Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Lung Examination: Abnormal
Содержание
- 1. Lung Examination: Abnormal
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. Слайд 4
- 5. Illustrative Pathological problemsConsolidationAtelectasisPleural effusionPneumothoraxMassDiffuse lung disease
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. StepsGeneral ExaminationMediastinal positionChest expansionLung resonanceBreath soundsAdventitious soundsVoice transmission
- 13. General ExaminationRespiratory ratePattern of breathingCyanosisClubbingWeightCoughHospital settingEffort of ventilationShape of thorax
- 14. Respiratory RateBradypnea: rate less than 8 per minute Tachypnea: rate greater than 25 per minute
- 15. Pattern of BreathingKussmalsSleep apneaCheyne strokesPursed lip breathingOrthopnoea:
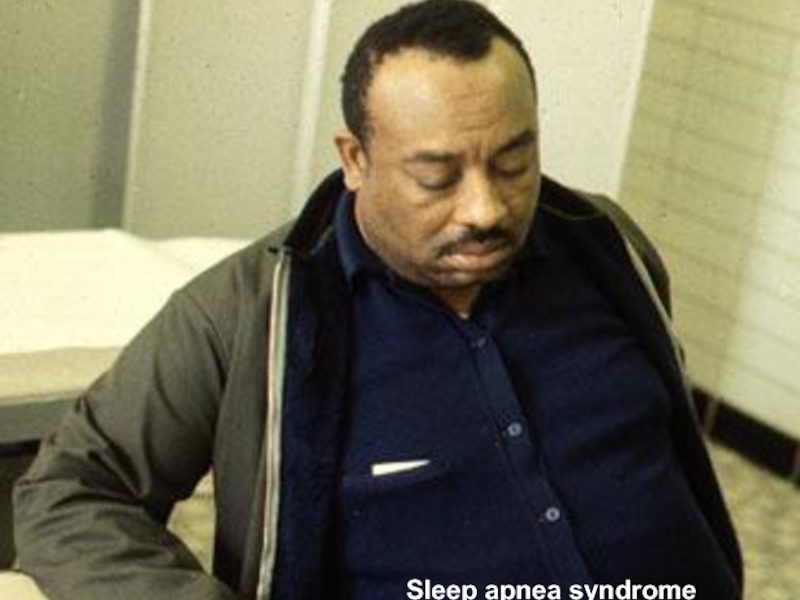
- 16. Sleep apnea syndrome
- 17. Central CyanosisResults from pulmonary dysfunction, the mucous
- 18. Central Cyanosis
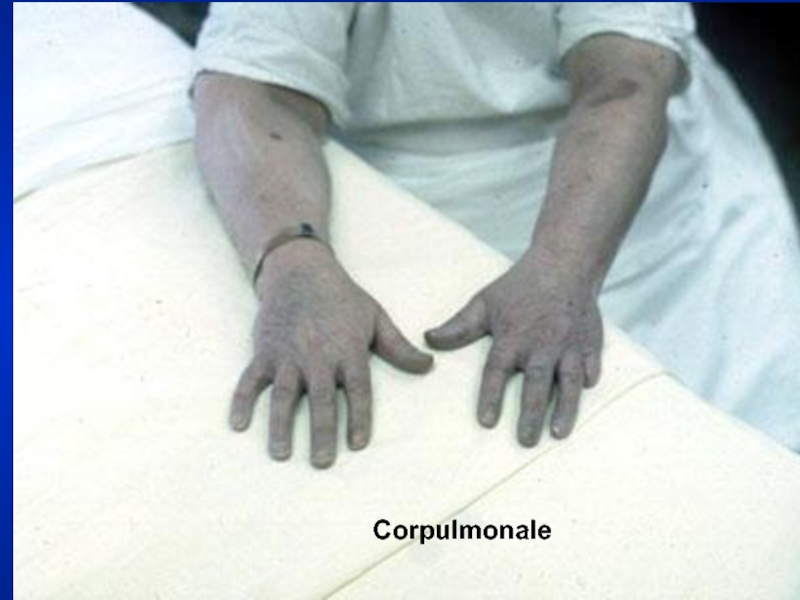
- 19. Corpulmonale
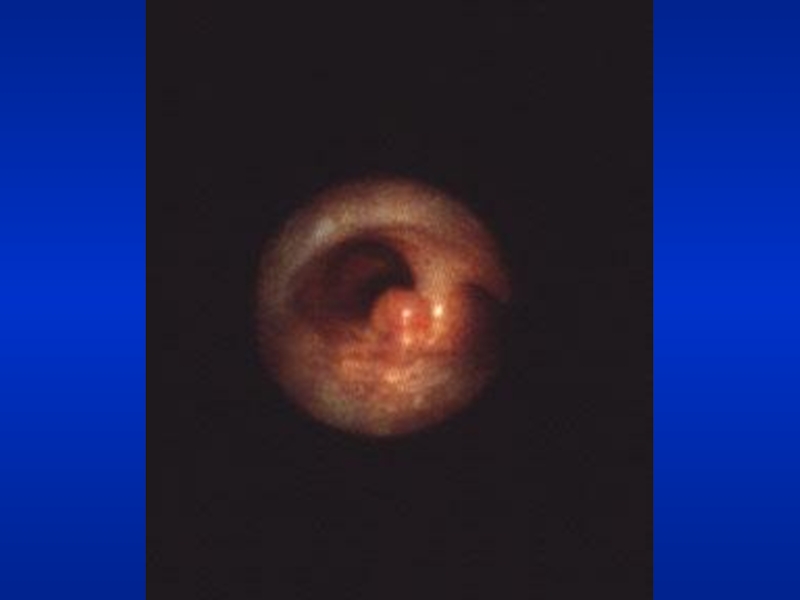
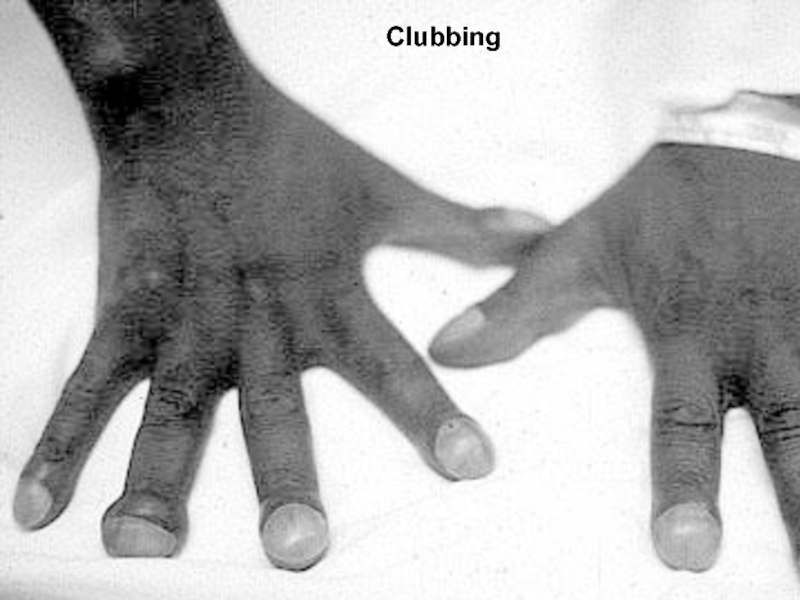
- 20. Clubbing
- 21. ClubbingIn clubbing, there is widening of the
- 22. Significance: Clubbing Observed In:Intrathoracic malignancy: Primary or
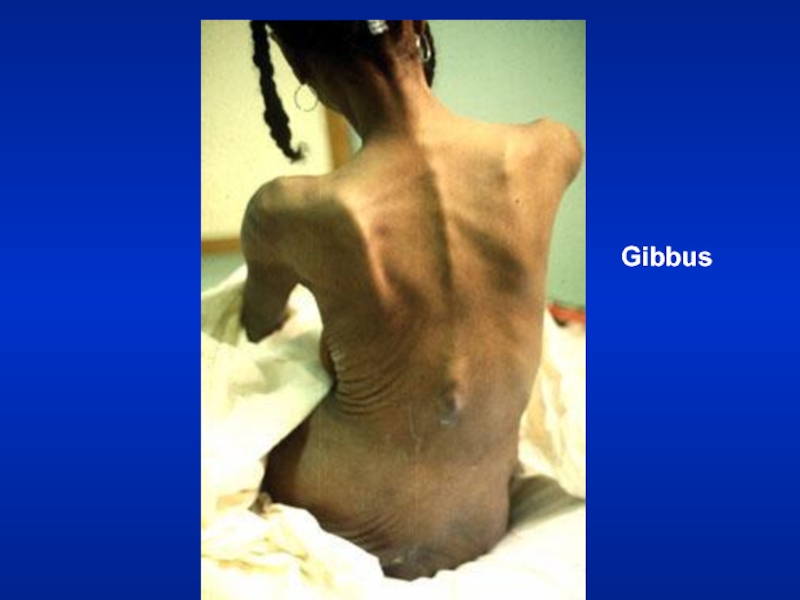
- 23. Gibbus
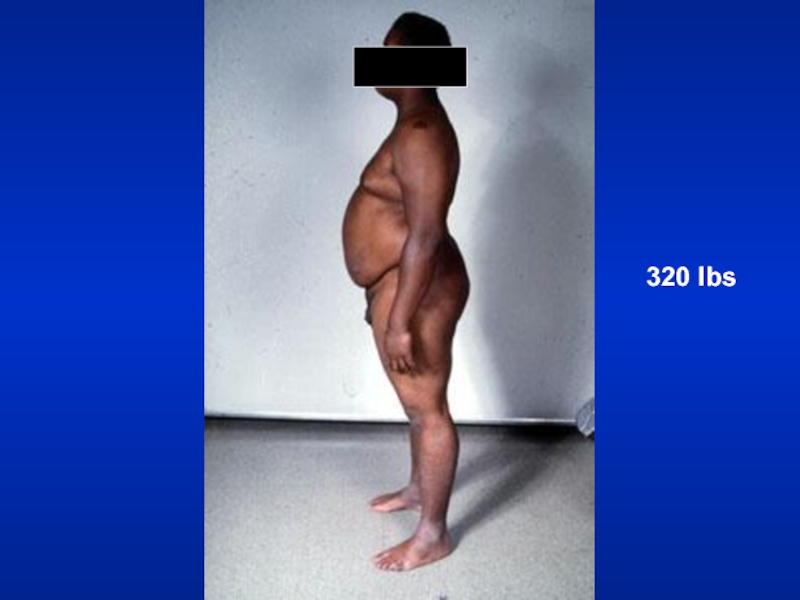
- 24. WeightEmaciation cachecticMalignancyTuberculosis
- 25. 320 lbs
- 26. WeightObese: Sleep apnea syndrome
- 27. 3 Layered sputum
- 28. CoughProductiveDryWhoopingBovine
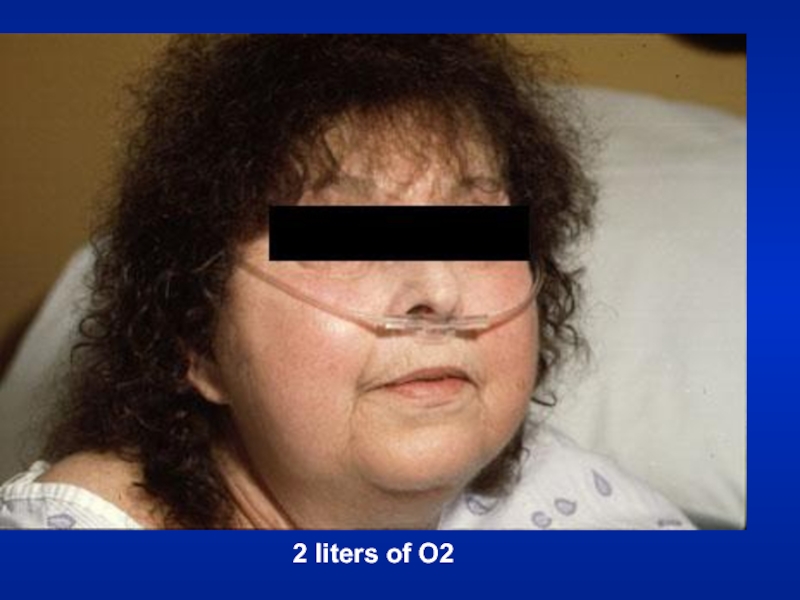
- 29. 2 liters of O2
- 30. Hospital SettingIsolation roomOxygen set up
- 31. Effort of VentilationPerson appears uncomfortable. Breathing seems
- 32. Resting Size and Shape of ThoraxBarrel chestKyphosisScoliosisPectus excavatumGibbus
- 33. Barrel ChestAP Diameter = Transverse Diameter
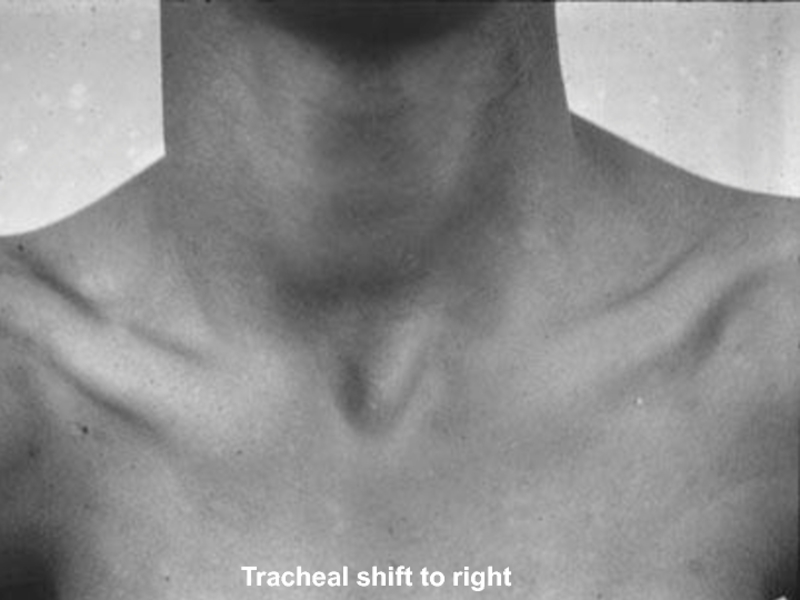
- 34. Tracheal Position: MediastinumAny deviation of the mediastinum
- 35. Tracheal shift to right
- 36. Chest ExpansionAsymmetrical chest expansion is abnormalThe abnormal
- 37. Percussion: Decreased or Increased Resonance is AbnormalDullnessDecreased
- 38. Breath Sounds: Diminished or AbsentIntensity of breath
- 39. BronchialBronchial breathing anywhere other than over the
- 40. Bronchial breathing
- 41. RhonchiRhonchi are long continuous adventitious sounds, generated
- 42. RhonchiAsthmaticContinuous
- 43. RhonchiLocalized rhonchi suggests obstruction of any etiology
- 44. Pleural RubNormal parietal and visceral pleura glide
- 45. Pleural rubScratching, GratingRelated to respiration
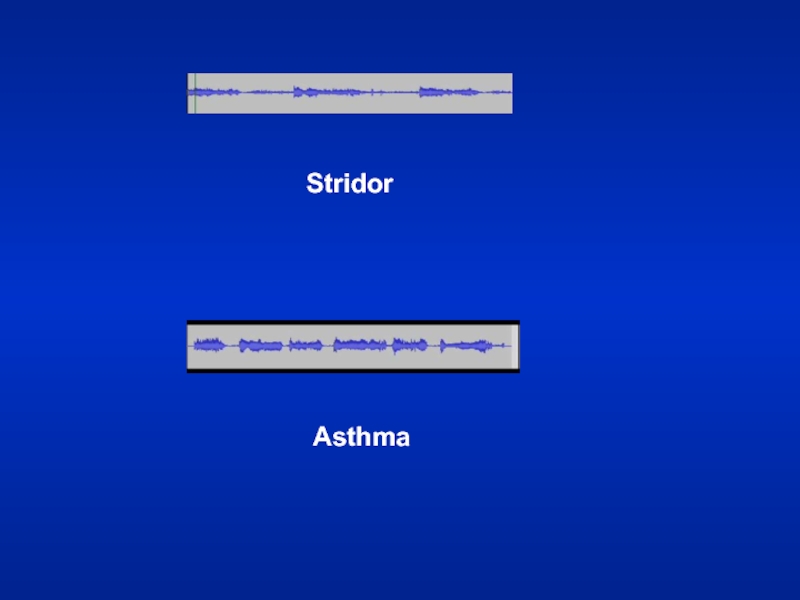
- 46. StridorLoud audible inspiratory rhonchi is called a stridor.Inspiratory rhonchi in general, implies large airway obstruction.
- 47. StridorAsthma
- 48. CracklesInterrupted adventitious sounds are called crackles.Make a
- 49. CracklesWhen the crackles are heard at the
- 50. Voice Transmission (tactile fremitus, vocal resonance)Asymmetrical voice
- 51. Voice Transmission (tactile fremitus, vocal resonance)Decreased: A
- 52. Voice TransmissionBronchophonyWhispering PectoroliquyNormal whisperEgophony
- 53. Скачать презентанцию
Illustrative Pathological problemsConsolidationAtelectasisPleural effusionPneumothoraxMassDiffuse lung disease
Слайды и текст этой презентации
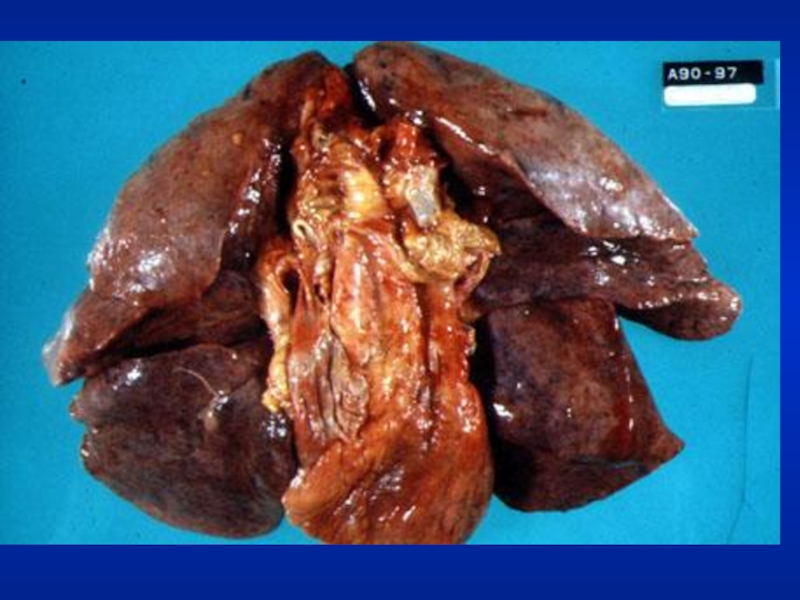
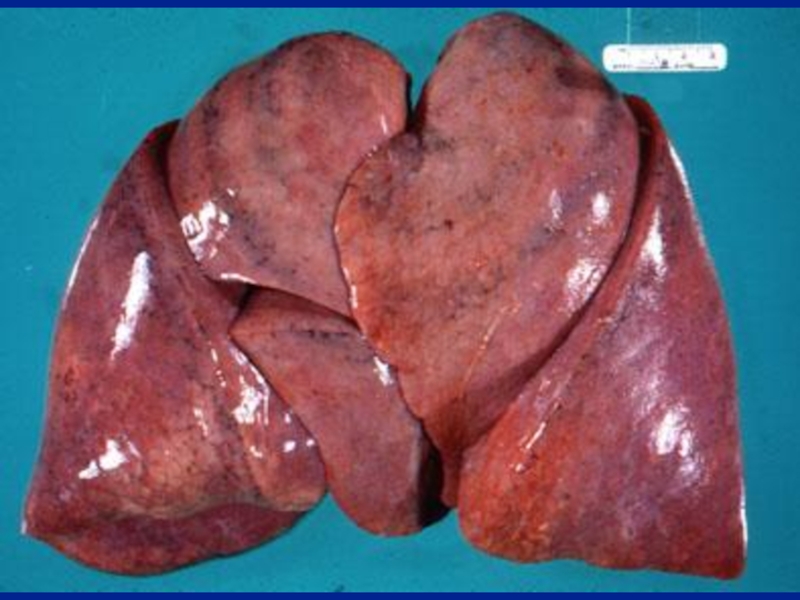
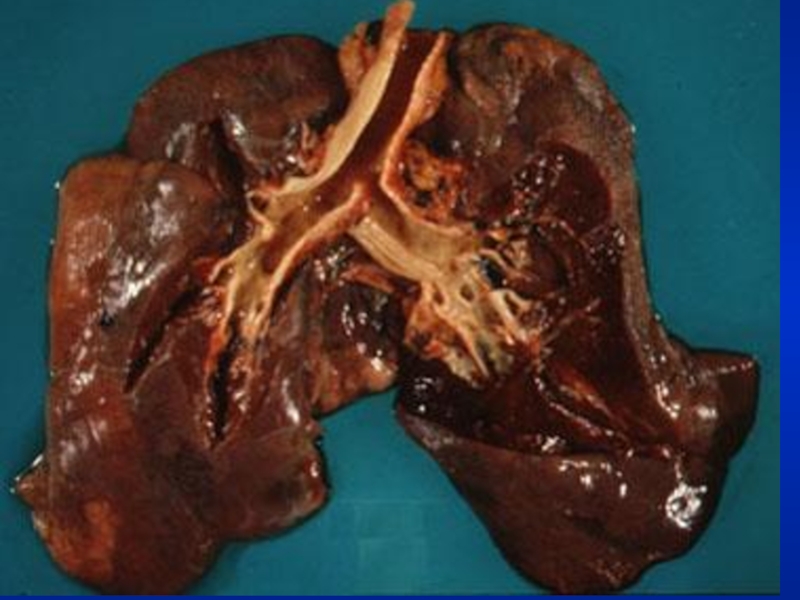
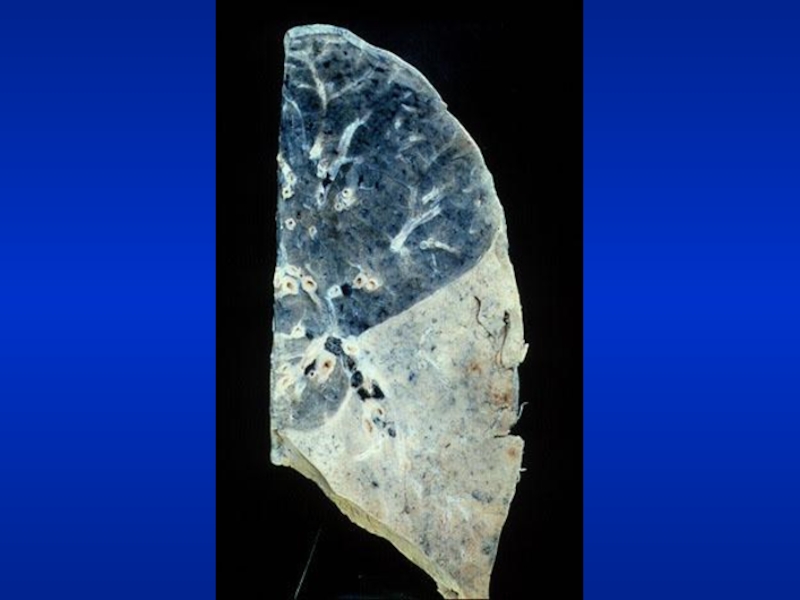
Слайд 5Illustrative Pathological problems
Consolidation
Atelectasis
Pleural effusion
Pneumothorax
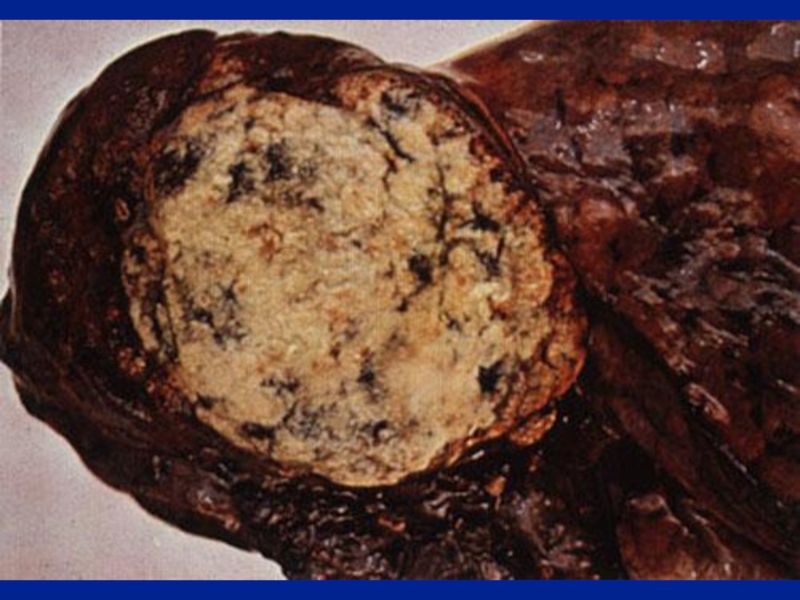
Mass
Diffuse lung disease
Слайд 12Steps
General Examination
Mediastinal position
Chest expansion
Lung resonance
Breath sounds
Adventitious sounds
Voice transmission
Слайд 13General Examination
Respiratory rate
Pattern of breathing
Cyanosis
Clubbing
Weight
Cough
Hospital setting
Effort of ventilation
Shape of thorax
Слайд 14Respiratory Rate
Bradypnea: rate less than 8 per minute
Tachypnea: rate
greater than 25 per minute
Слайд 15Pattern of Breathing
Kussmals
Sleep apnea
Cheyne strokes
Pursed lip breathing
Orthopnoea: Short of breath
in supine position, gets some relief by sitting or standing
up.Слайд 17Central Cyanosis
Results from pulmonary dysfunction, the mucous membrane of conjunctiva
and tongue are bluish.
If there was chronic hypoxemia and secondary
erythrocytosis, you can detect the conjunctival and scleral vessels to be full, tortuous and bluish.Слайд 21Clubbing
In clubbing, there is widening of the AP and lateral
diameter of terminal portion of fingers and toes giving the
appearance of clubbing.The angle between the nail and skin is greater than 180.
The periungual skin is stretched and shiny.
There is fluctuation of the nail bed.
One can feel the posterior edge of the nail.
Слайд 22Significance: Clubbing Observed In:
Intrathoracic malignancy: Primary or secondary (lung, pleural,
mediastinal)
Suppurative lung disease: (lung abscess, bronchiectasis, empyema)
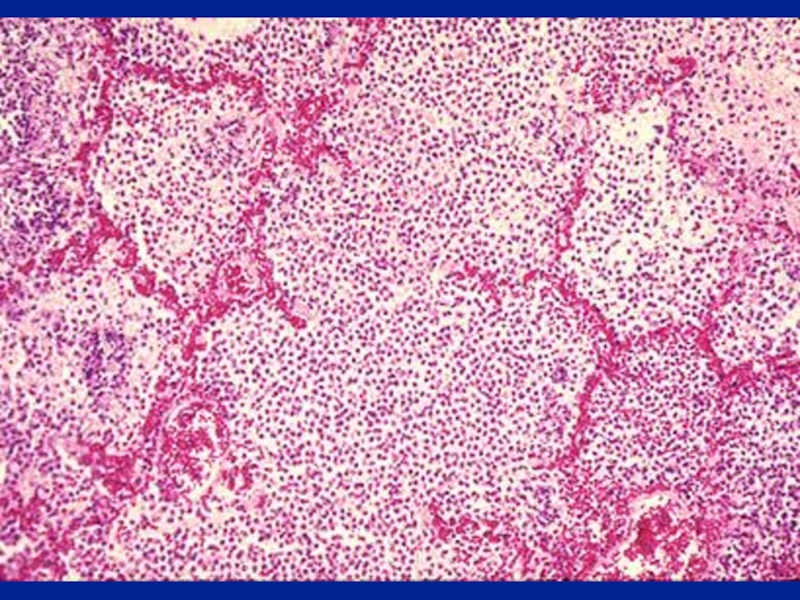
Diffuse interstitial fibrosis: Alveolar
capillary block syndromeIn association with other systemic disorders
Слайд 31Effort of Ventilation
Person appears uncomfortable. Breathing seems voluntary.
Accessory muscles are
in use, expiratory muscles are active and expiration is not
passive any more.The degree of negative pleural pressure is high.
The respiratory rate is increased.
Слайд 34Tracheal Position: Mediastinum
Any deviation of the mediastinum is abnormal
Lateral shift:
The mediastinum can be either pulled or pushed away from
the lesionPull: Loss of lung volume (Atelectasis, fibrosis, agenesis, surgical resection, pleural fibrosis)
Push: Space occupying lesions (pleural effusion, pneumothorax, large mass lesions)
Mediastinal masses and thyroid tumors
Слайд 36Chest Expansion
Asymmetrical chest expansion is abnormal
The abnormal side expands less
and lags behind the normal side
Any form of unilateral lung
or pleural disease can cause asymmetry of chest expansionGlobal expansion decrease
Слайд 37Percussion: Decreased or Increased Resonance is Abnormal
Dullness
Decreased resonance is noted
with pleural effusion and all other lung diseases
The dullness is
flat and the finger is painful to percussion with pleural effusionHyper resonance: Increased resonance can be noted either due to lung distention as seen in asthma, emphysema, bullous disease or due to Pneumothorax
Traube's space
Слайд 38Breath Sounds: Diminished or Absent
Intensity of breath sounds, in general,
is a good index of ventilation of the underlying lung.
Breath
sounds are markedly decreased in emphysema.Symmetry: If there is asymmetry in intensity, the side where there is decreased intensity is abnormal.
Any form of pleural or pulmonary disease can give rise to decreased intensity.
Harsh or increased: If the intensity increases there is more ventilation and vice versa.
Слайд 39Bronchial
Bronchial breathing anywhere other than over the trachea, right clavicle
or right inter-scapular space is abnormal.
In consolidation, the bronchial breathing
is low pitched and sticky and is termed tubular type of bronchial breathing.In cavitary disease, it is high pitched and hollow and is called cavernous breathing. You can simulate this sound by blowing over an empty coke bottle.
Слайд 41Rhonchi
Rhonchi are long continuous adventitious sounds, generated by obstruction to
airways.
When detected, note whether it is generalized or localized, during
inspiration or expiration, and the pitch.Diffused rhonchi would suggest a disease with generalized airway obstruction like asthma or COPD.
Слайд 43Rhonchi
Localized rhonchi suggests obstruction of any etiology e.g., tumor, foreign
body or mucous.
Mucous secretions will disappear with coughing, so would
the rhonchus.Expiratory rhonchi implies obstruction to intrathoracic airways.
Asthmatics can also have inspiratory rhonchi while it is uncommon in COPD.
Слайд 44Pleural Rub
Normal parietal and visceral pleura glide smoothly during respiration.
If
the pleura is roughened due to any reason, a scratching,
grating sound, related to respiration is heard.You can hear the sound by compressing harder with the stethoscope and making the patient take deep breaths.
It is localized and can be palpable.
Слайд 46Stridor
Loud audible inspiratory rhonchi is called a stridor.
Inspiratory rhonchi in
general, implies large airway obstruction.
Слайд 48Crackles
Interrupted adventitious sounds are called crackles.
Make a notation about timing,
intensity, effect with respiration, position, coughing and character.
Timing and Intensity
Crackles heard only at the end of inspiration are called fine crackles.When the surfactant is depleted, the alveoli collapse. Air enters the alveoli at the end of inspiration.
This sound is generated as the alveoli pop open from it's collapsed state.
Слайд 49Crackles
When the crackles are heard at the end of inspiration
and the beginning of expiration the fluid or secretions are
probably in respiratory bronchioles: medium crackles.If the crackles are heard throughout it implies the secretions are in bronchi: coarse crackles.
Слайд 50Voice Transmission (tactile fremitus, vocal resonance)
Asymmetrical voice transmission points to
disease on one side.
Increased:
Any situation where bronchial breathing is heard
the sounds become loud, sharp and distinct: Bronchophony.In extreme situations, the whispered words come clearly and distinctly: Whispering pectoriloquy.
Слайд 51Voice Transmission (tactile fremitus, vocal resonance)
Decreased: A quantitative decrease in
voice transmission could be due to any other form of
lung or pleural disease.Qualitative alteration:
A qualitative alteration of voice transmission is noted over consolidation and along the upper margin of pleural effusion: Egophony
The sound is like a nasal twang or goat bleating.