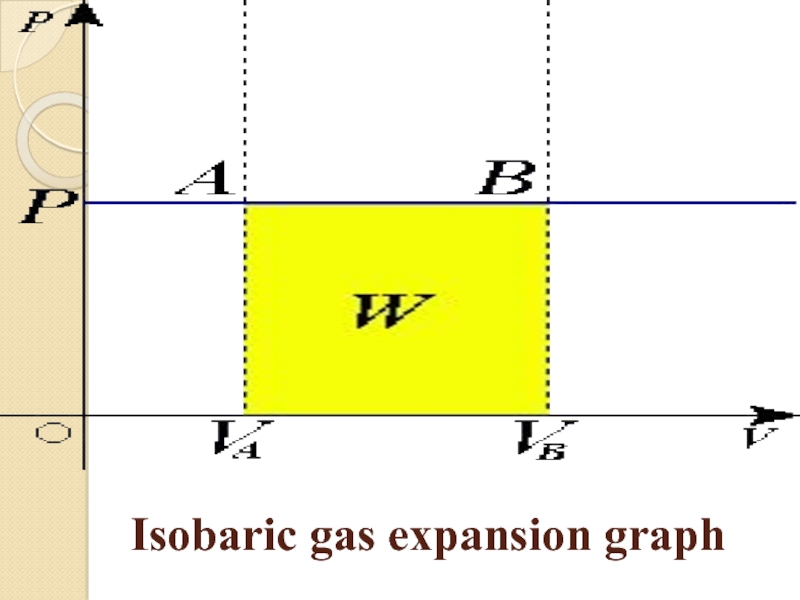
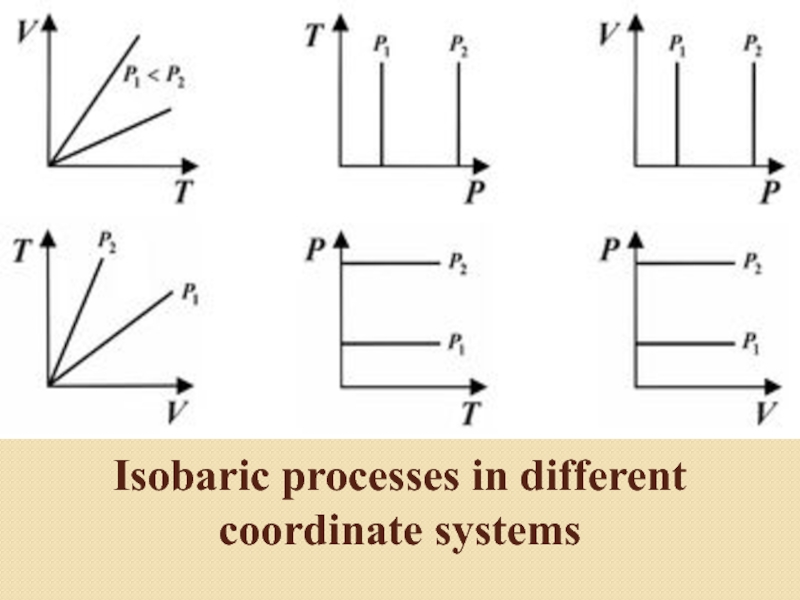
in the system at constant pressure and mass of gas.
According
to the Gay-Lussac law, in an ideal gas with an isobaric process, the ratio of volume to temperature is constant: V/T=constIf we use the Clapeyron – Mendeleev equation, then the work performed by a gas during gas expansion
The amount of heat received or given off by the gas is characterized by the change in enthalpy