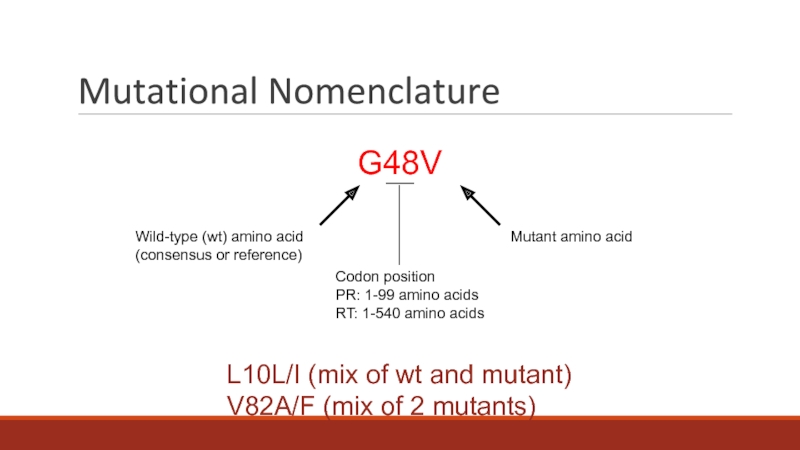
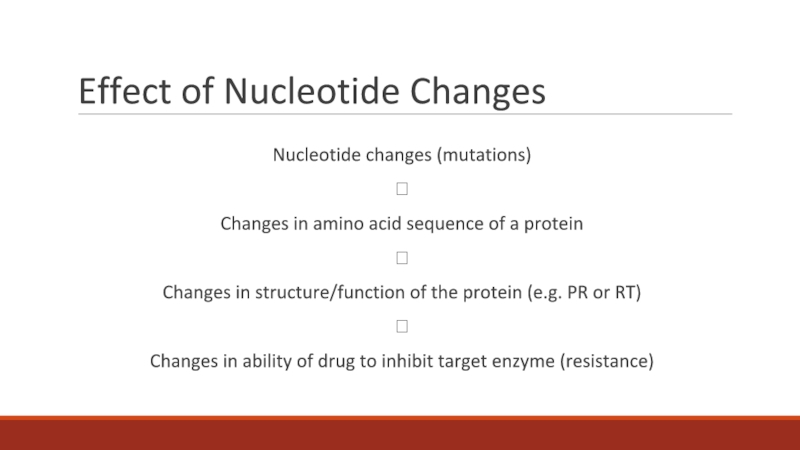
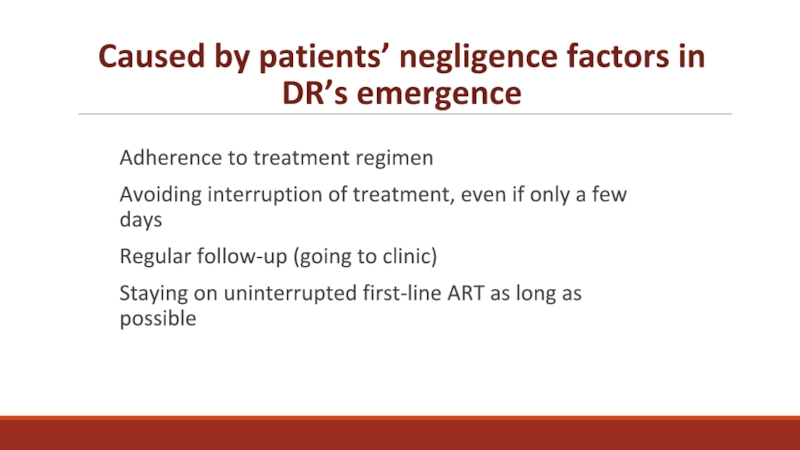
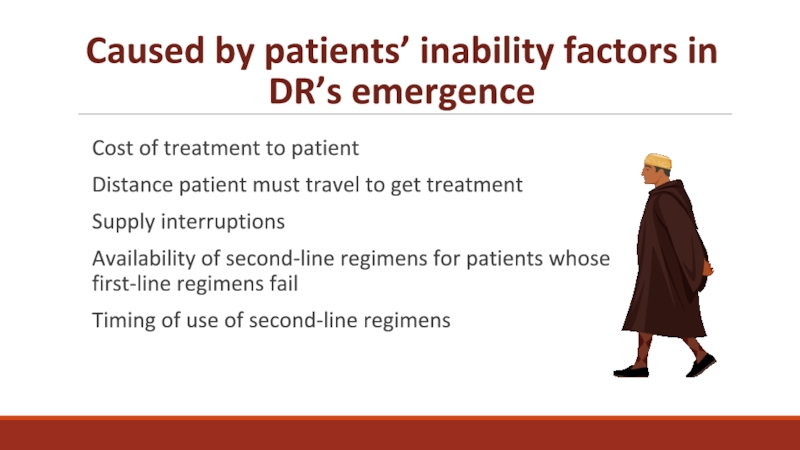
having claimed more than 35 million lives so far. In
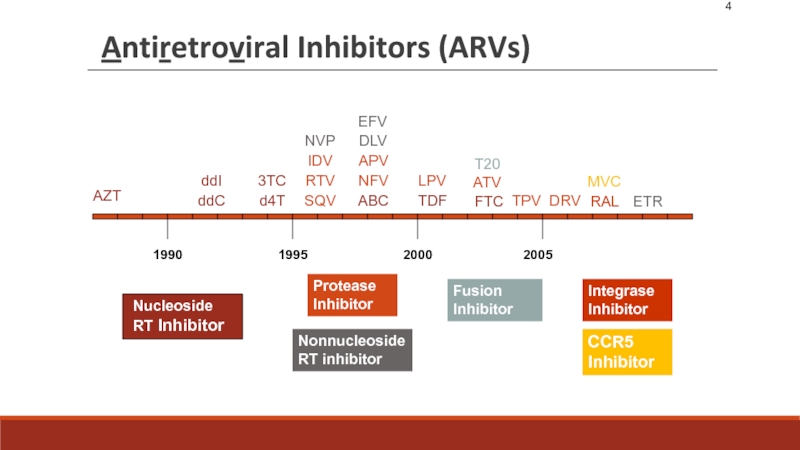
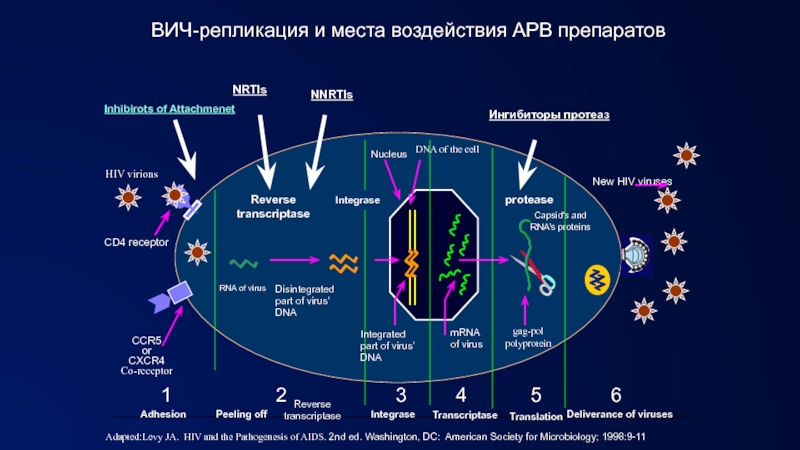
2015, 1.1 (940 000–1.3 million) million people died from HIV-related causes globally.There is no cure for HIV infection. However, effective antiretroviral (ARV) drugs can control the virus and help prevent transmission so that people with HIV, and those at substantial risk, can enjoy healthy, long and productive lives.
Key facts:
WHO. HIV/AIDS.Fact sheet.Updated November 2016