Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
GENERAL ECOLOGICAL CHARACTERITICS OF INDIAN POPULATION
Содержание
- 1. GENERAL ECOLOGICAL CHARACTERITICS OF INDIAN POPULATION
- 2. CONTENTSUNDERSTAND THE TERM POPULATION AND VARIOUS TYPES
- 3. POPULATIONa community of animals, plants, or humans
- 4. METHODS OF MEASURING POPULATION DENSITYTotal Counts:It is
- 5. POPULATION STUDY OF INDIA India is the second most
- 6. LINGUASTIC DEMOGRAPHY OF INDIA41.03% of the Indians
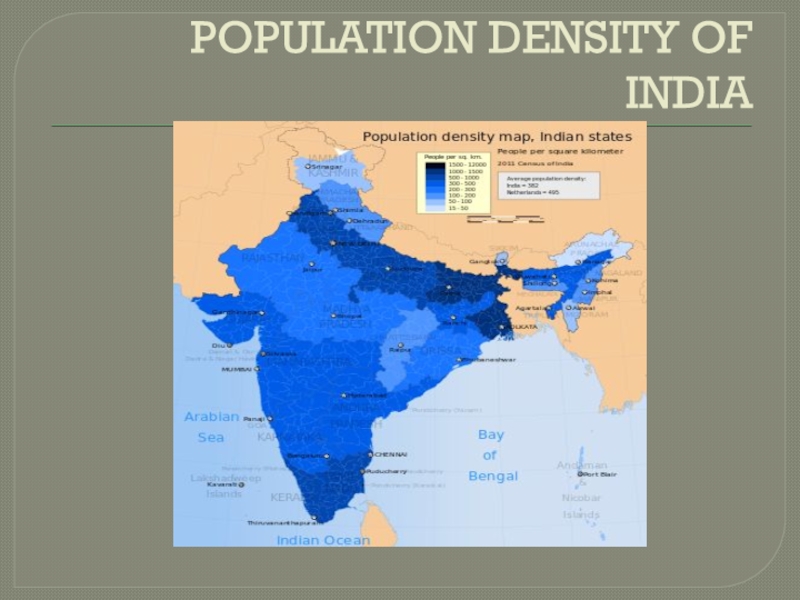
- 7. POPULATION DENSITY OF INDIA
- 8. ETHNIC GROUPS OF INDIA The national Census
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. BIRTH RATE AND DEATH RATE OF INDIA
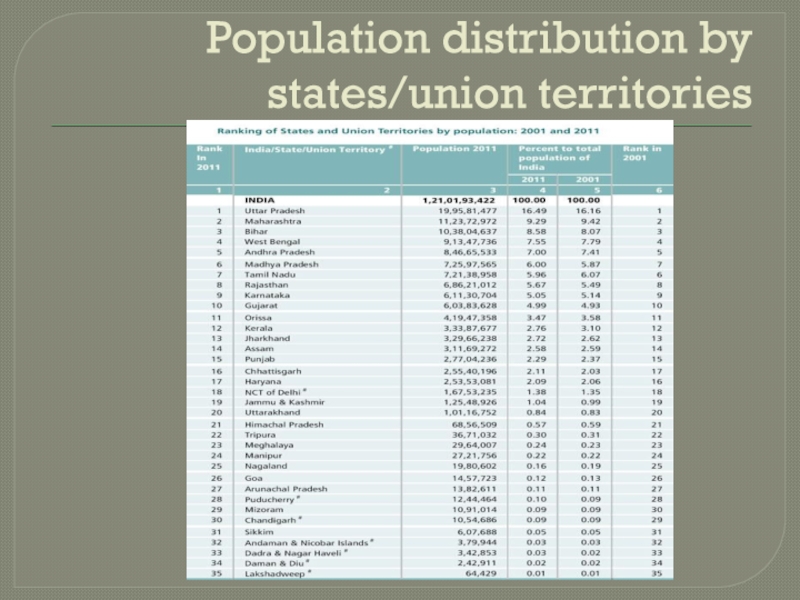
- 11. Population distribution by states/union territories
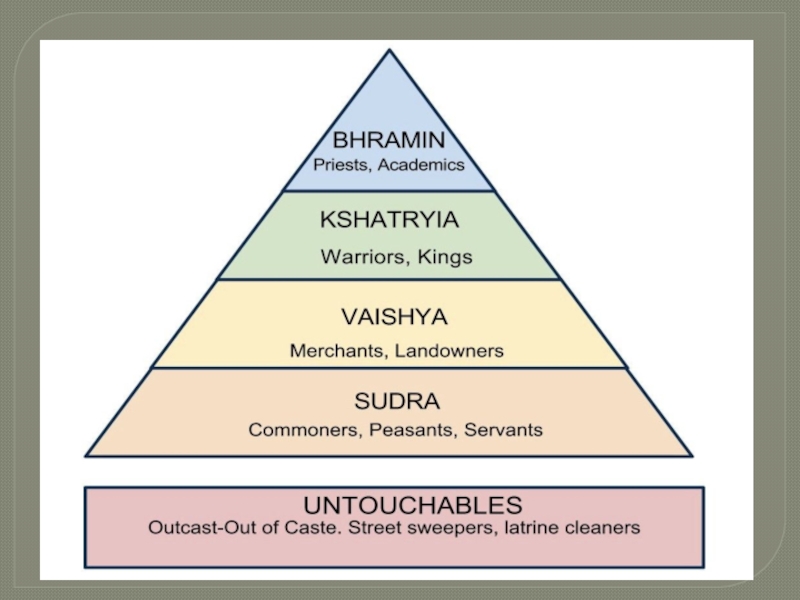
- 12. CASTE Caste and community statistics as recorded
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. AGE STRUCTUREAge structure:0–14 years: 27.34% (male 186,087,665/female 164,398,204)
- 15. OTHER CHARACTERISTICSPopulation growth rate :1.1% (2020 est)[102]Literacy rate74%
- 16. THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION
- 17. Скачать презентанцию
CONTENTSUNDERSTAND THE TERM POPULATION AND VARIOUS TYPES OF POPULATION IN NATUREPOPULATION DISTRIBUTION OF INDIA POPULATION SIZE OF INDIA HOW POPULATION IS DIVIDED IN INDIALINUASTICETHNICSTATE WISECASTE SYSTEM
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2CONTENTS
UNDERSTAND THE TERM POPULATION AND VARIOUS TYPES OF POPULATION IN
NATURE
POPULATION DISTRIBUTION OF INDIA
POPULATION SIZE OF INDIA
HOW POPULATION
IS DIVIDED IN INDIALINUASTIC
ETHNIC
STATE WISE
CASTE SYSTEM
Слайд 3POPULATION
a community of animals, plants, or humans among whose members
interbreeding occurs is called population
It is distingused into two types:
Monospecific
Population: Group of individual belong to the same speciesPolyspecific Population: Group of individual belong to different species
Population density: It is defined as number of individuals in relation to definite unit or space
Слайд 4METHODS OF MEASURING POPULATION DENSITY
Total Counts:It is the total counts
of all the organisms especially with large or conspicuous organisms
eg.census in human populationSampling methods : A small proportion of population is counted which is used to estimate the total population.It can be done by following way
Use of quadrate: Count all the individual of the several quadrate and extrapolate the average to the whole area.The shape and size of the quadrate vary with different organisms
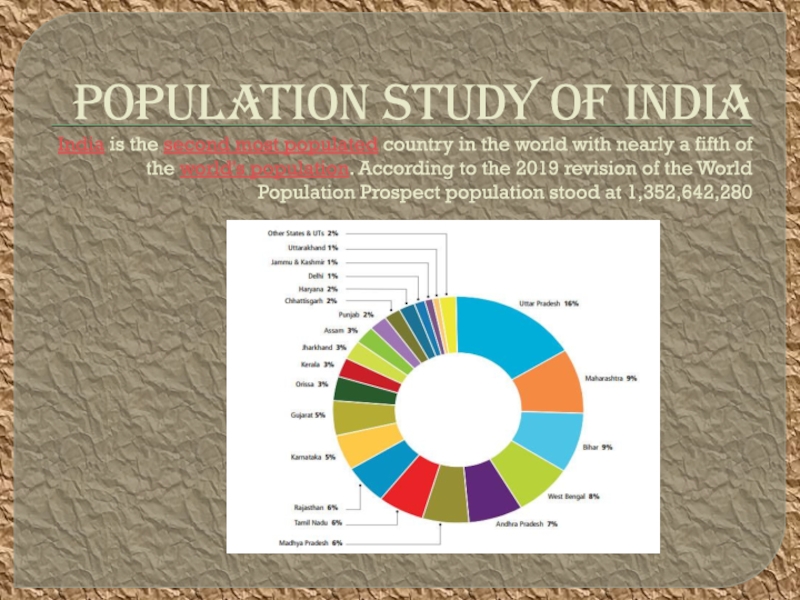
Слайд 5POPULATION STUDY OF INDIA India is the second most populated country in the world
with nearly a fifth of the world's population. According to the
2019 revision of the World Population Prospect population stood at 1,352,642,280Слайд 6LINGUASTIC DEMOGRAPHY OF INDIA
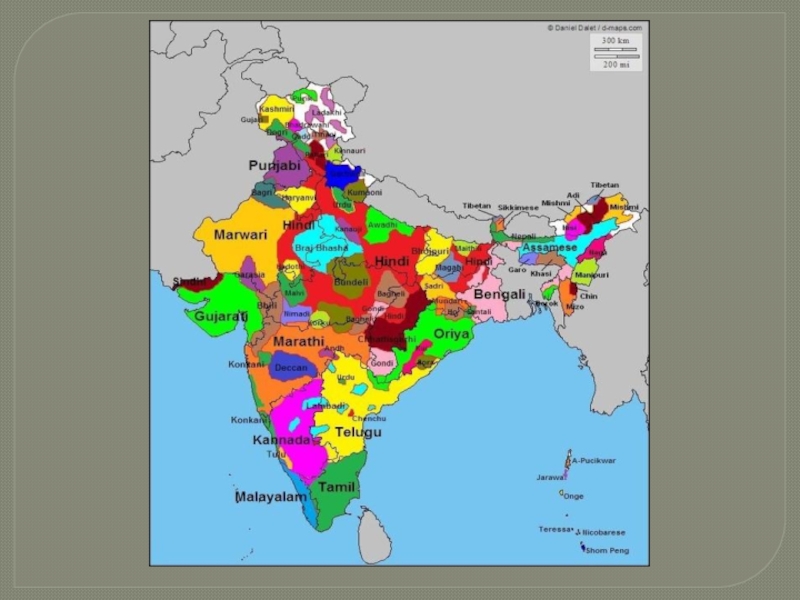
41.03% of the Indians speak Hindi while the rest
speak Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Maithili, Kannada, Malayalam, Marathi, Odia, Punjabi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu and a variety of other languages. There are a total
of 122 languages and 234 mother tongues. The 22 languages are Languages specified in the Eighth Schedule of Indian Constitution and 100 non-specified languages.Слайд 8ETHNIC GROUPS OF INDIA
The national Census of India does
not recognise racial or ethnic groups within India,[120] but recognises many of the
tribal groups as Scheduled Castes and Tribes (see list of Scheduled Tribes in India).According to a 2009 study published by Reich et al., the modern Indian population is composed of two genetically divergent and heterogeneous populations which mixed in ancient times (about 1,200–3,500 BP), known as Ancestral North Indians (ANI) and Ancestral South Indians (ASI). ASI corresponds to the Dravidian-speaking population of southern India, whereas ANI corresponds to the Indo-Aryan-speaking population of northern India
700,000 people from the United States live in India.
Between 300,000 and 1 million Anglo-Indians live in India.
Слайд 12CASTE
Caste and community statistics as recorded from "Socially and
Educationally Backward Classes Commission" (SEBC) or Mandal Commission of 1979.
This was completed in 1983.there has not yet been a proper consensus on contemporary figures
The caste system divides Hindus into four main categories - Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas and the Shudras.
Many believe that the groups originated from Brahma, the Hindu God of creation.
For centuries, caste has dictated almost every aspect of Hindu religious and social life, with each group occupying a specific place in this complex hierarchy.
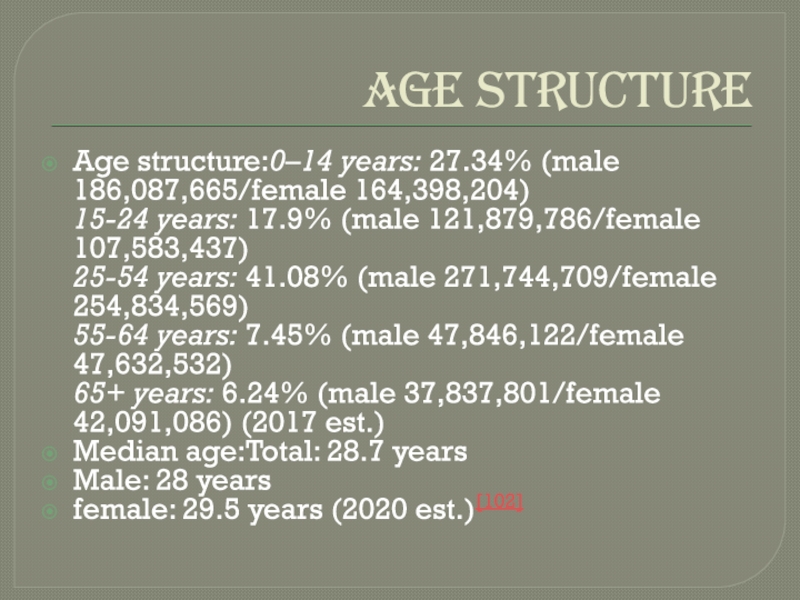
Слайд 14AGE STRUCTURE
Age structure:0–14 years: 27.34% (male 186,087,665/female 164,398,204)
15-24 years: 17.9% (male 121,879,786/female
107,583,437) 25-54 years: 41.08% (male 271,744,709/female 254,834,569) 55-64 years: 7.45% (male 47,846,122/female 47,632,532) 65+ years: 6.24%
(male 37,837,801/female 42,091,086) (2017 est.)Median age:Total: 28.7 years
Male: 28 years
female: 29.5 years (2020 est.)[102]
Слайд 15OTHER CHARACTERISTICS
Population growth rate :1.1% (2020 est)[102]
Literacy rate74% (age 7 and
above, in 2011)[103]
81.4% (total population, age 15–25, in 2006)[104]
Per cent
of population below poverty line:22% (2006 est.)Unemployment rate:7.8%





![GENERAL ECOLOGICAL CHARACTERITICS OF INDIAN POPULATION ETHNIC GROUPS OF INDIA The national Census of India does not ETHNIC GROUPS OF INDIA The national Census of India does not recognise racial or ethnic groups within India,[120] but recognises](/img/tmb/7/614653/92bf3622c4d1132ab395d856af0920d4-800x.jpg)


![GENERAL ECOLOGICAL CHARACTERITICS OF INDIAN POPULATION OTHER CHARACTERISTICSPopulation growth rate :1.1% (2020 est)[102]Literacy rate74% (age 7 and above, OTHER CHARACTERISTICSPopulation growth rate :1.1% (2020 est)[102]Literacy rate74% (age 7 and above, in 2011)[103] 81.4% (total population, age](/img/tmb/7/614653/51f016596d03687d5dfc7ae070aa7444-800x.jpg)