Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Marketing, lecture 10 ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D) 1 Slide 12-2 PRICING
Содержание
- 1. Marketing, lecture 10 ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D) 1 Slide 12-2 PRICING
- 2. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-5LECTURE QUESTIONS:Elements
- 3. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-6LECTURE QUESTIONS:Explain
- 4. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-7LECTURE QUESTIONS:The
- 5. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)NATURE AND IMPORTANCE OF PRICESlide 12-11What is a Price? Price Barter
- 6. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-80Price is
- 7. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-12 The price of three different purchases
- 8. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)NATURE AND IMPORTANCE
- 9. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-81A firm’s
- 10. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-17 Four approaches for selecting an approximate price level
- 11. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)GENERAL PRICING APPROACHESSlide
- 12. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)GENERAL PRICING APPROACHESSlide 12-23Demand-Oriented Approaches Target Pricing Bundle Pricing Yield Management Pricing
- 13. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-24 1.
- 14. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-25 2.
- 15. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-26 3.
- 16. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)GENERAL PRICING APPROACHESSlide
- 17. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)GENERAL PRICING APPROACHESSlide
- 18. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)ESTIMATING DEMAND AND
- 19. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-82A demand
- 20. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)ESTIMATING DEMAND AND
- 21. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-36 1.
- 22. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-37 2.
- 23. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-38 3.
- 24. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)ESTIMATING DEMAND AND REVENUESlide 12-39Fundamentals of Estimating Revenue Total Revenue
- 25. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-83Total revenue
- 26. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-40 Fundamental revenue concept
- 27. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)DETERMINING COST, VOLUME,
- 28. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-84Total cost
- 29. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-85Fixed cost
- 30. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-86Variable cost
- 31. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-42 Fundamental cost concepts
- 32. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)DETERMINING COST, VOLUME,
- 33. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-87Break-even analysis
- 34. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-46 1.
- 35. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-47 2.
- 36. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)PRICING OBJECTIVES AND
- 37. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-88Pricing objectives
- 38. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)PRICING OBJECTIVES AND
- 39. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)PRICING OBJECTIVES AND
- 40. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-89Pricing constraints
- 41. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)PRICING OBJECTIVES AND
- 42. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-54 1.
- 43. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-55 2.
- 44. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)SETTING A FINAL
- 45. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)SETTING A FINAL
- 46. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)SETTING A FINAL
- 47. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-62 1.
- 48. Marketing, lecture 10ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)Slide 12-63 2.
- 49. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-2
PRICING
PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
CHAPTER
Lecture 9_Pricing
Associate professor
of Plekhanov REA marketing department
Слайд 2Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-5
LECTURE QUESTIONS:
Elements of price.
Demand-oriented, cost-oriented,
profit-oriented, and competition-oriented approaches to pricing
Слайд 3Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-6
LECTURE QUESTIONS:
Explain what a demand
curve is and what price elasticity of demand means.
Explain the
role of revenues (sales) and costs in pricing decisions.Understand the value of break-even analysis.
Слайд 4Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-7
LECTURE QUESTIONS:
The objectives a firm
has in setting prices and the constraints on the range
of prices a firm can charge.Describe the special adjustments made to the approximate price level on the basis of geography, discounts, and allowances.
Слайд 5Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
NATURE AND IMPORTANCE
OF PRICE
Slide 12-11
What is
a Price?
Price
Barter
Слайд 6Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-80
Price is the money or
other considerations, including other goods and services, exchanged for the
ownership or use of a product.Price
Слайд 7Marketing, lecture 10
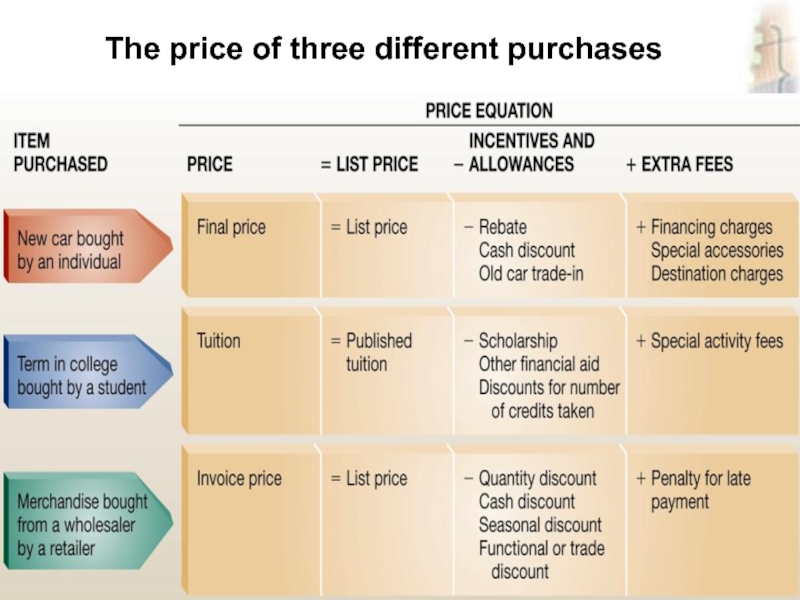
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-12
The price of three
different purchases
Слайд 8Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
NATURE AND IMPORTANCE
OF PRICE
Slide 12-16
Value
Pricing
Profit Equation
Price as an Indicator of Value
Price in the
Marketing MixСлайд 9Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-81
A firm’s profit equation is
as follows:
Profit = Total Revenue – Total Cost or
Profit =
(Unit Price x Quantity Sold) – Total Cost.Profit Equation
Слайд 10Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
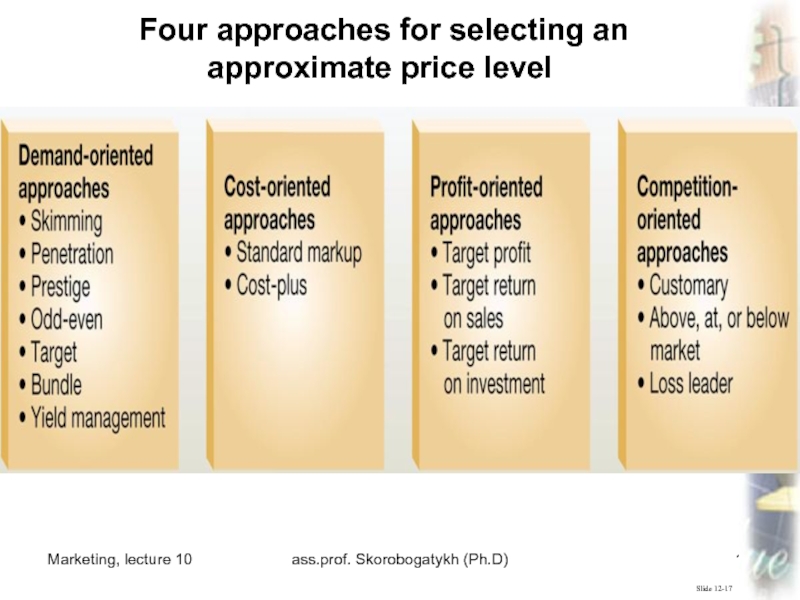
Slide 12-17
Four approaches for selecting
an approximate price level
Слайд 11Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
GENERAL PRICING APPROACHES
Slide 12-18
Demand-Oriented Approaches
Skimming
Pricing
Penetration Pricing
Prestige Pricing
Odd-Even Pricing
Слайд 12Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
GENERAL PRICING APPROACHES
Slide 12-23
Demand-Oriented Approaches
Target
Pricing
Bundle Pricing
Yield Management Pricing
Слайд 13Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-24
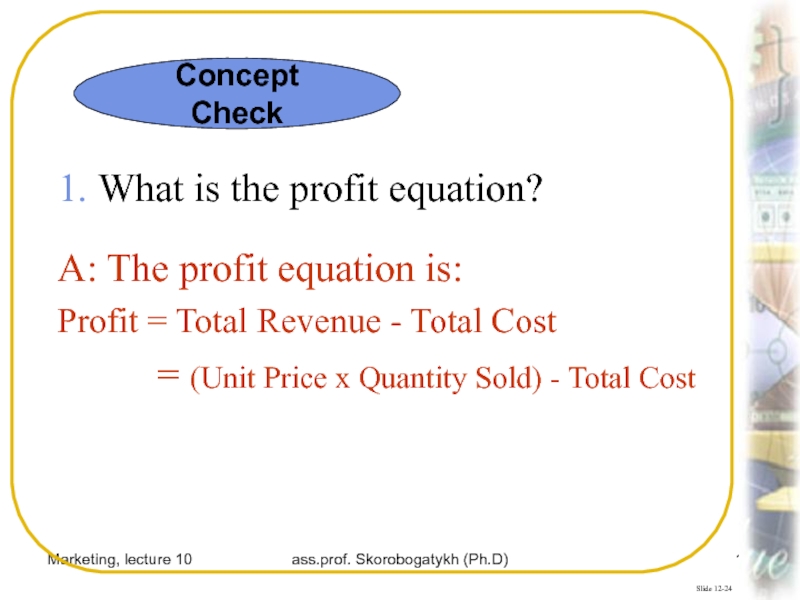
1. What is the
profit equation?
A: The profit equation is:
Profit = Total Revenue -
Total Cost= (Unit Price x Quantity Sold) - Total Cost
Concept Check
Слайд 14Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-25
2. What is the
difference between skimming and penetration pricing?
A: A firm introducing a
new product can use either skimming pricing to set the highest initial price that customers desiring the product are willing to pay or penetration pricing to set a low initial price to appeal immediately to the mass market.Concept Check
Слайд 15Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-26
3. What is odd-even
pricing?
A: Odd-even pricing involves setting prices a few dollars or
cents under an even number ($599.99 vs. $600.00). Psychologically, the $599.99 price feels lower than $600.00, even though the difference is 1 cent.Concept Check
Слайд 16Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
GENERAL PRICING APPROACHES
Slide 12-27
Cost-Oriented Approaches
Standard
Markup Pricing
Cost-Plus Pricing
Profit-Oriented Approaches
Target Profit Pricing
Target Return-on-Sales
Pricing Target Return-on-Investment Pricing
Слайд 17Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
GENERAL PRICING APPROACHES
Slide 12-29
Competition-Oriented Approaches
Customary
Pricing
Above-, At-, or Below-Market Pricing
Loss-Leader Pricing
Слайд 18Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
ESTIMATING DEMAND
AND REVENUE
Slide 12-30
Fundamentals of Estimating
Demand
Demand Curve
Consumer Tastes
Price & Availability of Similar
Products Consumer Income
Слайд 19Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-82
A demand curve shows the
number of products that will be sold at a given
price.Demand Curve
Слайд 20Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
ESTIMATING DEMAND
AND REVENUE
Slide 12-32
Fundamentals of Estimating
Demand
Movement Along vs.
Shift of a Demand Curve
Elastic Demand
Price
Elasticity of Demand Inelastic Demand
Слайд 21Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-36
1. What is loss-leader
pricing?
A: For a special promotion, retail stores deliberately sell a
product below its customary price to attract customers in hopes they will buy other products as well, particularly the discretionary items with large markups.Concept Check
Слайд 22Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-37
2. What are the
four demand factors that determine consumers’ willingness and ability to
pay for goods and services?A: They are price, consumer tastes, price and availability of similar products, and consumer income.
Concept Check
Слайд 23Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-38
3. What is the
difference between movement along a demand curve and a shift
in a demand curve?A: A movement along a demand curve occurs when the price is lowered and the quantity demanded increases (and vice versa), assuming that other factors remain unchanged. However, if these factors change, then the demand curve will shift.
Concept Check
Слайд 24Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
ESTIMATING DEMAND
AND REVENUE
Slide 12-39
Fundamentals of Estimating
Revenue
Total Revenue
Слайд 25Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-83
Total revenue is the total
money received from the sale of a product. Total revenue
(TR) equals the unit price (P) times the quantity sold (Q) or TR = P x Q.Total Revenue
Слайд 27Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
DETERMINING COST, VOLUME, AND PROFIT RELATIONSHIPS
Slide
12-41
The Importance of Controlling Costs
Total Cost
Fixed Cost
Variable
CostСлайд 28Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-84
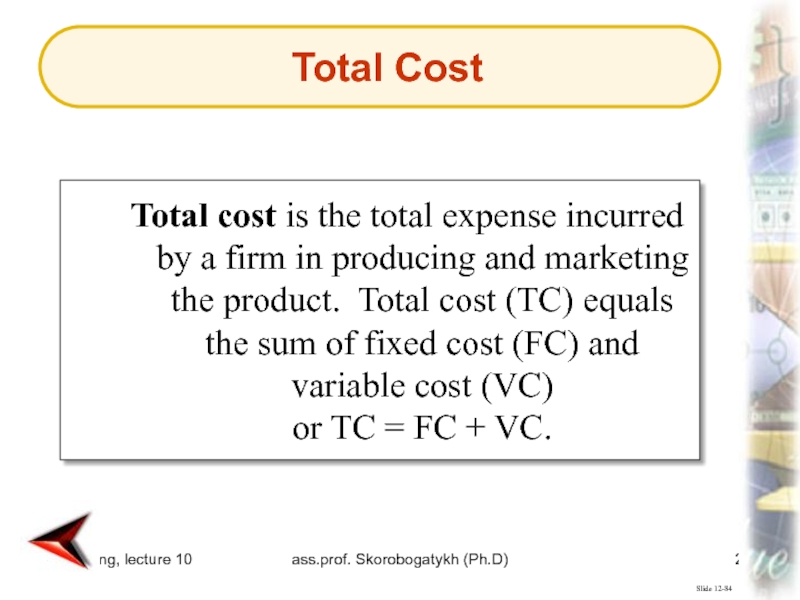
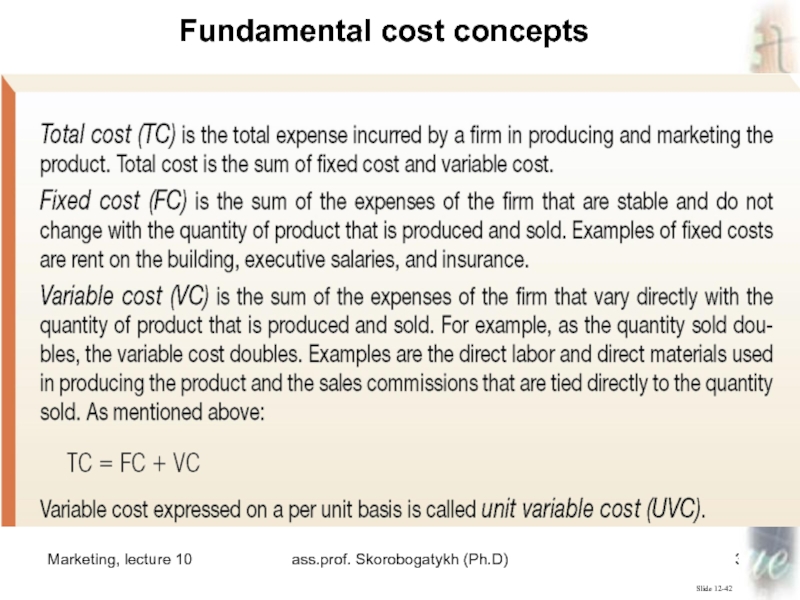
Total cost is the total
expense incurred by a firm in producing and marketing the
product. Total cost (TC) equals the sum of fixed cost (FC) and variable cost (VC) or TC = FC + VC.Total Cost
Слайд 29Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-85
Fixed cost (FC) is the
sum of the expenses of the firm that are stable
and do not change with the quantity of the product that is produced and sold. Examples include rent, executive salaries, and insurance.Fixed Cost
Слайд 30Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-86
Variable cost (VC) is the
sum of the expenses of the firm that vary directly
with the quantity of the product that is produced and sold. Examples include direct labor and direct materials used to produce the product and the sales commissions tied to the quantity sold.Variable Cost
Слайд 32Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
DETERMINING COST, VOLUME, AND PROFIT RELATIONSHIPS
Slide
12-43
Break-Even Analysis
Break-Even Point (BEP)
Applications of Break-Even Analysis
Calculating
a Break-Even Point Break-Even Chart
Слайд 33Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-87
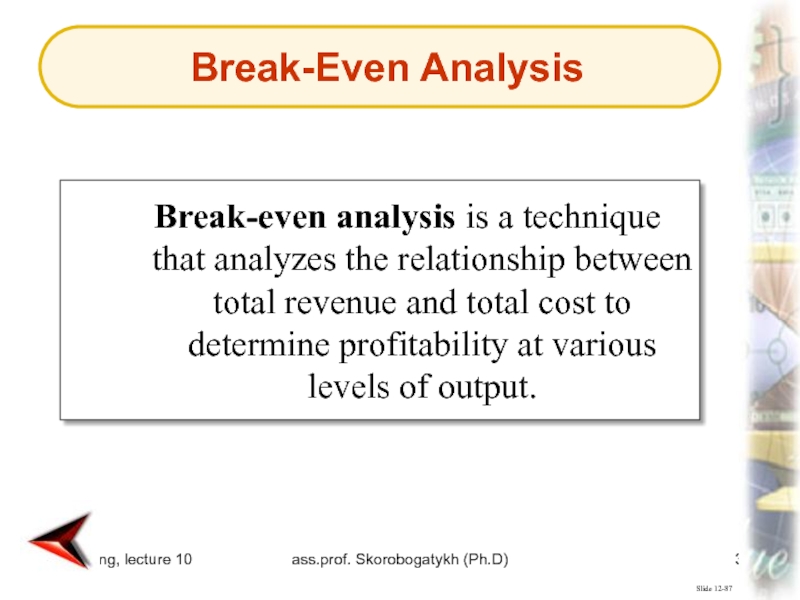
Break-even analysis is a technique
that
analyzes the relationship between total revenue and total cost to
determine profitability at various levels of output.Break-Even Analysis
Слайд 34Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-46
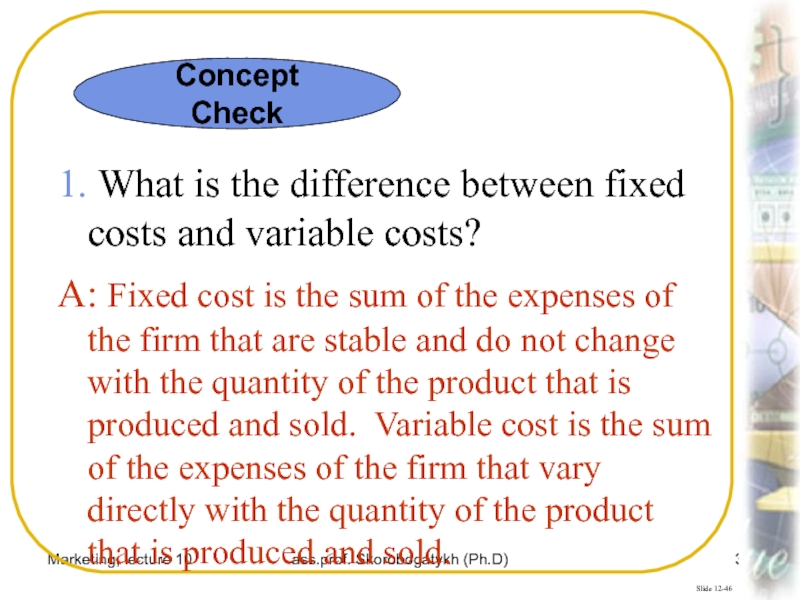
1. What is the
difference between fixed costs and variable costs?
A: Fixed cost is
the sum of the expenses of the firm that are stable and do not change with the quantity of the product that is produced and sold. Variable cost is the sum of the expenses of the firm that vary directly with the quantity of the product that is produced and sold.Concept Check
Слайд 35Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-47
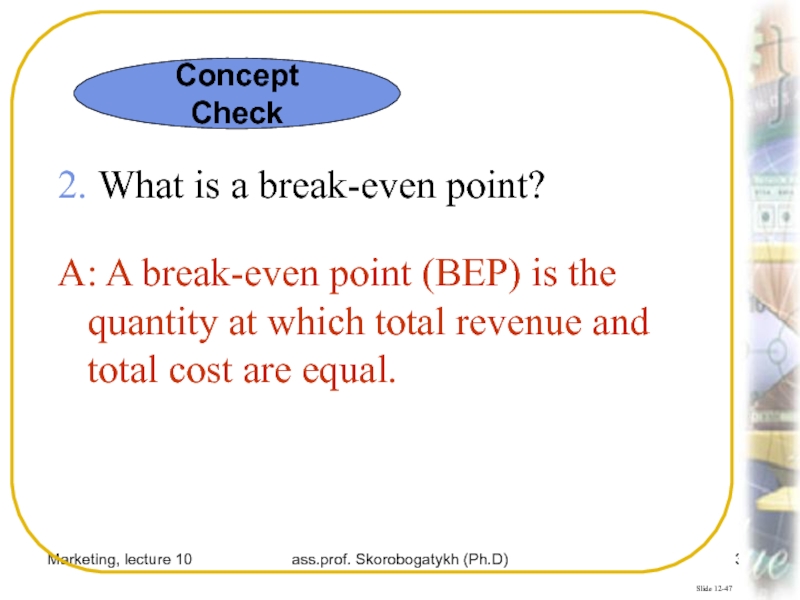
2. What is a
break-even point?
A: A break-even point (BEP) is the quantity at
which total revenue and total cost are equal.Concept Check
Слайд 36Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
PRICING OBJECTIVES AND CONSTRAINTS
Slide 12-48
Identifying Pricing
Objectives
Pricing Objectives
Profit
Managing for Long-Run Profits
Maximizing Current
Profits Target Return
Слайд 37Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-88
Pricing objectives specify the role
of price in an organization’s marketing and strategic plans.
Pricing Objectives
Слайд 38Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
PRICING OBJECTIVES AND CONSTRAINTS
Slide 12-50
Identifying Pricing
Objectives
Sales
Market Share
Unit Volume
Survival
Social Responsibility
Слайд 39Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
PRICING OBJECTIVES AND CONSTRAINTS
Slide 12-51
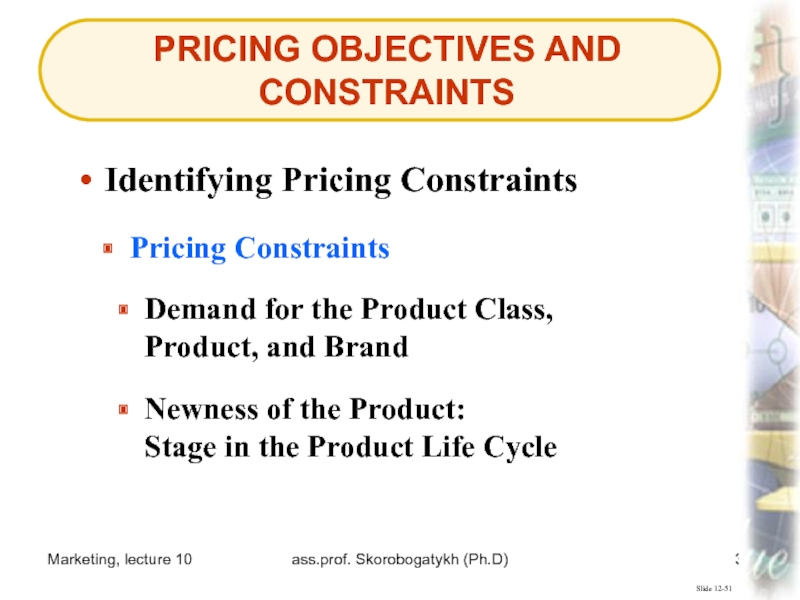
Identifying Pricing
Constraints
Pricing Constraints
Demand for the Product Class,
Product, and Brand
Newness of
the Product:
Stage in the Product Life CycleСлайд 40Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
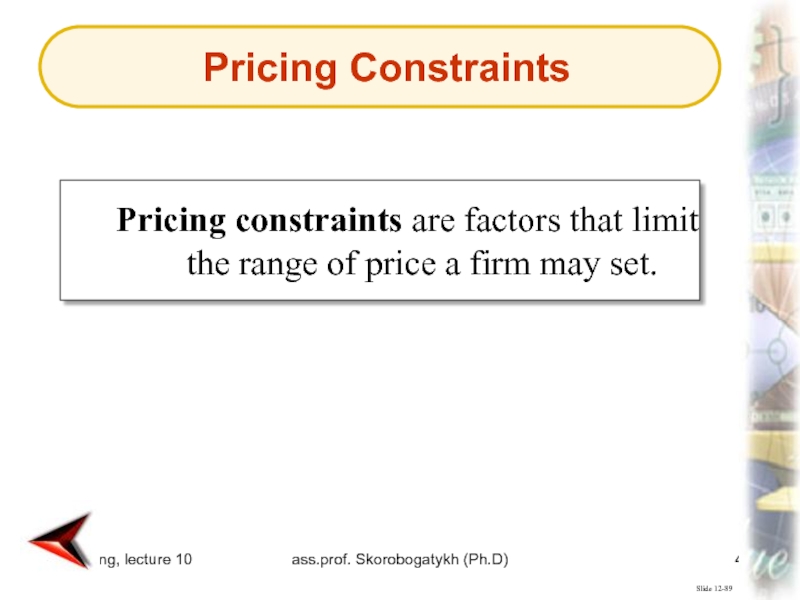
Slide 12-89
Pricing constraints are factors that
limit the range of price a firm may set.
Pricing Constraints
Слайд 41Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
PRICING OBJECTIVES AND CONSTRAINTS
Slide 12-53
Identifying Pricing
Constraints
Cost of Producing and
Marketing the Product
Competitors’ Prices
Legal and
Ethical Considerations Price Fixing
Price Discrimination
Deceptive Pricing
Predatory Pricing
Слайд 42Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-54
1. What is the
difference between pricing objectives and pricing constraints?
A: Pricing objectives specify
the role of price in an organization’s marketing and strategic plans. Pricing constraints are factors that limit the range of price a firm may set.Concept Check
Слайд 43Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-55
2. Explain what bait
and switch is and why it is an example of
deceptive pricing.A: This occurs when a firm offers a very low price on a product (the bait) to attract customers to a store, who then are persuaded to purchase a higher-priced item (the switch). Misleading consumers is both illegal and unethical.
Concept Check
Слайд 44Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
SETTING A FINAL PRICE
Slide 12-56
Step 1:
Set an Approximate Price Level
One-Price Policy
Step 2: Set the
List or Quoted Price Flexible-Price Policy
Слайд 45Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
SETTING A FINAL PRICE
Slide 12-59
Step 3:
Make Special Adjustments to the List or Quoted Price
Discounts
Quantity Discounts Seasonal Discounts
Trade (Functional) Discounts
Cash Discounts
Слайд 46Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
SETTING A FINAL PRICE
Slide 12-61
Step 3:
Make Special Adjustments to the List or Quoted Price
Allowances
Trade-in Allowances Promotional Allowances
Geographical Adjustments
FOB Origin Pricing
Uniform Delivered Pricing
Слайд 47Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-62
1. Why would a
seller choose a flexible-price policy over a one-price policy?
A: A
flexible-price policy involves setting different prices for products and services depending on individual buyers and purchasing situations in light of demand, cost, and competitive factors instead of setting one price for all buyers.Concept Check
Слайд 48Marketing, lecture 10
ass.prof. Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 12-63
2. What is the
purpose of (a) quantity discounts and (b) promotional allowances?
A: (a)
Quantity discounts encourage customers to buy larger quantities of a product. (b) Promotional allowances are used to encourage sellers to undertake certain advertising or selling activities to promote a product.Concept Check