Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Freezing lakes and lake ice Introduction (2) Growth and melting (3)
Содержание
- 1. Freezing lakes and lake ice Introduction (2) Growth and melting (3)
- 2. Lake ice seasonIce thickness--- stable ice ---Unstable
- 3. Warming climate ?Will the lake freeze
- 4. Ice phenologyFreezing dateStrongly connected to air temperature
- 5. BreakupFreezing80PE R E N N I A LFreezing and breakupExtrapolated from Kirillin et al. (2012)No ice
- 6. Lake ice time seriesIce phenologyfreezing datebreakup dateHow
- 7. Lake Kallavesi, Finland 1830 – 2014Trend 10
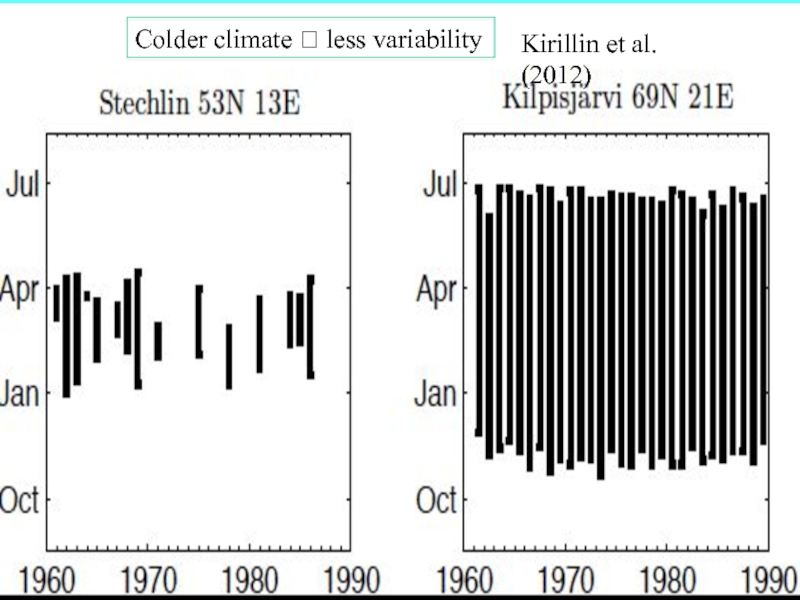
- 8. Colder climate less variabilityKirillin et al. (2012)
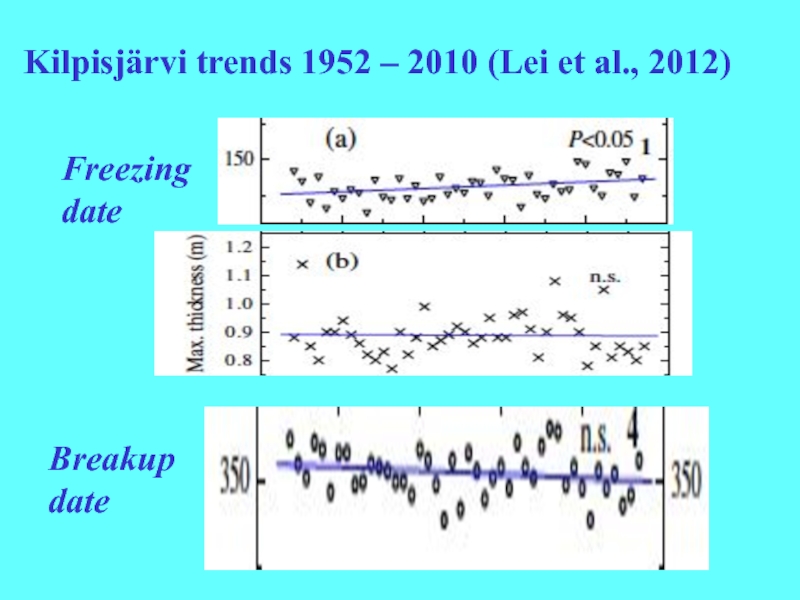
- 9. FreezingdateBreakupdateKilpisjärvi trends 1952 – 2010 (Lei et al., 2012)
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. 1st order: climate change impactFreezing date ~ 5
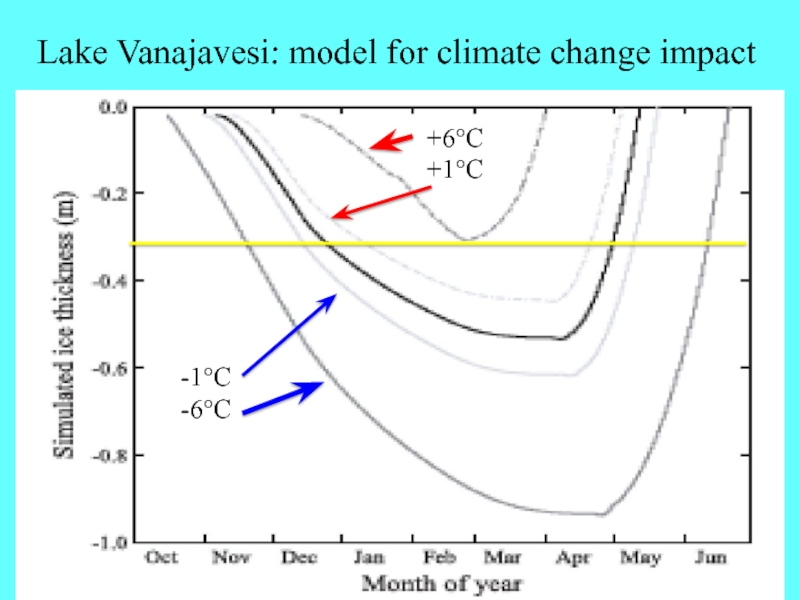
- 13. Lake Vanajavesi: model for climate change impact-1°C-6°C+6°C+1°C
- 14. Ice thickness cycle – albedo sensitivity, Prydz
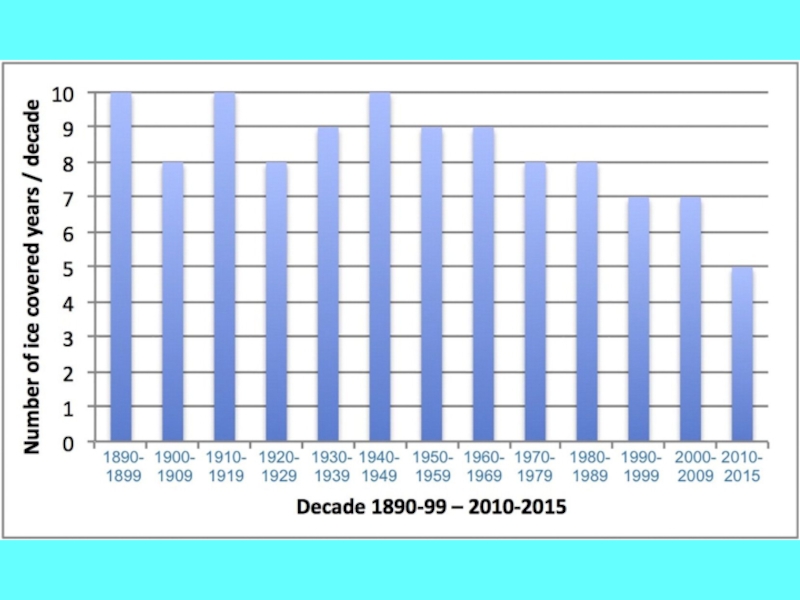
- 15. Lake Ladoga: Finnish – Soviet – Russian
- 16. Ice concentration AA = relative area of
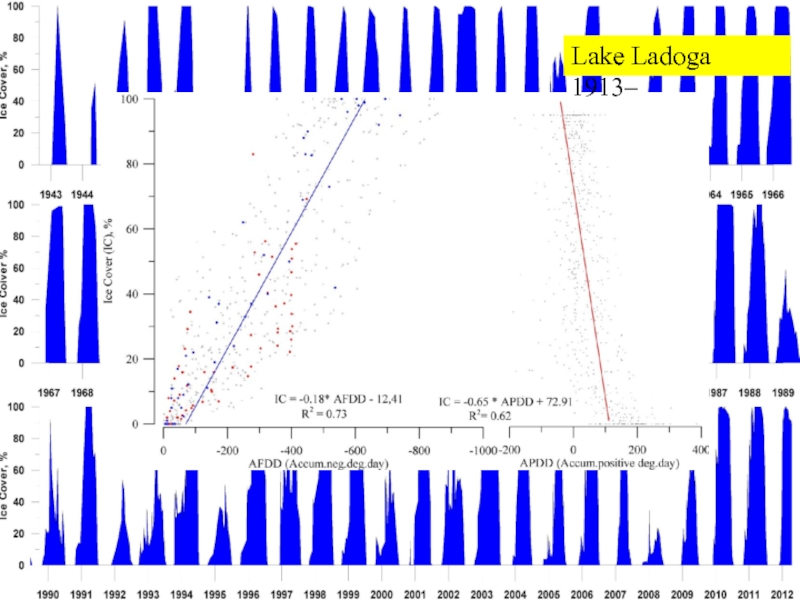
- 17. Lake Ladoga 1913–
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Summary: warming (?) Freezing day delaysMax annual
- 20. … consequences to water bodyShorter ice season
- 21. Climate warming Lake seasonsAnnual cycle:qualitative changesSummer stratification stronger Stable ice period shorter
- 22. Lake ice and society: climate change impactLake
- 23. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Freezing lakes and lake ice
Introduction
(2) Growth and melting
(3) Supraglacial lakes
(4)
Lake ice climatology
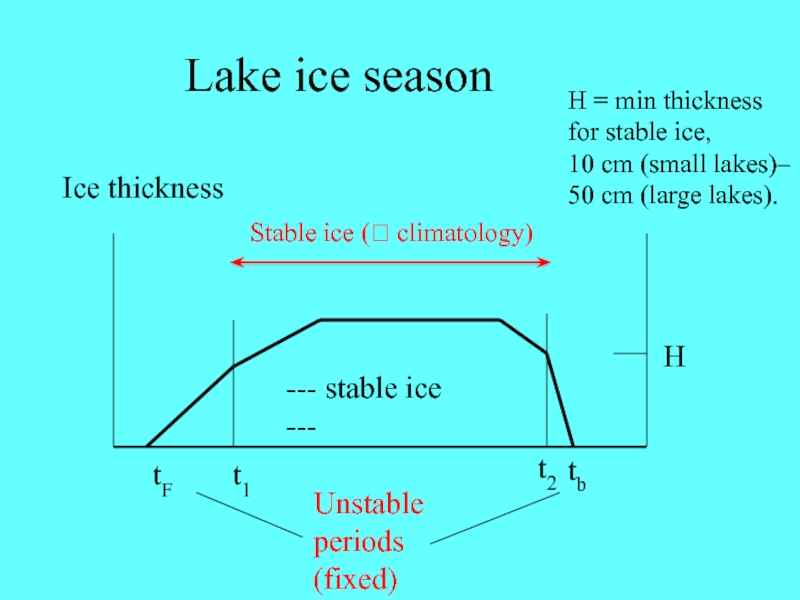
Слайд 2Lake ice season
Ice thickness
--- stable ice ---
Unstable periods
(fixed)
H
tF
tb
t1
t2
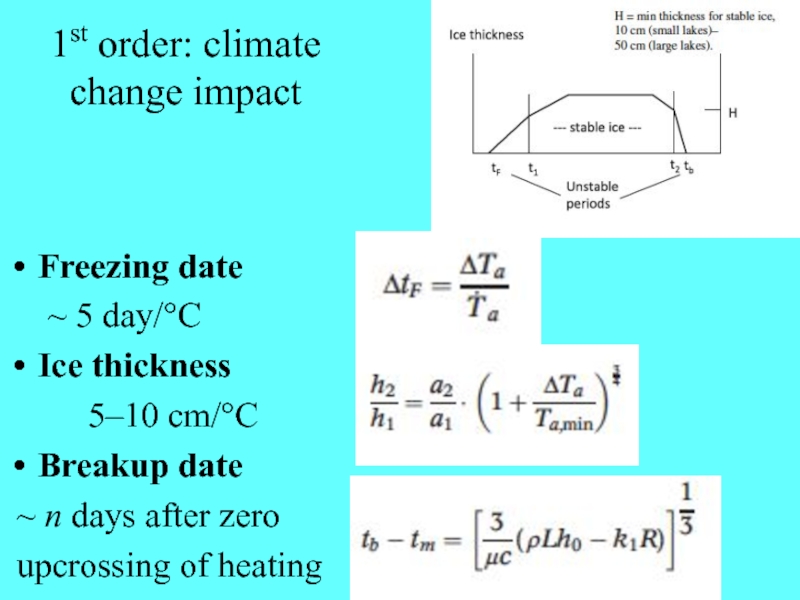
H = min
thickness for stable ice,
10 cm (small lakes)–
50 cm
(large lakes).Stable ice ( climatology)
Слайд 3Warming climate ?
Will the lake freeze in future ?
How
much are freezing date and break-up date affected ?
How much
is ice thickness affected ? And ice quality?Ice cover stability ?
Ice coverage ?
Слайд 4Ice phenology
Freezing date
Strongly connected to air temperature (long-wave radiation, turbulent
fluxes)
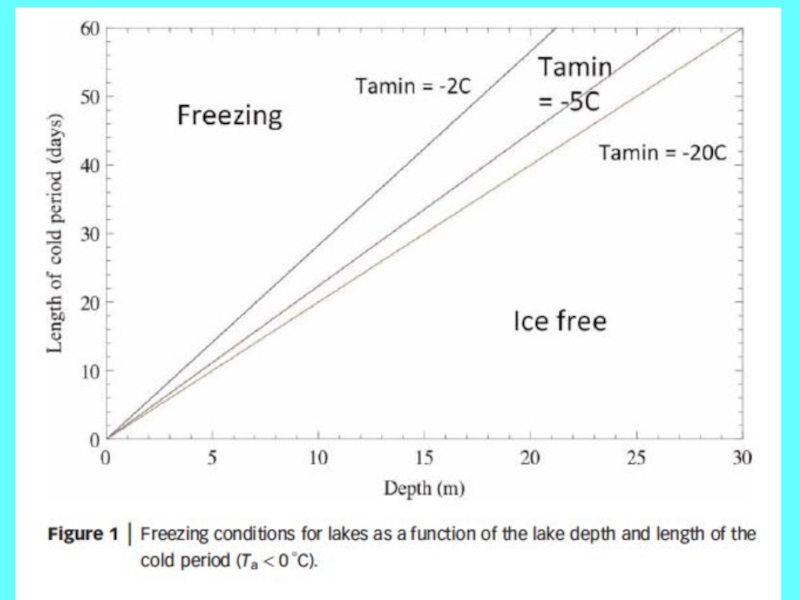
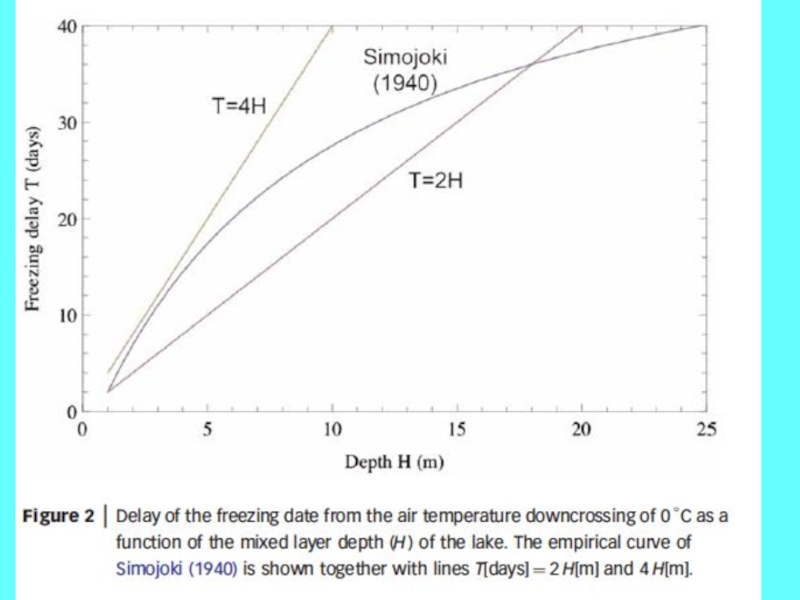
Connection depends on lake depth
Freezing after 0oC downcrossing
Air temperature falling
rate major factorBreakup date
Solar radiation driving force – no long-term trend
Ice and snow thickness – weak positive trend
Turnover day from negative to positive heat balance key factor
Degree-days correlate with net solar flux
time
Thickness ~ ✔ freezing-degree-days
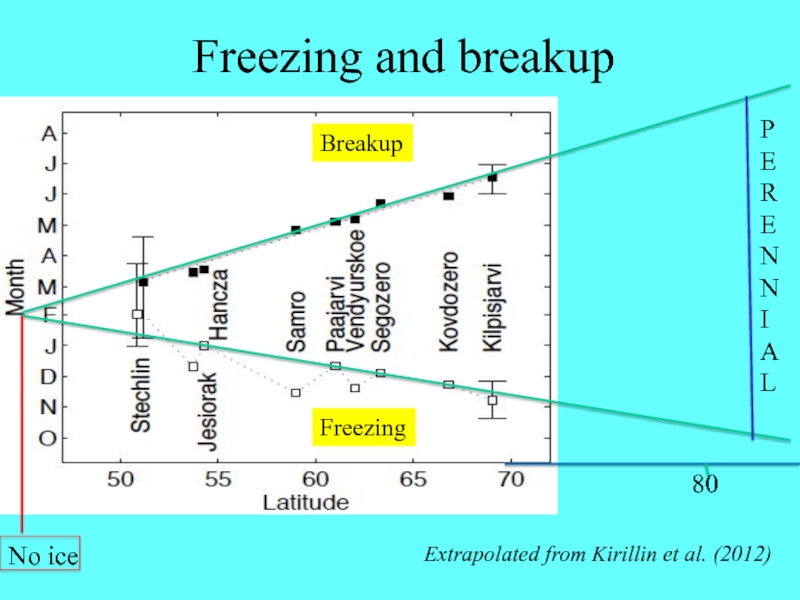
Слайд 5Breakup
Freezing
80
P
E
R
E
N
N
I
A
L
Freezing and breakup
Extrapolated from Kirillin et al. (2012)
No ice
Слайд 6Lake ice time series
Ice phenology
freezing date
breakup date
How to define?
Ice cover
properties
Ice thickness – max annual value
Ice concentration (large lakes)
Variability
independent winters
interannual
variability externally forced Aperiodic time series outcome
weak intra-seasonal connections
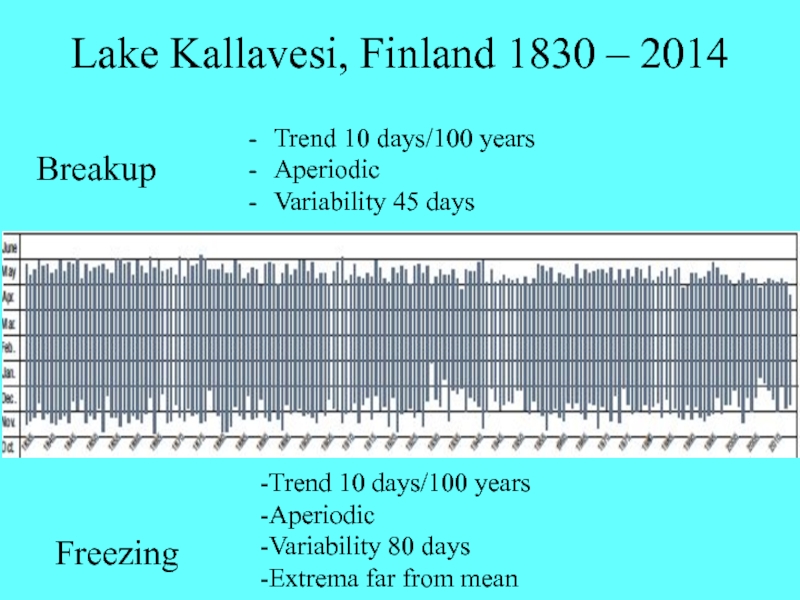
Слайд 7Lake Kallavesi, Finland 1830 – 2014
Trend 10 days/100 years
Aperiodic
Variability 80
days
Extrema far from mean
Trend 10 days/100 years
Aperiodic
Variability 45 days
Breakup
Freezing
Слайд 121st order: climate change impact
Freezing date
~ 5 day/°C
Ice thickness
5–10 cm/°C
Breakup
date
~ n days after zero
upcrossing of heating
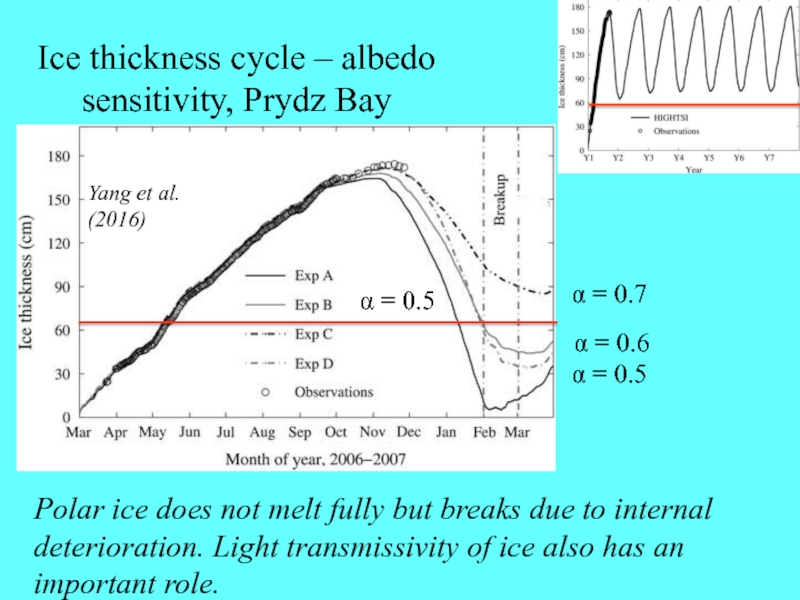
Слайд 14Ice thickness cycle – albedo sensitivity, Prydz Bay
a = 0.5
a
= 0.5
a = 0.7
a = 0.6
Polar ice does not melt
fully but breaks due to internal deterioration. Light transmissivity of ice also has an important role.Yang et al.
(2016)
Слайд 15Lake Ladoga: Finnish – Soviet – Russian data
1913 – 1937
Ice
charts and reports
1943 – 1992
Aircraft observations
Approx. twice a month
Plots
of ice distribution’1971 ->
NOAA and MODIS satellite images
On average 19 images /winter
Слайд 16Ice concentration A
A = relative area of ice in the
lake
Freezing depth: t = F(h)
Hypsographic curve = G(h)
Formally:
A(t) =
G[F-1(t)/max(h)Thus fall evolution of ice concentration is related on the hypsographic
curve. Also decrease of concentration depends on that as melting starts
From shallow parts. Wind and lake size add further modifications.
Слайд 19Summary: warming (?)
Freezing day delays
Max annual ice thickness likely
decreases
Ice quality (congelation ice/snow ice) ?
Period of stable ice cover
shortensTransient open water periods in smaller lakes than presently
Ice breakup date likely earlier
Слайд 20… consequences to water body
Shorter ice season
AND
More sunlight
More
transient open water periods
Improved oxygen level
How winter ecology will be
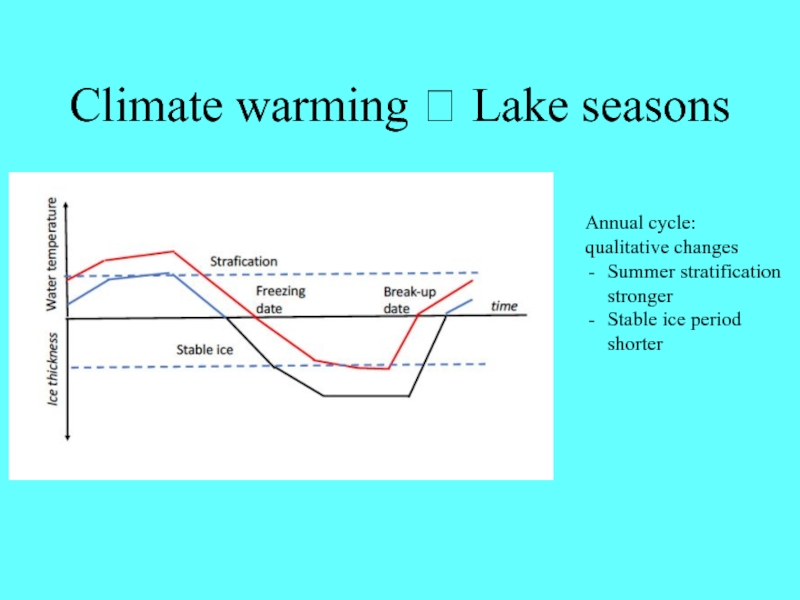
adapted?Слайд 21Climate warming Lake seasons
Annual cycle:
qualitative changes
Summer stratification stronger
Stable
ice period shorter
Слайд 22Lake ice and society: climate change impact
Lake ecology (+/- ?)
Traffic on-ice
Recreation: sport, fishing
ice-water bathing
Local weather changes
warmer surfaces
Open areas
may persist moisture fluxes, frazil ice
Snow is main question!
If the climate changes, not only the length of ice season and the thickness of ice change, but the quality of physics, ecology and practical life will be different.
Jacob Grimmer: Winter (1500s)