Слайд 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology #1
Saduakassova Shynar Muratovna
Hypertension in Pregnancy
Слайд 2Hypertension in Pregnancy
High risk factors
Etiology and pathophysiology
Classification
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Future Implications
Слайд 3High risk factors
Age - younger than 18 or older than
40 years
Multiple pregnancy
Has previous gestational hypertensive disorders
Disease of the circulatory
system
Chronic nephritis
Diabetic
Obesity
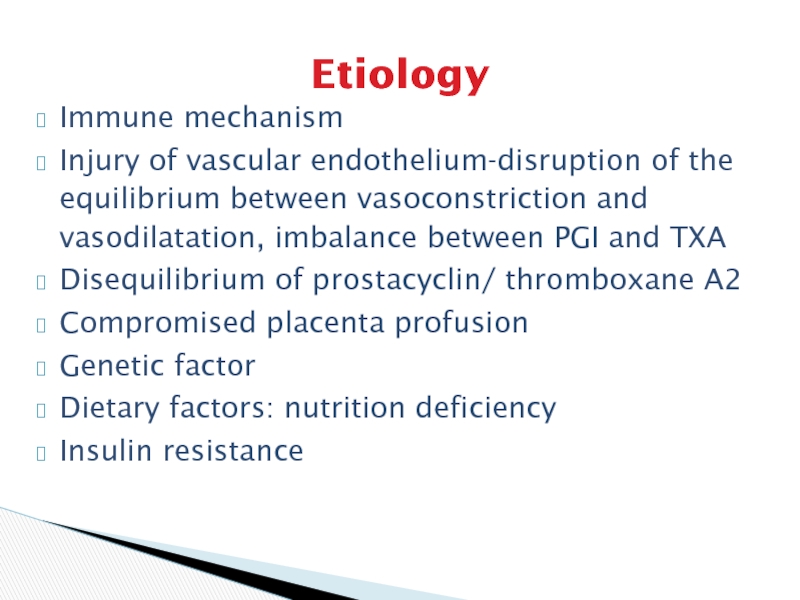
Слайд 4Etiology
Immune mechanism
Injury of vascular endothelium-disruption of the equilibrium between vasoconstriction
and vasodilatation, imbalance between PGI and TXA
Disequilibrium of prostacyclin/ thromboxane
A2
Compromised placenta profusion
Genetic factor
Dietary factors: nutrition deficiency
Insulin resistance
Слайд 5
Classification
Chronic hypertension
Gestational hypertension
Preeclampsia (gestational hypertension with proteinuria)
- mild preeclampsia
- severe
preeclampsia
- eclampsia
Слайд 6О10 Хроническая артериальная гипертензия, (существовавшая ранее гипертензия, диагностированная до 20
недель беременности или сохраняющаяся через 6 недель после родов)
О13 Гестационная
гипертензия (гипертензия, вызванная беременностью)
О14 Преэклампсия (гестационная гипертензия с протеинурией)
О14.0 Преэклампсия легкой степени
О14.1 Тяжелая преэклампсия
О15 Эклампсия
Классификация
Слайд 7Diagnosis: Hypertension
Mild hypertension (either):
SBP > 140
DBP > 90
Severe hypertension (either):
SBP
> 160
DBP > 110
BP > 4 hours apart
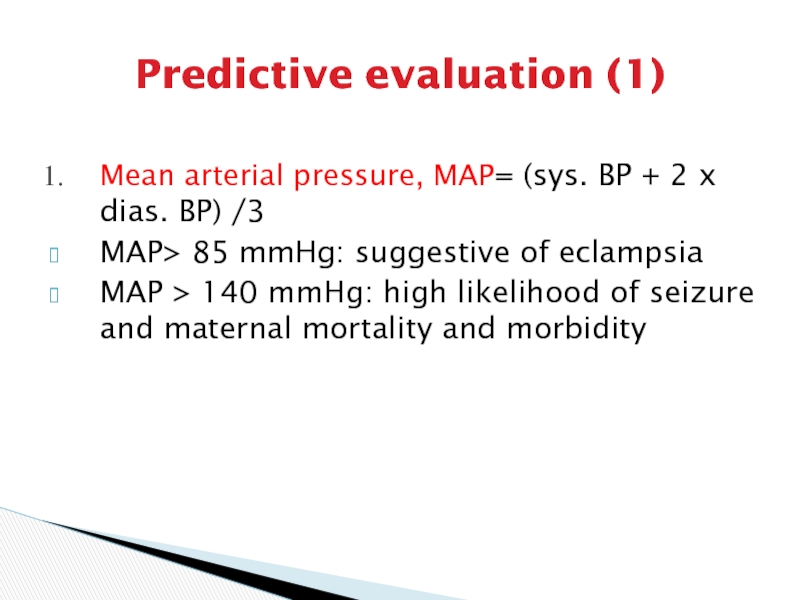
Слайд 8Predictive evaluation (1)
Mean arterial pressure, MAP= (sys. BP + 2
x dias. BP) /3
MAP> 85 mmHg: suggestive of eclampsia
MAP >
140 mmHg: high likelihood of seizure and maternal mortality and morbidity
Слайд 9Classification
Chronic hypertension proceeding pregnancy (essential or secondary to renal
disease, endocrine disease or other causes)
Presents before 20 week gestation
Persists
beyond 6 week postpartum
BP ≥ 140/90 mmHg
Слайд 10Classification
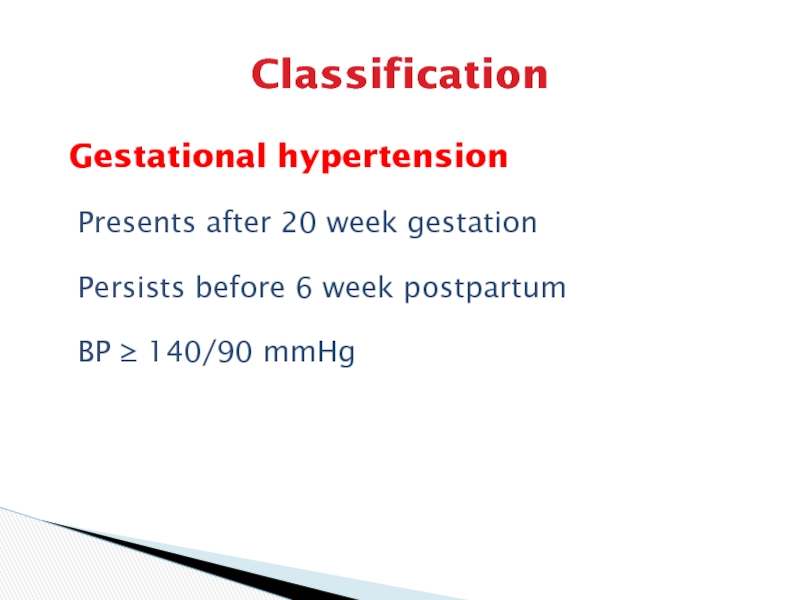
Gestational hypertension
Presents after 20 week gestation
Persists before 6 week
postpartum
BP ≥ 140/90 mmHg
Слайд 11Mild preeclampsia – mild hypertension with proteinuria ±edema
Легкая преэклампсия –
легкая гипертензия в сочетании с протеинурией ± отёки
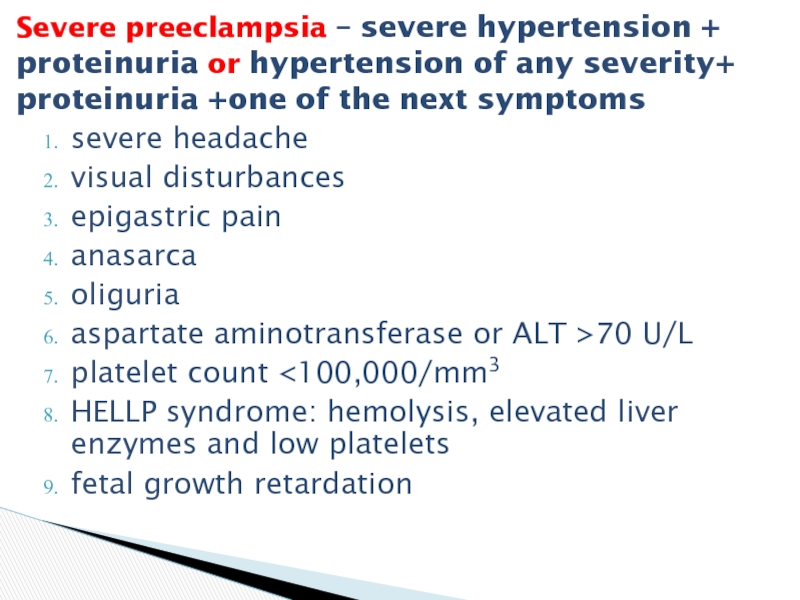
Слайд 12severe headache
visual disturbances
epigastric pain
anasarca
oliguria
aspartate aminotransferase or ALT >70 U/L
platelet count
retardation
Severe preeclampsia – severe hypertension + proteinuria or hypertension of any severity+ proteinuria +one of the next symptoms
Слайд 13сильная головная боль
нарушение зрения
боль в эпигастральной области и/или
тошнота, рвота
судорожная готовность
генерализованные отёки
олигоурия (менее 30 мл/час
или менее 500 мл мочи за 24 часа)
болезненность при пальпации печени
количество тромбоцитов ниже 100 x 106г/л
повышение уровня печёночных ферментов (АлАТ или АсАТ выше 70 МЕ/л)
HELLP-синдром
ВЗРП
Тяжёлая преэклампсия–
тяжёлая гипертензия + протеинурия или
гипертензия любой степени тяжести + протеинурия + один из следующих симптомов:
Слайд 14Blood (1)
Volume: reduced plasma volume
Normal physiologic volume expansion does
not occur
Generalized vasoconstriction and capillary leak
Hematocrit
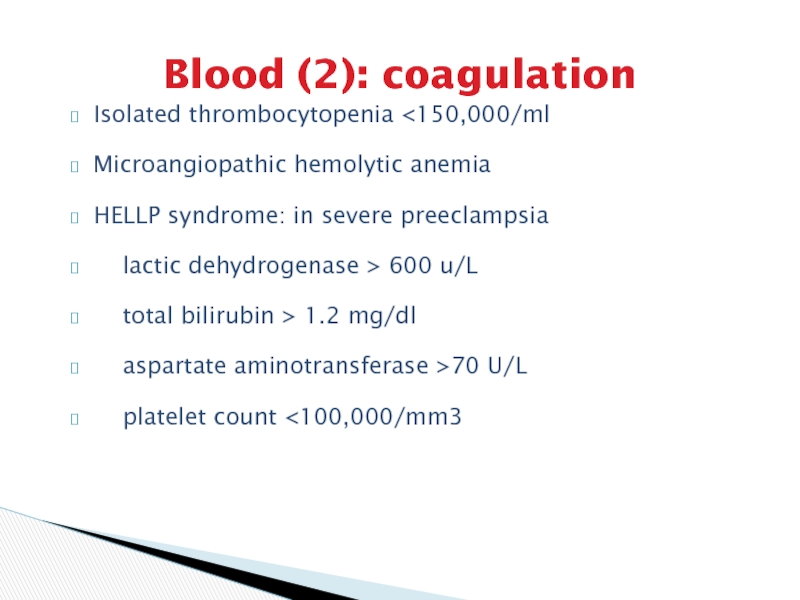
Слайд 15Blood (2): coagulation
Isolated thrombocytopenia
preeclampsia
lactic dehydrogenase > 600 u/L
total bilirubin
> 1.2 mg/dl
aspartate aminotransferase >70 U/L
platelet count <100,000/mm3
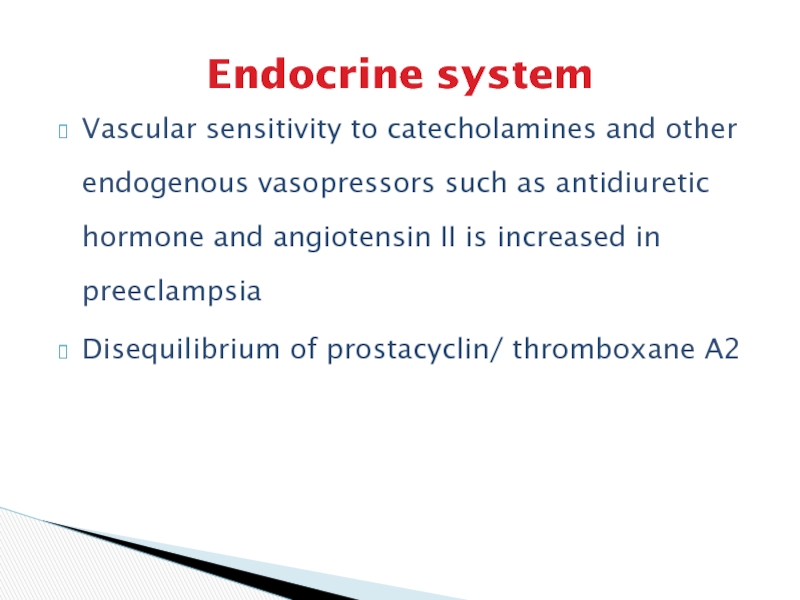
Слайд 16Endocrine system
Vascular sensitivity to catecholamines and other endogenous vasopressors such
as antidiuretic hormone and angiotensin II is increased in preeclampsia
Disequilibrium
of prostacyclin/ thromboxane A2
Слайд 17Clinical findings (1)
Symptoms and signs
Hypertension
Diastolic pressure ≥ 90 mmHg or
Systolic
pressure ≥ 140 mmHg or
Increase of 30/15 mmHg
Proteinuria
>300 mg/24-hr urine
collection or
+ or more on dipstick of a random urine
Слайд 18Clinical findings (2)
Edema
Weight gain: 1-2 lb/wk or 5 lb/wk is
considered worrisome
Degree of edema
Preeclampsia may occur in women with no
edema
Слайд 19Clinical findings (3)
Differing clinical picture in preeclampsia-eclampsia crises: patient may
present with
Eclamptic seizures
Liver dysfunction
Pulmonary edema
Abruptio placenta
Renal failure
Ascites and anasarca
Слайд 20Clinical findings (4)
Laboratory findings (1)
Blood test: elevated Hb or HCT,
in severe cases, anemia secondary to hemolysis, thrombocytopenia, decreased coagulation
factors
Urine analysis: proteinuria and hyaline cast, specific gravity > 1.020
Liver function: ALT and AST increase, LDH increase, serum albumin
Renal function: uric acid: 6 mg/dl, serum creatinine may be elevated
Слайд 21Clinical findings (5)
Laboratory findings (2)
Retinal check
Other tests: placenta function (ultrasound,
kardiotokography, doppler), fetal maturity, cerebral angiography etc.
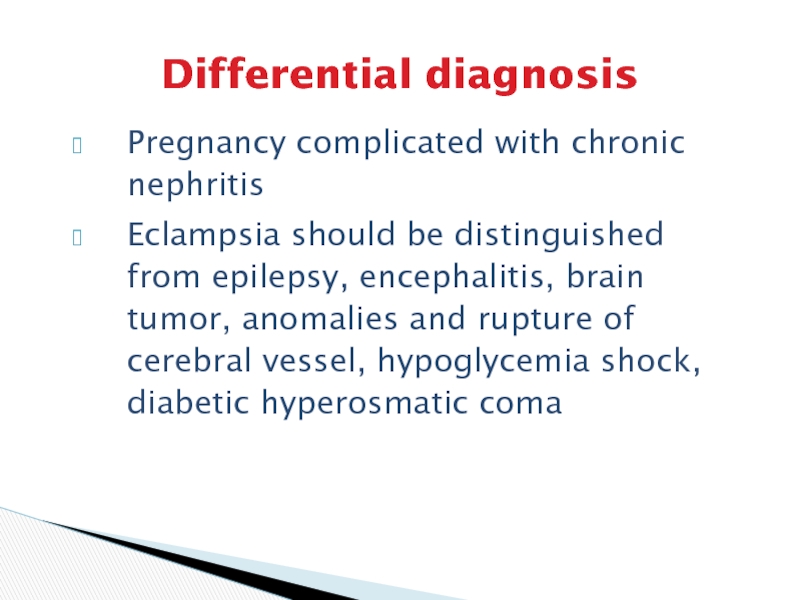
Слайд 22Differential diagnosis
Pregnancy complicated with chronic nephritis
Eclampsia should be distinguished from
epilepsy, encephalitis, brain tumor, anomalies and rupture of cerebral vessel,
hypoglycemia shock, diabetic hyperosmatic coma
Слайд 23Complications
Preterm delivery
Fetal risks: acute and chronic uteroplacental insufficiency
Intrapartum fetal distress
or stillbirth
Oligohydramnios
Слайд 24Prevention
Calcium supplementation: 1 g/24-hr
effective in high risk
group, not effective
in low risk women
Aspirin
(antithrombotic): 75-120 mg/24-hr
Good prenatal care and regular visits
Eclampsia cannot always be prevented, it may occur suddenly and without warning.
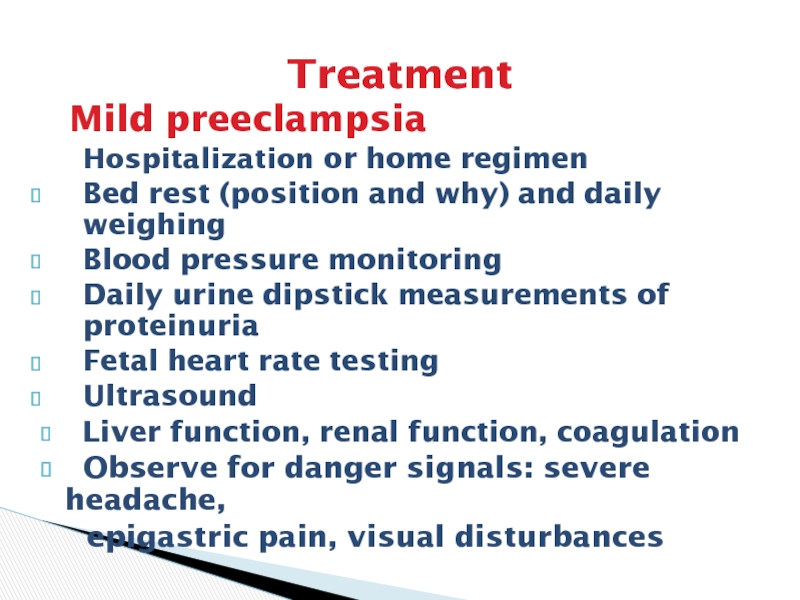
Слайд 25Treatment
Mild preeclampsia
Hospitalization or home regimen
Bed rest (position
and why) and daily weighing
Blood pressure monitoring
Daily urine dipstick measurements
of proteinuria
Fetal heart rate testing
Ultrasound
Liver function, renal function, coagulation
Observe for danger signals: severe headache,
epigastric pain, visual disturbances
Слайд 26Severe preeclampsia
Prevention of convulsion: magnesium sulfate or diazepam
Control of maternal
blood pressure: antihypertensive therapy
Initiation of delivery
Слайд 27Magnesium sulfate
Decreases the amount of acetylcholine released at the neuromuscular
junction
Blocks calcium entry into neurons
Vasodilates the smaller-diameter intracranial vessels
Слайд 28Magnesium sulfate
i.v. or i.m.
Starting dose - 5g dry
matter (20 ml 25% ) during 10-15 min i.v.
Maintenance dose
-1-2g/hr dry matter constant infusion during 12-24 hours
Total dose: 20-30 g/d
Слайд 29
Toxicity
Diminished or loss of patellar reflex
Diminished respiration
minute
Muscle paralysis
Blurred speech
Cardiac arrest
Слайд 30Reversal of toxicity:
Slow i.v. 10% 10,0 ml calcium gluconate
Oxygen
supplementation
Cardiorespiratory support
Слайд 31Antihypertensive therapy
Medications:
Hydrolazine: initial choice
Labetolol
Nifedipine
Nimoldipine
Methyldopa
Sodium nitroprusside
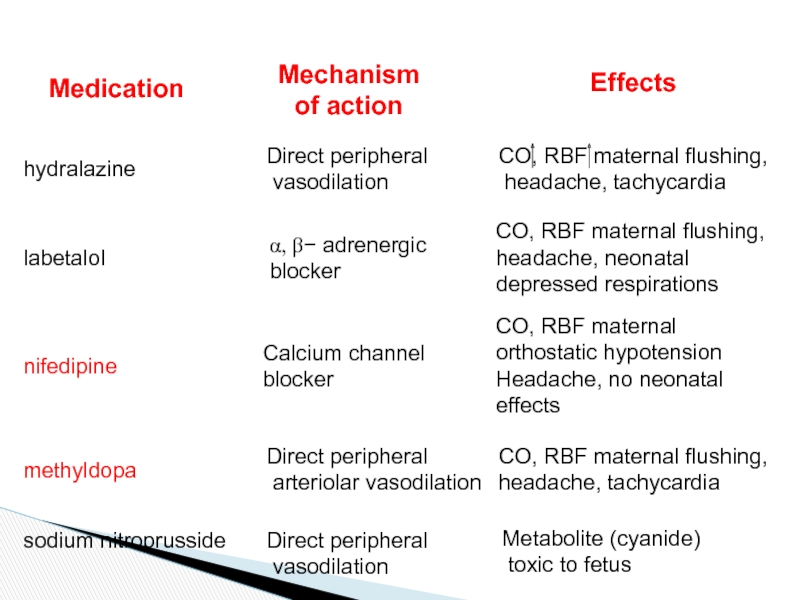
Слайд 32Medication
Mechanism
of action
Effects
hydralazine
Direct peripheral
vasodilation
CO, RBF maternal flushing,
headache, tachycardia
labetalol
a,
b- adrenergic
blocker
CO, RBF maternal flushing,
headache, neonatal depressed respirations
nifedipine
Calcium channel
blocker
CO, RBF maternal orthostatic hypotension
Headache, no neonatal effects
methyldopa
Direct peripheral
arteriolar vasodilation
CO, RBF maternal flushing,
headache, tachycardia
sodium nitroprusside
Direct peripheral
vasodilation
Metabolite (cyanide)
toxic to fetus
Слайд 33Delivery
Induction of labor
Immature cervix (
– cervical preparation by prostaglandins during 24-48 hours, amniotomia, oxytocin
Mature cervix (>6 points on the scale Bishop) – amniotomia, oxytocin
Cesarean section
Induction of labor unsuccessful
Induction of labor not possible
Maternal or fetal status is worsening
Abruptio placenta
Слайд 34Eclampsia
No aura preceding seizure
Multiple tonic-clonic seizures
Unconsciousness
Hyperventilation after seizure
Tongue
biting, broken bones, head trauma and aspiration, pulmonary edema and
retinal detachment
Слайд 35Delivery
Control of seizure
Control of hypertension: magnesium sulfate, diazepam, antihypertensive therapy
Delivery during 12 hours
Proper nursing care