W] Saying where your vehicle can get to (vehicles rolled down a gentle slope and along a flat surface). Rest of class asked: Can it?
Слайд 35Cross-curricular primary tasks
Maths
Listening, measuring and completing a graph about how
long learner’s step is.
Activity framework, worksheet and graph template
:
http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/maths/pdfs/how_long_is_your_step.pdf
Art and Design
[I] Watching a demonstration and following instructions on how to wrap present. Silent video presentation which teacher pauses and prompts with language.
[I] [f] Listening to instructions to make decorations to stick on wrapped presents e.g. Draw a star. Colour the star purple. Now give instructions for display.
Слайд 36Simple Maths/Science focuses within the English Curriculum
Halving and doubling bingo
Sink
or swim
Making representations from shapes
Слайд 37Returning to our question
Why use content/activities from other subjects ?
Make a list of reasons with another teacher.








![Day 8
Features of primary language classroom management Tiddler ‘story’ [W] Listening to an animal story with illustrations e.g. Tiddler ‘story’ [W] Listening to an animal story with illustrations e.g. ‘Tiddler’. Teacher reads the story](/img/thumbs/395e72f0b04d52b8d84f2ca4eb1ea894-800x.jpg)

![Day 8
Features of primary language classroom management Bike stories: Curious George and other bikes[W] Learners turn illustrations of Bike stories: Curious George and other bikes[W] Learners turn illustrations of a bike story ‘My new bike’](/img/thumbs/237f094a2fdcde415d2c1735f77f8e55-800x.jpg)







![Day 8
Features of primary language classroom management Making finger/potato/hand puppetsa simple hand [bag] puppetwww.youtube.com/watch?v=BnFdE7lbaBE Making finger/potato/hand puppetsa simple hand [bag] puppetwww.youtube.com/watch?v=BnFdE7lbaBE](/img/thumbs/46cfa7952f163adfb00eba655e620e60-800x.jpg)




![Day 8
Features of primary language classroom management Science[P] Listening to instructions for cutting out, vehicle outlines, making body Science[P] Listening to instructions for cutting out, vehicle outlines, making body of vehicle and showing how many](/img/thumbs/0725ba0bcd04e524aeba68109770e0f5-800x.jpg)