Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Planning Tools and Techniques
Содержание
- 1. Planning Tools and Techniques
- 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 4. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 5. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 6. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 7. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 8. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 9. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 10. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 11. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 12. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 13. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 14. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 15. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 16. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 17. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 18. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice HallB–Exhibit B–5 A Gantt Chart
- 19. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice HallB–Exhibit B–6 A Load Chart
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice HallB–Exhibit B–10 Breakeven Analysis
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 27. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 28. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 29. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 30. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 31. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 32. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 33. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 34. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Planning
Tools and
Techniques
editionСлайд 2Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Learning
Outcomes Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this
chapter.Techniques for Assessing the Environment
List the different approaches to assess the environment.
Explain what competitor intelligence is and ways that managers can do it legally and ethically.
Describe how managers can improve the effectiveness of forecasting.
List the steps in the benchmarking process.
Слайд 3Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Learning
Outcomes
Techniques for Allocating Resources
List the four techniques for allocating resources.
Describe
the different types of budgets.Explain what a Gantt chart and a load chart do.
Describe how PERT network analysis works.
Understand how to compute a breakeven point.
Describe how managers can use linear programming.
Слайд 4Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Assessing
the Environment
Environmental Scanning
The screening of large amounts of information to
anticipate and interpret change in the environment.Competitor Intelligence
The process of gathering information about competitors—who they are; what they are doing
Is not spying but rather careful attention to readily accessible information from employees, customers, suppliers, the Internet, and competitors themselves.
May involve reverse engineering of competing products to discover technical innovations.
Слайд 5Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Assessing
the Environment
Environmental Scanning (cont’d)
Global Scanning
Screening a broad scope of information
on global forces that might affect the organization.Has value to firms with significant global interests.
Draws information from sources that provide global perspectives on worldwide issues and opportunities.
Слайд 6Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Assessing
the Environment (cont’d)
Forecasting
The part of organizational planning that involves creating
predictions of outcomes based on information gathered by environmental scanning.Facilitates managerial decision making.
Is most accurate in stable environments.
Слайд 7Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Assessing
the Environment (cont’d)
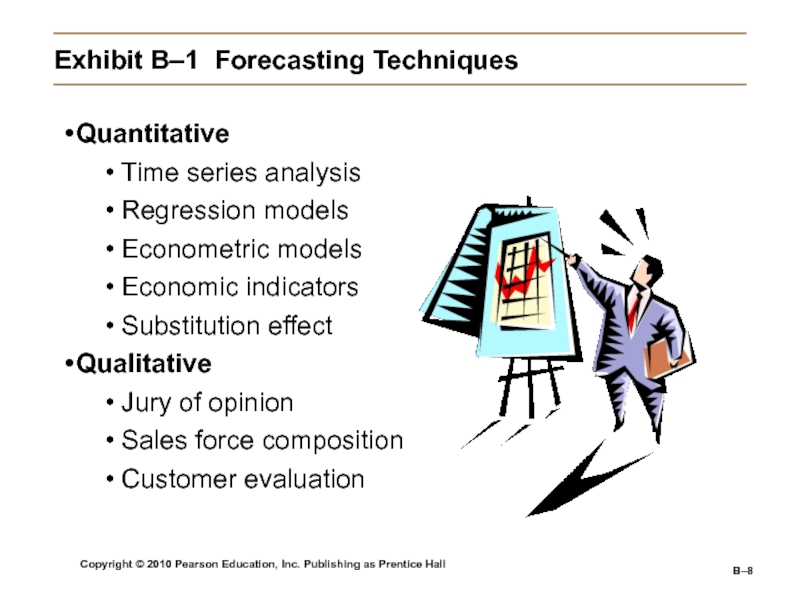
Forecasting Techniques
Quantitative forecasting
Applying a set of mathematical rules
to a series of hard data to predict outcomes (e.g., units to be produced).Qualitative forecasting
Using expert judgments and opinions to predict less than precise outcomes (e.g., direction of the economy).
Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR) Software
A standardized way for organizations to use the Internet to exchange data.
Слайд 8Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Exhibit
B–1 Forecasting Techniques
Quantitative
Time series analysis
Regression models
Econometric models
Economic indicators
Substitution effect
Qualitative
Jury of
opinionSales force composition
Customer evaluation
Слайд 9Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Making
Forecasting More Effective
Use simple forecasting methods.
Compare each forecast with its
corresponding “no change” forecast.Don’t rely on a single forecasting method.
Don’t assume that the turning points in a trend can be accurately identified.
Shorten the time period covered by a forecast.
Remember that forecasting is a developed managerial skill that supports decision making.
Слайд 10Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
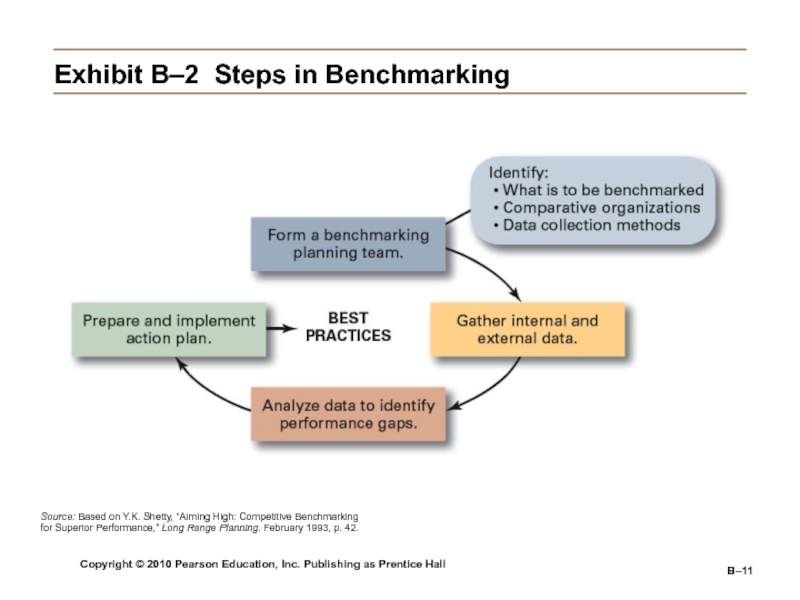
Benchmarking
The
search for the best practices among competitors and noncompetitors that
lead to their superior performance.By analyzing and copying these practices, firms can improve their performance.
Слайд 11Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Exhibit
B–2 Steps in Benchmarking
Source: Based on Y.K. Shetty, “Aiming High: Competitive
Benchmarking for Superior Performance,” Long Range Planning. February 1993, p. 42.Слайд 12Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Allocating
Resources
Types of Resources
The assets of the organization
Financial: debt, equity, and
retained earningsPhysical: buildings, equipment, and raw materials
Human: experiences, skills, knowledge, and competencies
Intangible: brand names, patents, reputation, trademarks, copyrights, and databases
Слайд 13Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Allocating
Resources: Budgeting
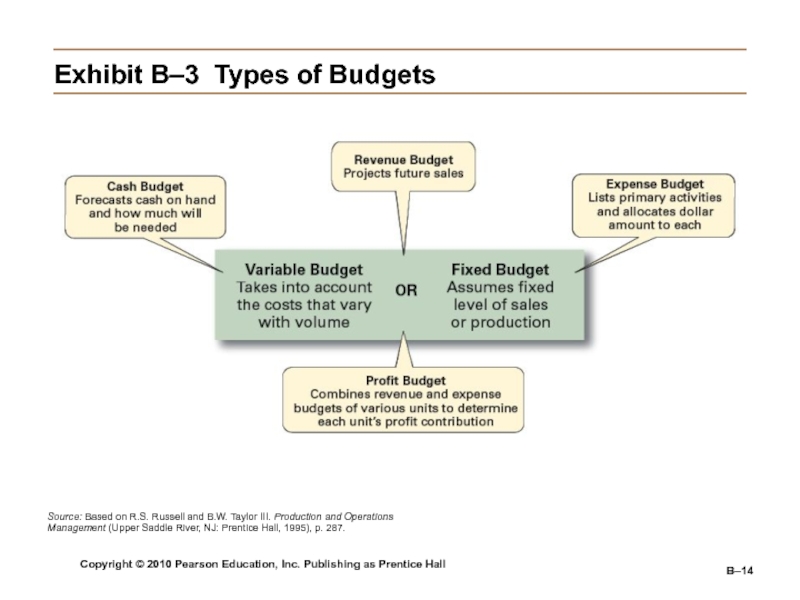
Budgets
Are numerical plans for allocating resources (e.g., revenues, expenses,
and capital expenditures).Are used to improve time, space, and use of material resources.
Are the most commonly used and most widely applicable planning technique for organizations.
Слайд 14Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Exhibit
B–3 Types of Budgets
Source: Based on R.S. Russell and B.W. Taylor
III. Production and Operations Management (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1995), p. 287. Слайд 15Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Exhibit
B–4 Suggestions for Improving Budgeting
Collaborate and communicate.
Be flexible.
Goals should drive budgets—budgets
should not determine goals.Coordinate budgeting throughout the organization.
Use budgeting/planning software when appropriate.
Remember that budgets are tools.
Remember that profits result from smart management, not because you budgeted for them.
Слайд 16Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Allocating
Resources: Scheduling
Schedules
Plans that allocate resources by detailing what activities have
to be done, the order in which they are to be completed, who is to do each, and when they are to be completed.Represent the coordination of various activities.
Слайд 17Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Allocating
Resources: Charting
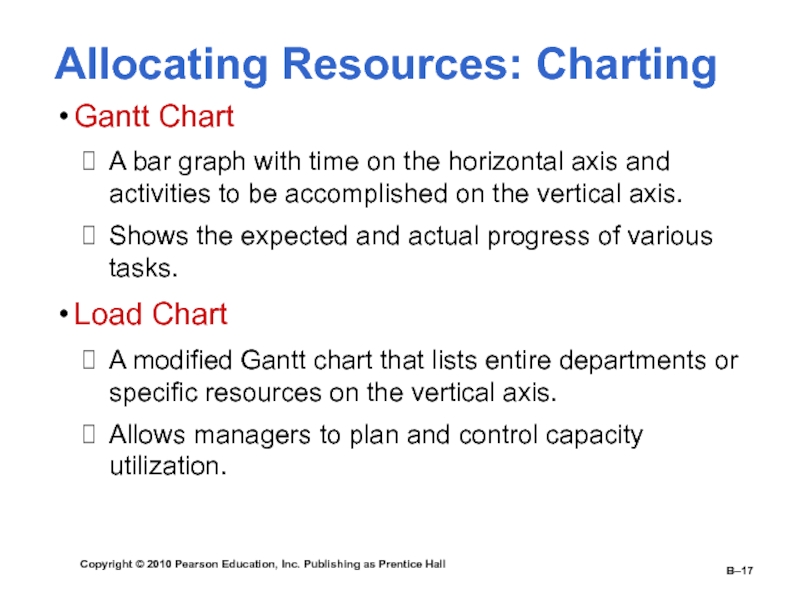
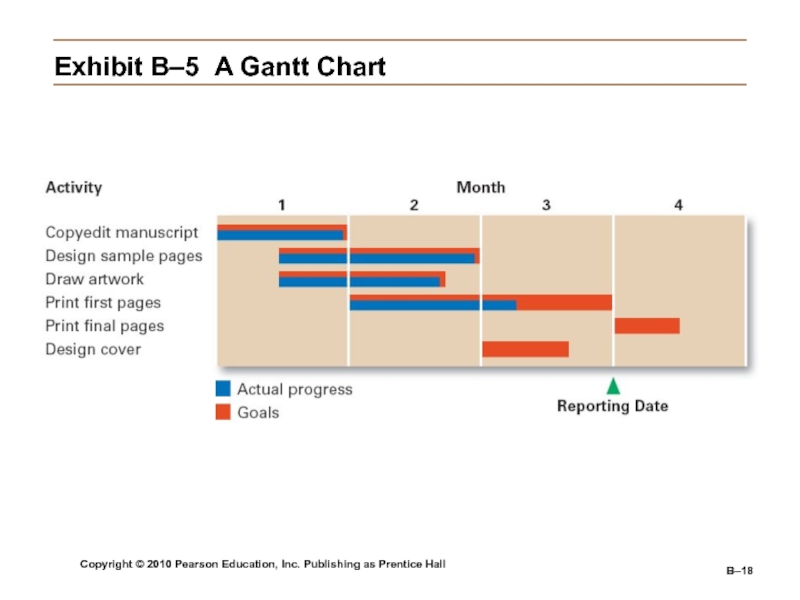
Gantt Chart
A bar graph with time on the horizontal
axis and activities to be accomplished on the vertical axis.Shows the expected and actual progress of various tasks.
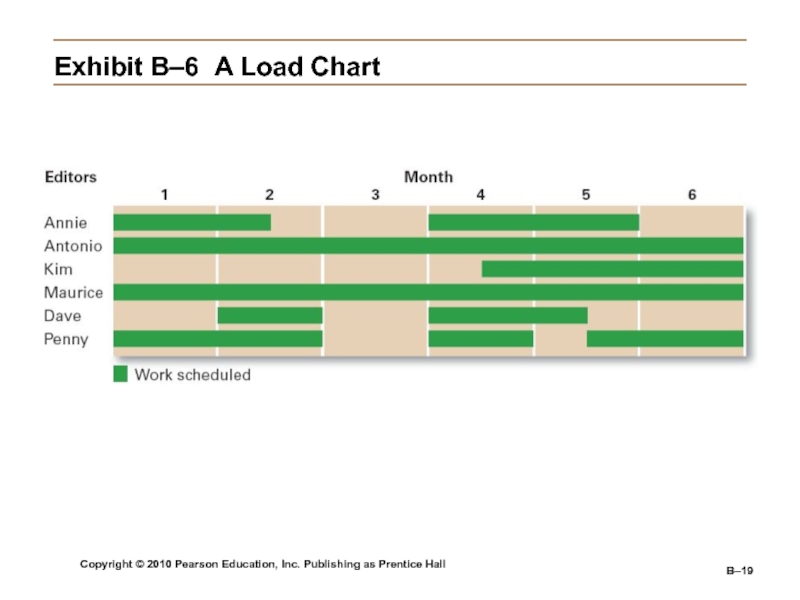
Load Chart
A modified Gantt chart that lists entire departments or specific resources on the vertical axis.
Allows managers to plan and control capacity utilization.
Слайд 18Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Exhibit
B–5 A Gantt Chart
Слайд 19Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Exhibit
B–6 A Load Chart
Слайд 20Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Allocating
Resources: Analysis
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
A flow chart diagram
that depicts the sequence of activities needed to complete a project and the time or costs associated with each activity.Events: endpoints for completion.
Activities: time required for each activity.
Slack time: the time that a completed activity waits for another activity to finish so that the next activity, which depends on the completion of both activities, can start.
Critical path: the path (ordering) of activities that allows all tasks to be completed with the least slack time.
Слайд 21Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Exhibit
B–7 Steps in Developing a PERT Network
Identify every significant activity that
must be achieved for a project to be completed.Determine the order in which these events must be completed.
Diagram the flow of activities from start to finish, identifying each activity and its relationship to all other activities.
Compute a time estimate for completing each activity.
Using the network diagram that contains time estimates for each activity, determine a schedule for the start and finish dates of each activity and for the entire project.
Слайд 22Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
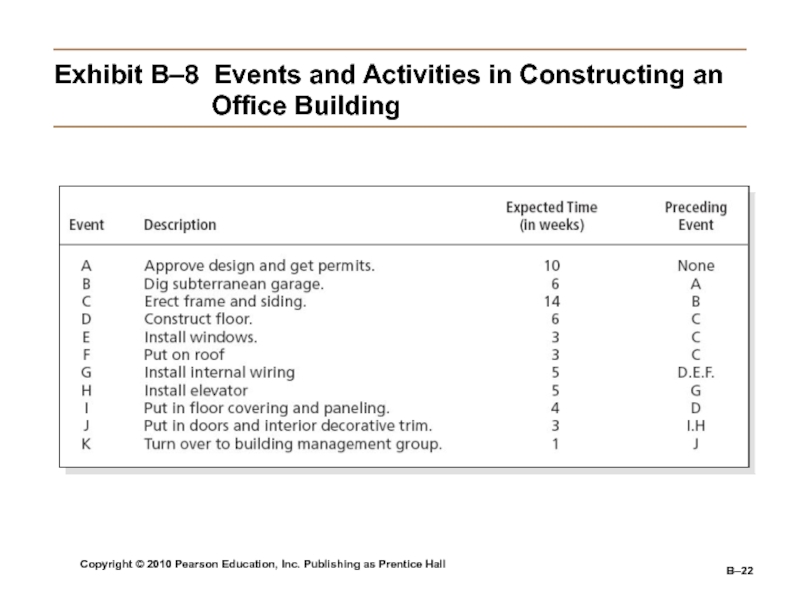
Exhibit
B–8 Events and Activities in Constructing an Office
BuildingСлайд 23Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
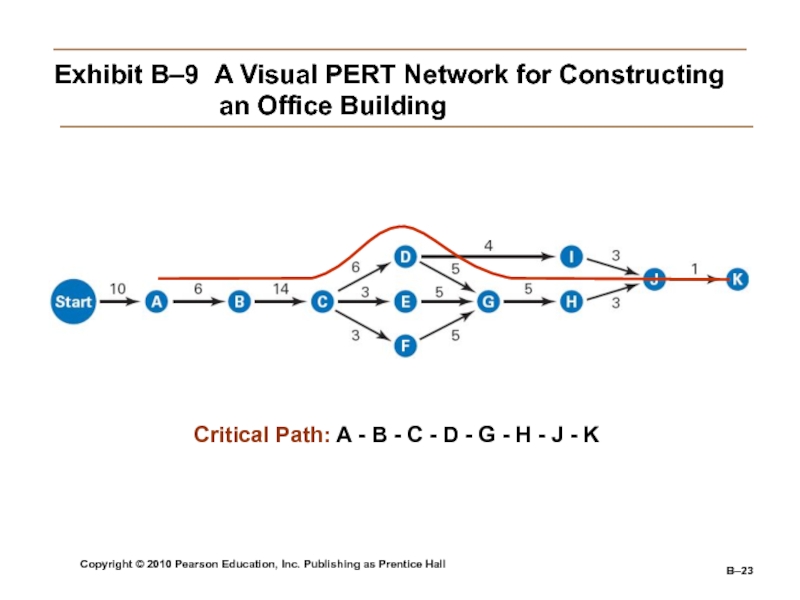
Exhibit
B–9 A Visual PERT Network for Constructing an
Office BuildingCritical Path: A - B - C - D - G - H - J - K
Слайд 24Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Allocating
Resources: Analysis (cont’d)
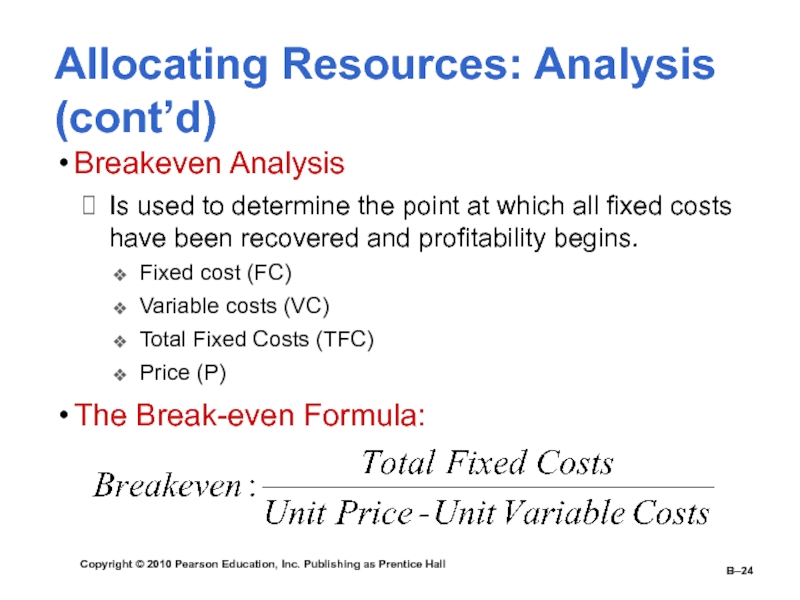
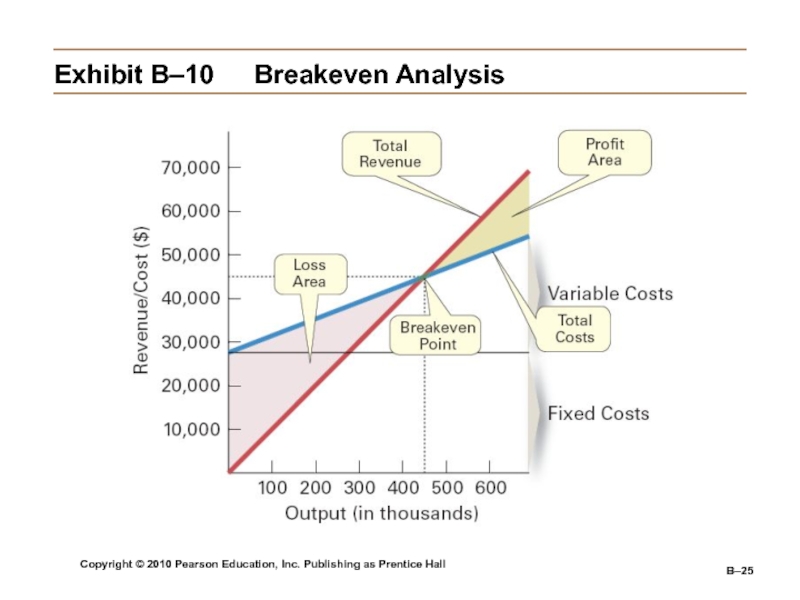
Breakeven Analysis
Is used to determine the point at
which all fixed costs have been recovered and profitability begins.Fixed cost (FC)
Variable costs (VC)
Total Fixed Costs (TFC)
Price (P)
The Break-even Formula:
Слайд 25Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Exhibit
B–10 Breakeven Analysis
Слайд 26Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Allocating
Resources: Analysis (cont’d)
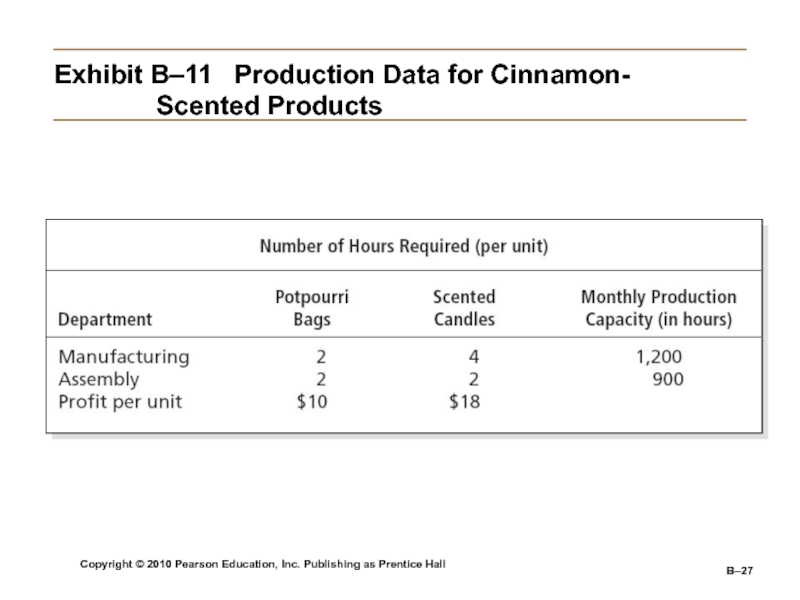
Linear Programming
A technique that seeks to solve resource
allocation problems using the proportional relationships between two variables.Слайд 27Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Exhibit
B–11 Production Data for Cinnamon-
Scented Products
Слайд 28Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
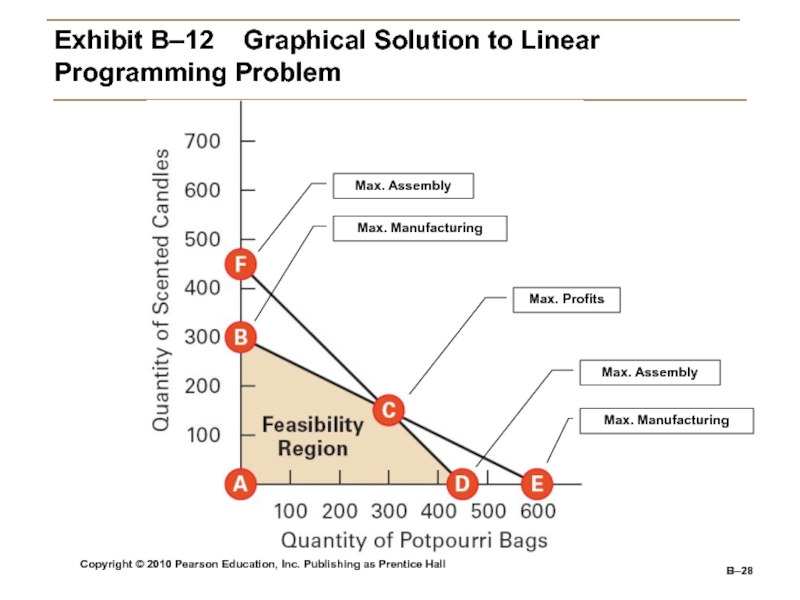
B–
Exhibit
B–12 Graphical Solution to Linear
Programming ProblemMax. Assembly
Max. Manufacturing
Max. Manufacturing
Max. Assembly
Max. Profits
Слайд 29Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Contemporary
Planning Techniques
Project
A one-time-only set of activities that has a definite
beginning and ending point time.Project Management
The task of getting a project’s activities done on time, within budget, and according to specifications.
Define project goals
Identify all required activities, materials, and labor
Determine the sequence of completion
Слайд 30Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
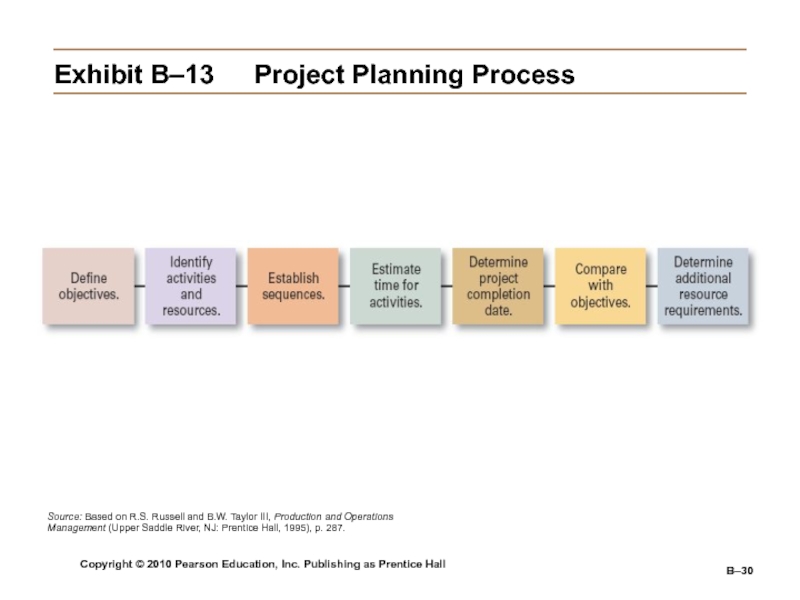
B–
Exhibit
B–13 Project Planning Process
Source: Based on R.S. Russell and B.W. Taylor
III, Production and Operations Management (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1995), p. 287.Слайд 31Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Contemporary
Planning Techniques (cont’d)
Scenario
A consistent view of what the future is
likely to be.Scenario Planning
An attempt not try to predict the future but to reduce uncertainty by playing out potential situations under different specified conditions.
Contingency Planning
Developing scenarios that allow managers determine in advance what their actions should be should a considered event actually occur.
Слайд 32Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
B–
Terms
to Know
environmental scanning
competitor intelligence
forecasts
quantitative forecasting
qualitative forecasting
benchmarking
resources
budget
scheduling
Gantt chart
load chart
PERT network
events
activities
slack time
critical
pathbreakeven analysis
linear programming
project
project management
scenario