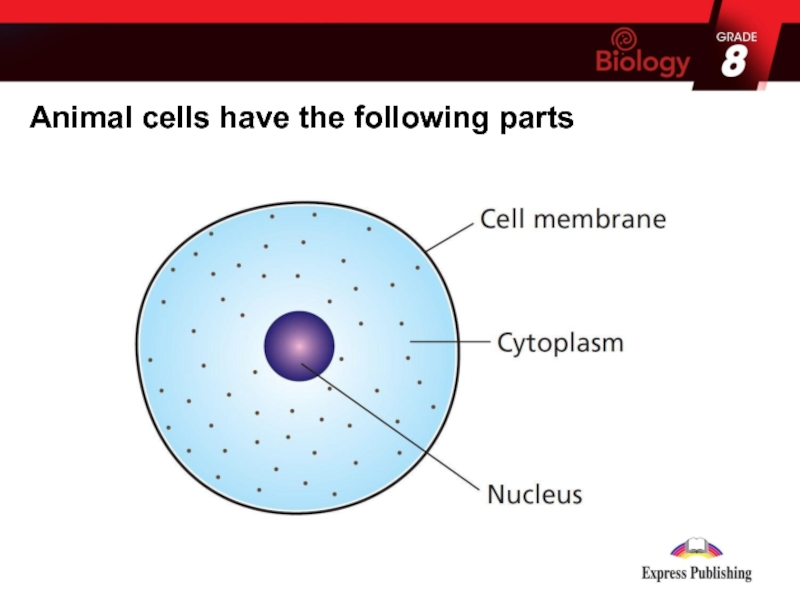
layer that surrounds the cell):
holds the contents of the cell
in placecontrols what passes in and out of the cell.
A nucleus (a round structure that controls the cell):
contains chromosomes
chromosomes contain genes
genes are made of DNA
genes control features such as eye colour and ability to form finger nails
genes are passed on from parents to offspring.
Cytoplasm (a liquid that surrounds the nucleus):
carries out some cell reactions
contains small structures such as mitochondria (for energy).