Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Merchandising Operations Horngren’s Accounting Lecture Twelve Lisa, Li 1
Содержание
- 1. Merchandising Operations Horngren’s Accounting Lecture Twelve Lisa, Li 1
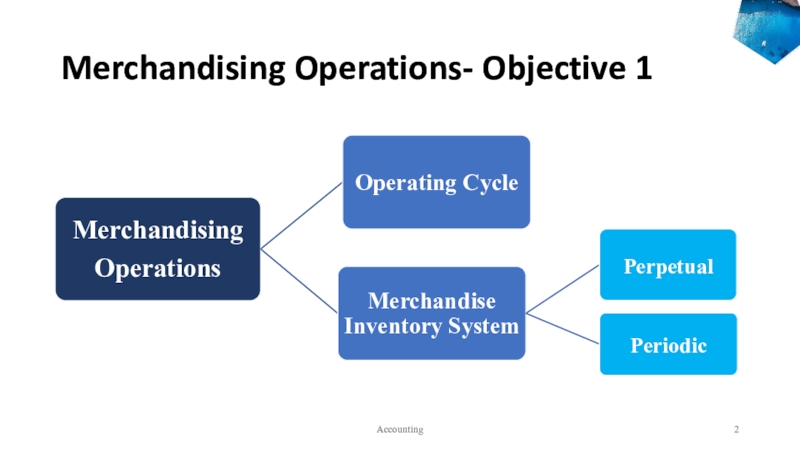
- 2. Merchandising Operations- Objective 1Accounting
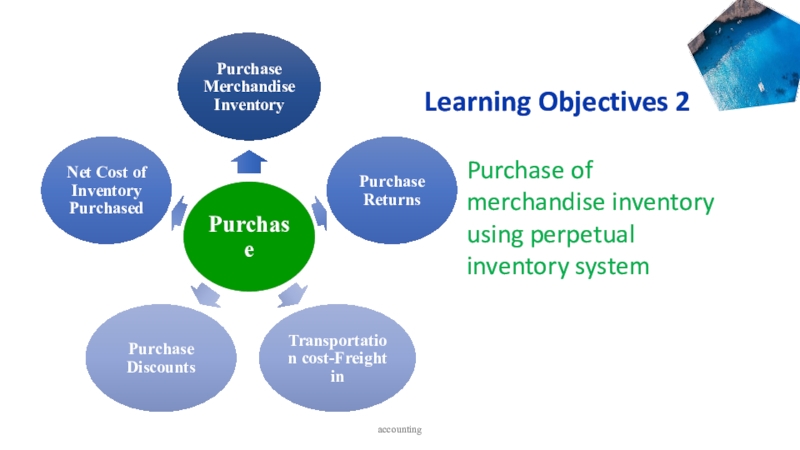
- 3. accounting Learning Objectives 2Purchase of merchandise inventory using perpetual inventory system
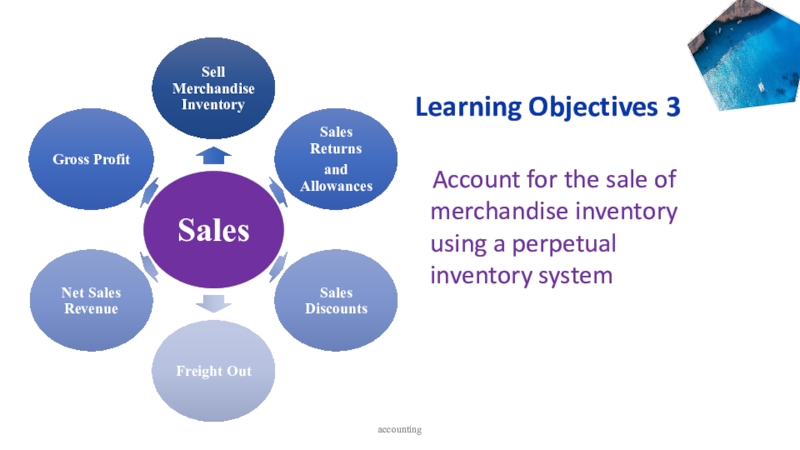
- 4. accounting Learning Objectives 3 Account
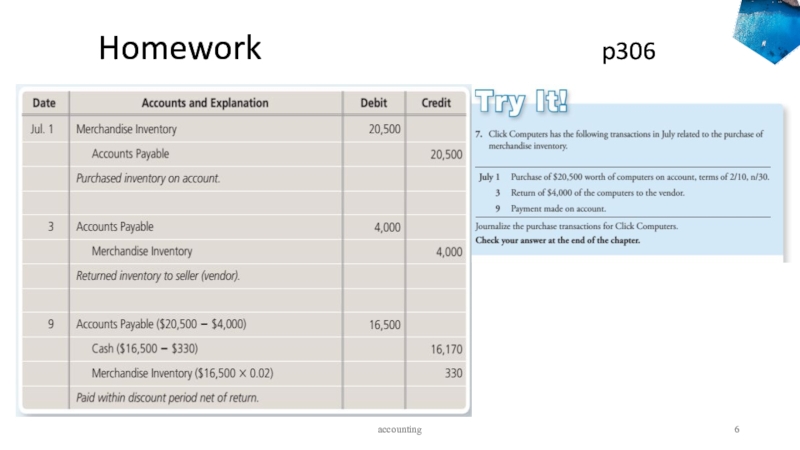
- 5. Homework
- 6. Homework
- 7. Homework
- 8. Homework
- 9. Learning Objectives –
- 10. Learning Objectives –
- 11. accounting Learning Objectives 3 Account
- 12. 4. Transportation Cost - Freight OutThe freight
- 13. 5. Net Sales RevenueFor the year, Smart
- 14. 5. Net Sales RevenueFor the year, Smart
- 15. 6. Gross ProfitThe difference between Net Sales
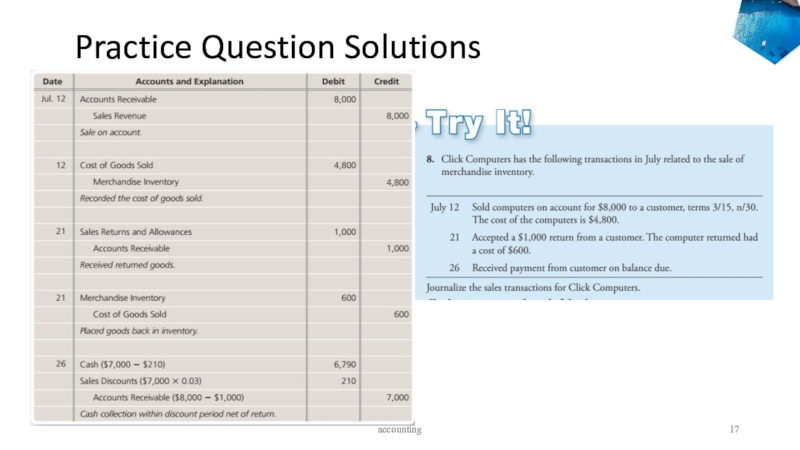
- 16. Practice Questions
- 17. Practice Question Solutionsaccounting
- 18. Learning Objectives 4 Adjust and close the accounts of a merchandising businessAccounting
- 19. Adjusting Merchandise InventoryAt the end of
- 20. Adjusting Merchandise InventorySmart Touch Learning’s Merchandise
- 21. Closing the Accounts of a MerchandiserClose R
- 22. 5-accounting Closing in a Merchandiser
- 23. Closing the Accounts of a MerchandiserAt this
- 24. Learning Objectives 5 Prepare a merchandiser’s financial statementsAccounting
- 25. Merchandiser’s Financial StatementsIncome StatementSingle-Step Income StatementMulti-Step Income
- 26. Single-Step Income StatementIncome statement format that groups
- 27. Multi-Step Income StatementMulti-step I/S format that
- 28. Multi-Step Income StatementCOGS: is also called
- 29. Operating Expenses: Expenses (other than COGS) that
- 30. Other revenues and expenses: Revenues or expenses
- 31. Statement of Owner’s Equity and the B/SA
- 32. Learning Objectives 6 Use the gross profit percentage to evaluate business performanceAccounting
- 33. Gross Profit PercentageMeasures the profitability of each
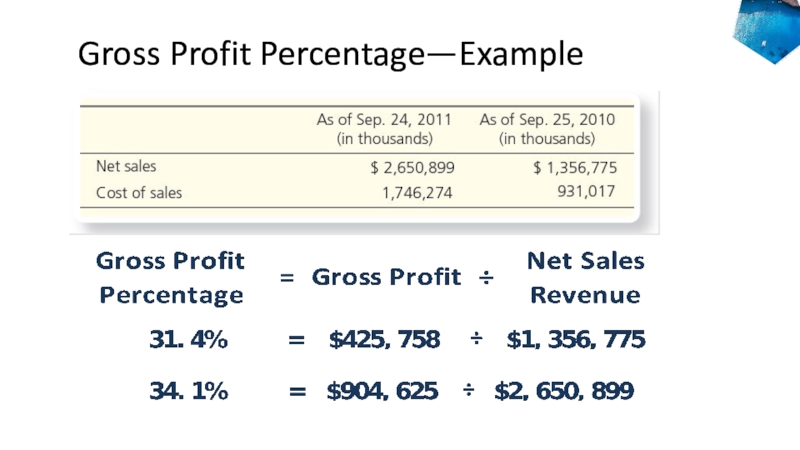
- 34. Gross Profit Percentage—Example
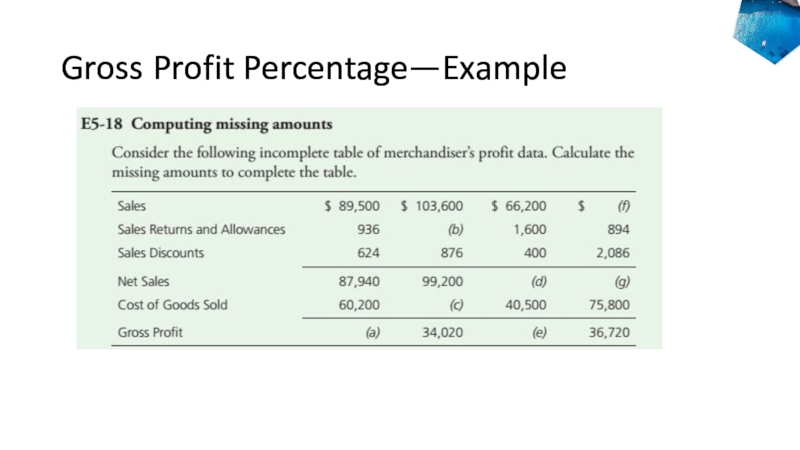
- 35. Gross Profit Percentage—Example
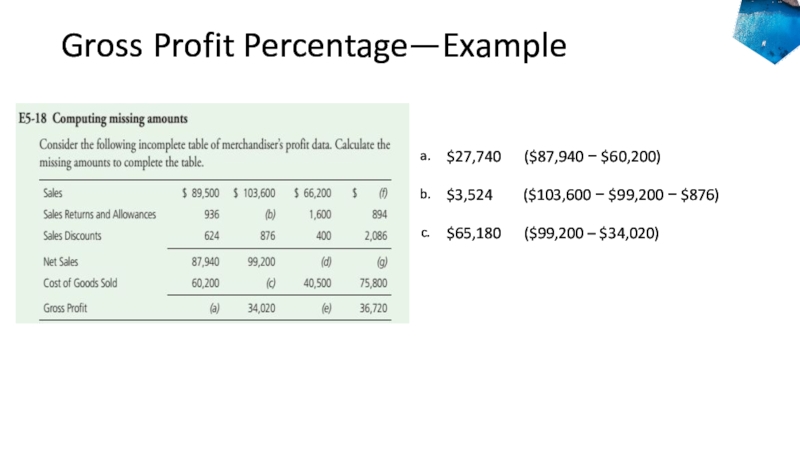
- 36. Gross Profit Percentage—Example
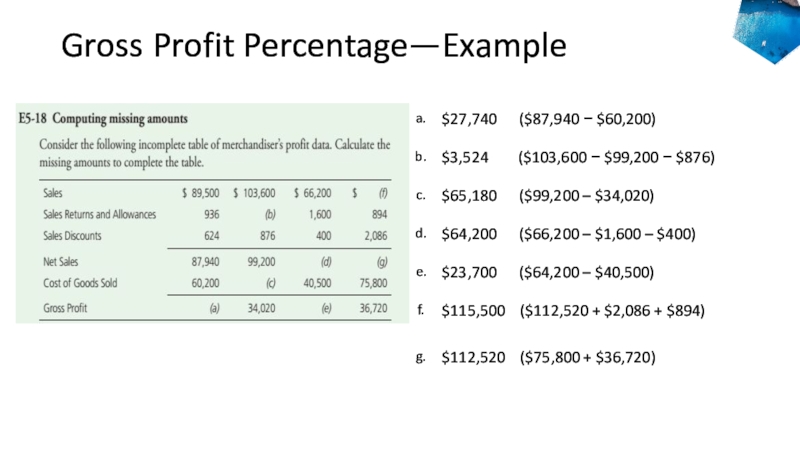
- 37. Gross Profit Percentage—Example
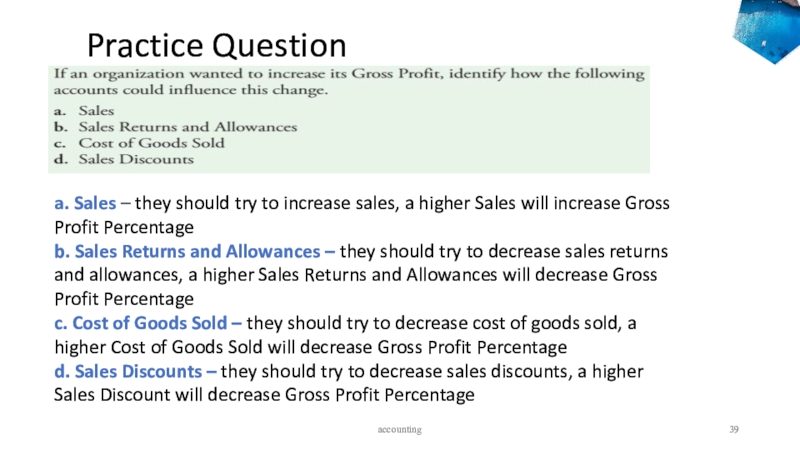
- 38. Practice Question accounting
- 39. Practice Question accounting a. Sales
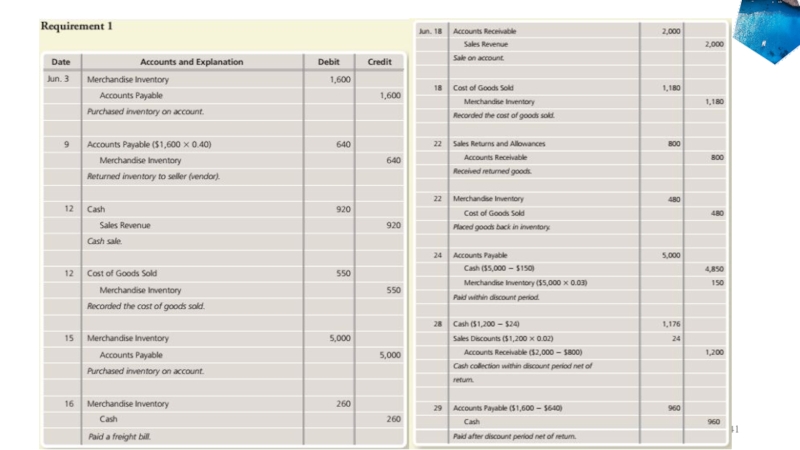
- 40. Example – Summary Problem 5-1Accounting
- 41. Accounting
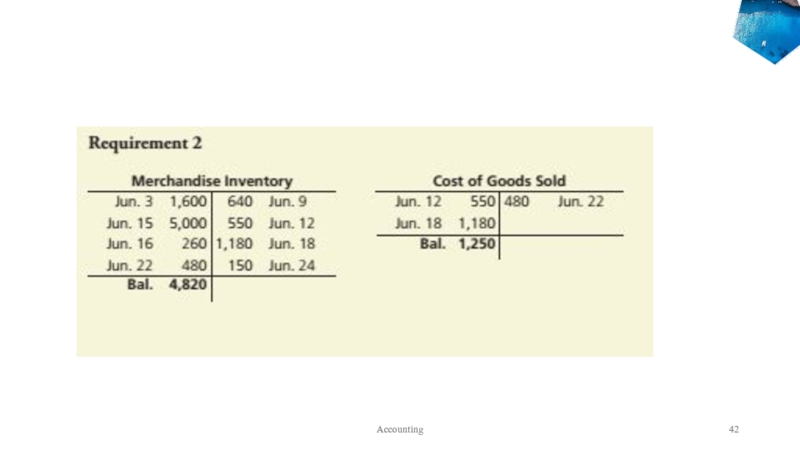
- 42. Summary Problem 5-1Accounting
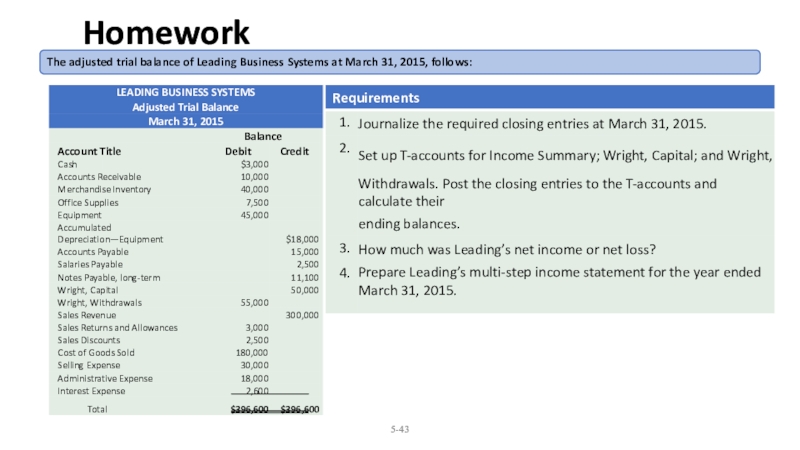
- 43. 5-The adjusted trial balance of Leading Business Systems at March 31, 2015, follows:Homework
- 44. The End of Chapter 5
- 45. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3accounting
Learning Objectives 2
Purchase of merchandise inventory using perpetual inventory
system
Слайд 4accounting
Learning Objectives 3
Account for the sale
of merchandise inventory using a perpetual inventory system
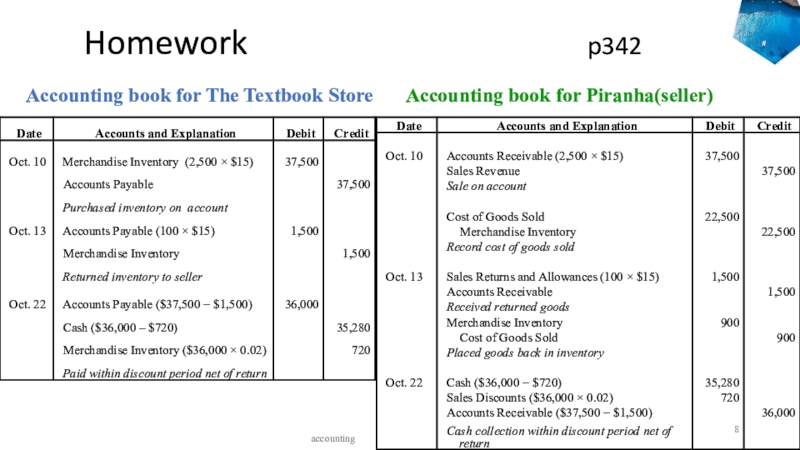
Слайд 8 Homework
p342
accounting
Accounting book for The Textbook Store
Accounting book for Piranha(seller)
Слайд 9Learning Objectives
– Chapter 5
Describe merchandising operations
and the two types of merchandise inventory systems
Account for the
purchase of merchandise inventory using a perpetual inventory systemAccount for the sale of merchandise inventory using a perpetual inventory system
Accounting
Слайд 10Learning Objectives
– Chapter 5
Adjust and close
the accounts of a merchandising business
Prepare a merchandiser’s financial statements
Use
the gross profit percentage to evaluate business performanceAccounting
Слайд 11accounting
Learning Objectives 3
Account for the sale
of merchandise inventory using a perpetual inventory system
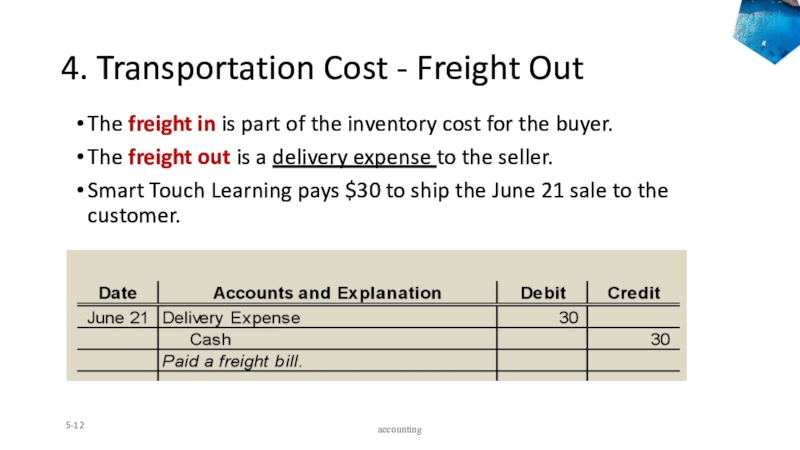
Слайд 124. Transportation Cost - Freight Out
The freight in is part
of the inventory cost for the buyer.
The freight out is
a delivery expense to the seller.Smart Touch Learning pays $30 to ship the June 21 sale to the customer.
5-
accounting
Слайд 135. Net Sales Revenue
For the year, Smart Touch Learning sells
$297,500 of merchandise inventory. They process $11,200 of sales returns
and allowances, and they award $5,600 of sales discounts.What is Net Sales Revenue for the year?
5-
accounting
Слайд 145. Net Sales Revenue
For the year, Smart Touch Learning sells
$297,500 of merchandise inventory. They process $11,200 of sales returns
and allowances, and they award $5,600 of sales discounts.What is Net Sales Revenue for the year?
5-
accounting
Слайд 156. Gross Profit
The difference between Net Sales Revenues and Cost
of Goods Sold
Indicates the amount available to cover operating expenses
For
this example, assume Smart Touch Learning’s Cost of Goods Sold is $199,500; its gross profit is calculated as follows:5-
accounting
Слайд 19 Adjusting Merchandise Inventory
At the end of the period, actual
inventory on hand may differ from the accounting records in
perpetual inventory system.This difference can occur because of:
Theft
Damage
Errors
‘Merchandise Inventory’ account must be adjusted at the end of the period
accounting
Слайд 20 Adjusting Merchandise Inventory
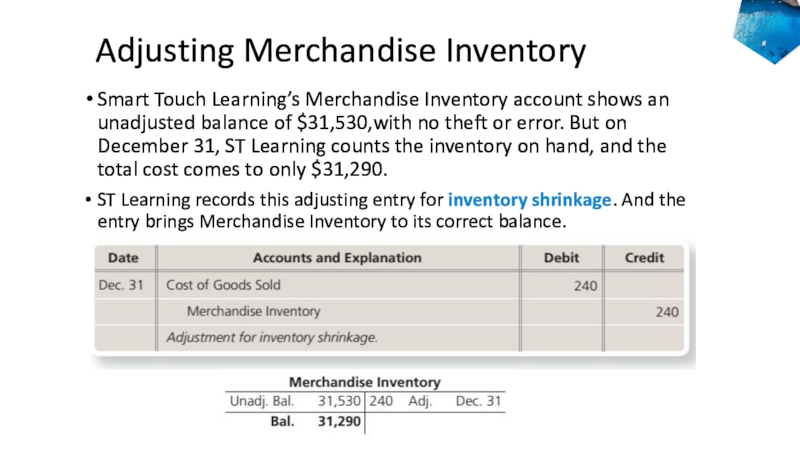
Smart Touch Learning’s Merchandise Inventory account shows
an unadjusted balance of $31,530,with no theft or error. But
on December 31, ST Learning counts the inventory on hand, and the total cost comes to only $31,290.ST Learning records this adjusting entry for inventory shrinkage. And the entry brings Merchandise Inventory to its correct balance.
accounting
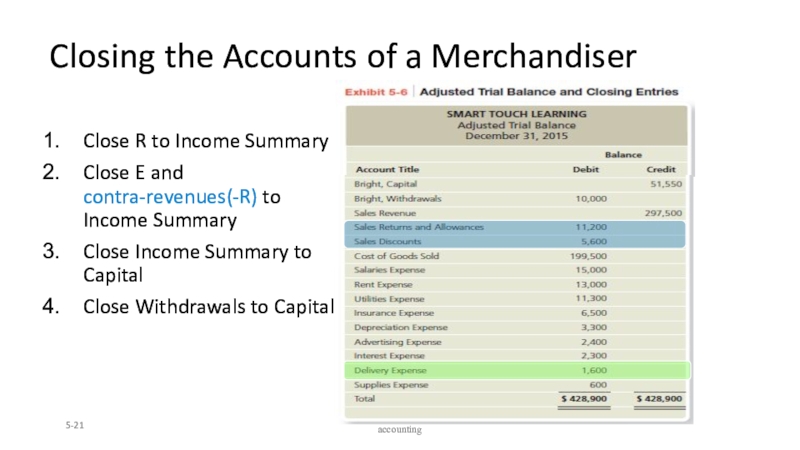
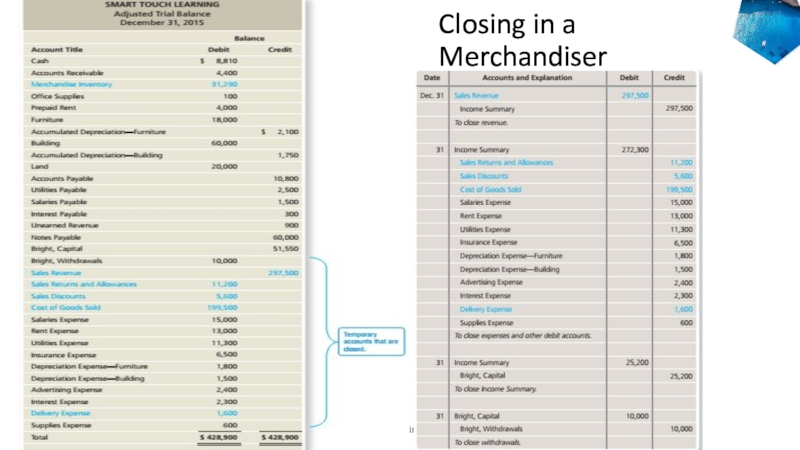
Слайд 21Closing the Accounts of a Merchandiser
Close R to Income Summary
Close
E and contra-revenues(-R) to Income Summary
Close Income Summary to Capital
Close
Withdrawals to Capital5-
accounting
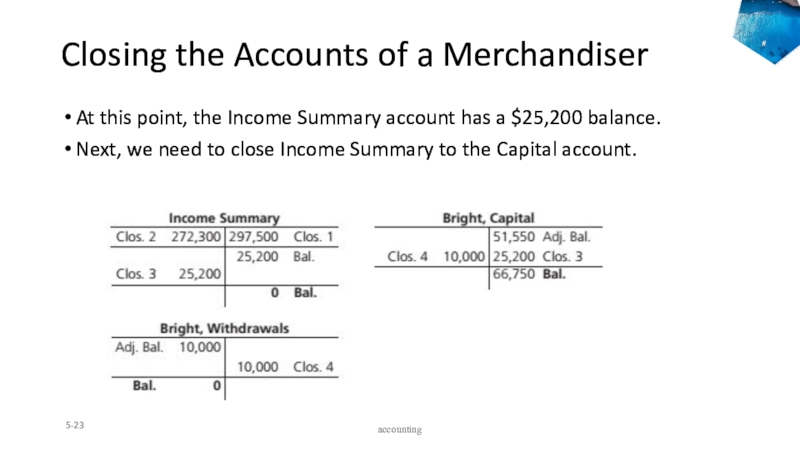
Слайд 23Closing the Accounts of a Merchandiser
At this point, the Income
Summary account has a $25,200 balance.
Next, we need to close
Income Summary to the Capital account.5-
accounting
Слайд 25Merchandiser’s Financial Statements
Income Statement
Single-Step Income Statement
Multi-Step Income Statement (common approach)
Change
in owner’s equity
Balance Sheet
The report format (A at top, L
and O/E at bottom)The account format (A at left, L and O/E at right)
Cash flow Statement
5-
accounting
Слайд 26Single-Step Income Statement
Income statement format that groups all revenues together
and then lists and deducts all expenses together without calculating
any subtotals.accounting
Слайд 27Multi-Step Income
Statement
Multi-step I/S format that contains subtotals to highlight
significant relationships.
Net Sales Revenue
Gross Profit (Gross Margin)
Operating Income
Net Income.
5-
accounting
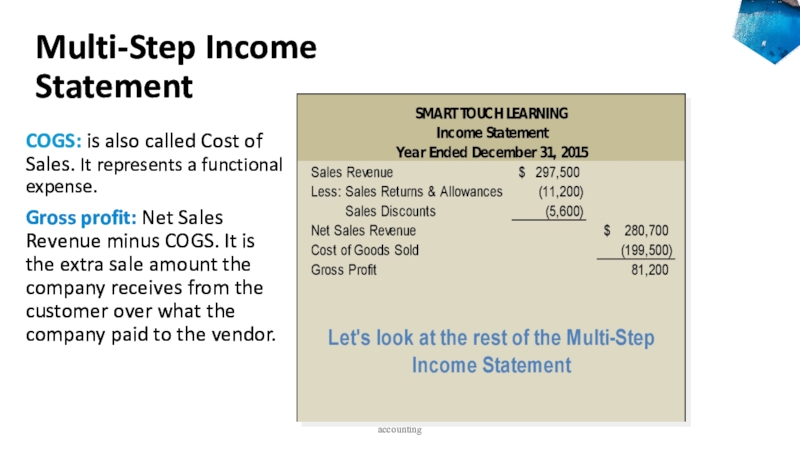
Слайд 28Multi-Step Income
Statement
COGS: is also called Cost of Sales. It
represents a functional expense.
Gross profit: Net Sales Revenue minus COGS.
It is the extra sale amount the company receives from the customer over what the company paid to the vendor. accounting
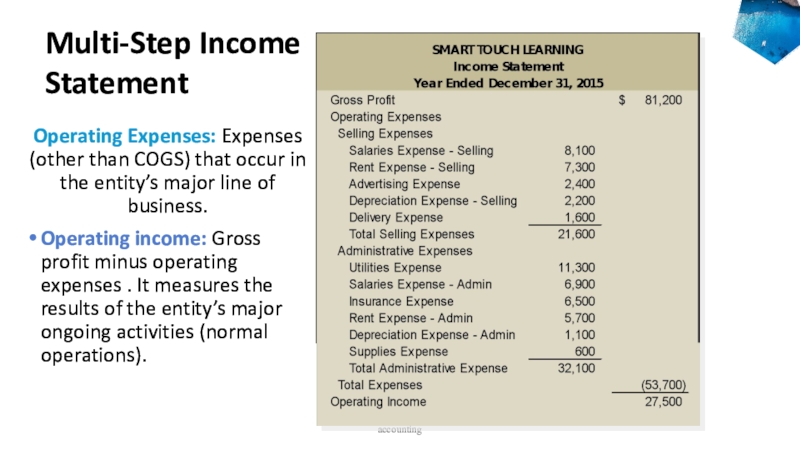
Слайд 29Operating Expenses: Expenses (other than COGS) that occur in the
entity’s major line of business.
Operating income: Gross profit minus operating
expenses . It measures the results of the entity’s major ongoing activities (normal operations).accounting
Multi-Step Income Statement
Слайд 30Other revenues and expenses: Revenues or expenses that are outside
the normal, day-to-day operations of a business, such as interest
expense, taxes, etc.Finally, Net Income is determined by subtracting Other Revenues and Expenses from Operating Income.
accounting
Multi-Step Income Statement
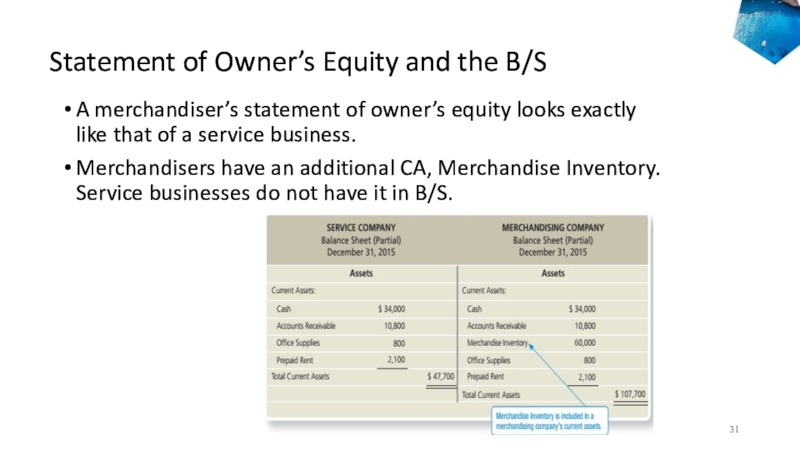
Слайд 31Statement of Owner’s Equity and the B/S
A merchandiser’s statement of
owner’s equity looks exactly like that of a service business.
Merchandisers have an additional CA, Merchandise Inventory. Service businesses do not have it in B/S.
Accounting
Слайд 32Learning Objectives 6
Use the gross profit percentage
to evaluate business performance
Accounting
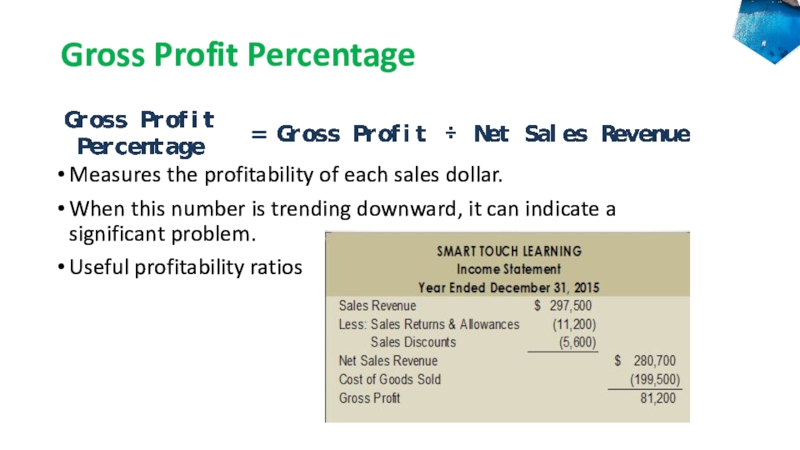
Слайд 33Gross Profit Percentage
Measures the profitability of each sales dollar.
When this
number is trending downward, it can indicate a significant problem.
Useful
profitability ratiosСлайд 39 Practice Question
accounting
a. Sales – they should
try to increase sales, a higher Sales will increase Gross
Profit Percentageb. Sales Returns and Allowances – they should try to decrease sales returns and allowances, a higher Sales Returns and Allowances will decrease Gross Profit Percentage
c. Cost of Goods Sold – they should try to decrease cost of goods sold, a higher Cost of Goods Sold will decrease Gross Profit Percentage
d. Sales Discounts – they should try to decrease sales discounts, a higher Sales Discount will decrease Gross Profit Percentage