Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Introduction To Economics
Содержание
- 1. Introduction To Economics
- 2. Week 1: Key terms and wordsProductionConsumptionGoodsServicesScarcityChoiceNatural resourcesLandLabourCapitalEnterpriseNeedsWantsChoiceOpportunity costModellingEconomic systemsPositive & NormativeMacroeconomicsMicroeconomics
- 3. What is Economics?Concerned with production…and with consumption…and
- 4. The major economics issuesWhat, how and for
- 5. What is the difference between “goods” …………..and “services”?
- 6. ScarcityThe fundamental problem of economicsUnlimited wantsLimited resourcesSo
- 7. Factors of production (Resources)Labour – human resourcesLand and raw materials – natural resourcesCapital – Manufactured resources
- 8. LabourLimited numberLimited skillsLocation EntrepreneursOrganise productive resourcesSpecialised form
- 9. Land and raw materials Land area is
- 10. CapitalManufactured resourcesFactoriesMachinesTransportOther equipmentInfrastructure – roads, communications etcLimited in quantity and by technology
- 11. Economics is also concerned with Demand and SupplyDemandRelated to wantsVirtually unlimitedSupplyRelated to resourcesLimited
- 12. Introduction to EconomicsEconomic Systems
- 13. Demand and supplyMarkets Demand for goods and
- 14. Question??????Is their any difference between needs and wants?
- 15. Economic SystemsCommand EconomiesFree Market EconomiesMixed Economies
- 16. Command EconomiesLand and capital collectively ownedState planning
- 17. Free Market EconomiesPrice mechanismShortage and surplusesShortage ->
- 18. Mixed EconomiesMixture of public (state) and private
- 19. TotallyplannedeconomyN. KoreaN. KoreaCubaChinaPolandPolandFranceFranceUKUSAUSAMid 1980sLate 2000sChinaHongKongCubaChina(HongKong)Classifying economic systemsUKTotallyfree-marketeconomy
- 20. Introduction to EconomicsTwo branches:Macro- and Microeconomics
- 21. MacroeconomicsMACRO – large, great (Greek)The economy as a wholeAggregate demand (spending)Aggregate supplyBroad issuesGrowthInflationUnemploymentInternational trade/Balance of payments
- 22. MicroeconomicsMICRO – small (Greek – tiny)Individual companiesIndividuals Supply of, demand for, particular goods and services
- 23. Fundamental choicesWhat should be produced?How should production be organised?For whom should production take place?Who chooses?Individuals/householdsFirmsGovernments
- 24. Opportunity Cost The cost of production or
- 25. DiscussionYou have all decided to study in
- 26. Economic modellingHow we describe economic conceptsDiagrammatical –
- 27. Economic modellingExamples:Production possibility curve Increasing opportunity costs Circular flow of goods and income
- 28. Production possibility curveHighly simplifiedChoiceIncreasing opportunity costs
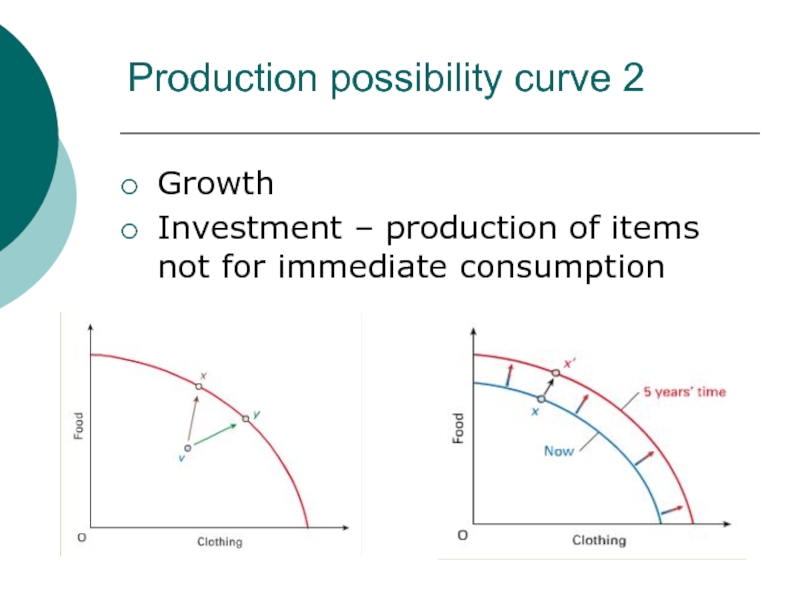
- 29. Production possibility curve 2GrowthInvestment – production of items not for immediate consumption
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. Economic analysis - modellingThe circular flow of
- 32. Goods and services£ConsumerexpenditureWages, rentdividends, etc.£Services of factors
- 33. Introduction to EconomicsPositive and Normative Statements
- 34. Is economics a science?Positive versus Normative EconomicsPositive statements – factsNormative statements - values
- 35. Слайд 35
- 36. Positive Statements Statements of factAccuracy can be testedObjective Examples?
- 37. Normative StatementsStatements of valueOpinionSubjective Cannot be proved or disprovedExamples?
- 38. Positive or normative?Should the new sales tax
- 39. Positive or normative?The gap between the
- 40. Скачать презентанцию
Week 1: Key terms and wordsProductionConsumptionGoodsServicesScarcityChoiceNatural resourcesLandLabourCapitalEnterpriseNeedsWantsChoiceOpportunity costModellingEconomic systemsPositive & NormativeMacroeconomicsMicroeconomics
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Week 1: Key terms and words
Production
Consumption
Goods
Services
Scarcity
Choice
Natural resources
Land
Labour
Capital
Enterprise
Needs
Wants
Choice
Opportunity cost
Modelling
Economic systems
Positive &
Normative
Слайд 3What is Economics?
Concerned with production
…and with consumption
…and with scarcity
…and anything
to do with the process of satisfying human wants
The study
of how we apply limited resources to unlimited wantsСлайд 4The major economics issues
What, how and for whom?
What goods and
services to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce?
Слайд 6Scarcity
The fundamental problem of economics
Unlimited wants
Limited resources
So we cannot have
everything we want
Generates a need to make choices
Слайд 7Factors of production (Resources)
Labour – human resources
Land and raw materials
– natural resources
Capital – Manufactured resources
Слайд 8Labour
Limited number
Limited skills
Location
Entrepreneurs
Organise productive resources
Specialised form of labour or
fourth factor of production?
Can make or break business
Слайд 9Land and raw materials
Land area is finite
Raw materials
are finite
diminish over time
are not evenly distributed between nations
Слайд 10Capital
Manufactured resources
Factories
Machines
Transport
Other equipment
Infrastructure – roads, communications etc
Limited in quantity and
by technology
Слайд 11Economics is also concerned with Demand and Supply
Demand
Related to wants
Virtually
unlimited
Supply
Related to resources
Limited
Слайд 13Demand and supply
Markets
Demand for goods and services
Supply of goods
and services
Price movements
Economic systems – level of control
Goal – To
use scarce resources to meet the needs and wants of people so as to improve their welfare (or well-being)Слайд 16Command Economies
Land and capital collectively owned
State planning - allocation of
resources:
Current consumption or future investment
Output of each industry/company
Distribution of output
between consumersСлайд 17Free Market Economies
Price mechanism
Shortage and surpluses
Shortage -> price rises
Surplus ->
price falls
Equilibrium: demand = supply
Land and capital privately owned
Firms seek
to maximise profitsConsumers seek best value for money
Workers seek to maximise wages
Слайд 18Mixed Economies
Mixture of public (state) and private sector ownership and
activity
State influence on key areas depending on government priorities
Price
and profit provide major incentivesIn practice ALL economies are a mixed
Key distinction – how much is government involved?
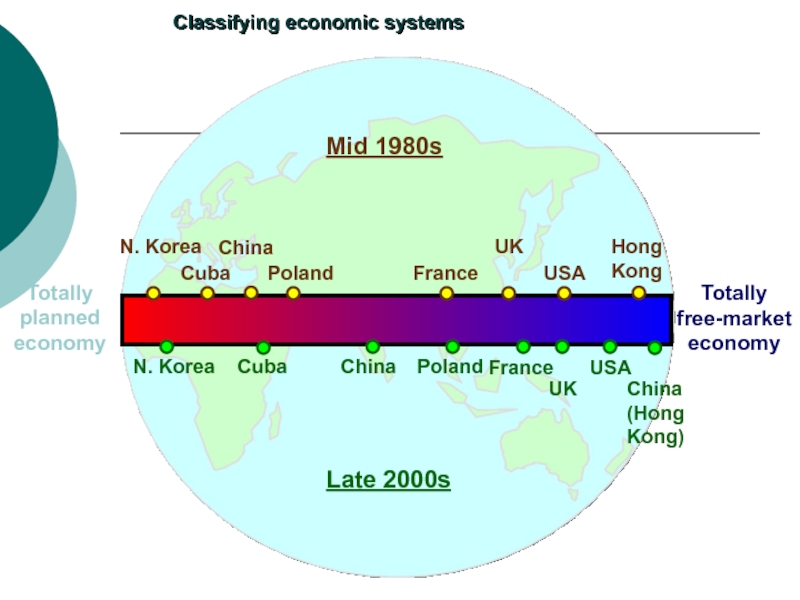
Слайд 19Totally
planned
economy
N. Korea
N. Korea
Cuba
China
Poland
Poland
France
France
UK
USA
USA
Mid 1980s
Late 2000s
China
Hong
Kong
Cuba
China
(Hong
Kong)
Classifying economic systems
UK
Totally
free-market
economy
Слайд 21Macroeconomics
MACRO – large, great (Greek)
The economy as a whole
Aggregate demand
(spending)
Aggregate supply
Broad issues
Growth
Inflation
Unemployment
International trade/Balance of payments
Слайд 22Microeconomics
MICRO – small (Greek – tiny)
Individual companies
Individuals
Supply of, demand
for, particular goods and services
Слайд 23Fundamental choices
What should be produced?
How should production be organised?
For whom
should production take place?
Who chooses?
Individuals/households
Firms
Governments
Слайд 24Opportunity Cost
The cost of production or consumption in terms
of the next best alternative, based on:
Rational choices:
Costs and benefits
Consequences
(positive or negative)Marginal costs
Marginal benefits
Слайд 25Discussion
You have all decided to study in the UK –
but you could have gone to a University in your
home countryWhat are the costs and benefits of your decision?
What is the opportunity cost of your studying in the UK?
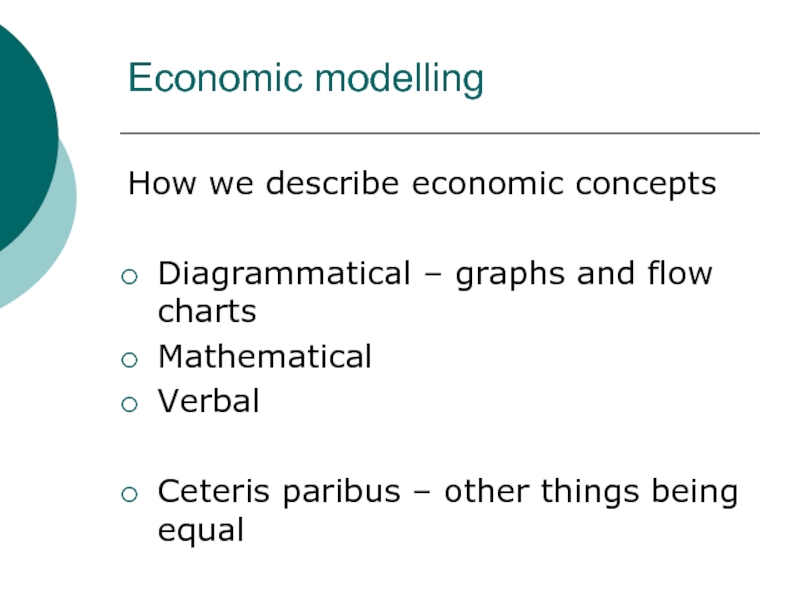
Слайд 26Economic modelling
How we describe economic concepts
Diagrammatical – graphs and flow
charts
Mathematical
Verbal
Ceteris paribus – other things being equal
Слайд 27Economic modelling
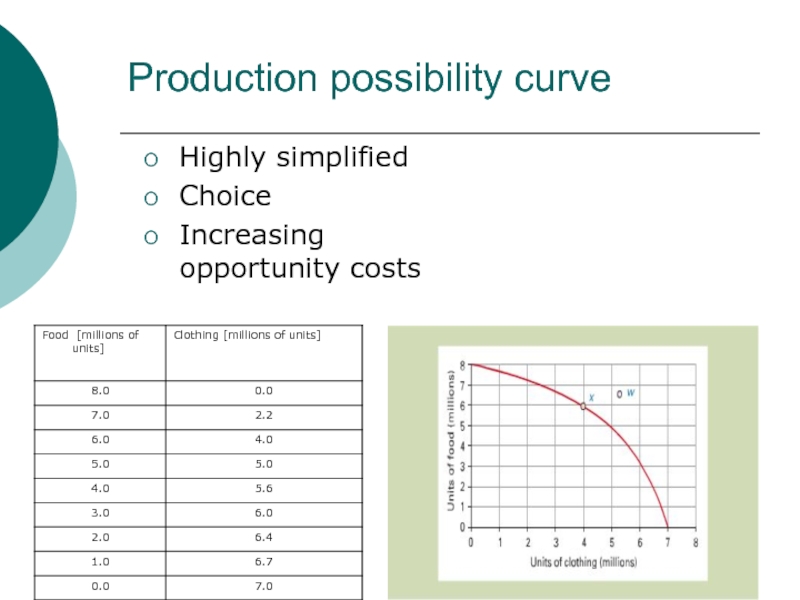
Examples:
Production possibility curve
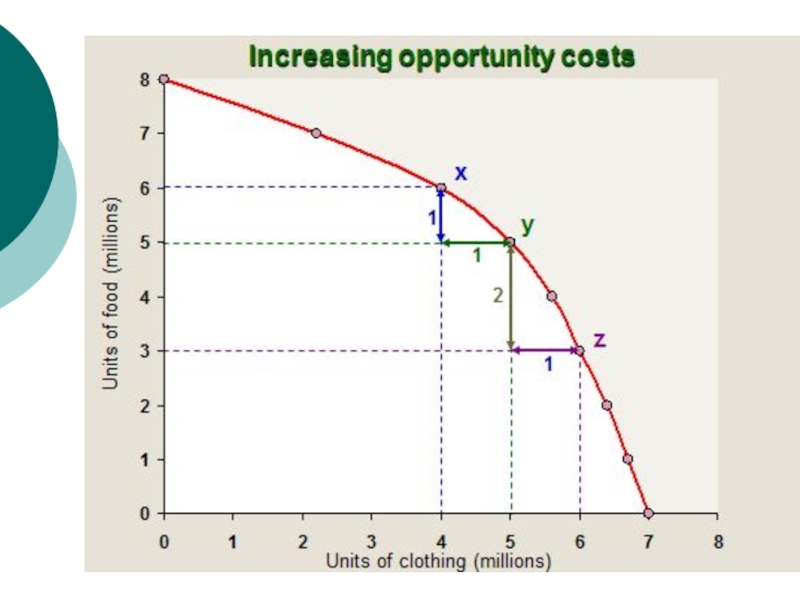
Increasing opportunity costs
Circular flow of
goods and income
Слайд 29Production possibility curve 2
Growth
Investment – production of items not for
immediate consumption
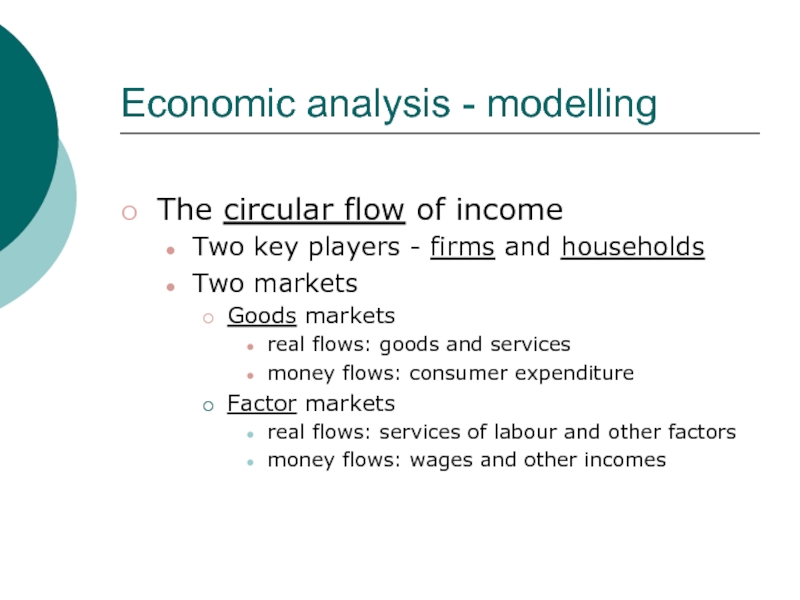
Слайд 31Economic analysis - modelling
The circular flow of income
Two key players
- firms and households
Two markets
Goods markets
real flows: goods and services
money
flows: consumer expenditureFactor markets
real flows: services of labour and other factors
money flows: wages and other incomes
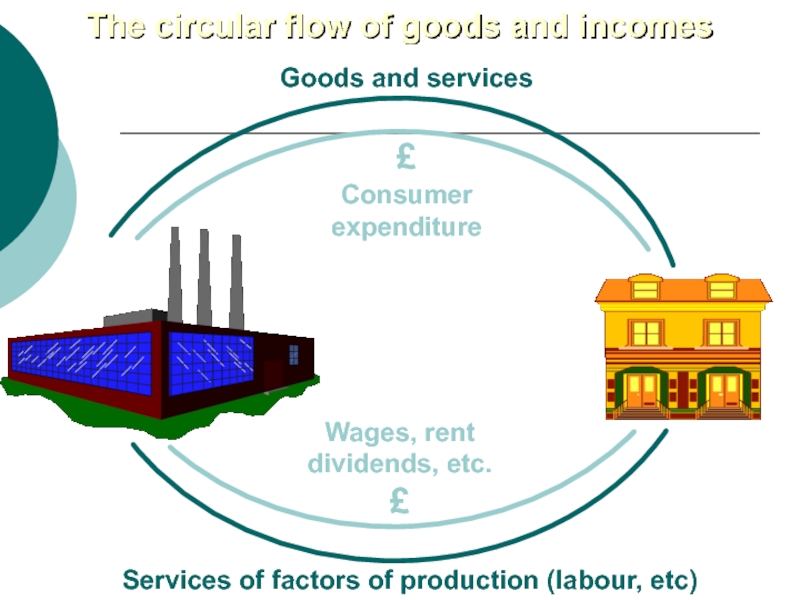
Слайд 32Goods and services
£
Consumer
expenditure
Wages, rent
dividends, etc.
£
Services of factors of production (labour,
etc)
The circular flow of goods and incomes
Слайд 34Is economics a science?
Positive versus Normative Economics
Positive statements – facts
Normative
statements - values
Слайд 37Normative Statements
Statements of value
Opinion
Subjective
Cannot be proved or disproved
Examples?
Слайд 38Positive or normative?
Should the new sales tax be introduced?
How much
revenue will the new sales tax bring next year?
How much
would that revenue increase if the tax were raised a further 5%?Should the new sales tax be raised?
Слайд 39
Positive or normative?
The gap between the rich and poor in
the UK is increasing.
The gap between the rich and poor
in the UK is too great.The gap between the rich and poor in the UK is useful in motivating the workforce