Слайд 1Constituent Structure of the Sentence. Syntactic Processes.
The traditional scheme of
sentence parsing.
The main sentence parts: the subject and the
predicate, their types.
The secondary sentence parts: attribute, object, adverbial modifier.
The structural scheme of the sentence. The elementary sentence.
Syntactic processes.
Слайд 22. The Subject
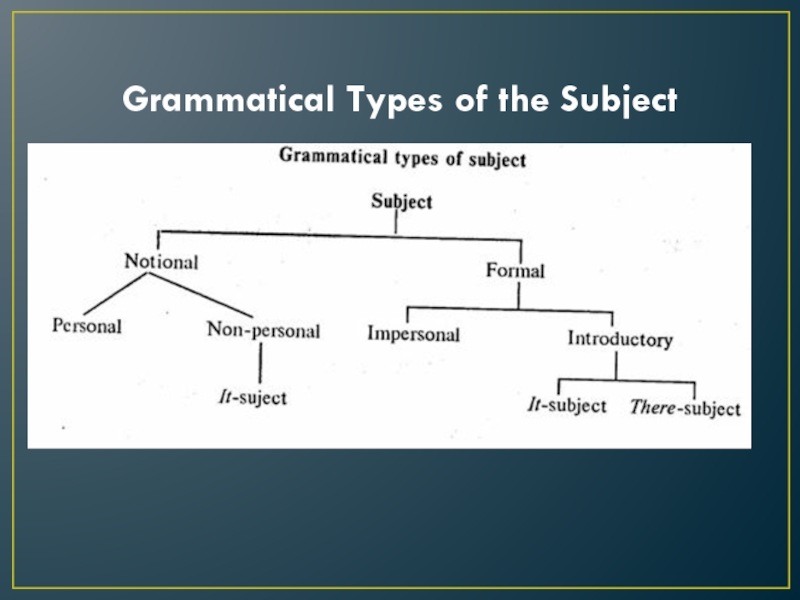
The subject is one of the two main
parts of the sentence.
It denotes the thing whose action
or characteristic is expressed by the predicate.
It may be expressed by different parts of speech.
Слайд 3Grammatical Types of the Subject
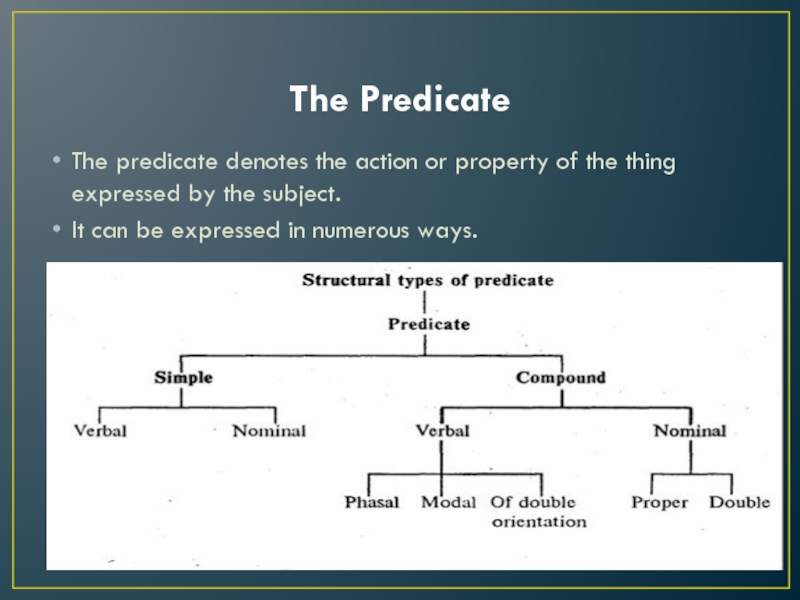
Слайд 4The Predicate
The predicate denotes the action or property of the
thing expressed by the subject.
It can be expressed in
numerous ways.
Слайд 5Sentences for Analysis
John runs quickly.
Did you have a sleep?
Nick, dishonest!
Jack
started training out at a health farm.
As we continued to
laugh his surprise gave way to annoyance.
Alfredo used to talk to me about it.
May I ask you a question?
He is said to be looking for a new job.
I felt sore for a minute.
Слайд 63. The Secondary Sentence Parts
The Object
1. Objects are divided into
direct, indirect and prepositional.
2. Objects are grouped into prepositional and
non-prepositional.
3. Prof. Pocheptsov singles out the following types of objects:
Object object (дополнение объекта)
e.g. He saw me. He looked at me.
Addressee object (дополнение адресата)
e.g. He gave her money. He wrote to me.
Subject object (дополнение субъекта)
e.g. He was exhausted by her outburst.
Слайд 7The Adverbial Modifier
It is a secondary part of the sentence
modifying a part of the sentence serving to characterise an
action or a property as to its quality or intensity, or to indicate the way an action is done, the time, place, cause, purpose, or condition, with which the action or the manifestation of the quality is connected.
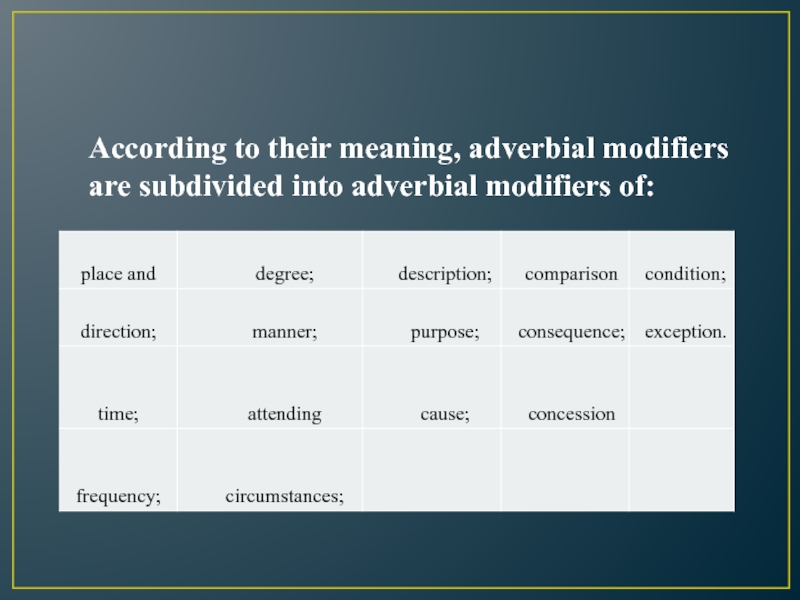
Слайд 8According to their meaning, adverbial modifiers
are subdivided into adverbial
modifiers of:
Слайд 9The Attribute
Attribute is a dependent element of a nominative phrase
that denotes an attributive quality of an object expressed by
a noun.
It is a secondary part of the sentence modifying a part of the sentence expressed by a noun, a pronoun, a cardinal numeral, and any substantivised word, and characterizing the thing named by these words as to its quality or property.
Слайд 10The Apposition
Apposition has been often regarded as a special kind
of attribute, and sometimes as a secondary part of a
sentence distinct from an attribute.
Apposition is a word or phrase referring to a part of the sentence expressed by a noun, and explaining and specifying its meaning by giving it another name.
Слайд 114. Structural Schemes of the Sentence. The Elementary Sentence
The structural
scheme of the sentence is a sentence structure minimal by
its composition and simplest by grammatical and semantic structure.
A construction built according to a structural scheme and realizing all of its components is called an elementary sentence.
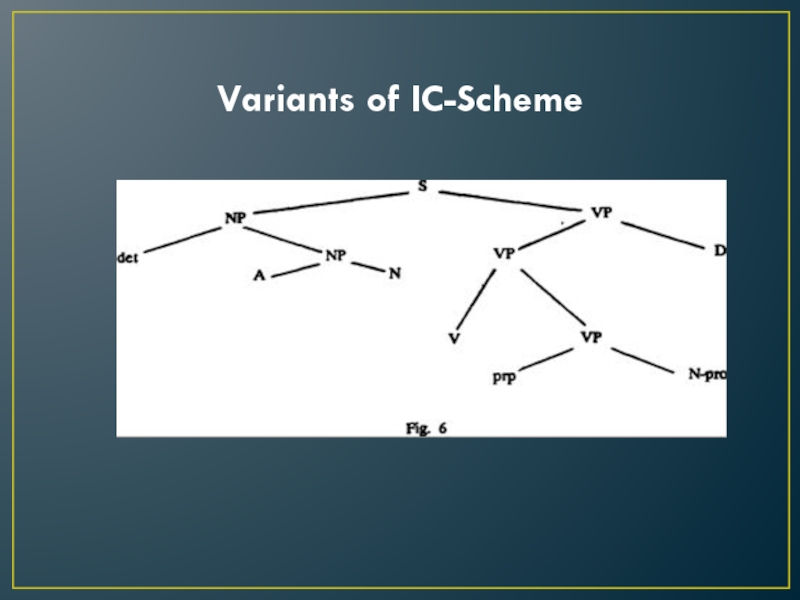
Слайд 12Prof. Pocheptsov lists some structural schemes for verbal sentences and
examples of corresponding elementary sentences:
Subject – predicate expressed by a
verb of non-directed action (Active Voice).
Subject – predicate expressed by a verb of non-prepositional-object directivity (Active Voice)– direct object.
Subject – predicate expressed by a verb requiring two non-prepositional objects: object of addressee and object of patient (Active voice) – non-prepositional object of addressee – non-prepositional object of patient.
Слайд 13Subject – predicate expressed by a verb of spatial directivity
(Active Voice) – adverbial modifier of place.
Subject – predicate expressed
by a verb of temporal directivity (Active Voice) – adverbial modifier of time.
Subject – predicate expressed by a verb of non-prepositional object directivity (Passive Voice).
Слайд 175. Syntactic Processes
Expansion / Extension (расширение) consists in adding of
some syntactic units to another unit.
The added elements have
the same syntactic status as the expanded element.
The simplest type of expansion is repetition of some element in a syntagmatic chain.
e.g. Good, good boy. I walked and walked
Слайд 18Addition (аддиция) takes place when each element of expansion relates
to others as both semantically and syntactically independent unit. (e.g.
She cried bitterly and with despair.)
Specification (спецификация) can be observed when one syntactic unit semantically develops the other, makes it more specific. (e.g. I’ll give you a call tomorrow, after 5 p.m.)
Слайд 19Complication is a syntactic process that consists in transforming the
structure of a syntactic unit from simple to complex.
The
complicacy of structure presupposes a mutual syntactic dependence of the unit’s constituents.
e.g. She cried. She began to cry.
Слайд 20Complication of the predicate. The following three types of complication
are singled out according to the morphological appurtenance of the
complicating element:
active-verbal complication (e.g. I have to go);
passive-verbal complication (e.g. He is expected to come);
adjectival complication (e.g. He is unlikely to come).
Слайд 21Complication of the object. Complication of the direct object is
possible after verbs of certain semantics.
It consists in adding
an infinitive, a participle, an adjective, or a prepositional group to a noun or a pronoun performing the function of the object.
The object and the complicating element stand in the relations of secondary predication.
e.g. I found him attractive. She considered me a fool.
Слайд 22Contamination has a restricted usage. It can be applied only
to the predicate.
The result of contamination is the so-called
double, or contaminated, predicate.
e.g. The sun shone glaring and dazzling.
Слайд 23Development (развертывание) is a modification of one element by another
element which depends on the former.
Syntactic groups that appear
in the result of development are of endocentric character, their syntactic behavior is that of the central element before it was modified
e.g.
N → AN: flower – beautiful flower;
V → VAdv: walked – walked slowly;
A → AdvA: beautiful – strikingly beautiful.
Слайд 24Adjunction (присоединение) is similar to development. It consists in modifying
words as syntactic elements with particles (e.g. only for you,
just in case, even at such a great sum).
Inclusion (включение) consists in inserting modal words and similar elements into a sentence. (e. g. Apparently, this is the only way out. A true friend, indeed.)
Isolation is a syntactic process aimed at accentuating some sentence member or sentence member group. (e. g. I used to. At home.)
Слайд 25Substitution (замещение) is a use of words with generalized structural
meaning instead of words and constructions with specific meaning which
were mentioned earlier.
e.g. Do you want me to open the window? – Yes, please do.
Representation (репрезентация) consists in using a part of some syntactic unit representing the whole unit.
e.g. Could you help me? – I will be happy to.
Слайд 26Ellipsis (опущение) takes place when a structurally needed element of
the construction is not explicitly used but only implied. The
omitted element can be restored from the context.
e.g. It seems so strange! – It is!