Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Non-Bank Financial Institutions
Содержание
- 1. Non-Bank Financial Institutions
- 2. Non-Bank Financial InstitutionsInsurance-typeLife and property and casualtyPension fundsAsset management firms and fundsSecurities firmsOthersFinance companiesMortgage bankersGovernment-sponsored agencies
- 3. Insurance LiabilitiesPromise to pay depending on contingencyLife
- 4. Insurance ServicesLife and annuity contractProbabilities usually not
- 5. Life Insurance ContractsAgeAgeRetirementRetirementDeathDeathWhole Life ContractLimited Pay LifePremiums, BenefitsPremiums, Benefits
- 6. Life Insurance Contracts (cont’d)AgeAgeRetirementRetirementDeathDeathEndowment PolicyLife and AnnuityPremiums, BenefitsPremiums, Benefits
- 7. Insurance DistributionLife insuranceOrdinaryGroupIndustrialCreditIndependent agentsEconomics of insurance marketingCompensation of agents and brokersPolitical power in the insurance industry
- 8. Insurance Company IncomeRevenue: Premium incomeEarned premiums Investment
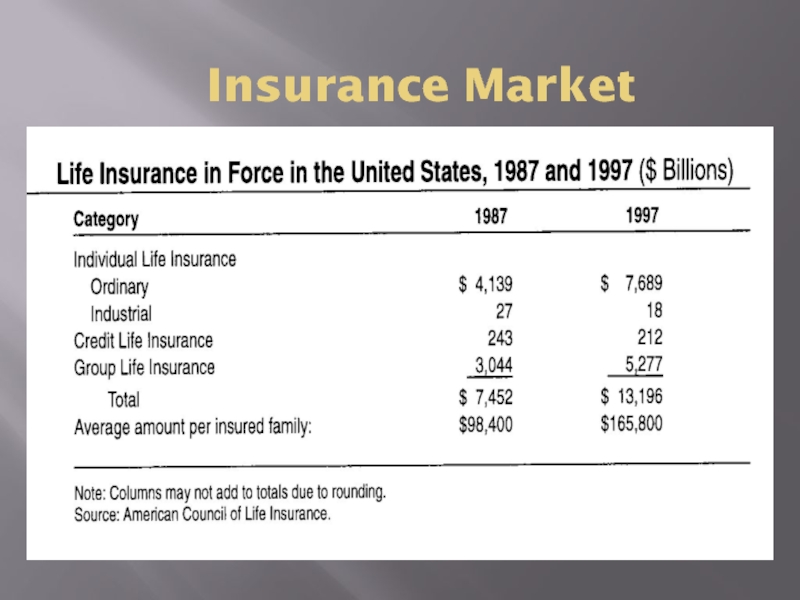
- 9. Insurance Market
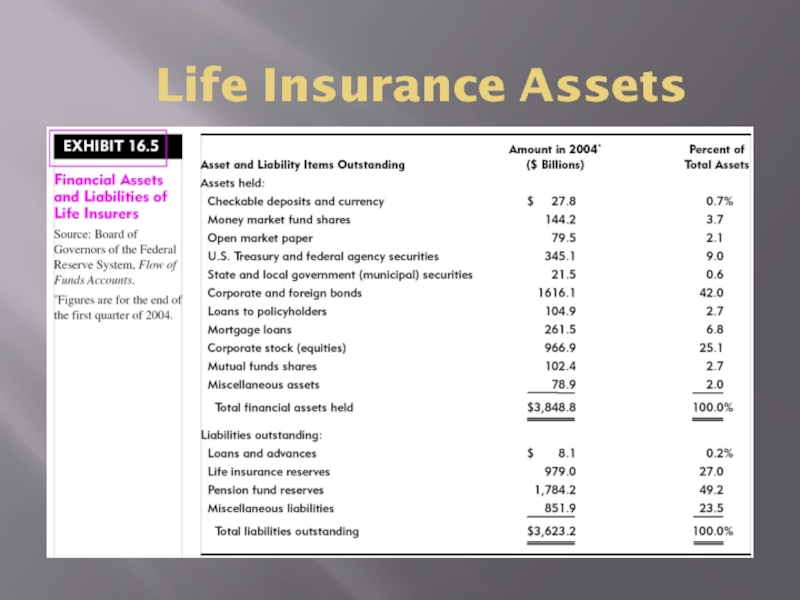
- 10. Life Insurance Assets
- 11. Role of Insurance EquityEquity in insurance is
- 12. Insurance Balance SheetsBalance sheet: liabilities are insurance
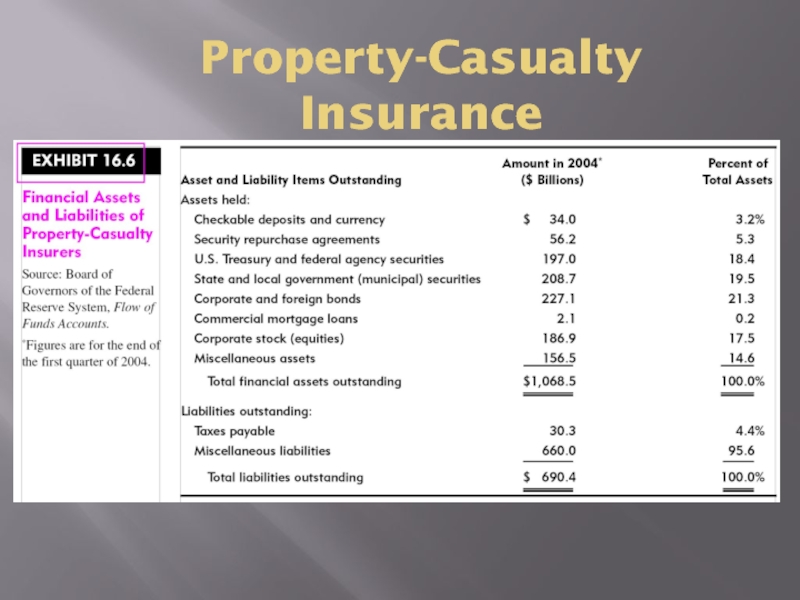
- 13. Property-Casualty Insurance
- 14. Contrast Life/Casualty InsuranceProbabilities of claims in life
- 15. Pension FundsPrivate versus state and local governmentDefined
- 16. Pension Fund Assets
- 17. Asset ManagementEconomics of the industryPerformance measurementPrincipal-agent problemsA
- 18. Asset Management FirmsRevenue: Management FeesBased on assets
- 19. Securities FirmsBrokersFind buyers for sellersOrganize marketsDealersProvide liquidity
- 20. Brokers and Investment BankingFull-line firms offer retail
- 21. Investment BankingBulge bracket firms (e.g. Morgan Stanley)
- 22. Securities Firm IncomeRevenue: Commissions
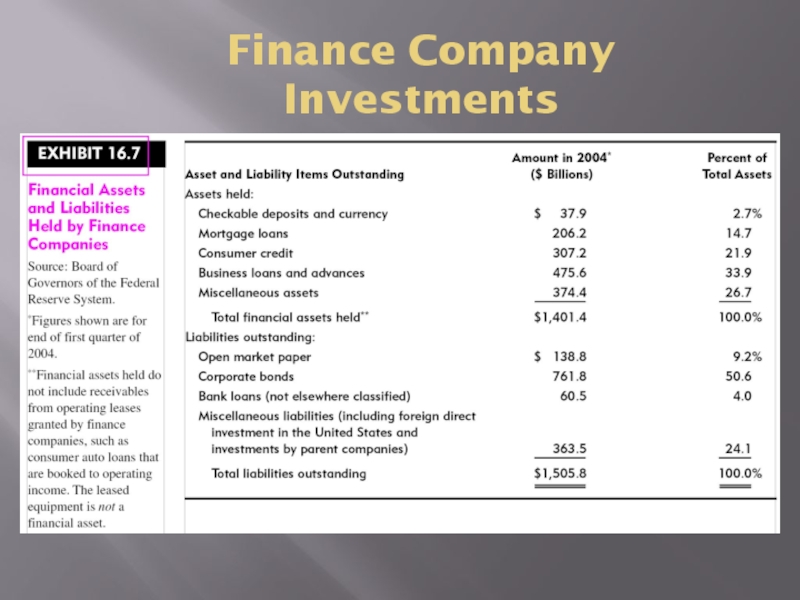
- 23. Finance CompaniesThree basic typesCaptive finance companies (owned
- 24. Finance Company Investments
- 25. Asset-Pools OriginationGovernment-sponsored agencies (GSEs)Federal National Mortgage Association
- 26. Other Financial FirmsMortgage banksInformation and advisory firmsClearing
- 27. Скачать презентанцию
Non-Bank Financial InstitutionsInsurance-typeLife and property and casualtyPension fundsAsset management firms and fundsSecurities firmsOthersFinance companiesMortgage bankersGovernment-sponsored agencies
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Non-Bank Financial Institutions
Insurance-type
Life and property and casualty
Pension funds
Asset management firms
and funds
Слайд 3Insurance Liabilities
Promise to pay depending on contingency
Life - Pay upon
death, or retirement
Property and casualty - Pay on occurrence of
accident or loss due to theft or hazard (fire, weather, earthquake, flood)Differences between life and accident
Life probabilities known with accuracy
Casualty has two risks: incidence and severity
Слайд 4Insurance Services
Life and annuity contract
Probabilities usually not influenced by insured
Cash
flows from coverage are predictable
Cancellations, lapses, policy loans
Casualty contract
Period short
Policy-holders
influence the incidence and severity of claimsСлайд 5Life Insurance Contracts
Age
Age
Retirement
Retirement
Death
Death
Whole Life Contract
Limited Pay Life
Premiums, Benefits
Premiums, Benefits
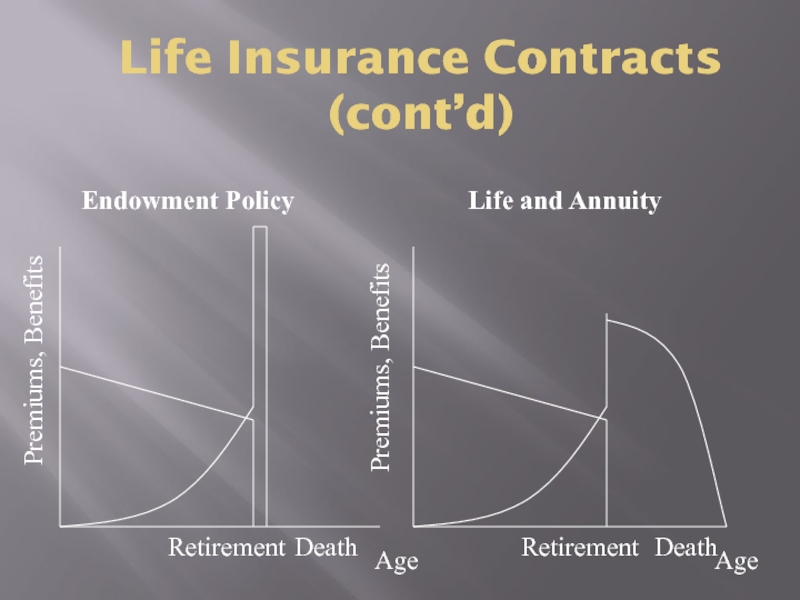
Слайд 6Life Insurance Contracts (cont’d)
Age
Age
Retirement
Retirement
Death
Death
Endowment Policy
Life and Annuity
Premiums, Benefits
Premiums, Benefits
Слайд 7Insurance Distribution
Life insurance
Ordinary
Group
Industrial
Credit
Independent agents
Economics of insurance marketing
Compensation of agents and
brokers
Political power in the insurance industry
Слайд 8Insurance Company Income
Revenue: Premium income
Earned premiums
Investment income
Expenses: Policy Benefits and
Losses
Direct payments to claimants
Loss expenses (evaluation, processing)
Marketing expenses
Non-interest expense
Labor
and related expensesCommunication, fees
Слайд 11Role of Insurance Equity
Equity in insurance is sometimes referred to
as surplus since it represents premium collections above claims payments
Income
is approximately:Premiums + investment income – claims
Income/loss adds to/subtracts from equity
Equity or surplus absorbs large surges in claims as in catastrophes (e.g. Katrina)
Слайд 12Insurance Balance Sheets
Balance sheet: liabilities are insurance reserves, unearned premiums,
and surplus (plus equity capital)
Assets are investments in corporate and
municipal bonds, real estate, equities, Balance sheet management consists of matching asset risks to liability risks
Many liabilities have long tails or durations
Слайд 14Contrast Life/Casualty Insurance
Probabilities of claims in life insurance are well
known (vital statistics yield accurate actuarial estimates)
Moral hazard limited in
life insuranceDollar claims in casualty insurance are affected by incidence and severity of damages and may have more are affected by incidence and severity of damages and may have more systematic risk
Слайд 15Pension Funds
Private versus state and local government
Defined benefit versus defined
contribution
Self-directed pension plans
Pensions, taxes, and responsibilities
Corporate tax treatment
Personal tax treatment
Corporate
responsibilities under ERISAСлайд 17Asset Management
Economics of the industry
Performance measurement
Principal-agent problems
A “temporary” disequilibrium
Historical perspective
Services
provided by asset managers
Issues in asset management
Слайд 18Asset Management Firms
Revenue: Management Fees
Based on assets under management
Expenses: Research
Costs
Analysts (labor expense)
Data and computer expenses
Marketing expenses
Non-interest expense
Overhead labor
and related expensesCommunication, fees
Слайд 19Securities Firms
Brokers
Find buyers for sellers
Organize markets
Dealers
Provide liquidity to market
Hold inventories
and take price risk
Securities originators
Design and place financial instruments for
primary market issuersСлайд 20Brokers and Investment Banking
Full-line firms offer retail and institutional trading,
securities origination and financial advisory services, and market-making services
Clearing
brokers (e.g. Bear Stearns) present securities for settlementWire houses transmit orders to other firms for execution
Слайд 21Investment Banking
Bulge bracket firms (e.g. Morgan Stanley) are largest investment
banking firms
Regional firms (e.g. Wedbush Morgan) operate in local
marketsBoutique firms specialize in certain types of transactions (e.g high tech or health care)
Terms are not mutually exclusive
Слайд 22Securities Firm Income
Revenue:
Commissions
Fees - Advisory, investment banking, asset management Gains (and losses)
and interestExpenses: Labor costs Communications and space Clearing fees Borrowing costs
Слайд 23Finance Companies
Three basic types
Captive finance companies (owned by manufacturer, e.g.
GMAC)
Commercial finance companies and financial firm affiliates (owned by banks
or other financial firms, e.g. Foothill Group)Consumer or personal finance companies (specialized in high-risk finance, like Household Finance)
Funding sources - Bank credit, commercial paper, affiliate company financing
Слайд 25Asset-Pools
Origination
Government-sponsored agencies (GSEs)
Federal National Mortgage Association (FNMA or Fannie
May)
Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (FHLMC or Freddie Mac)
Student
Loan Marketing Corporation (SLMC or Sallie May)Private originators
Servicing
Servicing fees and costs
Transactions in servicing portfolios
Слайд 26Other Financial Firms
Mortgage banks
Information and advisory firms
Clearing firms and depositories
Exchanges
and communication networks
Clear differences between types are eroding, but traditionally
were due toRegulation, taxation, and charters
Specialization and expertise
Historical evolution