Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Overview of Common Types of Parasite Life Cycles
Содержание
- 1. Overview of Common Types of Parasite Life Cycles
- 2. Definitions of HostsMany parasites have more than
- 3. Definitions of HostsDefinitive host – a host
- 4. Definitions of HostsDefinitive host – a host
- 5. Definitions of HostsDefinitive host – a host
- 6. Definitions of HostsVector- any agent, either animate
- 7. Definitions of HostsVector- any agent, either animate
- 8. Definitions of HostsVector- any agent, either animate
- 9. OutlineMonogenea: Direct Life Cycles and Autoinfection (Complex
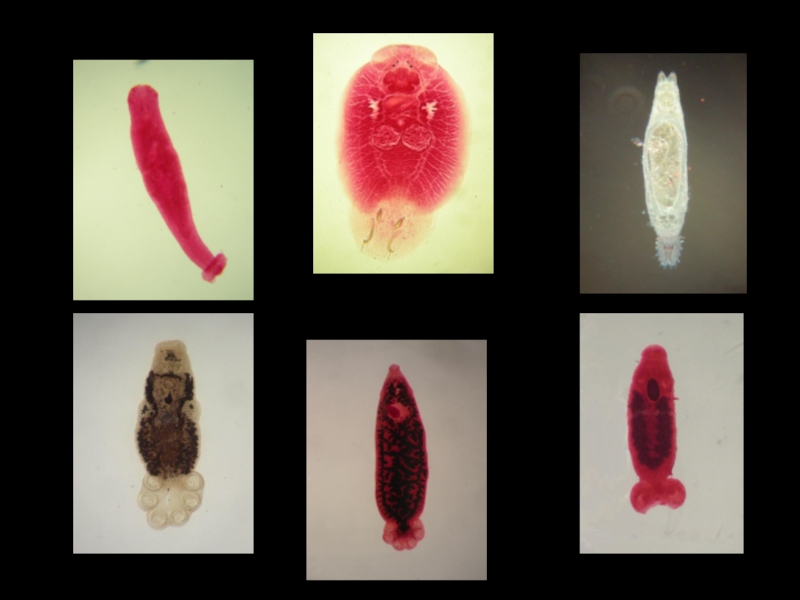
- 10. Platyhelminthes
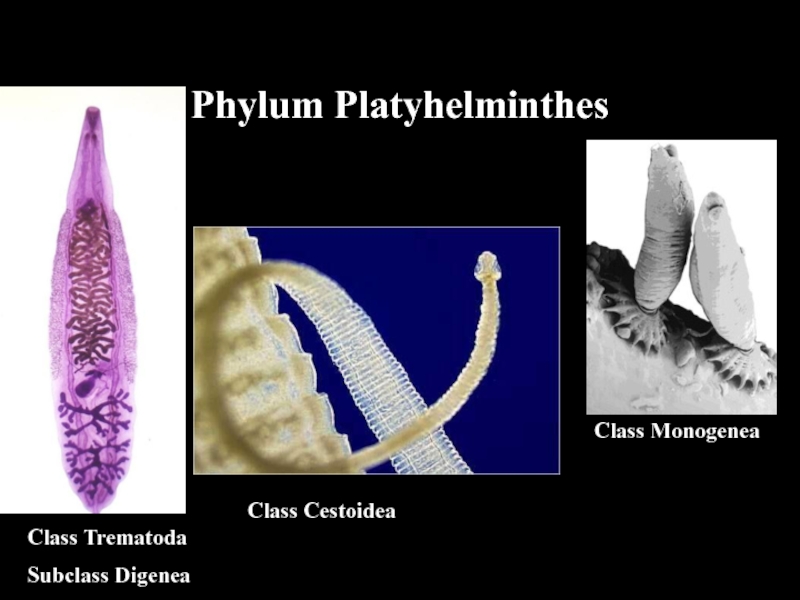
- 11. Phylum PlatyhelminthesClass TrematodaSubclass DigeneaClass CestoideaClass Monogenea
- 12. Class Monogenea:Most ecto-parasites of fish.Some endo-parasites of
- 13. Opisthaptor (Haptor)Ciliated larva
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. Слайд 15
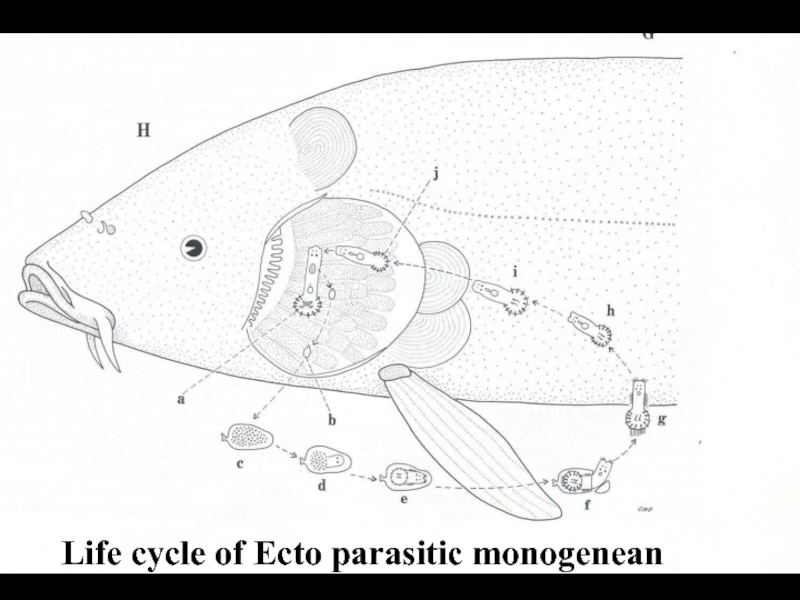
- 16. Life cycle of Ecto parasitic monogenean
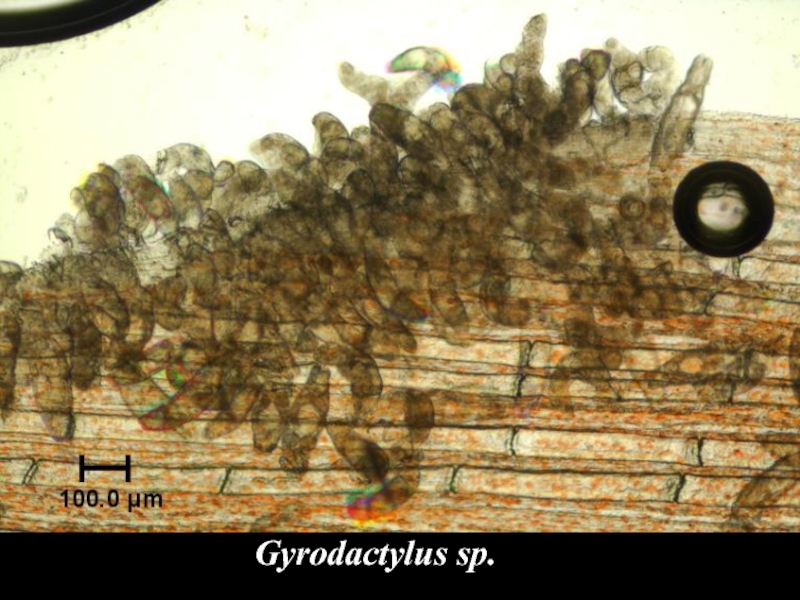
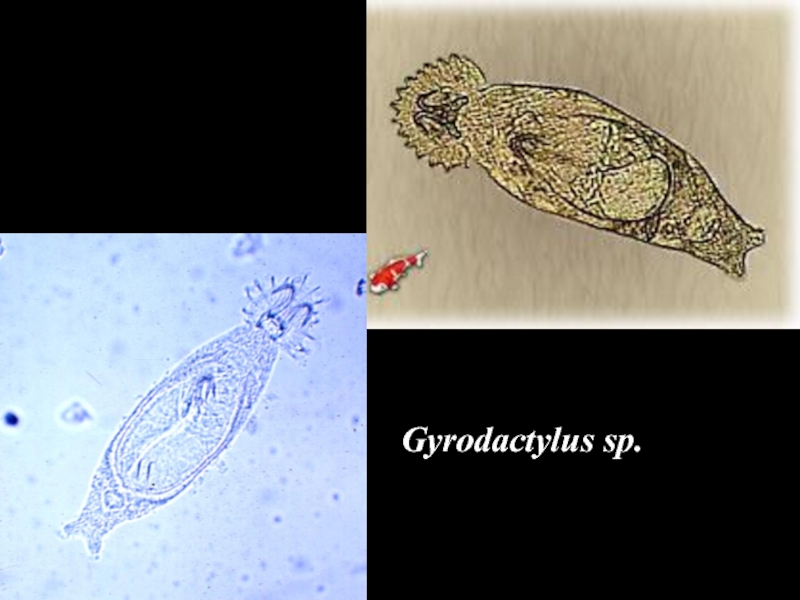
- 17. Gyrodactylus sp.
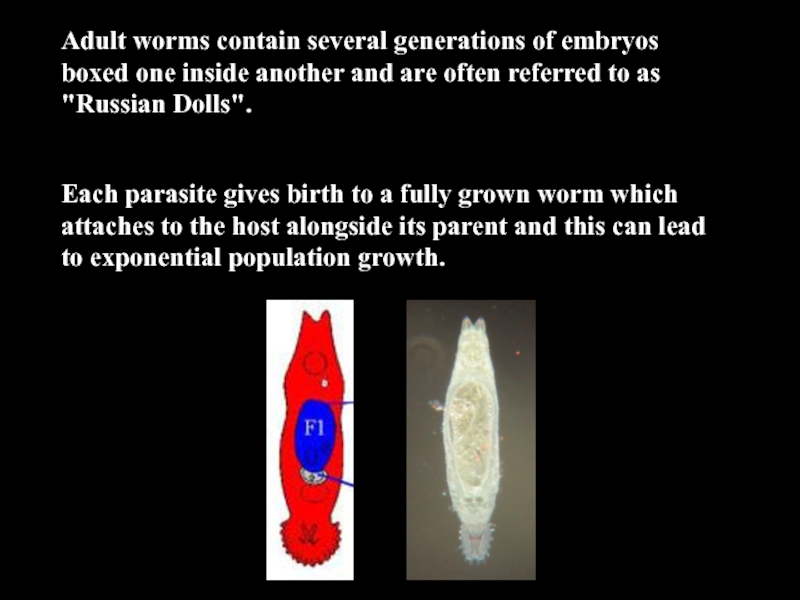
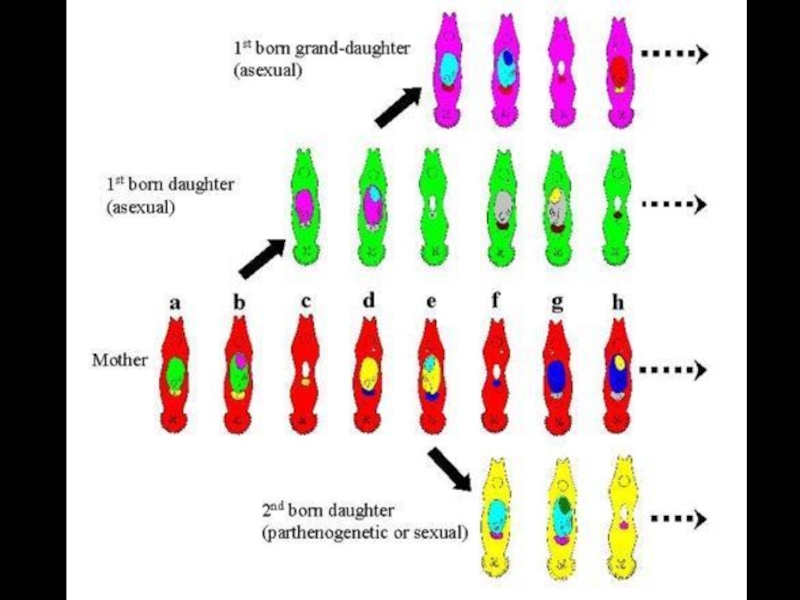
- 18. Adult worms contain several generations of embryos
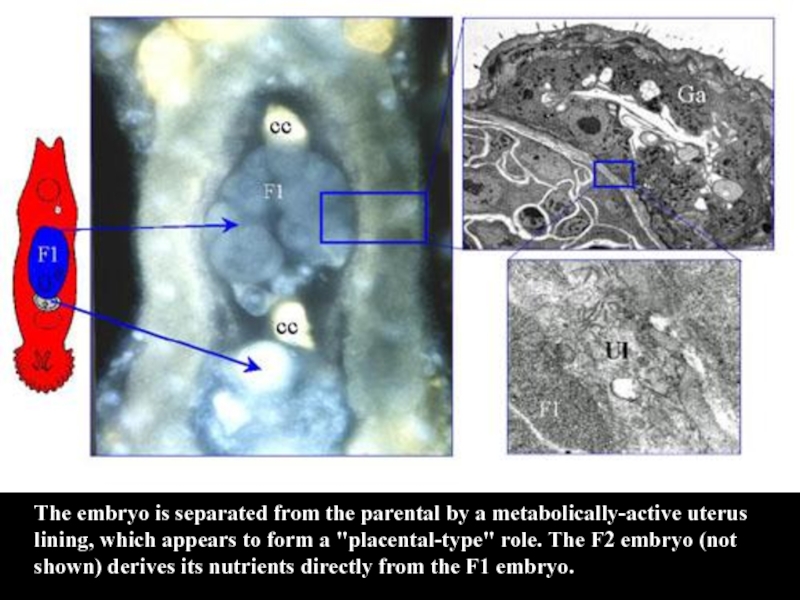
- 19. The embryo is separated from the parental
- 20. Gyrodactylus The reproductive biology of Gyrodactylus is
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Gyrodactylus sp.
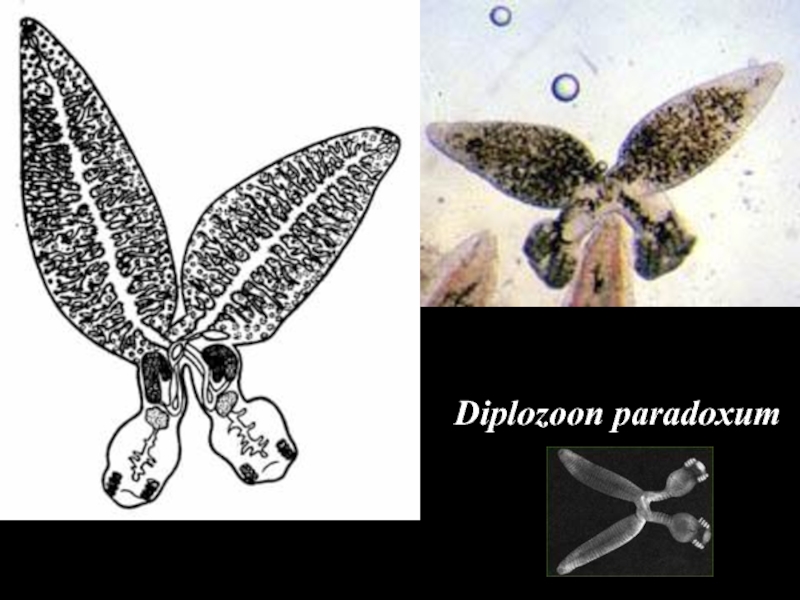
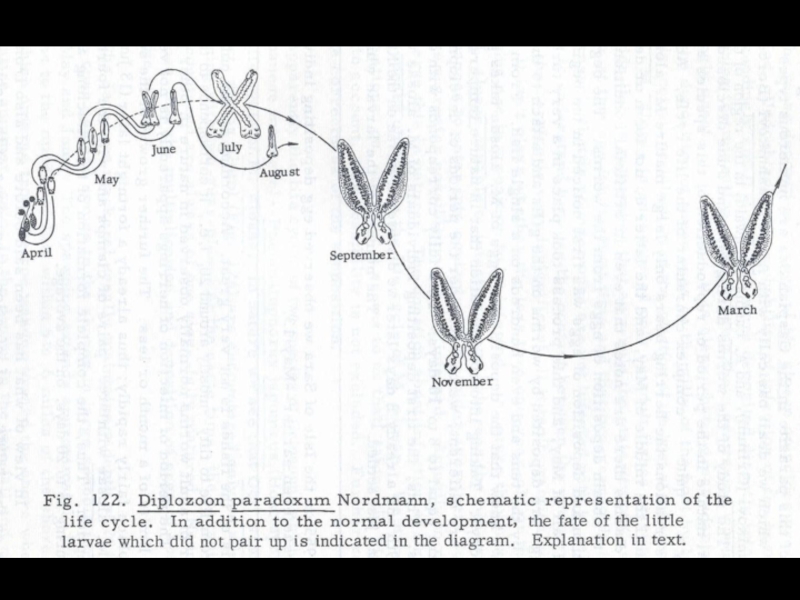
- 23. Diplozoon paradoxum
- 24. Слайд 24
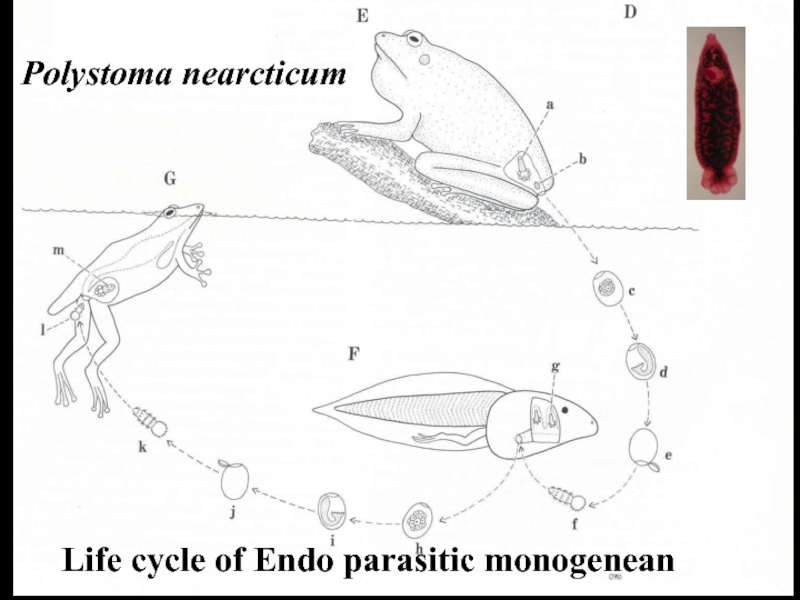
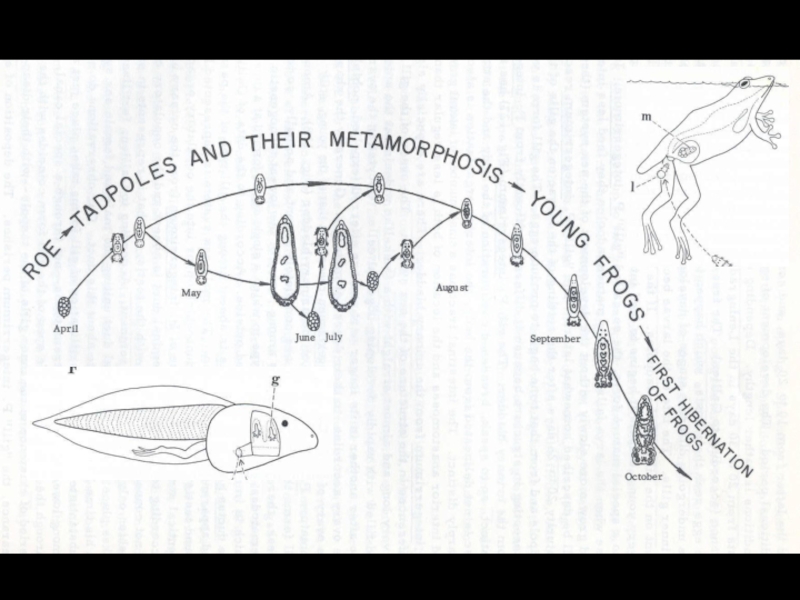
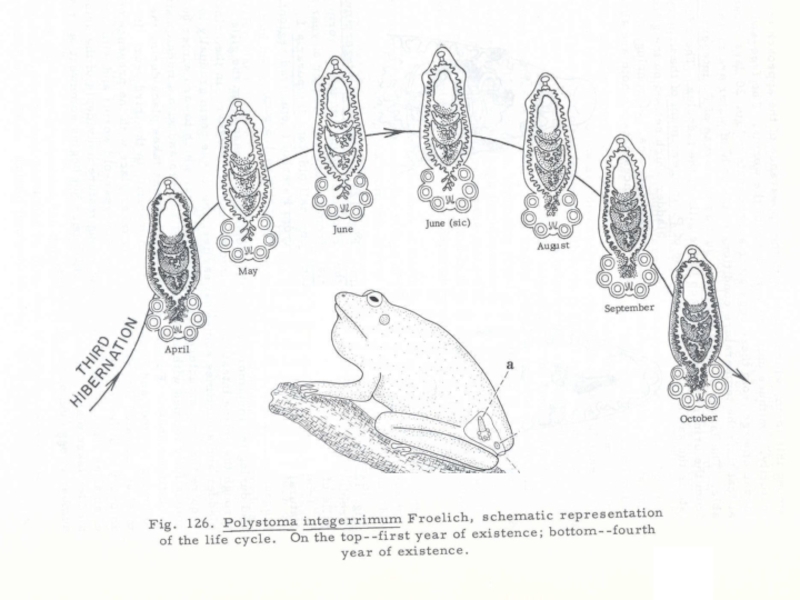
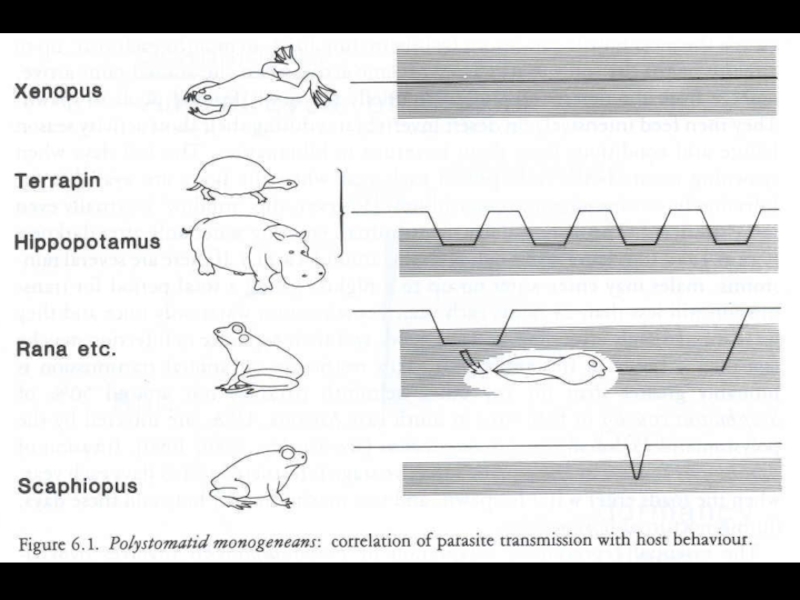
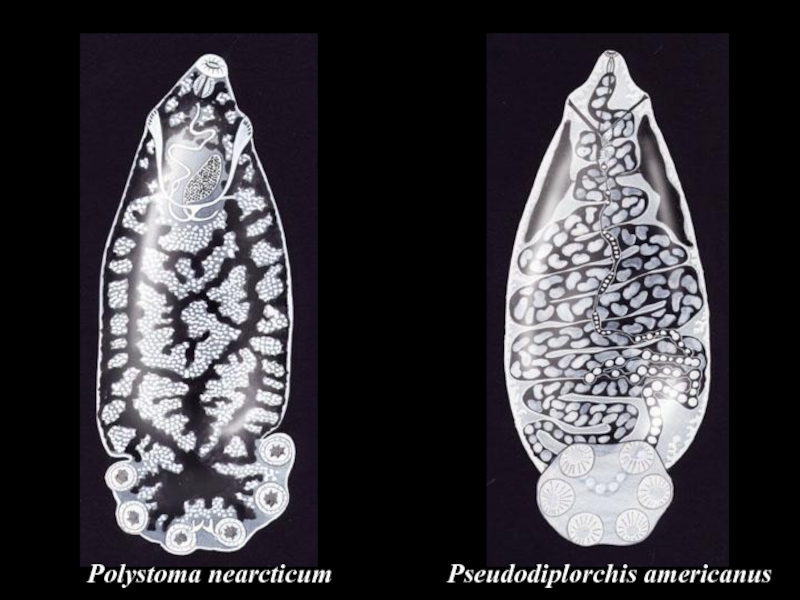
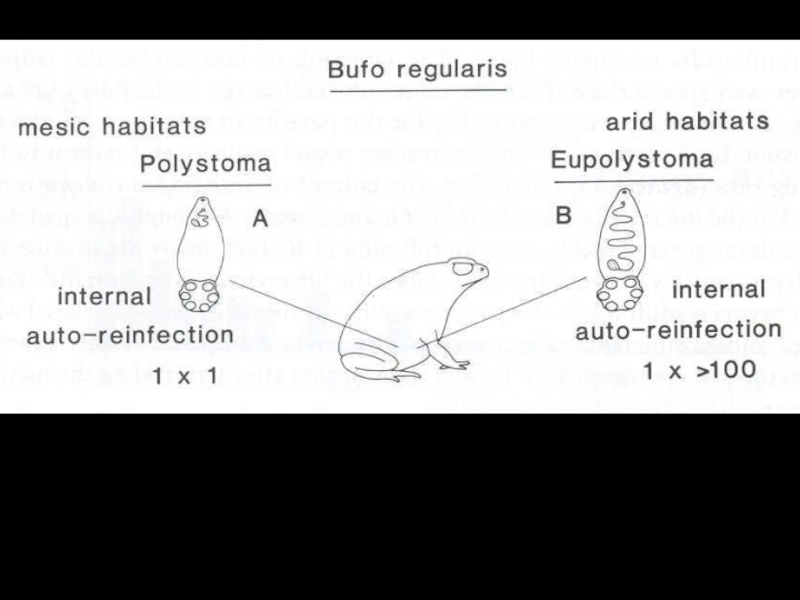
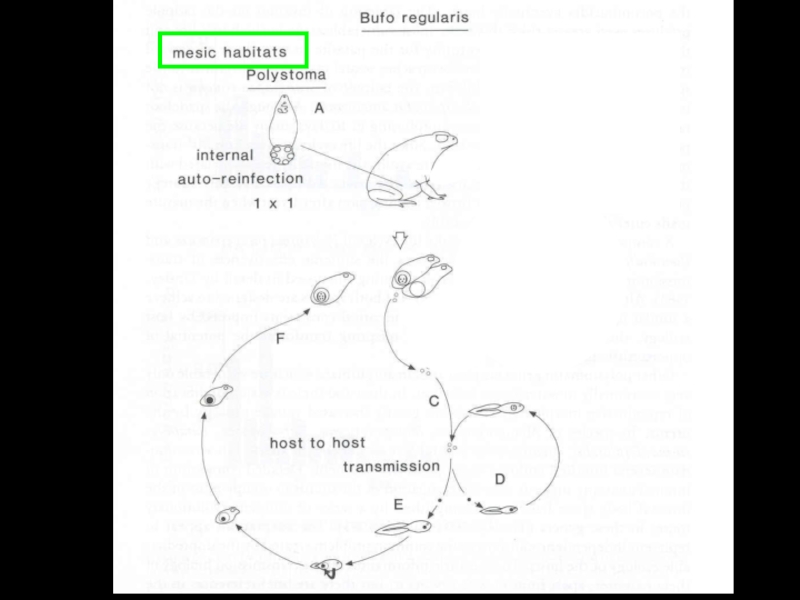
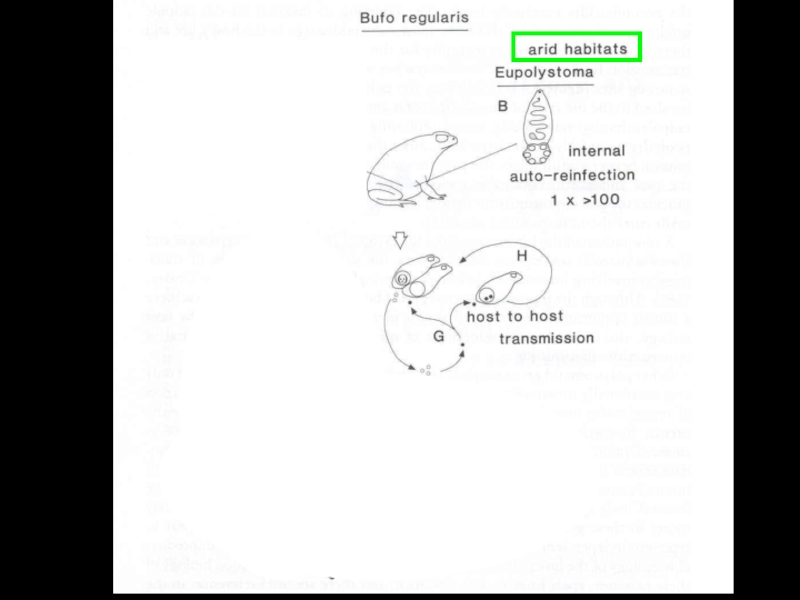
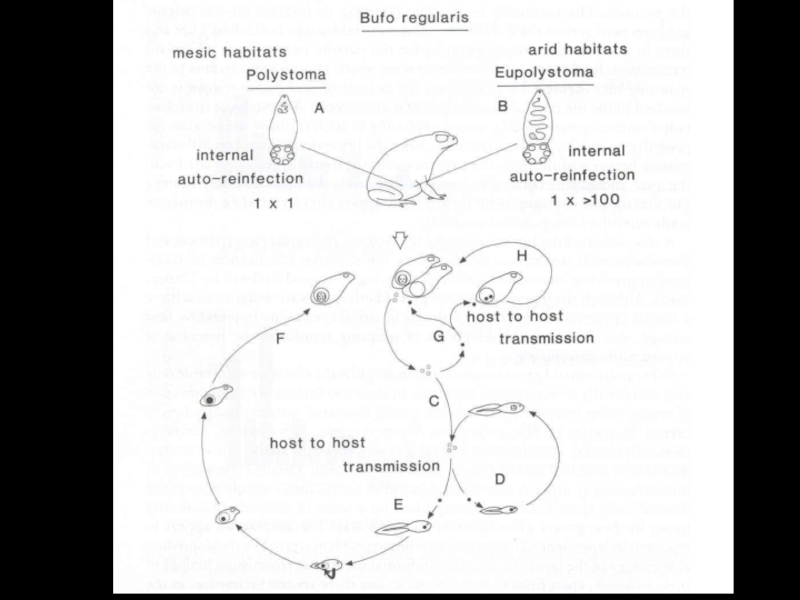
- 25. Polystoma nearcticumLife cycle of Endo parasitic monogenean
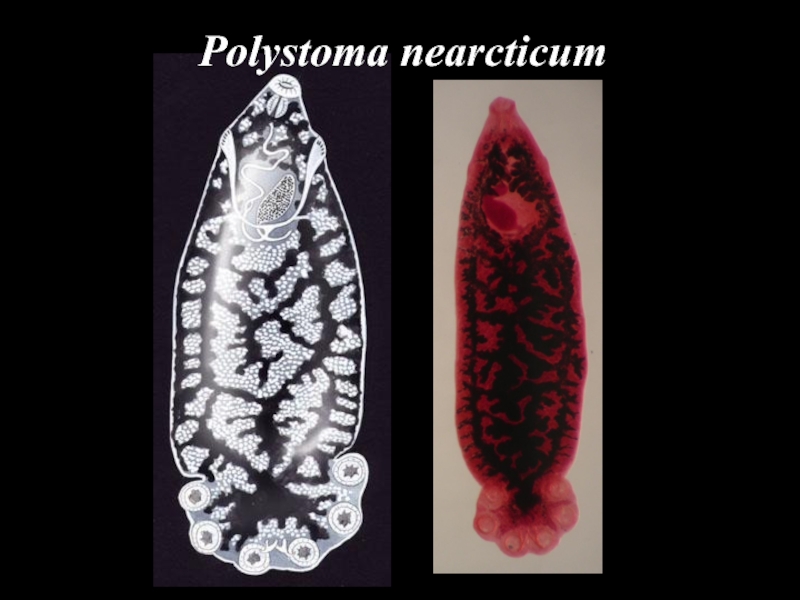
- 26. Polystoma nearcticum
- 27. Слайд 27
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. Spadefoot toad
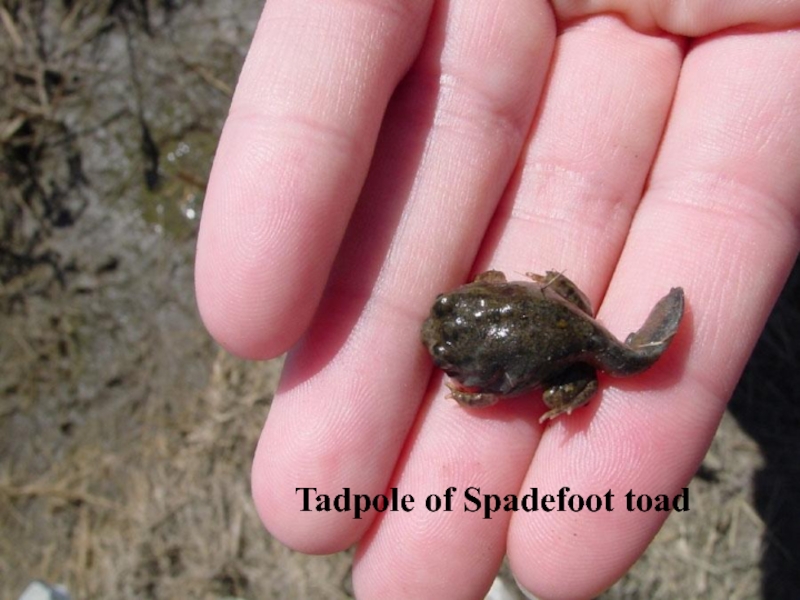
- 31. Tadpole of Spadefoot toad
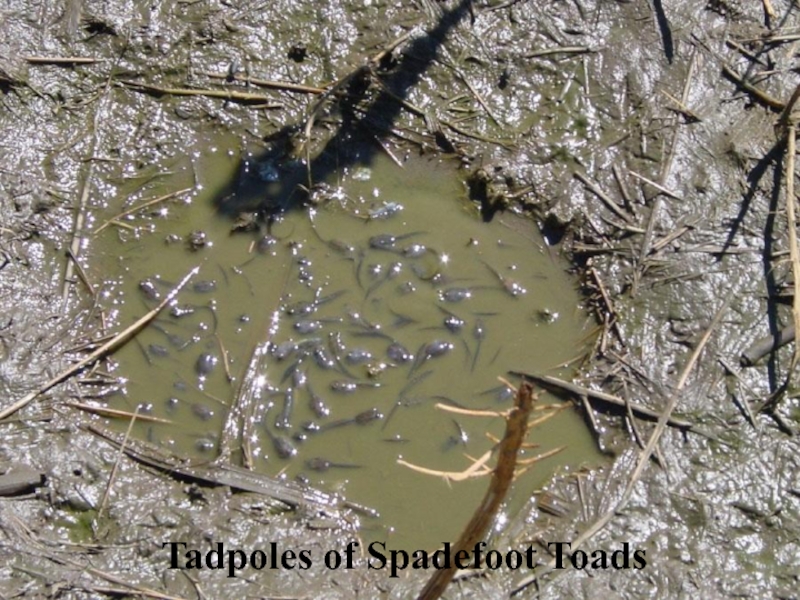
- 32. Tadpoles of Spadefoot Toads
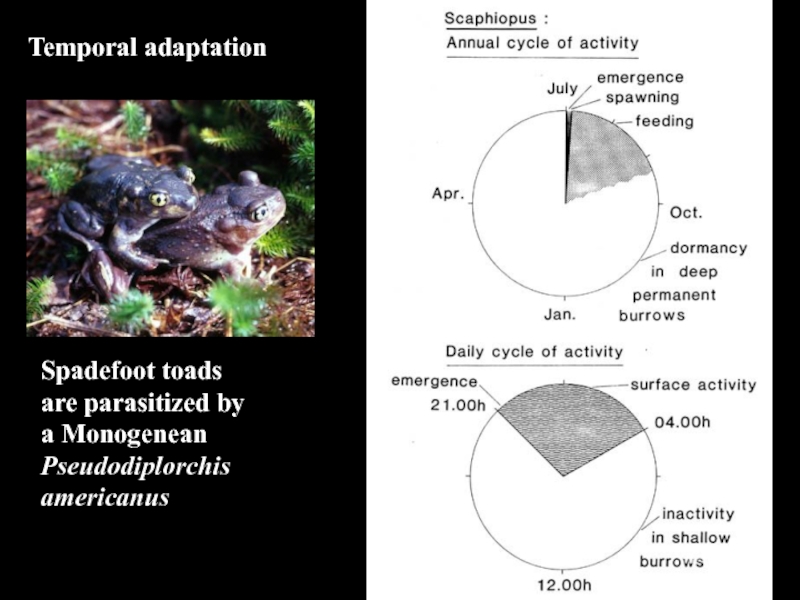
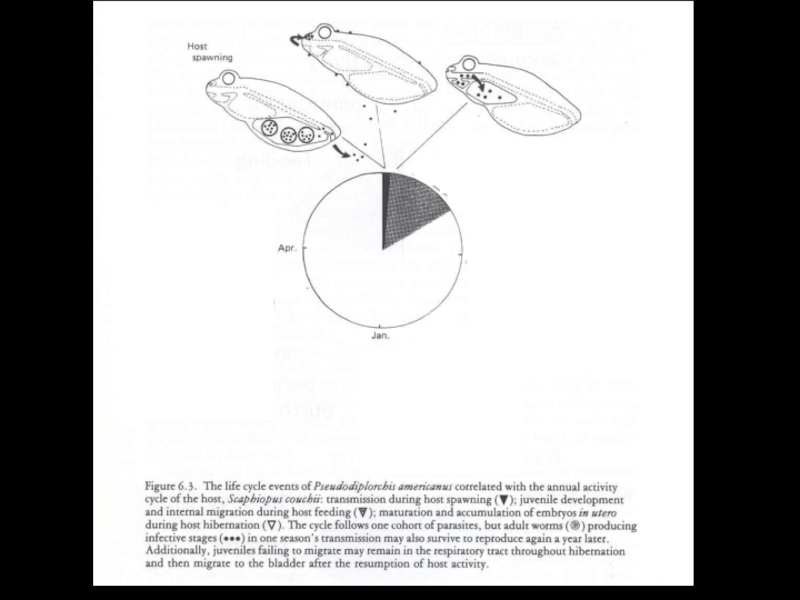
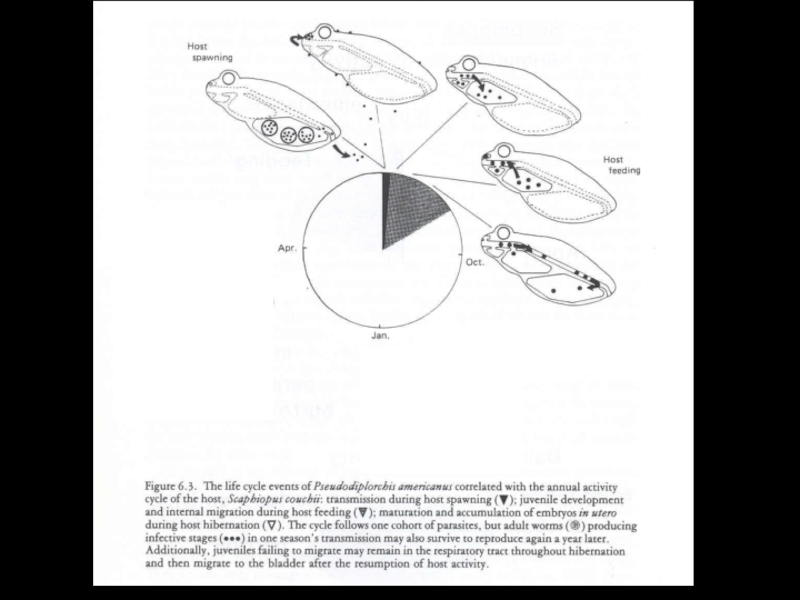
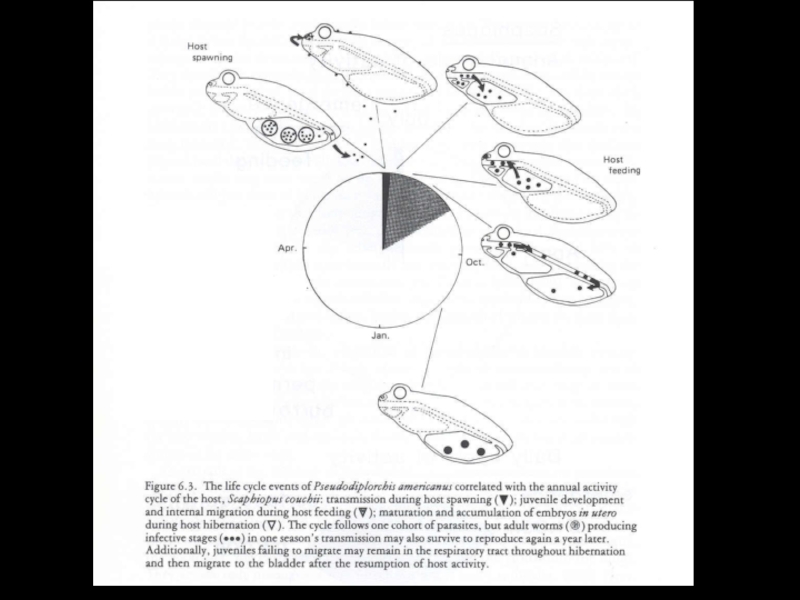
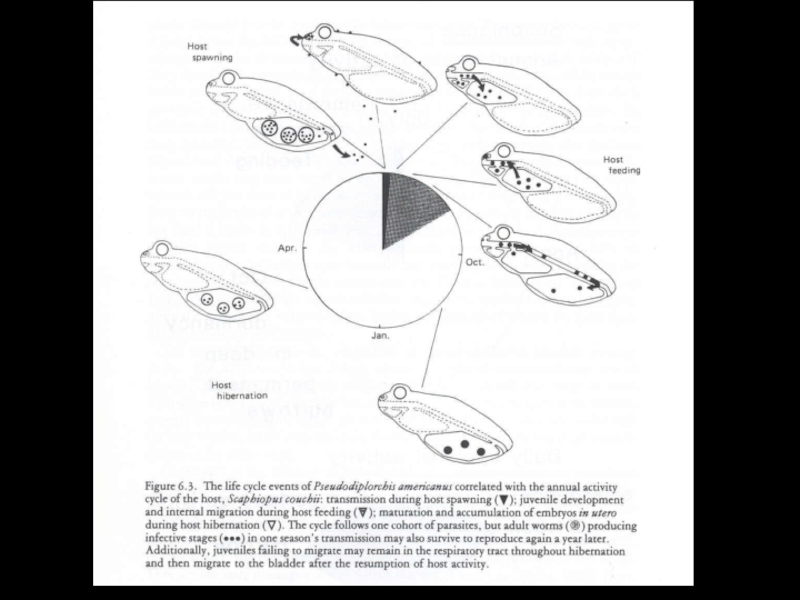
- 33. Temporal adaptationSpadefoot toadsare parasitized bya Monogenean Pseudodiplorchis americanus
- 34. Pseudodiplorchis americanusPolystoma nearcticum
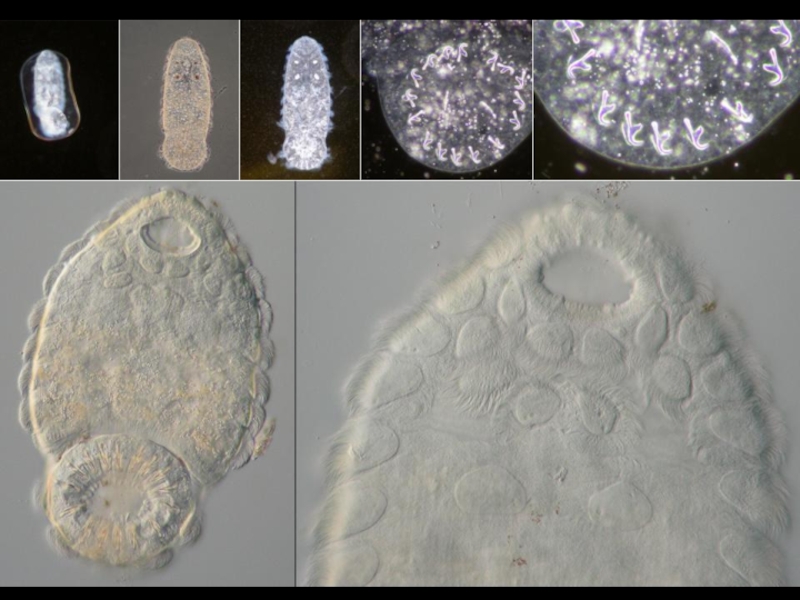
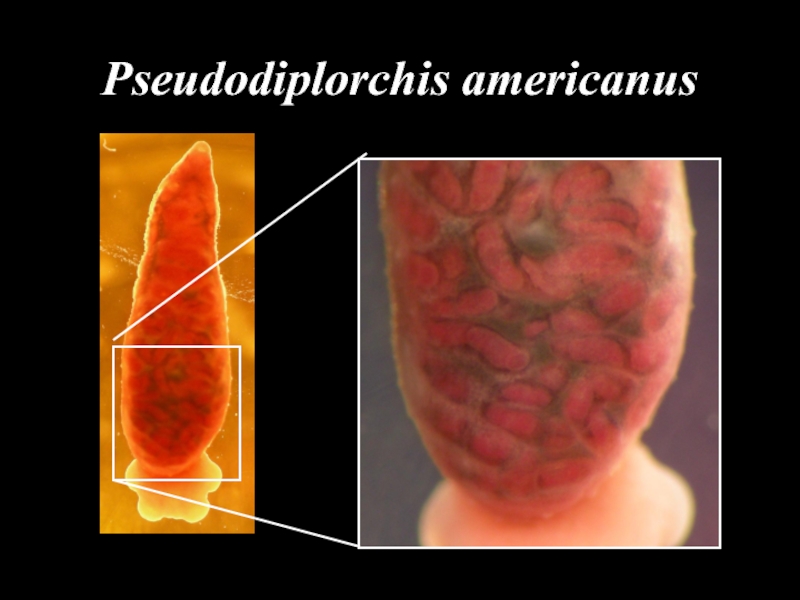
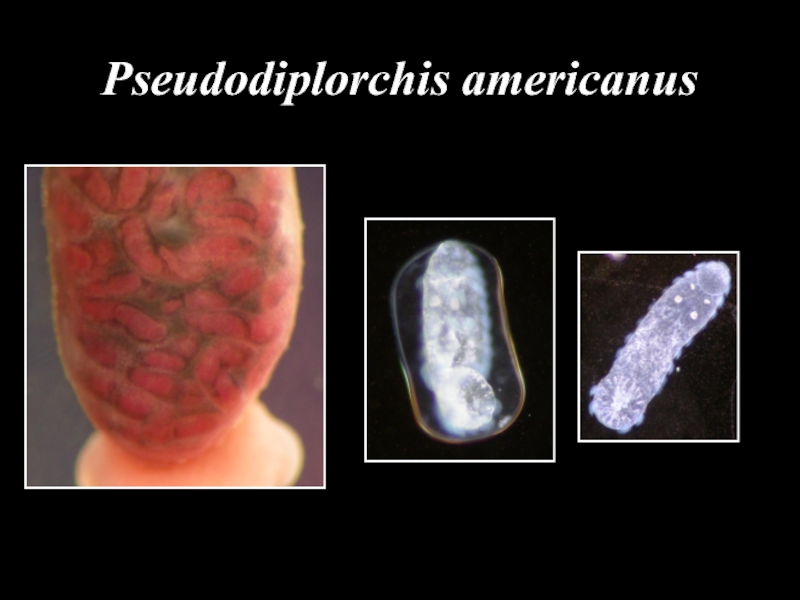
- 35. Pseudodiplorchis americanus
- 36. Pseudodiplorchis americanus
- 37. Pseudodiplorchis americanus
- 38. Слайд 38
- 39. Слайд 39
- 40. Слайд 40
- 41. Слайд 41
- 42. Слайд 42
- 43. Слайд 43
- 44. Слайд 44
- 45. Слайд 45
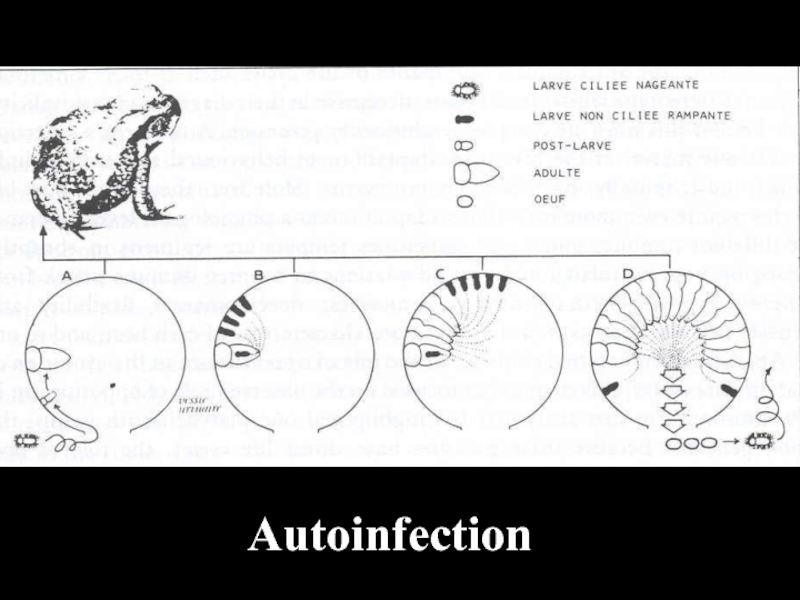
- 46. Autoinfection
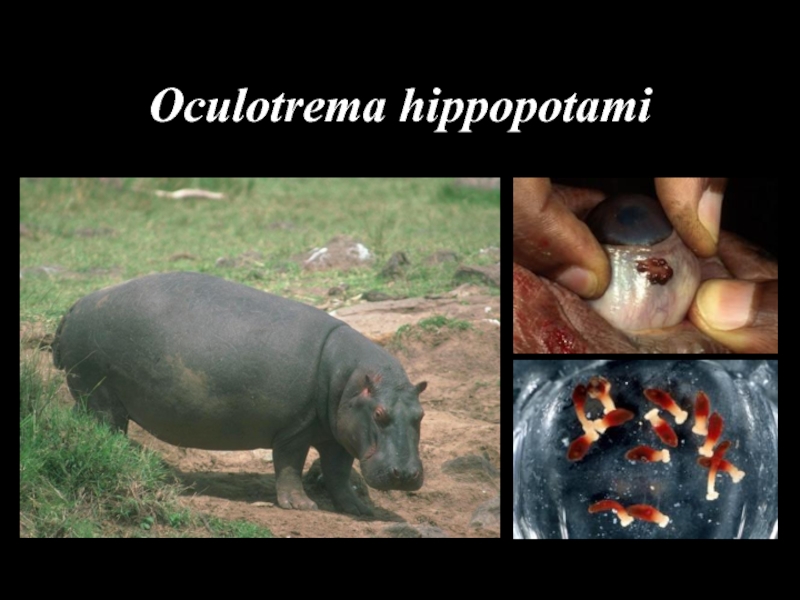
- 47. Oculotrema hippopotami
- 48. Скачать презентанцию
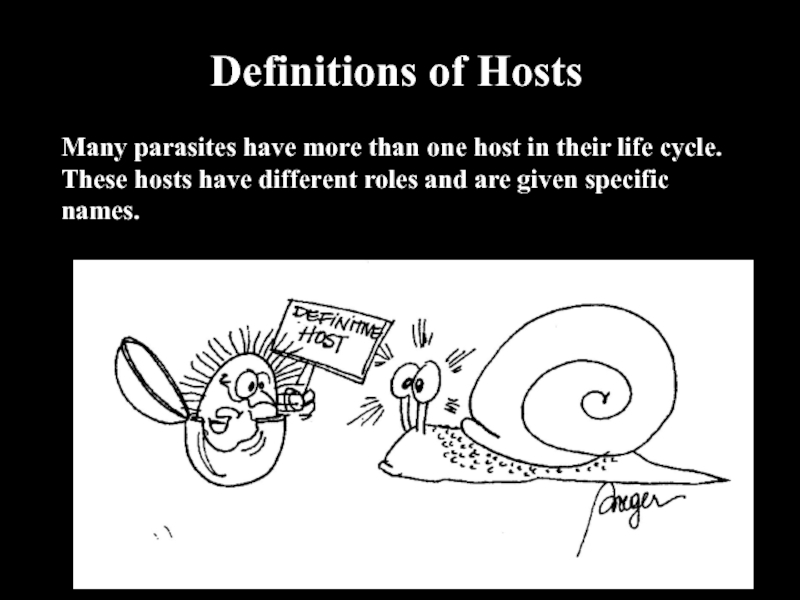
Definitions of HostsMany parasites have more than one host in their life cycle. These hosts have different roles and are given specific names.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3Definitions of Hosts
Definitive host – a host in which the
parasite reaches sexual maturity and undergoes reproduction.
Слайд 4Definitions of Hosts
Definitive host – a host in which the
parasite reaches sexual maturity and undergoes reproduction.
Intermediate – a
host in which the parasite undergoes larval development but does not reach sexual maturity.Слайд 5Definitions of Hosts
Definitive host – a host in which the
parasite reaches sexual maturity and undergoes reproduction.
Intermediate – a
host in which the parasite undergoes larval development but does not reach sexual maturity.Paratenic host (Transport host) – a host in which a parasite survives without undergoing further development. A paratenic host accumulates and maintains stages of a parasite, and although beneficial, is not essential to the life cycle.
Слайд 6Definitions of Hosts
Vector- any agent, either animate or inanimate (such
as wind, water, or arthropod) that transmits an infectious organism.
Слайд 7Definitions of Hosts
Vector- any agent, either animate or inanimate (such
as wind, water, or arthropod) that transmits an infectious organism.
Biological
Vector- a vector in which a parasite lives or develops. The parasite undergoes morphologic change and/or multiplication, and the vector is usually essential for the life cycle.Слайд 8Definitions of Hosts
Vector- any agent, either animate or inanimate (such
as wind, water, or arthropod) that transmits an infectious organism.
Biological
Vector- a vector in which a parasite lives or develops. The parasite undergoes morphologic change and/or multiplication, and the vector is usually essential for the life cycle.Mechanical Vector- a vector which transmits a parasite by mechanical means only. It may be living or non-living and is not essential for the parasite’s life cycle.
Слайд 9Outline
Monogenea: Direct Life Cycles and Autoinfection (Complex or Simple?)
Trematoda (Digenea):
Complex Life Cycles
Difficulty of Solving Life Cycles Example Cestodes (Tapeworms)
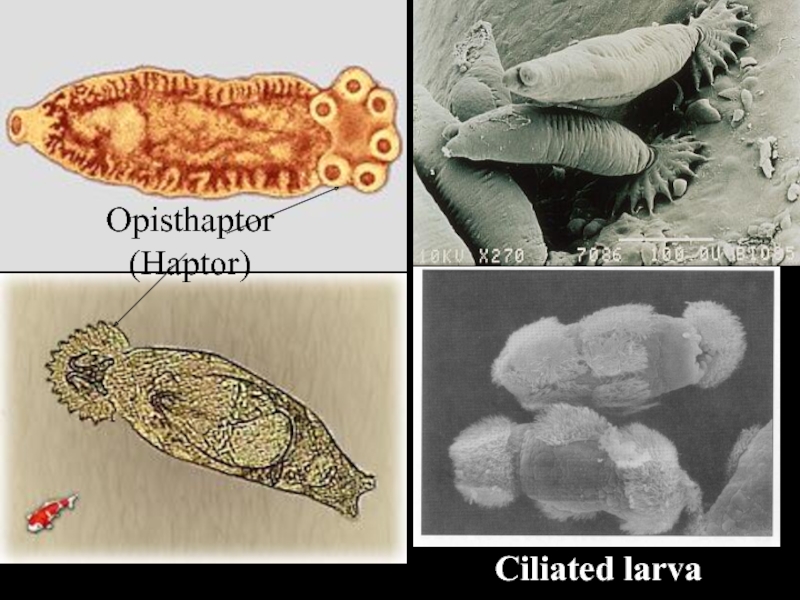
Слайд 12Class Monogenea:
Most ecto-parasites of fish.
Some endo-parasites of urinary bladder and
mouth of amphibians and reptiles.
Body covered by tegument.
Posterior hooks with
opisthaptor (haptor).Direct life cycle with single host.