Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Information and communication technologies
Содержание
- 1. Information and communication technologies
- 2. Name of discipline: «Information and communication technologies»
- 3. Subject: 1. Основные направления развития ИКТ. Стандартизация
- 4. LITERATURE1 Main literature1.1 June J. Parsons, New
- 5. Lecture 1. ICT in Core Sectors of Development. ICT Standardization
- 6. Definition of ICT. Subject ICT and its
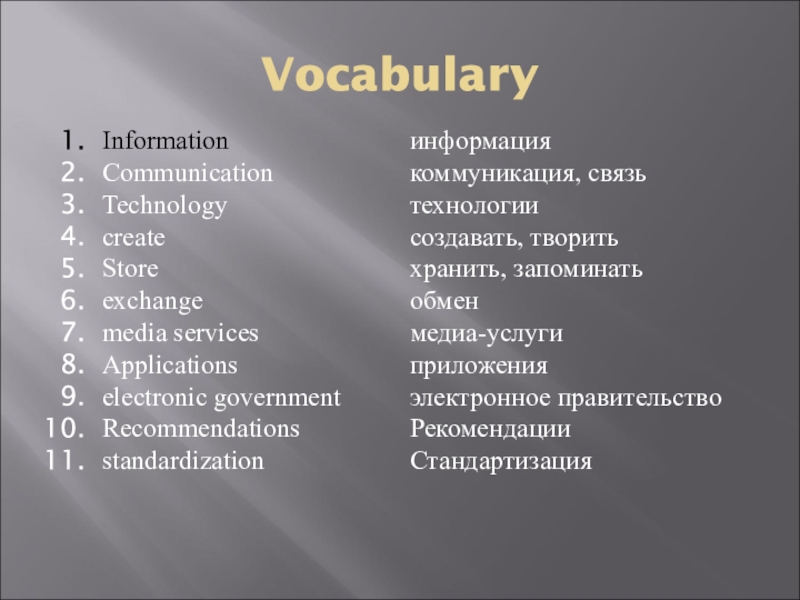
- 7. Vocabulary
- 8. 1. Definition of ICTICT is an acronym
- 9. INFORMATION Information refers to the knowledge obtained
- 10. 2. Main directions of development of ICTICT
- 11. 3. Standardization in ICT. ICT and program
- 12. 3. Standardization in ICTThe Study Groups of ITU’s Telecommunication
- 13. Recommendations are standards that define how telecommunication
- 14. ETSI – the European Telecommunications Standards InstituteCEN
- 15. ICT and program of the UN of the Sustainable Development of the Millennium (SDG)
- 16. Sustainable Development GoalsGoal 1: Eradicate extreme poverty
- 17. Goals
- 18. The role of ICT in the UN
- 19. ICTs have incredible potential to improve development
- 20. Скачать презентанцию
Name of discipline: «Information and communication technologies» Number of credits 3 (1+1+1) Lecture 15 Practical lessons 15 Laboratory work 15 Examination Test
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1«Information and communication technologies»
«Информационно-коммуникационные технологии» на английском
Слайд 2Name of discipline: «Information and communication technologies» Number of credits 3
(1+1+1)
Lecture 15
Practical lessons 15
Laboratory work 15
Examination Test
Слайд 3Subject:
1. Основные направления развития ИКТ. Стандартизация в ИКТ (ICT
in Core Sectors of Development. ICT Standardization)
2. Введение в компьютерные
системы. Архитектура компьютерных систем. (Introduction to computer systems. Architecture of computer systems)3. Операционные системы и программное обеспечение (Computer Software. Operating systems. Desktop applications)
4. Человеко-компьютерное взаимодействие (Human-computer interaction)
5. Базы данных (Databases)
6. Анализ и управление данными (Data Analysis and Data Management)
7. Сети и телекоммуникация (Networking and telecommunications)
8. Кибербезопасность, этика и доверие (Cyber Security, Ethics and Trust)
9. Интернет технологии (Internet Technology)
10. Облачные и мобильные технологии (Cloud and Mobile technology)
11. Мультимедийные технологии (Multimedia technologies
12. Smart технологии (Smart technology)
13. E-технологии. E-бизнес. E-образование. Социальные сети. E-правительство. (E-technology. E-business. E-Learning. Social networks. E-gov.)
14. Информационные технологии в профессиональной сфере. Промышленные ИКТ. (IT in professional sphere. Industrial ICT.)
15. Перспективы развития ИКТ (Perspectives of ICT development)
Слайд 4LITERATURE
1 Main literature
1.1 June J. Parsons, New Perspectives on Computer
Concepts 18th Edition—Comprehensive, Thomson Course Technology, a division of Thomson
Learning, Inc Cambridge, MA, COPYRIGHT © 2016; ISBN-10: 1-4239-0610-1, ISBN-13: 978-1-4239-0610-0.1.2 Reema Thareja Fundamentals of Computers. – Oxford University press: Oxford, 2014. - 288p
1.3 George Beekman. Computer Confluence: Exploring Tomorrow's Technology. ISBN 0130661880, 9780130661883. Prentice Hall, 2003
1.4 Симонович С.В. и др. Информатика. Базовый курс: учебное пособие для высших технических учебных заведений. – СПб.: Питер, 2011. – 639 с.
2 Additional literature
2.1 Thomas M. Connolly, et al. Database Systems: A practical approach to Design, Implementation, and Management. 4th Edition ISBN: 0321210255 Addison-Wesley, 2004
2.2 H. L. Capron. Computers: Tools for an Information Age. Addison-Wesley, 1998.
2.3 Roqers Y., H. Sharp, J. Preece. Interaction design beyond human - computer interaction - Third Edition.- Italy: WILEY & Sons Ltd, 2011.- 585 р.
2.4 Ducket, J. Beginning Web Programming with HTML, XHTML, and CSS: 2th ed. / Jon Ducket.- U.S.A: Wiley Publishing. Inc, 2008.- 739с. ISBN 978-1-0-470-25931-3.
2.5 Stephen P Borgatti, Martin G. Everett, Jeffrey C. Johnson Analyzing Social Networks Paperback, 2013
2.6 Уша Рани Вьясулу Редди. Серия учебников по ИКТР для молодежи. Учебник 1: Введение в ИКТ для развития. UN-APCICT/ESCAP 2011
2.7 Дейтел Х. М., Дейтел П. Дж., Чофнес Д. Р. Операционные системы. Часть 1. Основы и принципы. – М.: Бином-Пресс, 2011. – 677 c.
2.8 Ярочкин В.И. Информационная безопасность: Учебник для вузов. – М.: Акад. Проект, 2008. – 544 c.
2.9 Голицына О.Л. Базы данных: Учебное пособие. – М.: Форум, 2012. – 400 c.
2.10 Keith Worden, W.A. Bullough, J. Haywood. Smart Technologies. World Scientific Pub Co Inc (April 14, 2003)
Слайд 6Definition of ICT. Subject ICT and its purposes
Main directions
of development of ICT
Standardization in ICT. ICT and program of
the UN of the Sustainable Development of the Millennium (SDG)Слайд 81. Definition of ICT
ICT is an acronym that stands for Information
Communications Technology
ICT is the technology required for information processing, in
particular, the use of electronic computers, communication devices and software applications to convert, store, protect, process, transmit and retrieve information from anywhere, anytime. Слайд 9INFORMATION Information refers to the knowledge obtained from reading, investigation,
study or research. The tools to transmit information are the
telephone, television and radio. Information is knowledge and helps us to fulfill our daily tasks.COMMUNICATION Communication is an act of transmitting messages. It is a process whereby information is exchanged between individuals using symbols, signs or verbal interactions. Communication is important in order to gain knowledge.
TECHNOLOGY Technology is the use of scientific knowledge, experience and resources to create processes products that fulfill human needs.
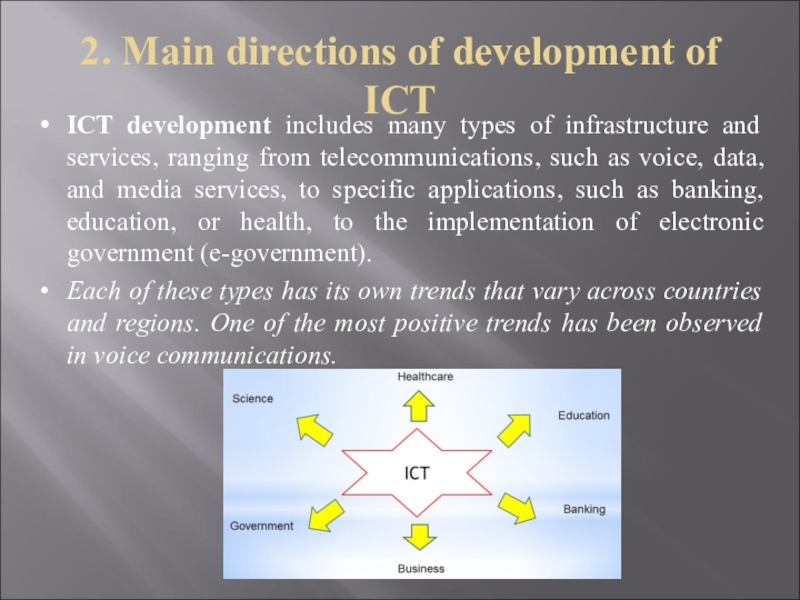
Слайд 102. Main directions of development of ICT
ICT development includes many
types of infrastructure and services, ranging from telecommunications, such as
voice, data, and media services, to specific applications, such as banking, education, or health, to the implementation of electronic government (e-government).Each of these types has its own trends that vary across countries and regions. One of the most positive trends has been observed in voice communications.
Слайд 113. Standardization in ICT. ICT and program of the UN of
the Sustainable Development of the Millennium (SDG)
ICT standardisation is the
voluntary cooperation for the development of technical specifications that outlines the agreed properties for a particular product, service, or procedure.Слайд 123. Standardization in ICT
The Study Groups of ITU’s Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T)
assemble experts from around the world to develop international standards known as ITU-T
Recommendations which act as defining elements in the global infrastructure of information and communication technologies (ICTs). Standards are critical to the interoperability of ICTs and whether we exchange voice, video or data messages, standards enable global communications by ensuring that countries’ ICT networks and devices are speaking the same language.Слайд 13Recommendations are standards that define how telecommunication networks operate and
interwork.
ITU-T Recommendations are non-binding, however they are generally complied
with due to their high quality and because they guarantee the interconnectivity of networks and enable telecommunication services to be provided on a worldwide scale.Слайд 14ETSI – the European Telecommunications Standards Institute
CEN – the European
Committee for Standardization
CENELEC – the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization
Тhe
European standardisation organisations:Слайд 16Sustainable Development Goals
Goal 1: Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
Goal 2:
Achieve universal primary education
Goal 3: Promote gender equality and empower
womenGoal 4: Reduce child mortality rate
Goal 5: Improve maternal health
Goal 6: Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases
Goal 7: Ensure environmental sustainability
Goal 8: Develop a global partnership for development
Слайд 18The role of ICT in the UN Sustainable Development Goals
The
goals were created through a collaboration of the UN Development
Programme (UNDP) and the UN Development Group (UNDG), which commenced an unprecedented global conversation among a diverse group of stakeholders over the last three years. The 17 goals are very ambitious, aiming to end poverty, extreme hunger, ensure quality education for everyone, improve healthcare, end gender inequality, protect, restore and promote sustainable use of ecosystems, etc. to improve social and economic development and end inequality.Слайд 19ICTs have incredible potential to improve development outcomes in both the
developing and the developed world, and it is self-evident that
digital inclusion is necessary for sustainable development in the 21st century.ICTs enhance our capability to measure progress toward all the SDGs, evaluate the methods used to achieve them, learn what is working and not working, and improve the timeliness and quality of decision making.
ICTs provide opportunities to streamline and enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the activities we undertake across the development landscape.
ICTs provide access to a whole new range of digitally-enabled products and services which strengthen local economies, local innovation and local communities.
ICTs are already empowering billions of individuals around the world – by helping them make better-informed decisions, by providing access to education resources and health information, and by delivering services such as mobile banking, e-government and social media networks.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4764_NwlLAw