Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Informatics Class 3
Содержание
- 1. Informatics Class 3
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. Strategic Information System Gain Competitive AdvantageAn advantage
- 4. Strategic Information System ContinuedThe goals, processes, products,
- 5. Strategic ManagementSWOT AnalysisProduct Life CycleQuality Preference…Strategic management
- 6. Information Technology – Supports Strategic ManagementInnovative applications:
- 7. Information Technology – Supports Strategic Management (Continued)Cost
- 8. Competitive IntelligenceInformation-gathering drives business performance by increasing
- 9. Porter’s Competitive Forces ModelThe threat of entry
- 10. Competitive ForcesPorter’s Competitive Forces Model
- 11. We develop a Competitor AnalysisFirst Competitive ForceWhat
- 12. Second Competitive ForceWe Analyze the Entry BarriersIf
- 13. We Analyze the Substitute ProductsThird Competitive ForceProducts
- 14. We Analyze the Supply ChainFourth & Fifth
- 15. Generic Strategies – Developing a Sustained Competitive
- 16. Generic Strategies – Developing a Sustained Competitive
- 17. Generic Strategies – Developing a Sustained Competitive
- 18. The Value ChainAccording to the value chain
- 19. The Value Chain (Continued)Unlike the primary activities,
- 20. The Value Chain (Continued)Secondary ActivitiesPrimary ActivitiesValue
- 21. The Value Chain ( Air carrier)Secondary ActivitiesPrimary ActivitiesValue
- 22. The Value Chain (Continued)InternalE-BillingE-Payments
- 23. The Value SystemA firm’s value chain is
- 24. Global CompetitionMany companies are operating in a
- 25. Sustaining a Strategic Information System (SIS)Strategic information
- 26. You questions ?
- 27. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2 Objectives
Describe strategic
information systems (SISs) and explain their advantages.
Describe Porter’s competitive forces
model and how information technology helps companies improve their competitive positions.Describe 12 strategies companies can use to achieve competitive advantage in their industry.
Describe Porter’s value chain model and its relationship to information technology.
Describe representative SISs and the advantage they provide to organizations.
Discuss the challenges associated with sustaining competitive advantage.
Слайд 3Strategic Information System
Gain Competitive Advantage
An advantage over competitors in
some measure such as cost, quality, or speed
A difference in
the Value Chain DataImproving Core Competency(reduce disadvantage)
Employee productivity
Operational efficiency
Any information system--EIS, OIS, TPS, KMS-- that changes the goals, processes, products, or environmental relationships to help an organization gain a competitive advantage or reduce a competitive disadvantage.
Слайд 4Strategic Information System Continued
The goals, processes, products, or environmental relationships
that help an organization gain a competitive advantage or reduce
a competitive disadvantage.Слайд 5Strategic Management
SWOT Analysis
Product Life Cycle
Quality Preference
…
Strategic management is the way
an organization maps or crafts the strategy of its future
operations.Слайд 6Information Technology – Supports Strategic Management
Innovative applications: Create innovative applications
that provide direct strategic advantage to organizations.
Competitive weapons: Information systems
themselves are recognized as a competitive weaponChanges in processes: IT supports changes in business processes that translate to strategic advantage
Links with business partners: IT links a company with its business partners effectively and efficiently.
Слайд 7Information Technology – Supports Strategic Management (Continued)
Cost reductions: IT enables
companies to reduce costs.
Relationships with suppliers and customers: IT can
be used to lock in suppliers and customers, or to build in switching costs.New products: A firm can leverage its investment in IT to create new products that are in demand in the marketplace.
Competitive intelligence: IT provides competitive (business) intelligence by collecting and analyzing information about products, markets, competitors, and environmental changes .
Слайд 8Competitive Intelligence
Information-gathering drives business performance
by increasing market knowledge
improving
knowledge management
raising the quality of strategic planning
One of the
most important aspects in developing a competitive advantage is to acquire information on the activities and actions of competitors.However once the data has been gathered it must be processed into information and subsequently business intelligence. Porters 5 Forces is a well-known framework that aids in this analysis.
Слайд 9Porter’s Competitive Forces Model
The threat of entry of new competitors
The
bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of customers (buyers)
The threat
of substitute products or servicesThe competition among existing firms in the industry
The model recognizes five major forces that could enlarge a company’s position in a given industry.
External Competitive Forces
Слайд 11We develop a Competitor Analysis
First Competitive Force
What Drives them?
What are
they Doing and can do?
What are their strengths & weaknesses?
Is
competition intense?Слайд 12Second Competitive Force
We Analyze the Entry Barriers
If nothing slows entry
of competitors competition will become intense.
Incumbent Reaction?
What Actions are required
to build market share?Production Process?
Слайд 13We Analyze the Substitute Products
Third Competitive Force
Products or services from
another industry enter the market
Customers becoming acclimated to using substitutes
Is
the substitute market growing?Слайд 14We Analyze the Supply Chain
Fourth & Fifth Competitive Forces
Who controls
the transaction?
Each element adds value – question who captures it?
The
SuppliersThe Buyers
Слайд 15Generic Strategies – Developing a Sustained Competitive Advantage
Analyzing the forces
that influence a company’s competitive position will assist management in
crafting a strategy aimed at establishing a sustained competitive advantage. To establish such a position, a company needs to develop a strategy of performing activities differently than a competitor.Cost leadership strategy: Produce products and/or services at the lowest cost in the industry.
Differentiation strategy: Offer different products, services, or product features.
Niche strategy: Select a narrow-scope segment (niche market) and be the best in quality, speed, or cost in that market.
Слайд 16Generic Strategies – Developing a Sustained Competitive Advantage (Continued)
Growth strategy:
Increase market share, acquire more customers, or sell more products.
Alliance strategy: Work with business partners in partnerships, alliances, joint ventures, or virtual companies.
Innovation strategy: Introduce new products and services, put new features in existing products and services, or develop new ways to produce them.
Operational effectiveness strategy: Improve the manner in which internal business processes are executed so that a firm performs similar activities better than rivals.
Слайд 17Generic Strategies – Developing a Sustained Competitive Advantage (Continued)
Customer-orientation strategy:
Concentrate on making customers happy
Time strategy: Treat time as a
resource, then manage it and use it to the firm’s advantage.Entry-barriers strategy: Create barriers to entry.
Lock in customers or suppliers strategy: Encourage customers or suppliers to stay with you rather than going to competitors.
Increase switching costs strategy: Discourage customers or suppliers from going to competitors for economic reasons.
Our goal is to perform activities differently than a competitor. Those activities can be linked in a Value Chain Model.
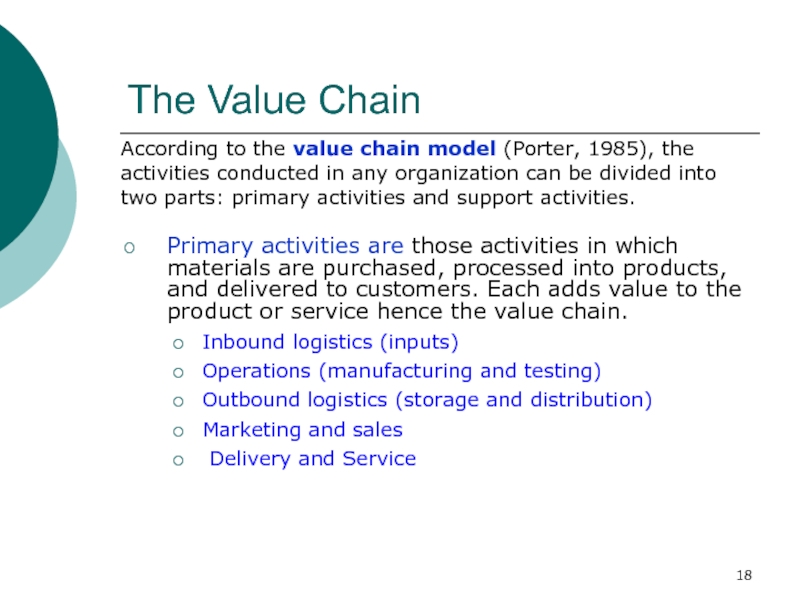
Слайд 18The Value Chain
According to the value chain model (Porter, 1985),
the activities conducted in any organization can be divided into
two parts: primary activities and support activities.Primary activities are those activities in which materials are purchased, processed into products, and delivered to customers. Each adds value to the product or service hence the value chain.
Inbound logistics (inputs)
Operations (manufacturing and testing)
Outbound logistics (storage and distribution)
Marketing and sales
Delivery and Service
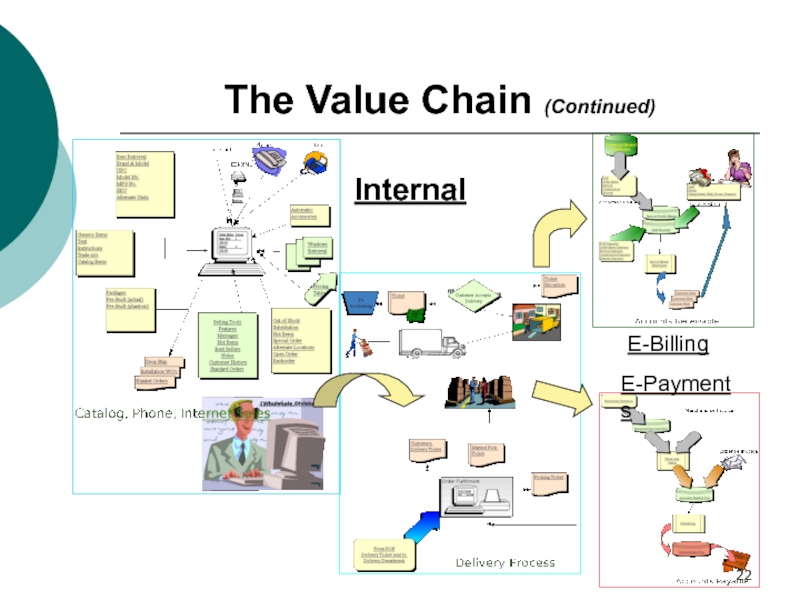
Слайд 19The Value Chain (Continued)
Unlike the primary activities, which directly add
value to the product or service, the support activities are
operations that support the creation of value (primary activities)The firm’s infrastructure (accounting, finance, management)
Human resources management
Technology development (R&D)
Procurement
The initial purpose of the value chain model was to analyze the internal operations of a corporation, in order to increase its efficiency, effectiveness, and competitiveness. We can extend that company analysis, by systematically evaluating a company’s key processes and core competencies to eliminate any activities that do not add value to the product.
Слайд 23The Value System
A firm’s value chain is part of a
larger stream of activities, which Porter calls a value system.
A value system includes the suppliers that provide the inputs necessary to the firm and their value chains. This also is the basis for the supply chain management concept. Many of these alliances and business partnerships are based on Internet connectivityare called interorganizational information systems (IOSs)
These Internet-based EDI systems offer strategic benefits
Faster business cycle
Automation of business procedures
Reduced operational costs
Greater advantage in a aggressive competitive environment
Слайд 24Global Competition
Many companies are operating in a global environment. Doing
business in this environment is becoming more challenging as the
political environment improves and as telecommunications and the Internet open the door to a large number of buyers, sellers, and competitors worldwide. This increased competition is forcing companies to look for better ways to compete globally.Global dimensions along which management can globalize
Product
Markets & Placement
Promotion
Where value is added to the product
Competitive strategy
Use of non-home-country personnel - labor
Multidomestic Strategy: Zero standardization along the global dimensions. Global Strategy: Complete standardization along the global dimensions.
Слайд 25Sustaining a Strategic Information System (SIS)
Strategic information systems are designed
to establish a profitable and sustainable position against the competitive
forces in an industry. Due to advances in systems development it has become increasingly difficult to sustain an advantage for an extended period. Experience also indicates that information systems, by themselves, can rarely provide a sustainable competitive advantage. Therefore, the major problem that companies now face is how to sustain their competitive advantage.One popular approach is to use inward systems that are not visible to competitors. These proprietary systems allow the company to perform the activities on their value chain differently than their competitors.