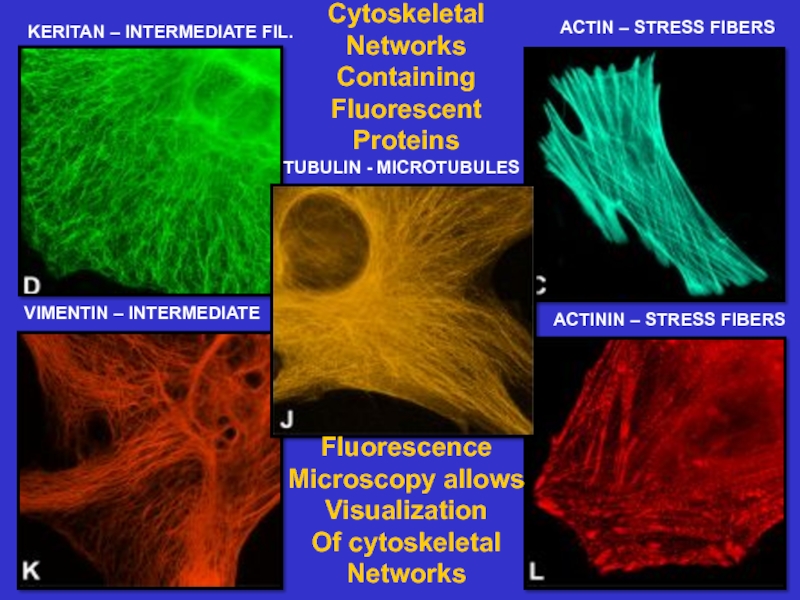
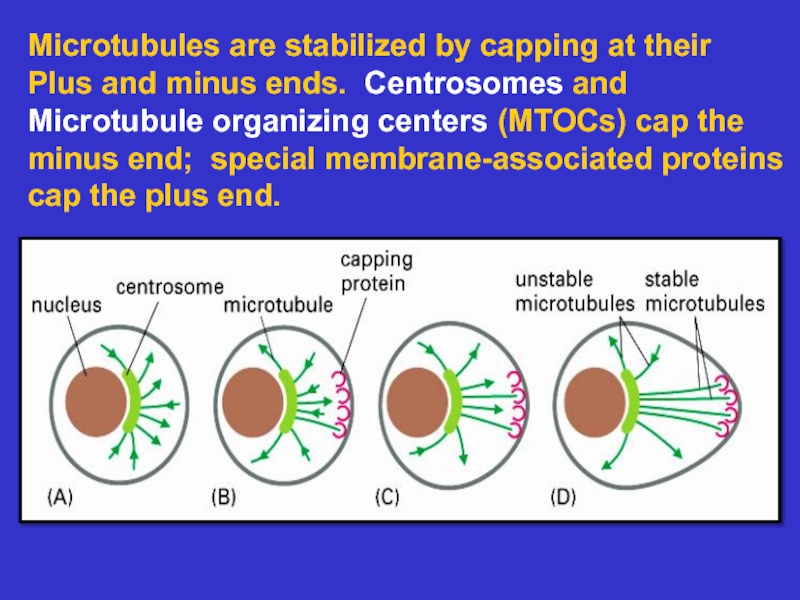
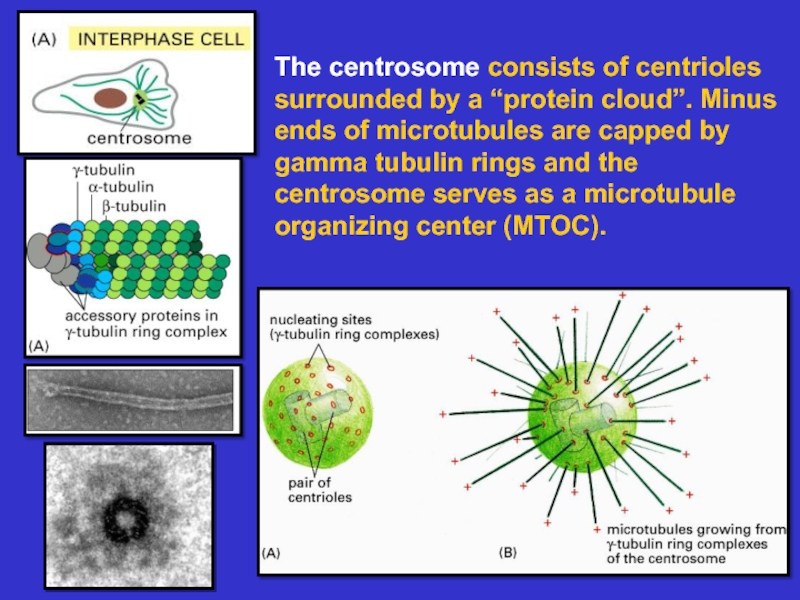
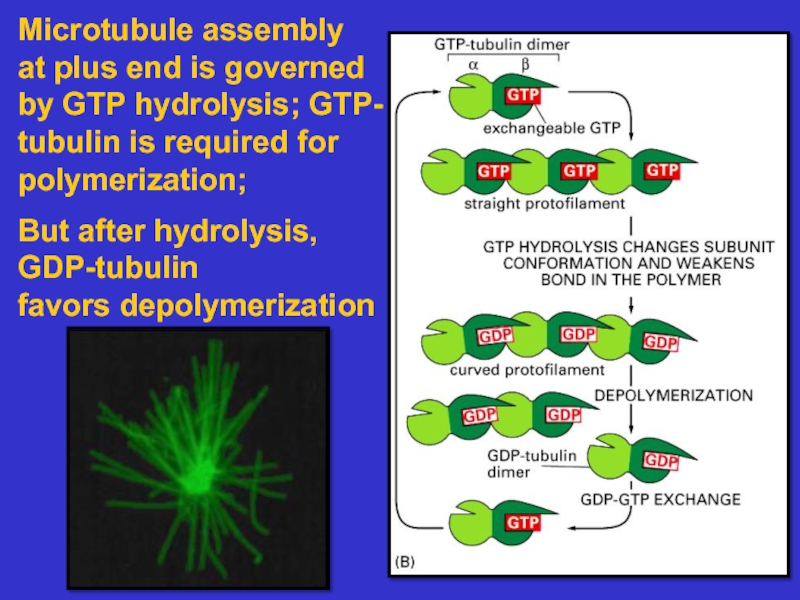
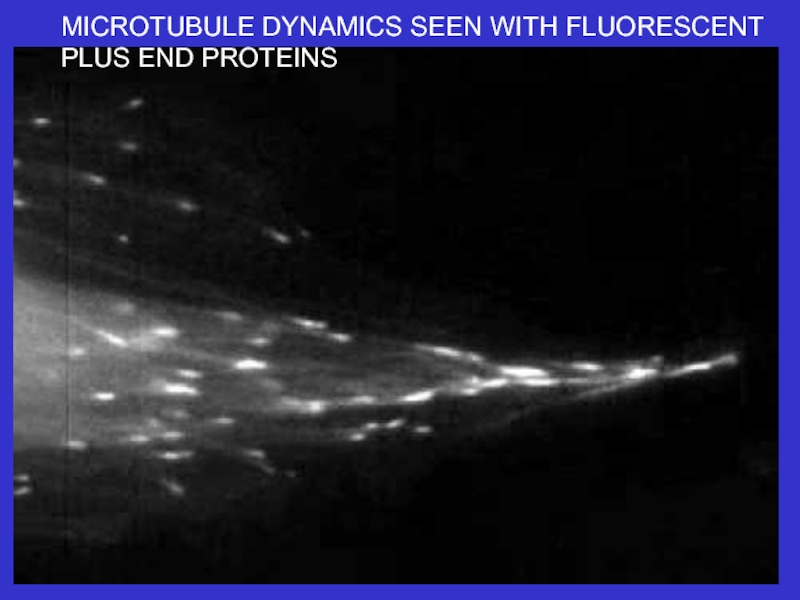
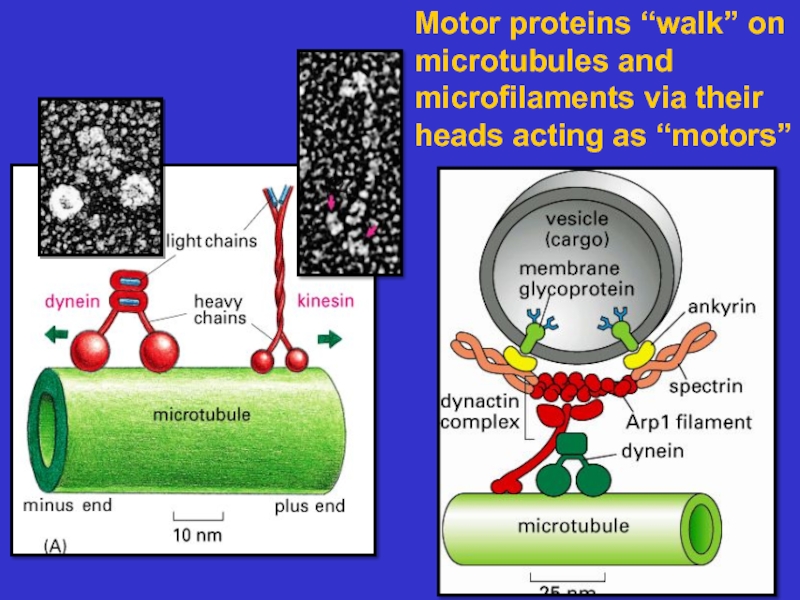
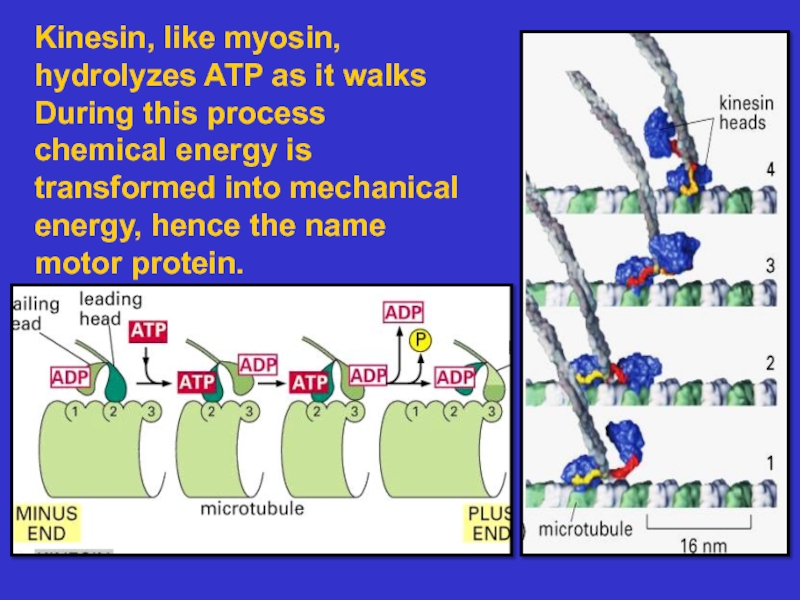
many filament-associated
proteins including molecular motors
Microfilaments – composed of
actin, thesefilaments form dynamic networks that form
the basis for cell shape and movement
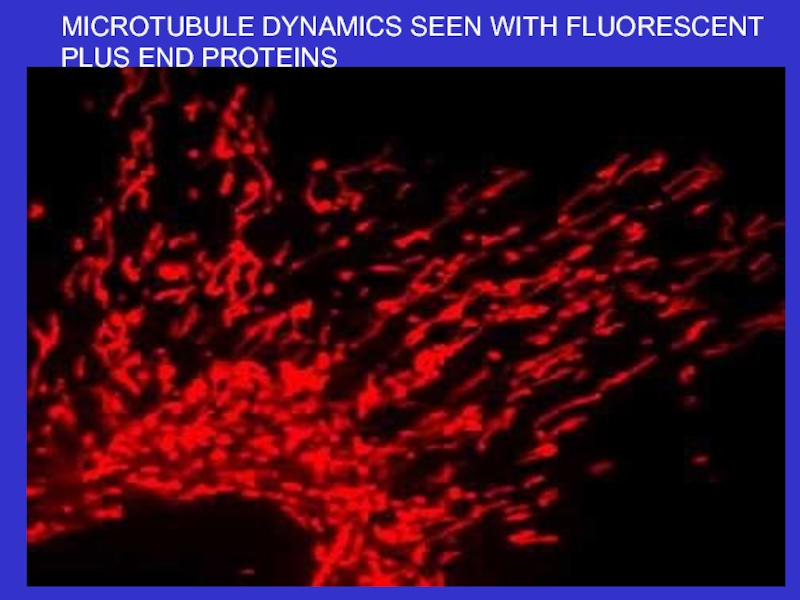
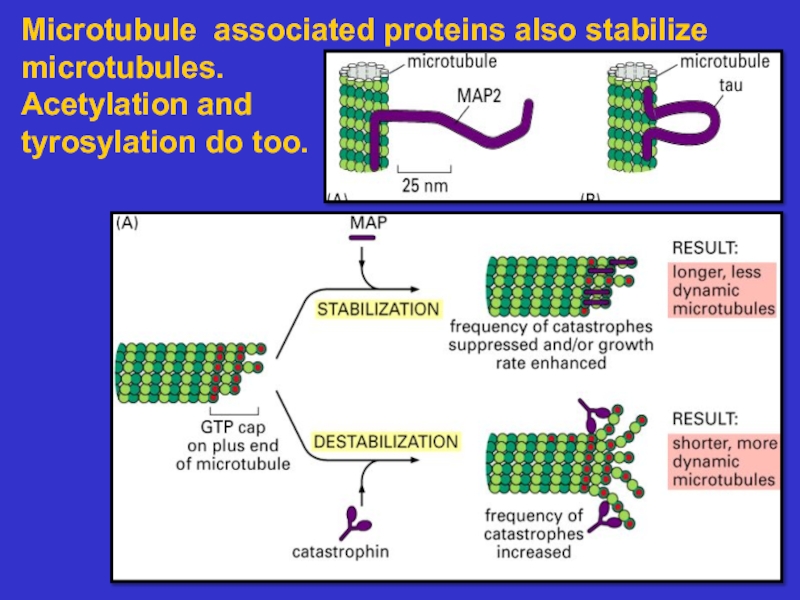
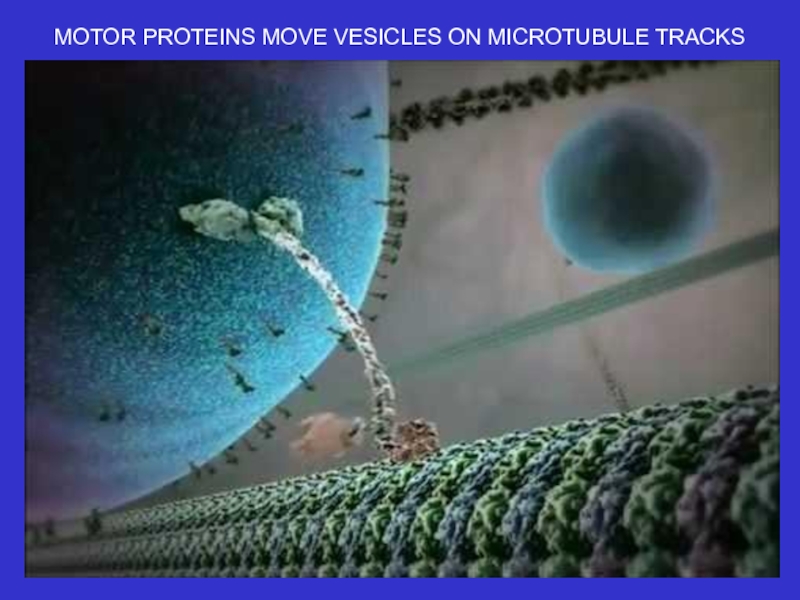
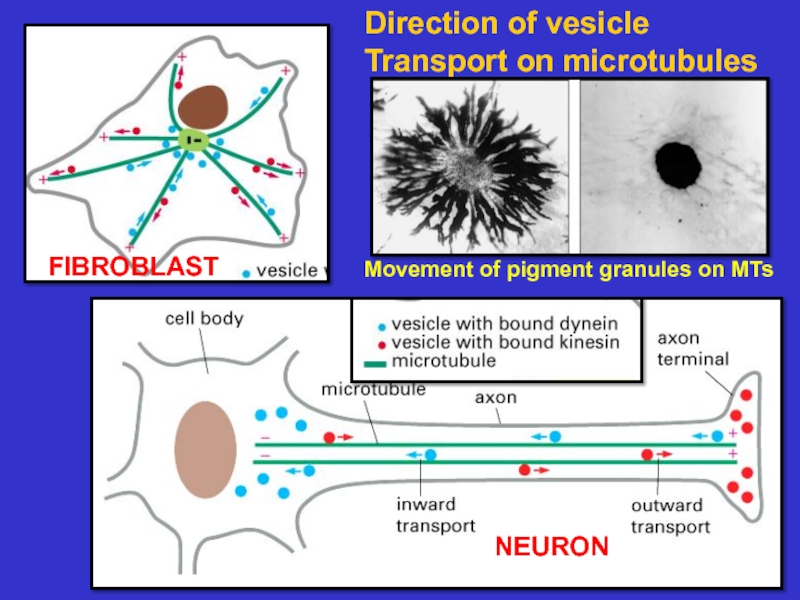
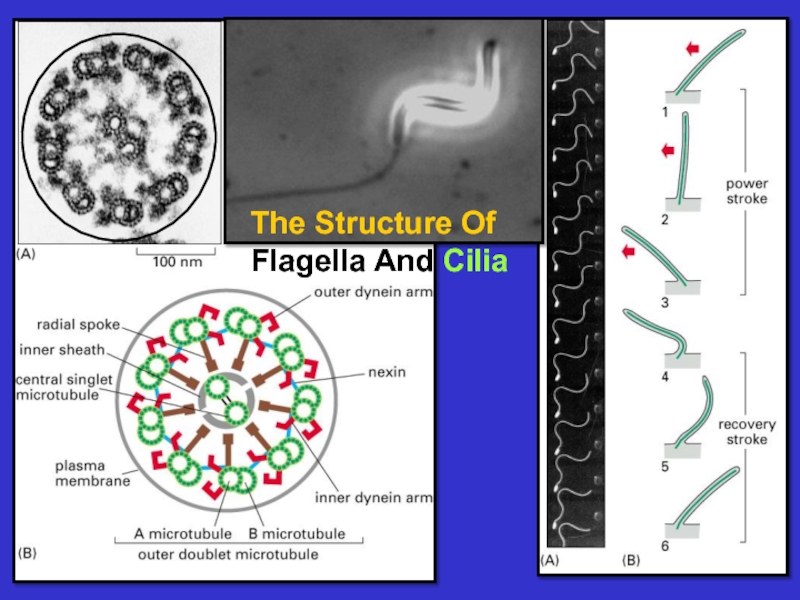
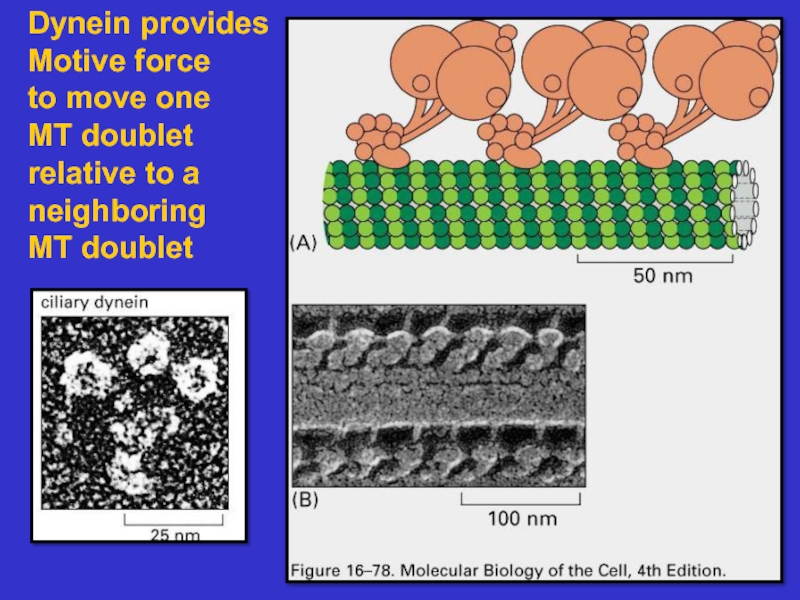
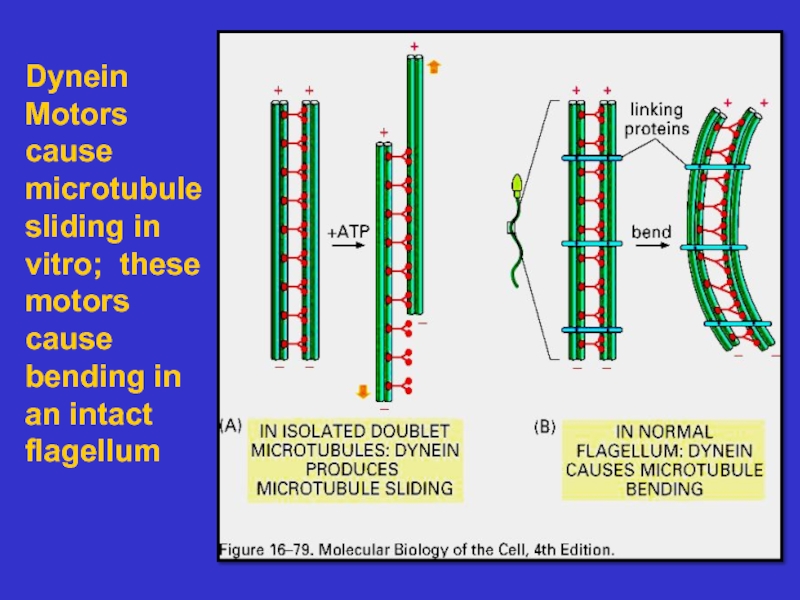
Microtubules – composed of tubulin, these
tubules act as tracks on which to move
vesicles and organelles. They also form the
basis of cilia and flagella. They are dynamic.
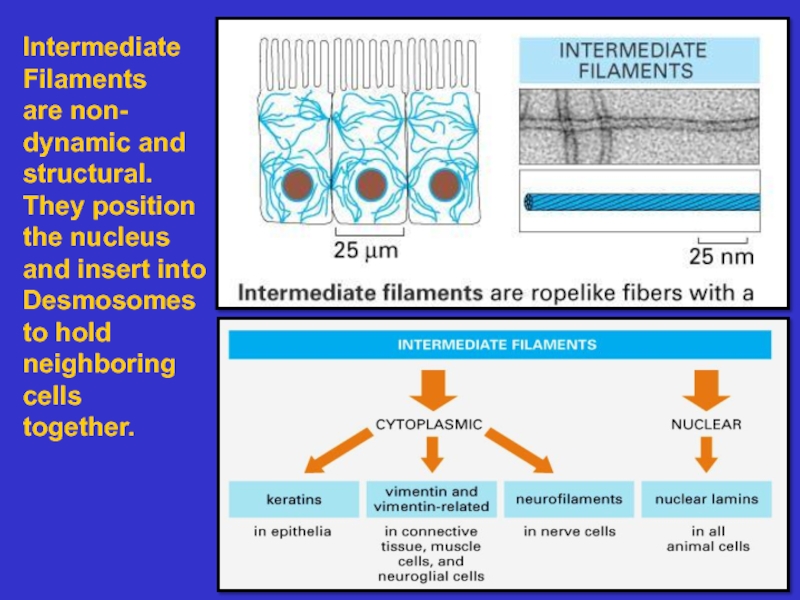
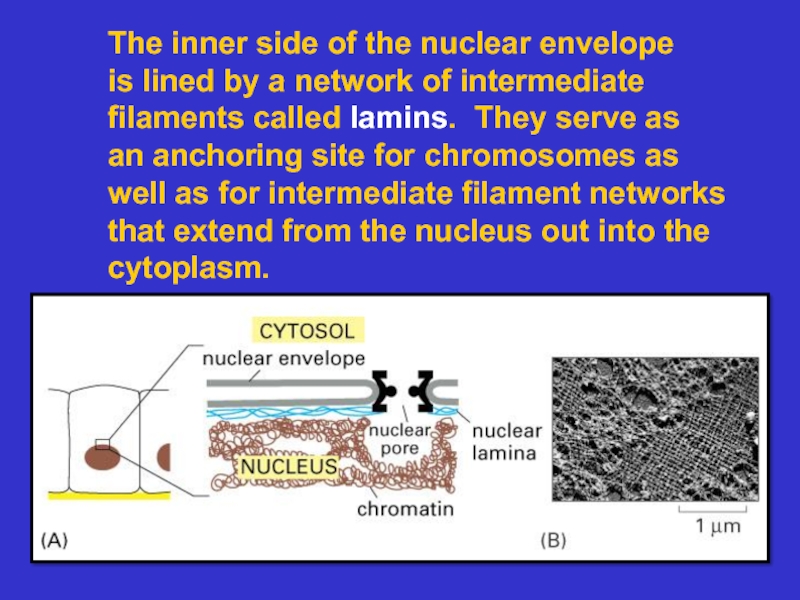
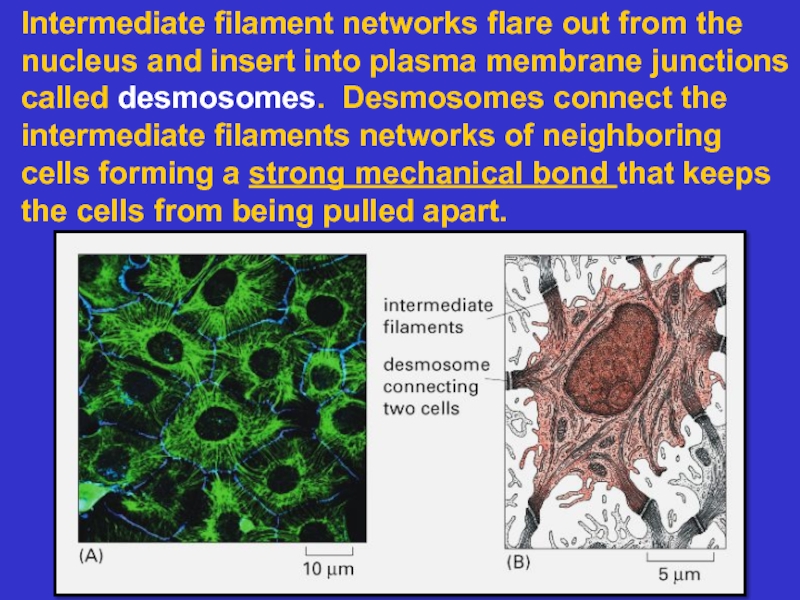
Intermediate filaments – composed of proteins
that associate to form rope-like structures
that are of high mechanical strength. They
position organelles and form a strong, long
lasting cell superstructure.