Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Motion 1.Motion 2.Types of motion 3. Speed 4. Vectors 5.Distance, Time
Содержание
- 1. Motion 1.Motion 2.Types of motion 3. Speed 4. Vectors 5.Distance, Time
- 2. In physics, motion is a change in
- 3. Types of motion1.Uniform motion2.Linear motion3.non-uniform motion4.Circular motion4.Projectile
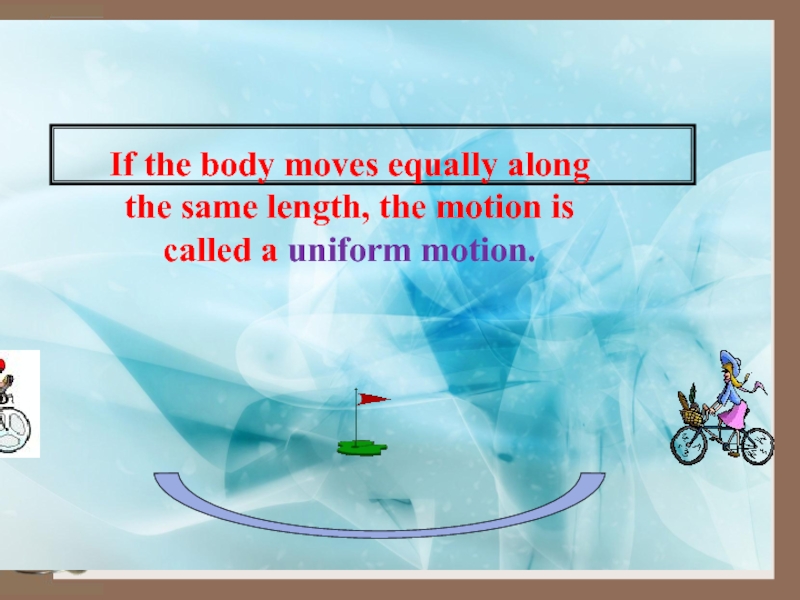
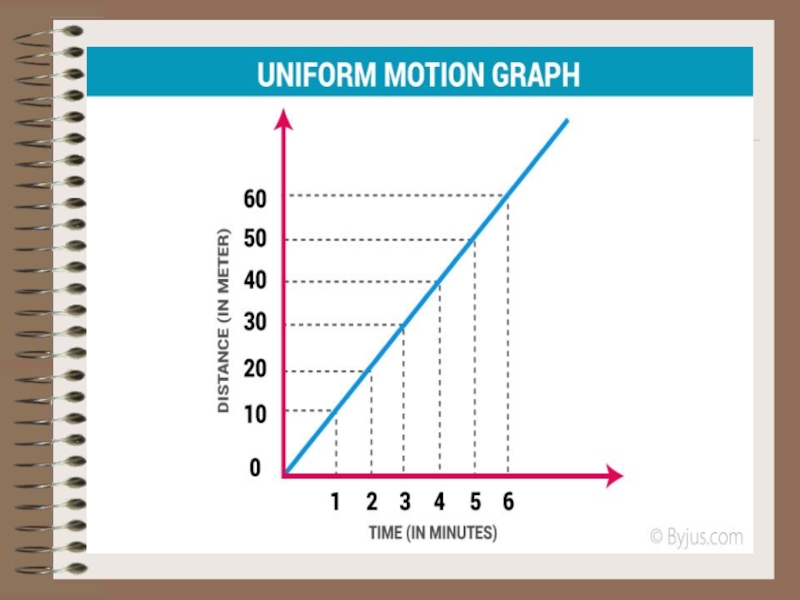
- 4. If the body moves equally along
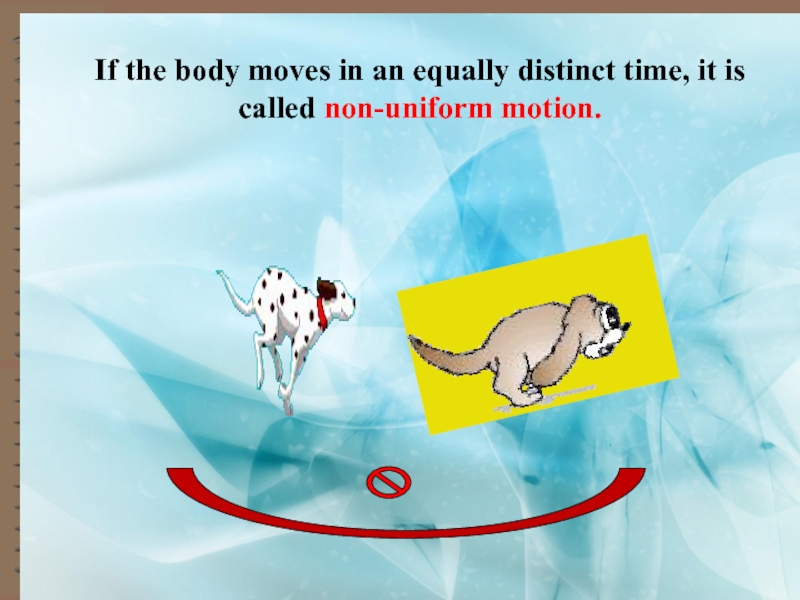
- 5. If the body moves in an equally distinct time, it is called non-uniform motion.
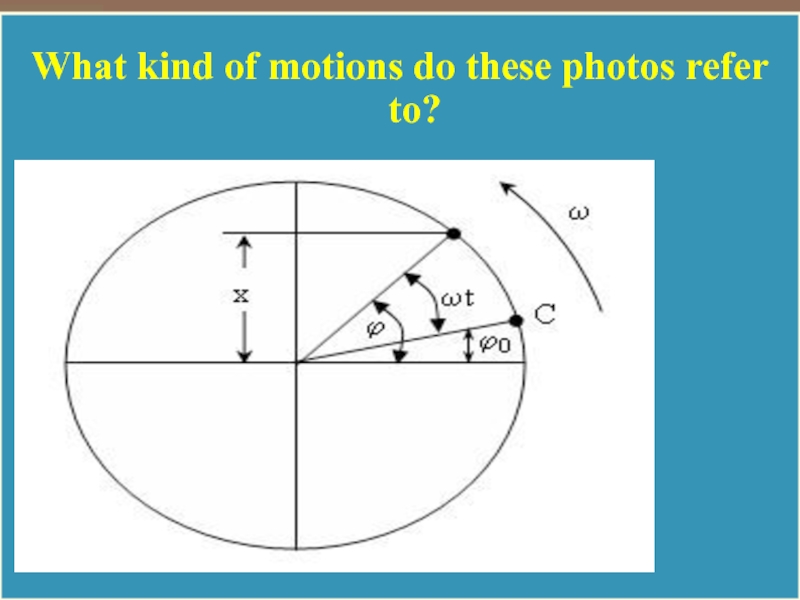
- 6. What kind of motions do these photos
- 7. Circular Motion
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. 2-1. SpeedDefinitions:SpeedThe rate at which something moves
- 12. 2-1. SpeedVelocityDistanceTime
- 13. 2-1. SpeedAverage speed is the total distance
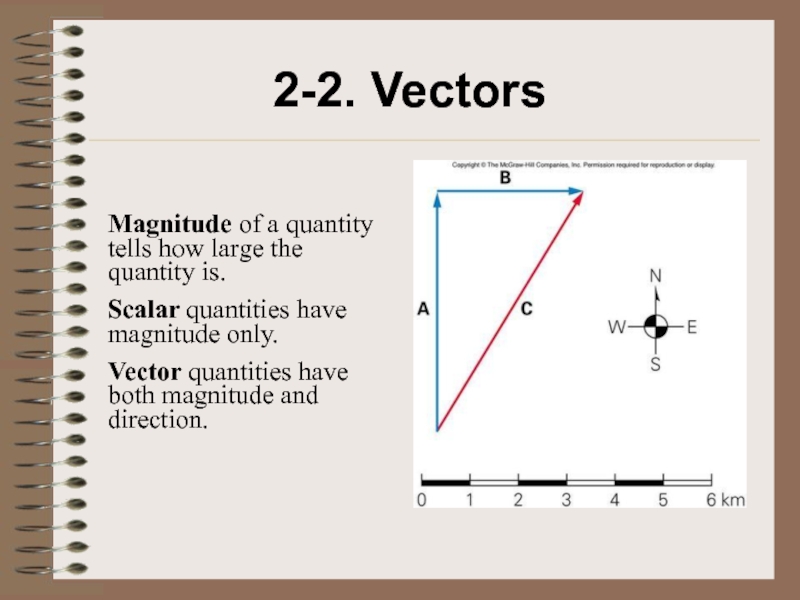
- 14. 2-2. VectorsMagnitude of a quantity tells how
- 15. 2-2. VectorsVelocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction.
- 16. 2- 4. Distance, Time (V1 +
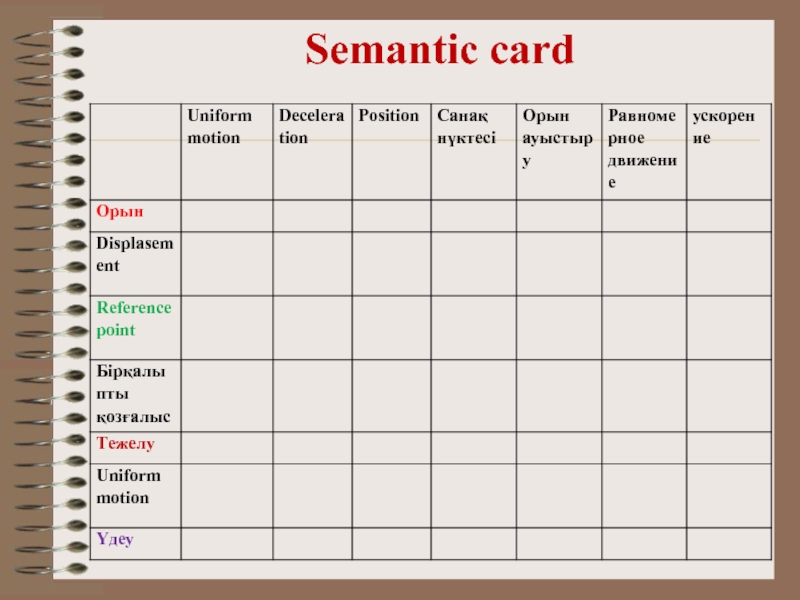
- 17. Semantic card
- 18. Скачать презентанцию
In physics, motion is a change in position of an object over time. Motion is described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, time, and speed.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3Types of motion
1.Uniform motion
2.Linear motion
3.non-uniform motion
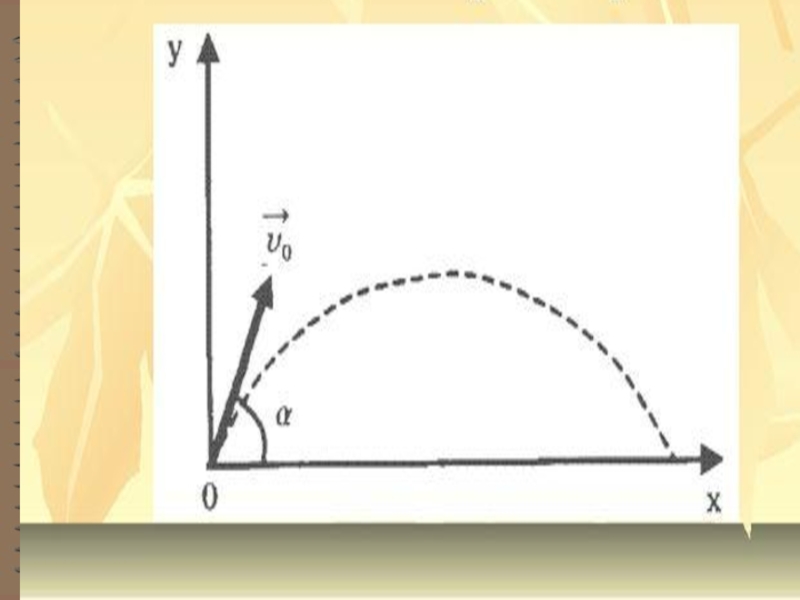
4.Circular motion
4.Projectile motion
5.Elliptic motion
6.Accelerated and decelerated motion
7.Motion with constant acceleration or deceleration
Слайд 112-1. Speed
Definitions:
Speed
The rate at which something moves a given distance.
Faster
speeds = greater distances
General formula for speed:
Speed = distance /
timeAbbreviations commonly used:
d = distance t = time v = speed
v = d/t
Слайд 132-1. Speed
Average speed is the total distance traveled by an
object divided by the time taken to travel that distance.
Instantaneous speed is an object's speed at a given instant of time.Слайд 142-2. Vectors
Magnitude of a quantity tells how large the quantity
is.
Scalar quantities have magnitude only.
Vector quantities have both magnitude and
direction.Слайд 162- 4. Distance, Time
(V1 + V2)
Vavg =
2
d = vavg t
(20mph + 60mph)
= 40mph
2
30mph 2hr = 60miles