Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
lnternational Marketing Chapter 6 Global market strategy
Содержание
- 1. lnternational Marketing Chapter 6 Global market strategy
- 2. Global marketing strategy – overviewGlobal market segmentationGlobal targetingGlobal product positioningEntry and expanison strategies
- 3. A. Global marketing strategyA strategy is a
- 4. Corporate’ strategic planning It is an
- 5. 1. Mission Statements A company's mission
- 6. To Bring inspiration and innovation to
- 7. To make people happy
- 8. No cynicism Nurturing and promulgation of "wholesome
- 9. "To give ordinary folk the chance to buy the same thing as rich people."
- 10. "To experience the joy of advancing and applying technology for the benefit of the public."
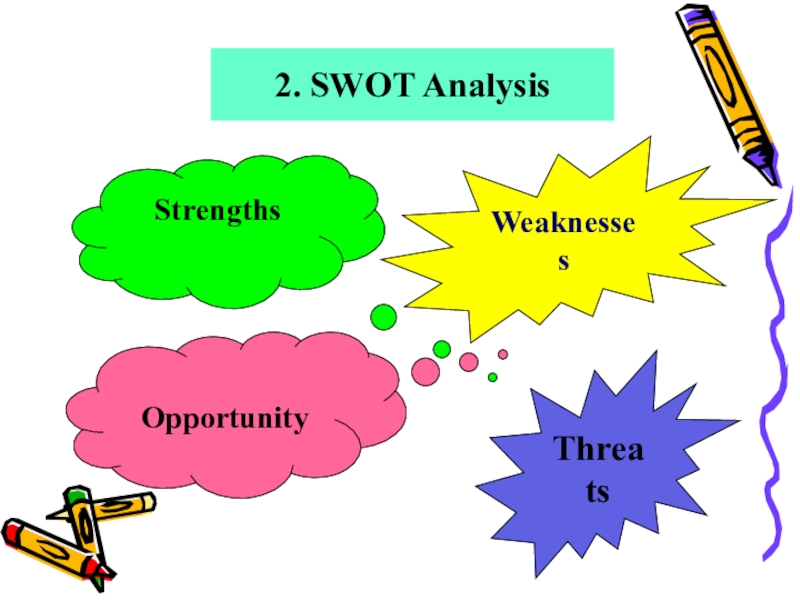
- 11. 2. SWOT AnalysisStrengths WeaknessesOpportunityThreats
- 12. Strengths: attributes of the organization that are
- 13. CASE
- 14. Слайд 14
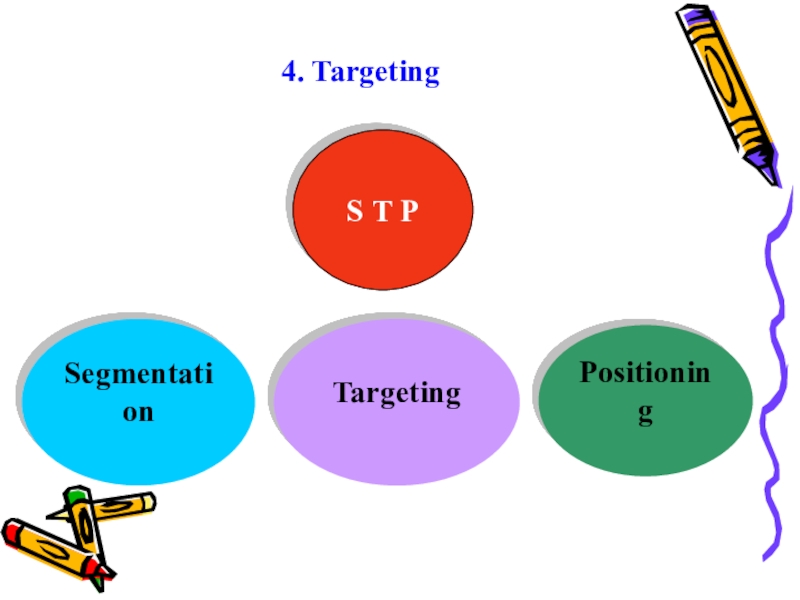
- 15. 4. TargetingS T PSegmentationTargetingPositioning
- 16. B. Global market segmentationThe process of subdividing
- 17. Слайд 17
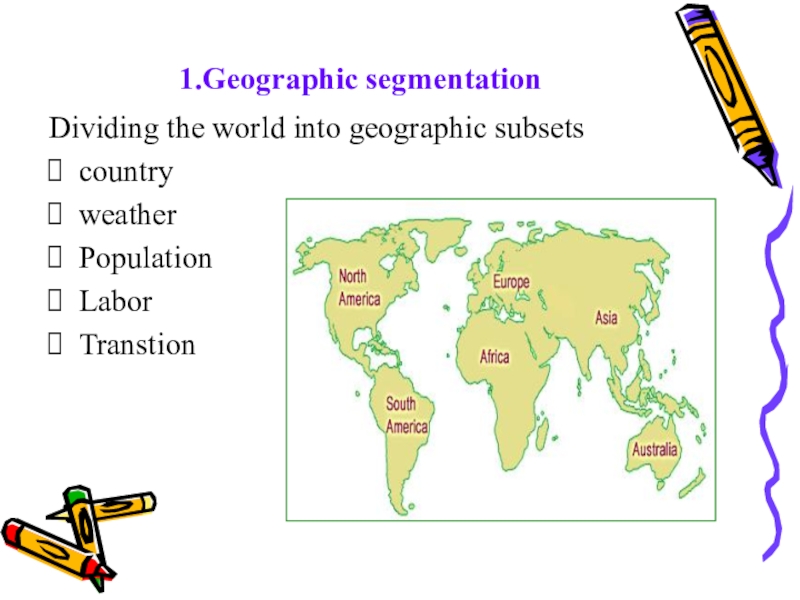
- 18. 1.Geographic segmentationDividing the world into geographic subsetscountryweatherPopulationLabor Transtion
- 19. 2. Demographic segmentationAgeGenderIncomeEducationOccupationSocial classRegion
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Poundland is a British-based variety store chain
- 22. Poundland boast a loyal customer base, with
- 23. 10-10-2930-5050+
- 24. C. Psychographic segmentationAttitudesValuesLifestylePurchase occasion
- 25. D. Behavior segmentationWether people buy and use
- 26. CASE
- 27. VS
- 28. CCTVCCTV1CCTV2CCTV3,11 CCTV4,9 CCTV5 CCTV6,8 CCTV7CCTV10 CCTV12 CCTV13 CCTV14
- 29. BBC0-6: CBeebies 6-12: CBBC 16-341.BBC12.BBC23.BBC34.BBC45.BBCNews
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. C. Global targeting Targeting is the
- 32. 1.Undifferentiated marketing A market-coverage strategy
- 33. 2. Differentiated marketing strategy The firm
- 34. CASE 1
- 35. CASE 2 Airline companies
- 36. 3. Concentrated Marketing The organisation concentrates its marketing effort on one particular segment.
- 37. D.Global product positioning After the organisation
- 38. CASE 1
- 39. Super-luxury marque,sells barely 800 cars a year
- 40. Last year, Mr Robertson personally signed letters
- 41. CASE 2
- 42. CASE 3
- 43. CASE 4
- 44. CASE 5"man always remember love because of romantic only"
- 45. Слайд 45
- 46. E.Entry and expansion strategies When
- 47. 1. Exporting Exporting is the
- 48. Exporting requires a partnership between exporter, importer,
- 49. CASE
- 50. Advantages:Manufacturing is home based thus, it is
- 51. 2. Licensing Licensing is defined as
- 52. Advantages Good way to start in foreign
- 53. Слайд 53
- 54. 3. Franchise A franchise business
- 55. An individual who purchases and runs a
- 56. Слайд 56
- 57. Businesses with a good track record of
- 58. Слайд 58
- 59. Shanghai GM is a joint venture between
- 60. 4. Joint venturesJoint ventures can be
- 61. CASE
- 62. Xi’an Jiaotong – Liverpool University (XJTLU) is
- 63. As part of its goal to offer
- 64. Advantages Sharing of risk and ability to
- 65. Disadvantages: Partners do not have full control
- 66. 5. Ownership The most extensive form
- 67. 6. Merger & acquisition Mergers and
- 68. A merger is a legal consolidation of
- 69. CASE 1
- 70. The marriage between Geely and Volvo, largely
- 71. CASE 2
- 72. SummaryGlobal market segmentation: Geographic segmentation; Demographic segmentation;
- 73. Reference海尔的营销策略 孙健 企业管理出版社经营战略(哈佛商学院MBA课程) 阿尔弗雷德.钱德勒 中国国际广播出版社http://www.infofranchise.cn/ (特许经营信息)http://www.ftchinese.com/(海外并购新闻案例)
- 74. Слайд 74
- 75. Скачать презентанцию
Global marketing strategy – overviewGlobal market segmentationGlobal targetingGlobal product positioningEntry and expanison strategies
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Global marketing strategy – overview
Global market segmentation
Global targeting
Global product positioning
Entry
and expanison strategies
Слайд 3A. Global marketing strategy
A strategy is a plan of action
designed to achieve a particular goal.
A marketing strategy is
a process that can allow an organization to concentrate its limited resources on
the greatest opportunities to increase sales and
achieve a sustainable competitive advantage.
It should be centered around the key concept that
customer satisfaction is the main goal.
Слайд 4Corporate’ strategic planning
It is an organization's process of
defining its strategy, or direction, and making decisions on allocating
its resources to pursue this strategy, including its capital and people.Set mission statement
Situational analysis (SWOT)
Set objectives
Targeting
Слайд 51. Mission Statements
A company's mission statement is a
constant
reminder to its employees of why the
company exists and what the founders envisioned when
they put their fame and fortune at risk to breathe
life into their dreams.
Слайд 6 To Bring inspiration and innovation
to every athlete in
the world.
Serving the sports and athletic
industry, NIKE Inc is known for manufacturing shoes, gear and apparel, particularly for athletes in a whole range of sports such as baseball, golf, tennis, football, etc. Слайд 8No cynicism
Nurturing and promulgation of "wholesome American values"
Creativity,
dreams and imagination
Fanatical attention to consistency and detail
Preservation
and control of the Disney "magic" Слайд 12Strengths: attributes of the organization that are helpful to achieving
the objective.
Weaknesses: attributes of the organization that are harmful
to achieving the objective. Opportunities: external conditions that are helpful to achieving the objective.
Threats: external conditions which could do damage to the business's performance.
Слайд 16B. Global market segmentation
The process of subdividing a market into
distint subsets of customers that behave
in the same way
or have similar needs.Слайд 181.Geographic segmentation
Dividing the world into geographic subsets
country
weather
Population
Labor
Transtion
Слайд 21Poundland is a British-based variety store chain which sells every
item in its stores for £1
Poundland, unlike many of
its rivals, have been one of the few to report strong sales in a time of economic crisis, with 2012-2013 revenue expected to reach £400mСлайд 22Poundland boast a loyal customer base, with
roughly
2 million predominantly female shoppers every week . Poundland also
attract students and the elderly who typically watch their budgets and look for bargains.The retailer has been keen in recent years to move away from their reputation of only appealing to low-income households, as they continue to expand into mainstream shopping centres and districts, with an increasing number of higher earning consumers in the market for a bargain.
Слайд 25D. Behavior segmentation
Wether people buy and use a product
When to
but the product
Usage rate (Heavy,medium,light,nonuser)
User status (Potential user,nonusers,ex-
users,regulars,first-timers)brand loyalty
Слайд 31C. Global targeting
Targeting is the second stage of
the STP process. After the market has been separated into
its segments, the marketer will select a segment or series of segments and 'target' it/themСлайд 321.Undifferentiated marketing
A market-coverage strategy in which
a firm decides to ignore market segment differences and go
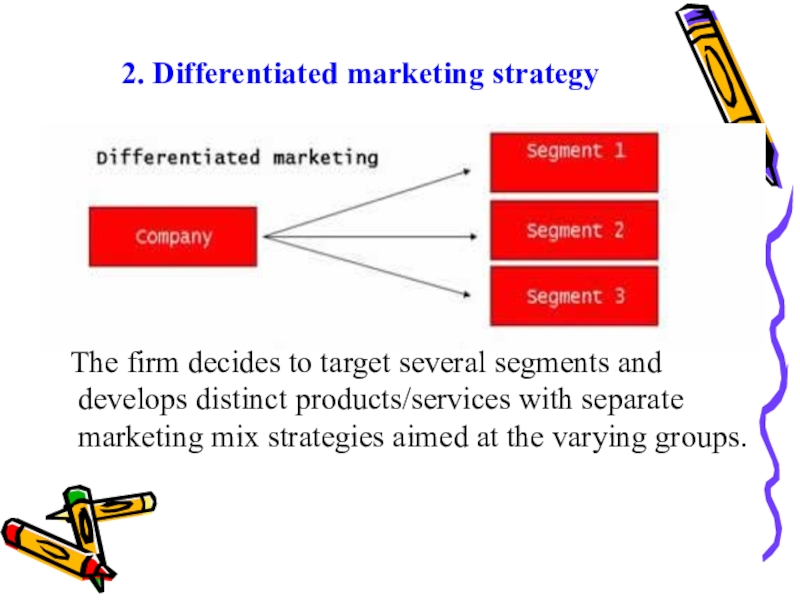
after the whole market with one offer .Слайд 332. Differentiated marketing strategy
The firm decides to
target several segments and develops distinct products/services with separate marketing
mix strategies aimed at the varying groups.Слайд 35CASE 2
Airline companies offering first, business
(segment 1) or economy class tickets (segment 2) , with
separate marketing programmes to attract the different groups.Слайд 363. Concentrated Marketing
The organisation concentrates its marketing
effort on one particular segment.
Слайд 37D.Global product positioning
After the organisation has selected its
target market, the next stage is to decide how it
wants to position itself within that chosen segment. Positioning refers to ‘how organisations want their consumers to see their product’.Слайд 39Super-luxury marque,sells barely 800 cars a year .
The
company's target customers are people with liquid assets worth at
least $30m, a group Capgemini estimates numbers about 85,000 worldwide.The marque's main point of contact with existing and potential customers is through its 74 independently owned dealerships worldwide. It chooses dealers who “live in the same world, drive the same cars, have the same yachts and aircraft” as its customers .
Слайд 40Last year, Mr Robertson personally signed letters to all of
its 2,700 customers of the past three years, and sent
out a coffee-table album to the cars' former owners. The book features individual testimonials from buyers such as Japanese fashion designer Nigo, now on his third Phantom.Слайд 46E.Entry and expansion strategies
When an organisation has
made a decision to enter an overseas market, there are
a variety of options open to it. These options vary with cost, risk and the degree of control which can be exercised over them.Слайд 471. Exporting
Exporting is the most traditional
and well established form of operating in foreign markets.
It can
be defined as the marketing of goods produced in one country into another. Whilst no direct manufacturing is required in an overseas country,significant investments in marketing are required. Слайд 48Exporting requires a partnership between exporter, importer, government and transport.
Without these four coordinating activities the risk of failure is
increased. Contracts between buyer and seller are a must.Слайд 50Advantages:
Manufacturing is home based thus, it is less risky than
overseas based
Gives an opportunity to "learn" overseas markets before investing
in bricks and mortarReduces the potential risks of operating overseas.
Disadvantage:
overseas agents , lack of control
Слайд 512. Licensing
Licensing is defined as "the method of
foreign operation whereby a firm in one country agrees to
permit a company in another country to use the manufacturing, processing, trademark, know-how or some other skill provided by the licensor".Слайд 52Advantages
Good way to start in foreign operations and open
the door to low risk manufacturing relationships
Capital not
tied up in foreign operationDisadvantages:
Licensees become competitors
Слайд 543. Franchise
A franchise business is a method
a company uses to distribute its products or services through
retail outlets owned by independent, third party operators.The independent operator does business using the marketing methods, trademarked goods and services and the "goodwill" and name recognition developed by the company. In exchange, the independent operator pays an initial fee and royalties to the owner of the franchise.
Слайд 55An individual who purchases and runs a franchise
is called a “ franchisee”. The franchisee purchases a franchise
from the “franchisor.”The franchisee must follow certain rules and guidelines already established by the franchisor, and the franchisee must pay an ongoing franchise royalty fee, as well as an up-front, one-time franchise fee to the franchisor.
Слайд 57Businesses with a good track record of profitability.
Businesses with
broad geographic appeal.
Businesses which are relatively easy to operate.
Businesses which are relatively inexpensive to operate.
Businesses which are easily duplicated
Слайд 59Shanghai GM is a joint venture between GM and SAIC
Motor that manufactures and sells Chevrolet, Buick, Cadillac, and Opel
brand automobiles in mainland China.It was founded on June 12, 1997 with 50% investment each from each partner. In February 2010, SAIC acquired an additional 1% stake in the joint venture for US$85 million and assistance in securing a US$400 million line of credit to boost SAIC's total share of Shanghai General Motors to 51% .
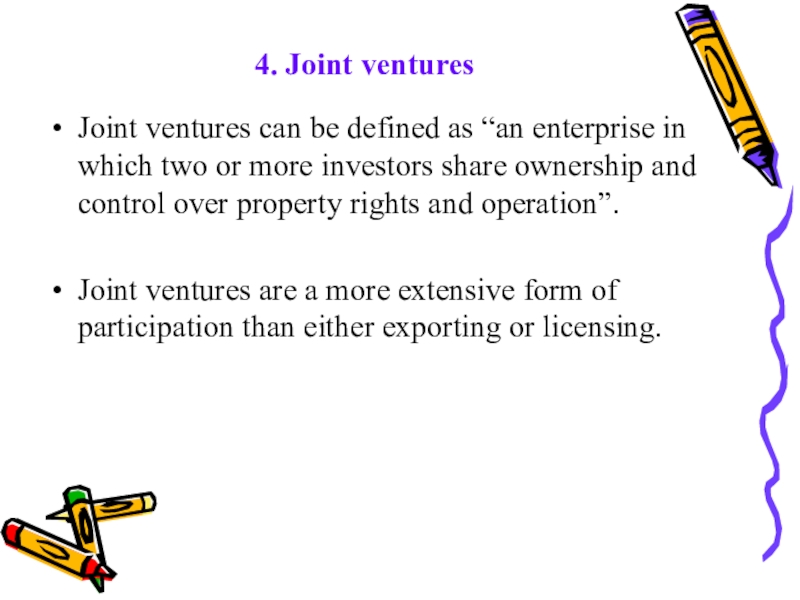
Слайд 60 4. Joint ventures
Joint ventures can be defined as “an
enterprise in which two or more investors share ownership and
control over property rights and operation”.Joint ventures are a more extensive form of participation than either exporting or licensing.
Слайд 62Xi’an Jiaotong – Liverpool University (XJTLU) is a new international
university jointly founded by Xi’an Jiaotong University China and the
University of Liverpool UK as a joint venture.The University offers undergraduate degree programmes and awards both its own Chinese degree and a degree from the University of Liverpool.
Слайд 63As part of its goal to offer a unique international
educational experience, XJTLU students can transfer to complete part of
their studies in Liverpool via a range of options.Programmes are commonly referred to (n+m) where n years of study will be in XJTLU and m at the University of Liverpool. 2+2 or 4+1.
Слайд 64Advantages
Sharing of risk and ability to combine the local
in-depth knowledge with a foreign partner with know-how in technology
or processJoint financial strength
May be the source of supply for a third country.
Слайд 65Disadvantages:
Partners do not have full control of management
May be
impossible to recover capital if need be
Partners may have different
views on expected benefits.Слайд 665. Ownership
The most extensive form of participation is
100% ownership and this involves the greatest commitment in capital
and managerial effort.The ability to communicate and control 100% may outweigh any of the disadvantages of joint ventures and licensing. However, as mentioned earlier, repatriation of earnings and capital has to be carefully monitored. The more unstable the environment the less likely is the ownership pathway an option.
Слайд 676. Merger & acquisition
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A)
are both an aspect of corporate strategy, corporate finance and
management dealing with the buying, selling, dividing and combining of different companies and similar entities that can help an enterprise grow rapidly in its sector or location of origin, or a new field or new location, without creating a subsidiary, other child entity or using a joint venture.Слайд 68A merger is a legal consolidation of two companies into
one entity.
An acquisition is the purchase of one business or
company by another company or other business entity. Such purchase may be of 100%, or nearly 100%, of the assets or ownership equity of the acquired entity (in which case the target company still exists as an independent legal entity controlled by the acquirer). Слайд 70The marriage between Geely and Volvo, largely a result of
the global economic recession, is definitely
a milestone in
the development of not only the two companies but the Chinese auto industry. It marks the largest acquisition of an overseas carmaker by a Chinese company, and is China's biggest foray into the ownership of a big luxury brand. Geely's move is seen as emblematic of the shift in the global car industry's center of gravity from the US and western Europe to China.