Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Hematologic changes of pregnancy
Содержание
- 1. Hematologic changes of pregnancy
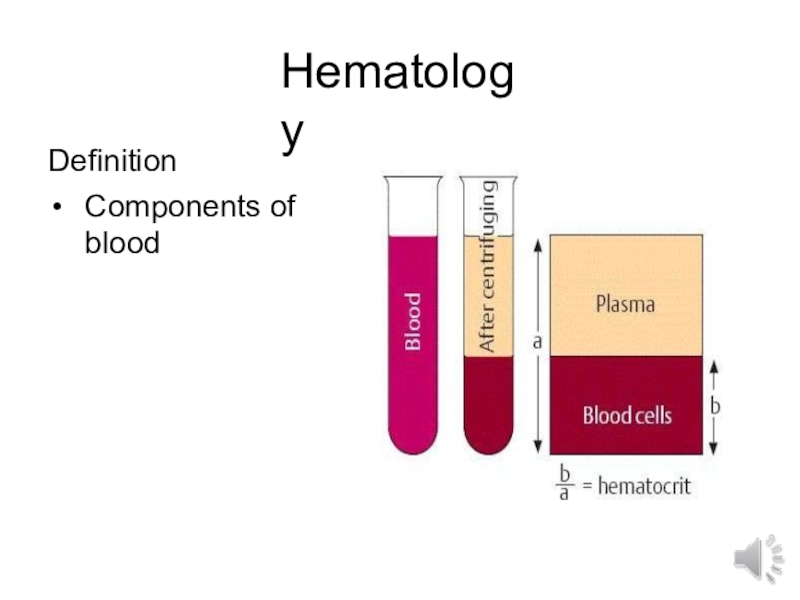
- 2. HematologyDefinitionComponents of blood
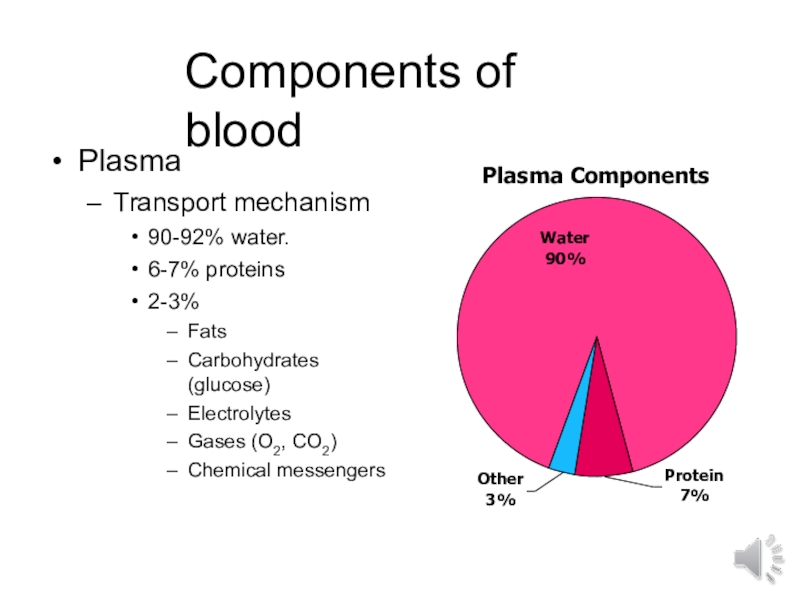
- 3. Components of bloodPlasmaTransport mechanism90-92% water.6-7% proteins2-3%FatsCarbohydrates (glucose)ElectrolytesGases (O2, CO2)Chemical messengersPlasma ComponentsOther 3%Protein 7%Water 90%
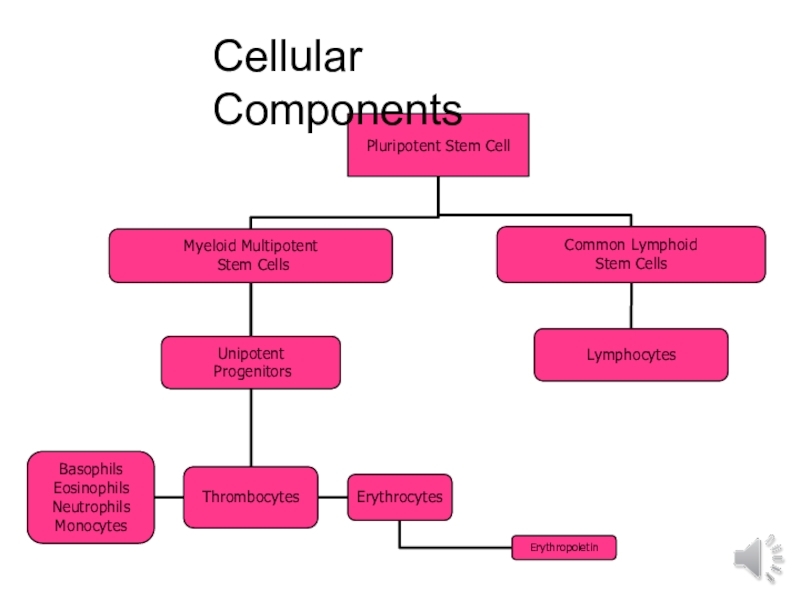
- 4. Pluripotent Stem CellMyeloid MultipotentStem CellsCommon Lymphoid Stem CellsUnipotent ProgenitorsBasophils Eosinophils Neutrophils MonocytesLymphocytesErythrocytesThrombocytesErythropoietinCellular Components
- 5. Platelets (Thrombocytes)MegakaryocytesThrombopoietinThrombocytopeniaThrombocytosis
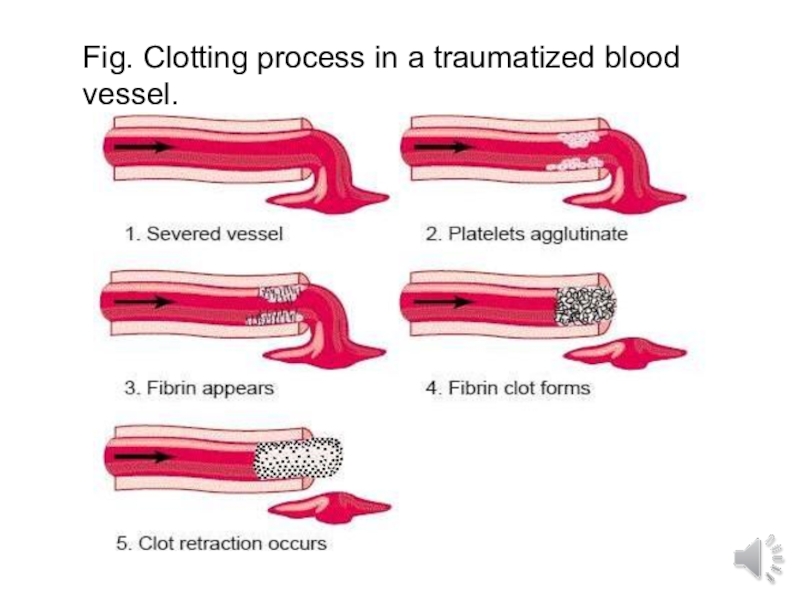
- 6. Fig. Clotting process in a traumatized blood vessel.
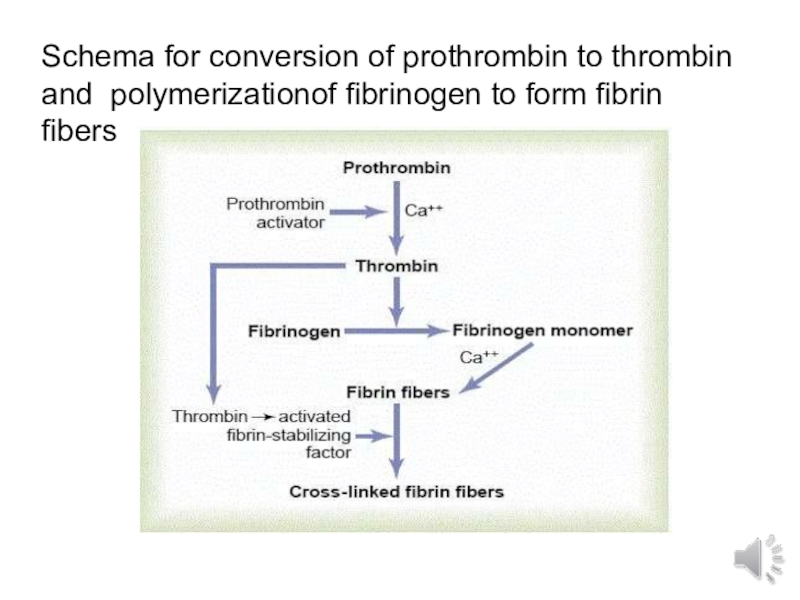
- 7. Schema for conversion of prothrombin to thrombin and polymerizationof fibrinogen to form fibrin fibers
- 8. Pregnancy changesThe Most significant changes are:Physiologic anemiaNeutrophiliaMild thrombocytopeniaIncreased procoagulant factorsDiminished fibrinolysis
- 9. Plasma volumeIncreased by 10 to 15 %Total
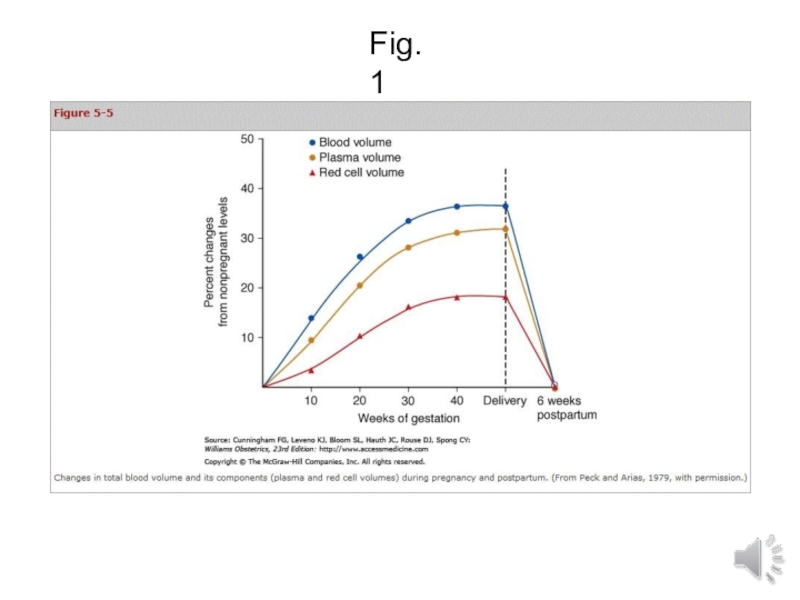
- 10. Fig.1
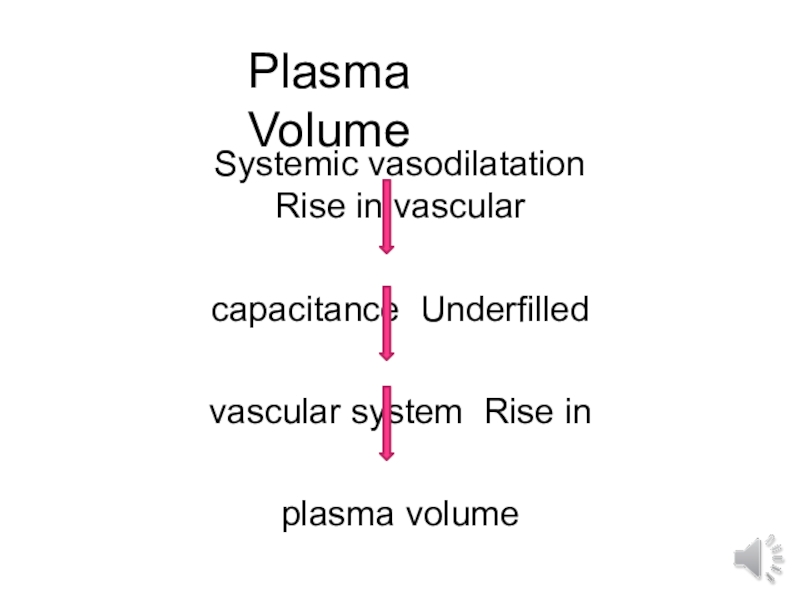
- 11. Plasma VolumeSystemic vasodilatationRise in vascular capacitance Underfilled vascular system Rise in plasma volume
- 12. Pregnancy-induced hypervolemia has important functions:To meet the
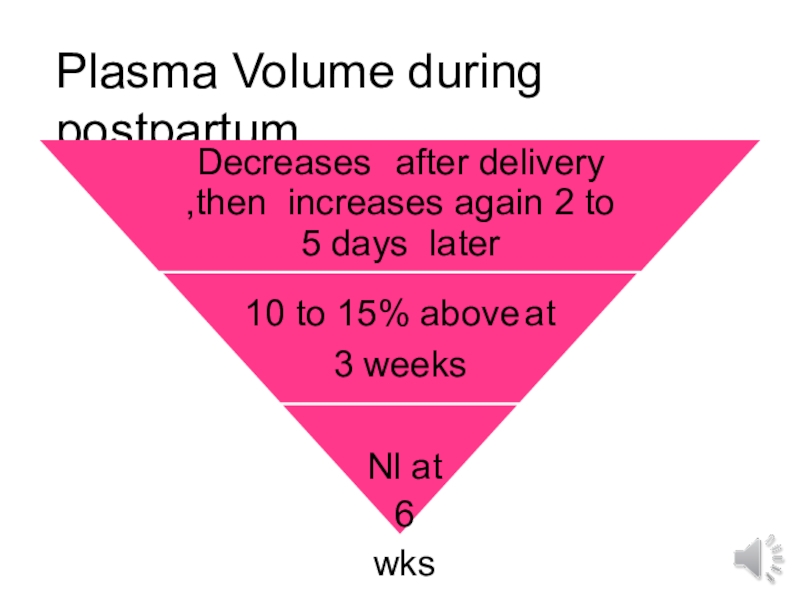
- 13. Plasma Volume during postpartumDecreases after delivery ,then increases
- 14. RED BLOOD CELLS 20 to 30% (250 to
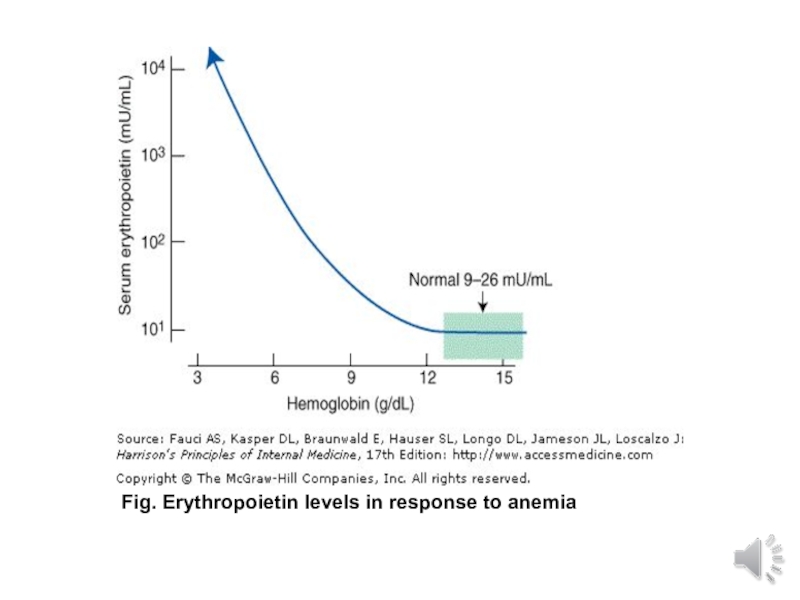
- 15. Fig. Erythropoietin levels in response to anemia
- 16. physiological or dilutional anemia of pregnancyObserved in
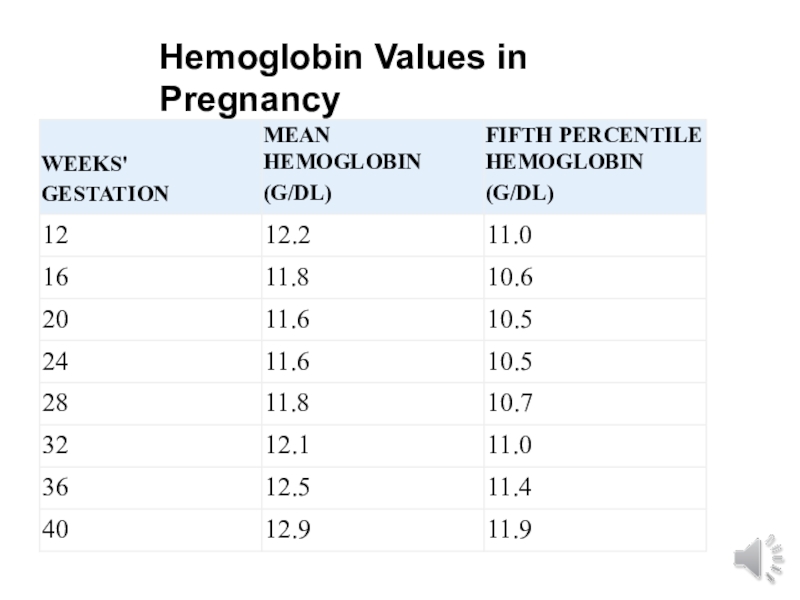
- 17. Hemoglobin Values in Pregnancy
- 18. PLATELET COUNTMean PLT slightly lower than healthy non pregnant womandue to the effects of hemodilutionincreased platelet consumption
- 19. Thrombocytopeniamost significant obstetrical consideration concerning platelet physiology
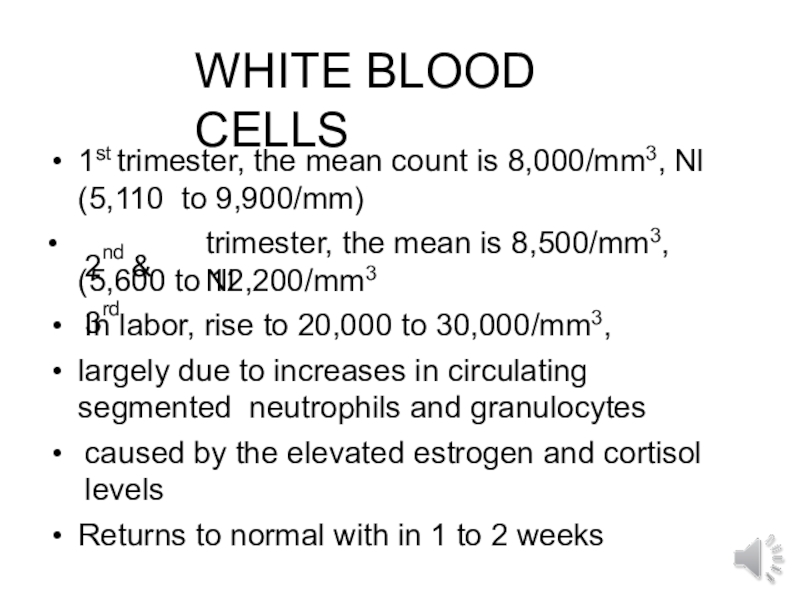
- 20. WHITE BLOOD CELLS1st trimester, the mean count
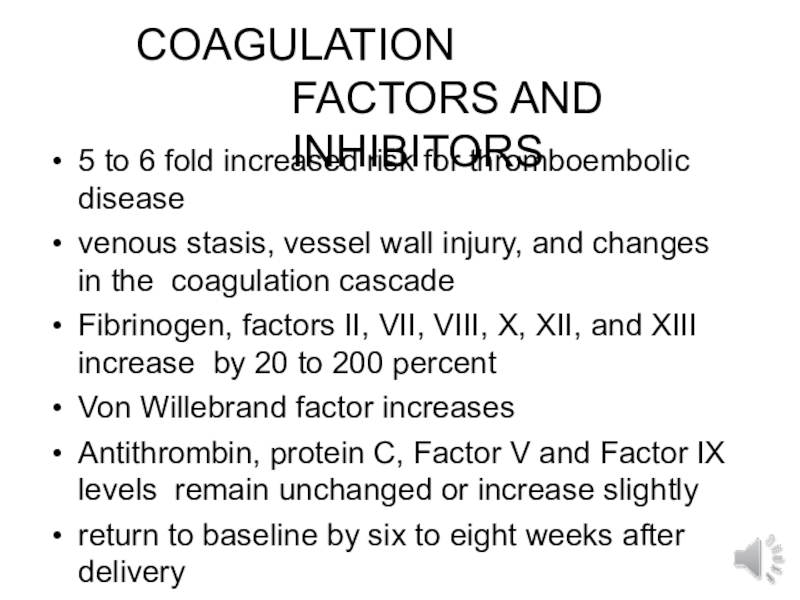
- 21. COAGULATION FACTORS AND INHIBITORS5 to 6 fold
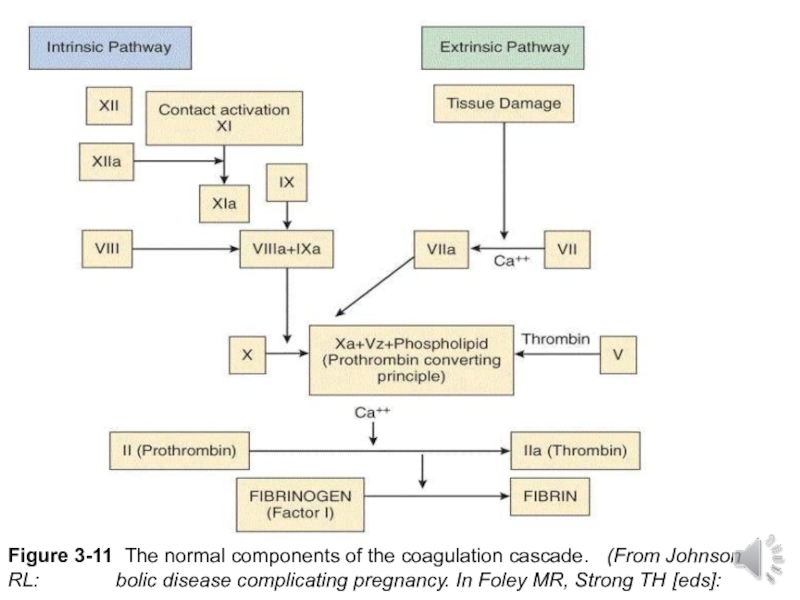
- 22. Figure 3-11 The normal components of the
- 23. Key pointsMaternal plasma volume increases 50 percent
- 24. References:Guyton and Hall ,Text book of medical
- 25. Скачать презентанцию
HematologyDefinitionComponents of blood
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3Components of blood
Plasma
Transport mechanism
90-92% water.
6-7% proteins
2-3%
Fats
Carbohydrates (glucose)
Electrolytes
Gases (O2, CO2)
Chemical messengers
Plasma
Components
Слайд 4
Pluripotent Stem Cell
Myeloid Multipotent
Stem Cells
Common Lymphoid Stem Cells
Unipotent Progenitors
Basophils Eosinophils
Neutrophils Monocytes
Lymphocytes
Erythrocytes
Thrombocytes
Erythropoietin
Cellular Components
Слайд 7Schema for conversion of prothrombin to thrombin and polymerizationof fibrinogen
to form fibrin fibers
Слайд 8Pregnancy changes
The Most significant changes are:
Physiologic anemia
Neutrophilia
Mild thrombocytopenia
Increased procoagulant factors
Diminished
fibrinolysis
Слайд 9Plasma volume
Increased by 10 to 15 %
Total gain at term
averages 1100 to 1600ml Total volume 4700ml to 5200ml ,
i.e.
30 to 50% above non pregnant , Fig.1Слайд 11Plasma Volume
Systemic vasodilatation
Rise in vascular capacitance Underfilled vascular system Rise
in plasma volume
Слайд 12Pregnancy-induced hypervolemia has important functions:
To meet the metabolic demands of
the enlarged uterus & hypertrophied vascular system.
To provide an abundance
of nutrients and elements to support the rapidly growing placenta and fetus.To protect the mother and in turn the fetus, against the deleterious effects of impaired venous return in the supine and erect positions.
To safeguard the mother against the adverse effects of blood loss associated with parturition.
Слайд 13Plasma Volume during postpartum
Decreases after delivery ,then increases again 2 to
5 days later
10 to 15% above at
3 weeks
Nl at 6 wks
Слайд 14RED BLOOD CELLS
20 to 30% (250 to 450 mL) above
nonpregnant iron supplemented
15 to 20% above nonpregnant not on iron supplement
Life
span slightly decreasedErythropoietin levels increase by 50 %
Слайд 16physiological or dilutional anemia of pregnancy
Observed in healthy pregnant woman
Greatest
during late 2nd to early 3rd trimester lowest Hgb at
28 to 36wksNearer to term Hgb increases
Anemia cut off point: <11 g/dL 1st and 3rd trimesters and < 10.5 g/dL 2nd trimester, for black Americans 0.8g/dl less
Слайд 18PLATELET COUNT
Mean PLT slightly lower than healthy non pregnant woman
due to
the effects of hemodilution
increased platelet consumption
Слайд 19Thrombocytopenia
most significant obstetrical consideration concerning platelet physiology in pregnancy
Gestational or
incidental thrombocytopenia is characterized :
mild asymptomatic
occurring in the third trimester
without
any historynot associated with maternal, fetal, or neonatal sequelae and
spontaneously resolves postpartum
Platelet counts are typically >70,000/microL, with
about two-thirds being 130,000 to 150,000 microL
Слайд 20WHITE BLOOD CELLS
1st trimester, the mean count is 8,000/mm3, Nl
(5,110 to 9,900/mm)
•
2nd & 3rd
trimester, the mean is 8,500/mm3, Nl
(5,600
to 12,200/mm3In labor, rise to 20,000 to 30,000/mm3,
largely due to increases in circulating segmented neutrophils and granulocytes
caused by the elevated estrogen and cortisol levels
Returns to normal with in 1 to 2 weeks
Слайд 21COAGULATION FACTORS AND INHIBITORS
5 to 6 fold increased risk for
thromboembolic disease
venous stasis, vessel wall injury, and changes in the
coagulation cascadeFibrinogen, factors II, VII, VIII, X, XII, and XIII increase by 20 to 200 percent
Von Willebrand factor increases
Antithrombin, protein C, Factor V and Factor IX levels remain unchanged or increase slightly
return to baseline by six to eight weeks after delivery
Слайд 22Figure 3-11 The normal components of the coagulation cascade. (From Johnson
RL:
bolic disease complicating pregnancy. In Foley MR, Strong TH [eds]:
Слайд 23Key points
Maternal plasma volume increases 50 percent during pregnancy
RBC volume
increases approximately 18 to 30 percent
hematocrit normally decreases during gestation
but not below 30 percentPregnancy is a hypercoagulable state increases in the levels of the platelets
majority of the procoagulant factors increase and
fibrinolytic system decreases and in some of the natural inhibitors of coagulation
Слайд 24References:
Guyton and Hall ,Text book of medical physiology , 11th
edition
Williams Obstetrics,Cunningham, Leveno, Bloom, Hauth, Rouse, Spong, 23rd edition
Obstetrics normal
and problem pregnancies, Steven G. Gabbe,Jennifer R.Niebyl, Joe leigh simpson, 5th EditionTHANK YOU