Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
SCHISTOSOMIASIS
Содержание
- 1. SCHISTOSOMIASIS
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. Schistosomes are prevalent in rural and outlying
- 4. 1851 - Bilharz opened pathogen of urinal
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. It is difficult to know how many
- 9. Intestinal schistosomiasis, caused by Schistosoma japonicum, S.
- 10. Source of the infection: S. mansoni, and
- 11. Eggs are excreted in human urine and
- 12. Mature male and female worms pair and
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. ADULT PARASITES DO NOT GO OUT FROM
- 16. Groups of risk: workers of rice and
- 17. IMMUNITY Natural - human immunity against schistosoma
- 18. PATHOGENESIS 1. Sensitization
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. 1. Stage of infection:
- 21. 2. Stage of maturation (Japanese sch. -
- 22. 3.Stage of impending invasion (3-7 years):Common to
- 23. Intestinal schistosomiasis:characterized by lesions of large intestine
- 24. Stage of late invasion: - Simmer’s fibrosis
- 25. Japanese schistosomiasis: 1. The worms produce
- 26. LABORATORY DIAGNOSTICS: 1. Microscopy detection of eggs
- 27. 5. Clinical methods – X-ray
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Слайд 29
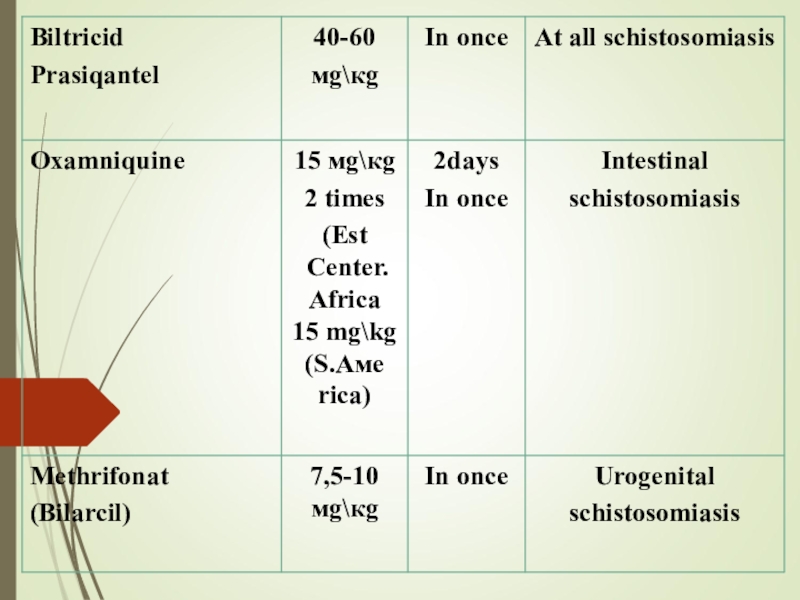
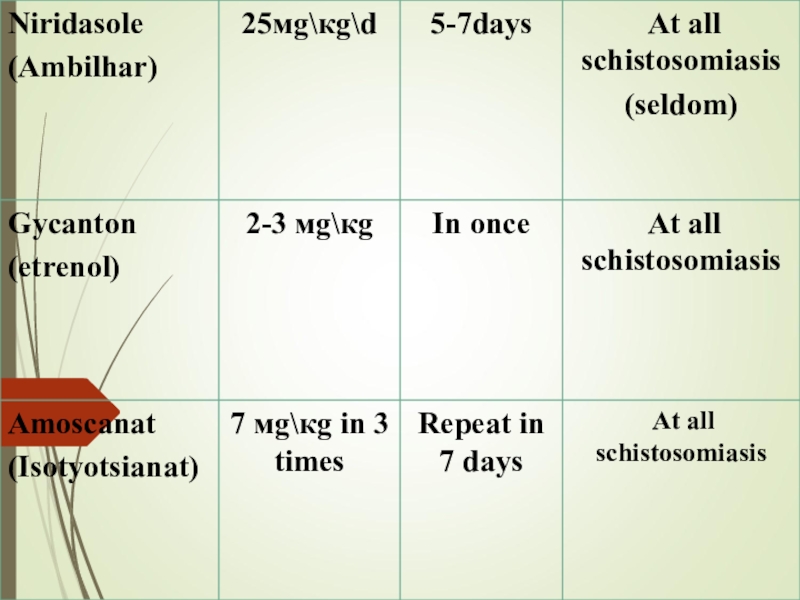
- 30. PREVENTION 1. Straggle with the intermediate hosts
- 31. Don't worry! Be happy!
- 32. Скачать презентанцию
Schistosomiasis - infectious diseases caused by a group of tropical parasites with a primary lesion of urogenital organs and digestive system.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3 Schistosomes are prevalent in rural and outlying city areas of
74 countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America.
In Central
China and Egypt the disease poses a major health risk.Schistosomiasis – had been included (WHO) in the 6 tropical diseases, taking second place in importance after malaria.
First symptoms of schistosomiasis were described in 1550-1225 in Egypt.
The birthplace of schistosomiasis - area of the Great African lakes.
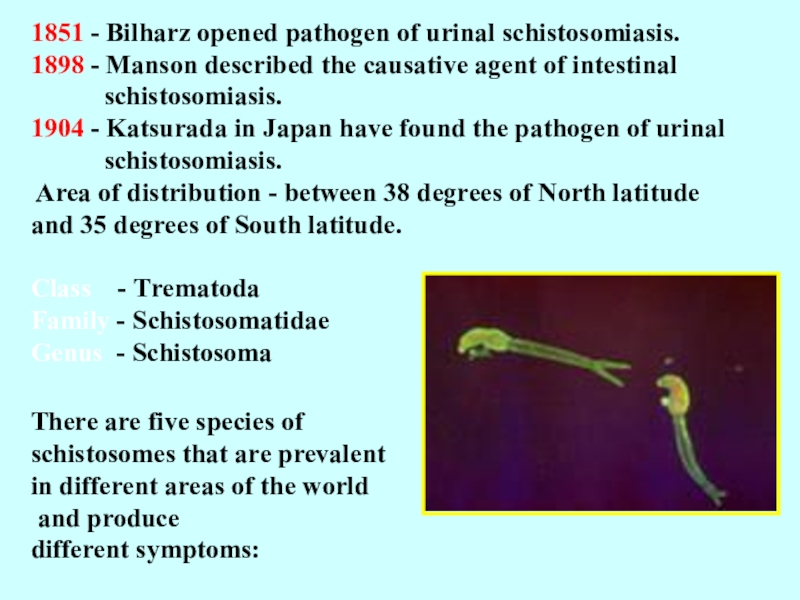
Слайд 41851 - Bilharz opened pathogen of urinal schistosomiasis. 1898 -
Manson described the causative agent of intestinal
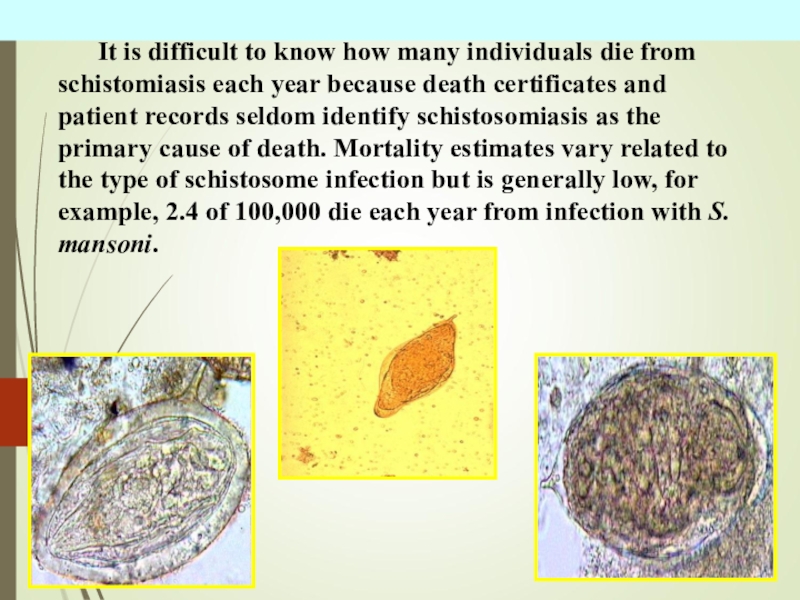
schistosomiasis. 1904 - Katsurada in Japan have found the pathogen of urinal schistosomiasis. Area of distribution - between 38 degrees of North latitude and 35 degrees of South latitude. Class - Тrematoda Family - Schistosomatidae Genus - Schistosoma There are five species of schistosomes that are prevalent in different areas of the world and produce different symptoms:Слайд 8 It is difficult to know how many individuals die from
schistomiasis each year because death certificates and patient records seldom
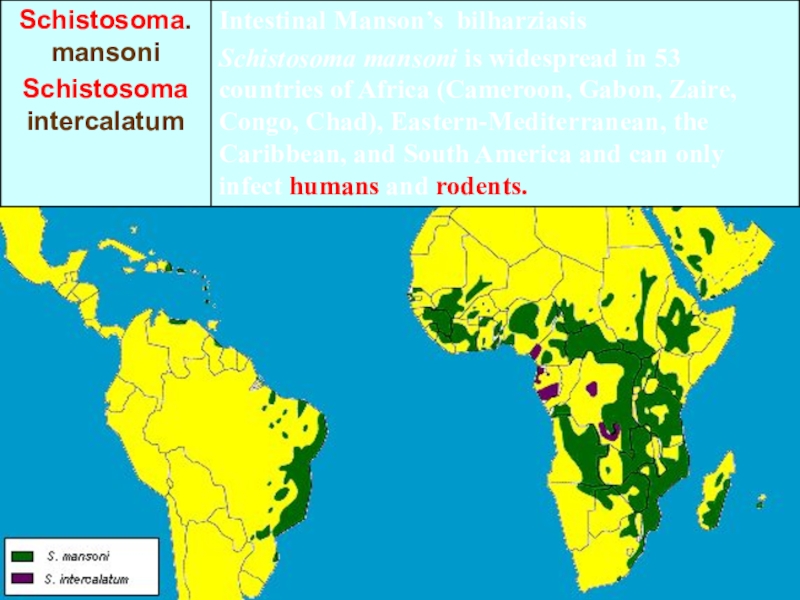
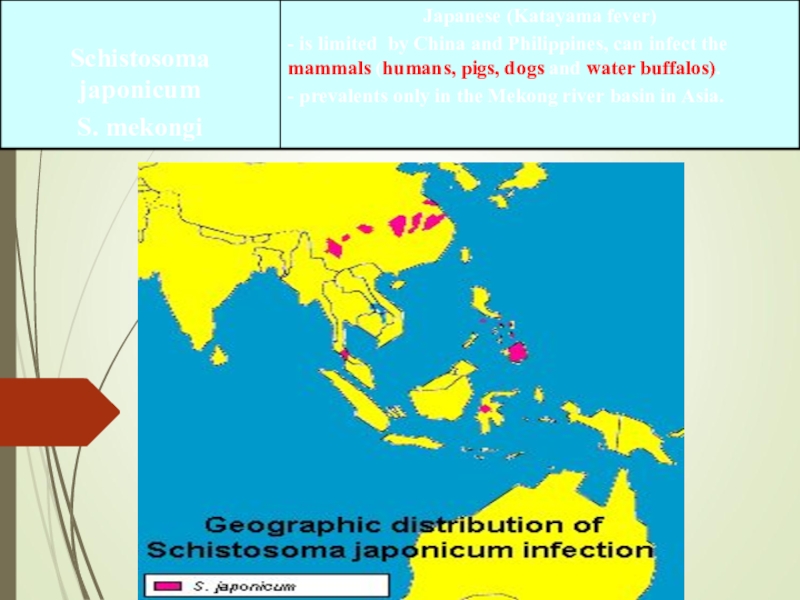
identify schistosomiasis as the primary cause of death. Mortality estimates vary related to the type of schistosome infection but is generally low, for example, 2.4 of 100,000 die each year from infection with S. mansoni.Слайд 9Intestinal schistosomiasis, caused by Schistosoma japonicum,
S. mekongi, S. mansoni,
and S. intercalatum can lead to serious complications of the
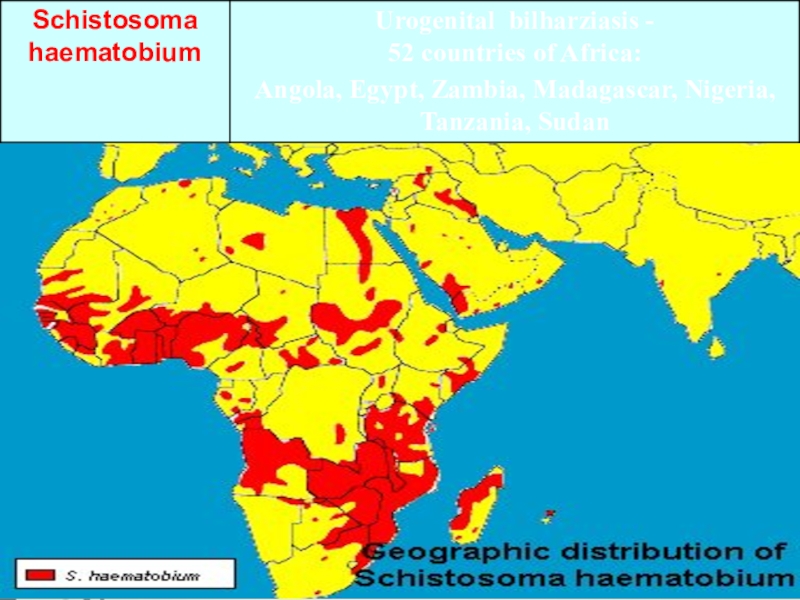
liver and spleen.Urinary schistosomiasis is caused by S. haematobium.
Слайд 10 Source of the infection: S. mansoni, and S. intercalatum - human,
rats, monkey
S. mekongi – man, dog
Schistosoma japonicum – man, home
and
wild animals, large and small
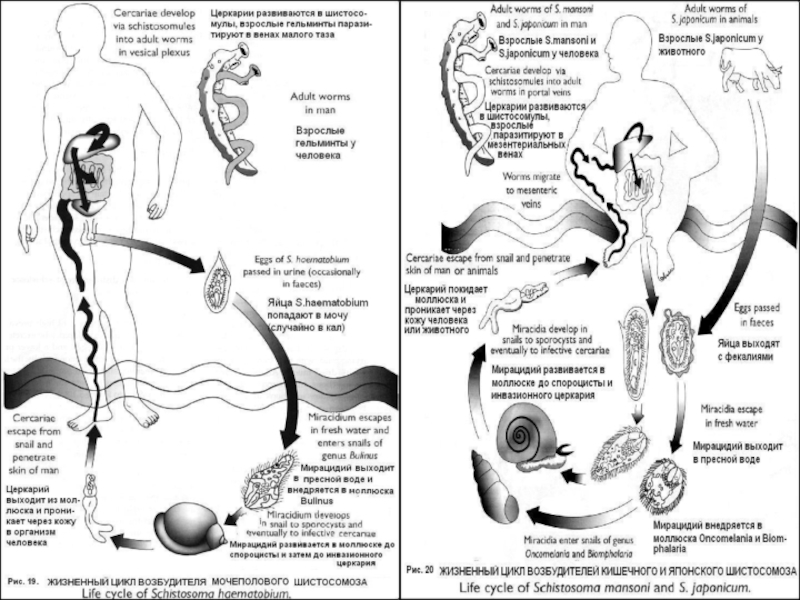
cattle.All five species are transmitted by the same mechanism – percutaneous - through direct contact with fresh water infeсted with the free-living form of the parasite known as cercariae.
Building of dams, irrigation systems, reservoirs and the movements
of refugee groups introduce and spread schistosomiasis.
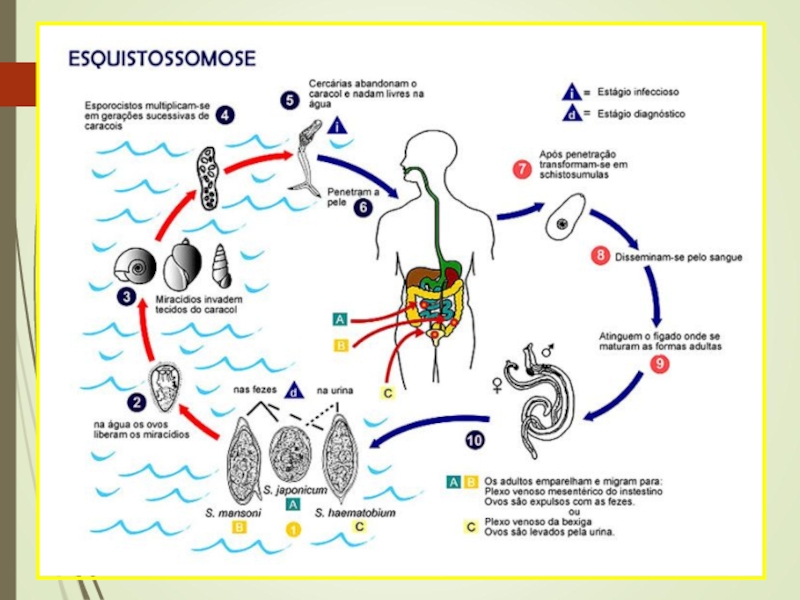
Слайд 11Eggs are excreted in human urine and feces in areas
with poor sanitation, contaminate freshwater sources.
The eggs break open
to release a form of the parasite called miracidium. Freshwater snails become infested with the miracidium, which multiply inside the snail and mature into multiple cercariae that the snail ejects into the water.
The cercariae, which survive outside a host for 48 hours, quickly penetrate in the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth or gastrointestinal tract.
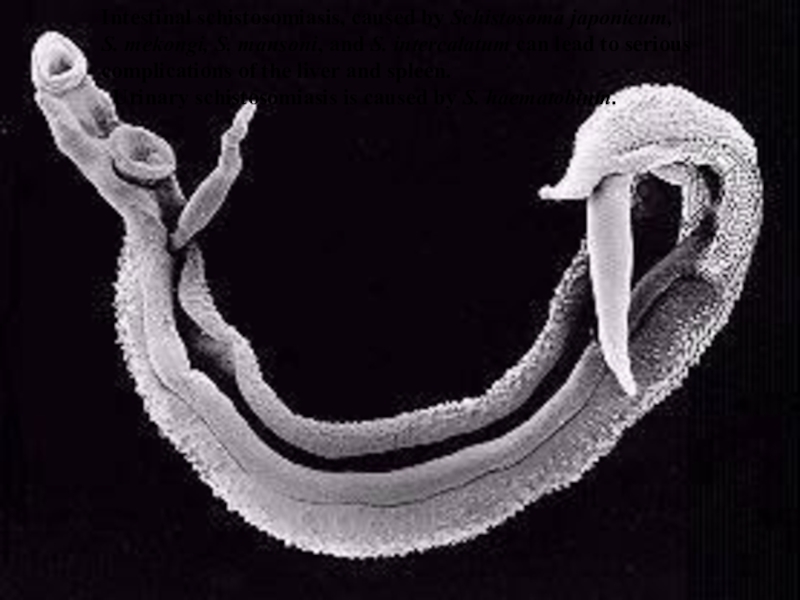
Inside the human body, the worms penetrate the wall of the nearest vein and travel to the liver where they grow and sexually mature.
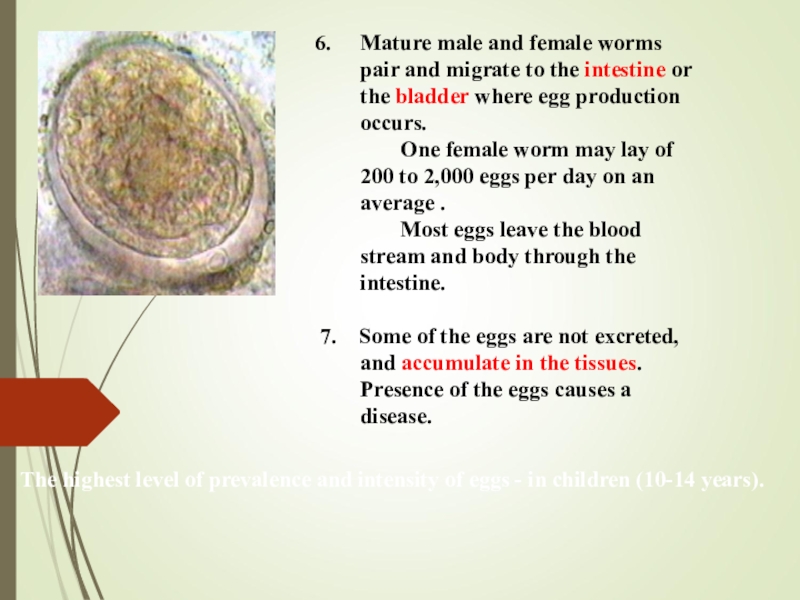
Слайд 12Mature male and female worms pair and migrate to the
intestine or the bladder where egg production occurs.
One female worm may lay of 200 to 2,000 eggs per day on an average . Most eggs leave the blood stream and body through the intestine.
7. Some of the eggs are not excreted, and accumulate in the tissues. Presence of the eggs causes a disease.
The highest level of prevalence and intensity of eggs - in children (10-14 years).
Слайд 15
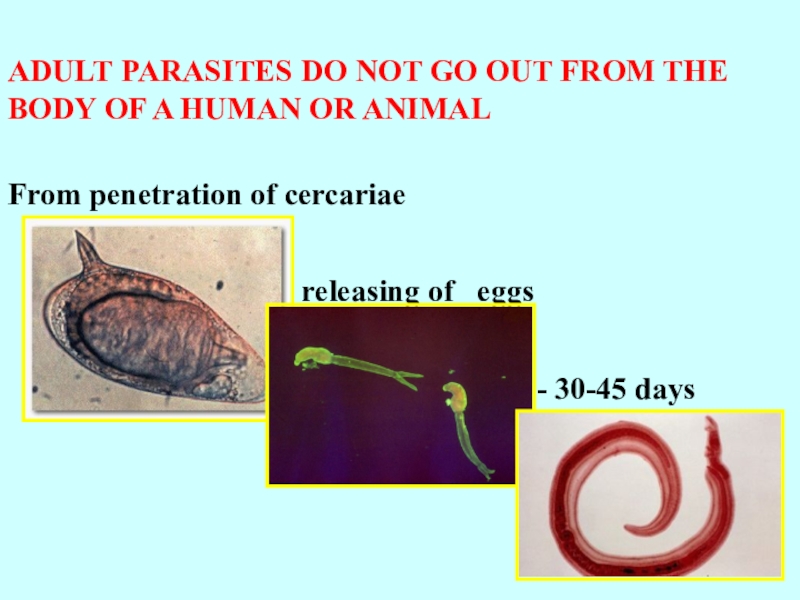
ADULT PARASITES DO NOT GO OUT FROM THE BODY OF
A HUMAN OR ANIMAL
From penetration of cercariae
up to releasing of eggs
- 30-45 days
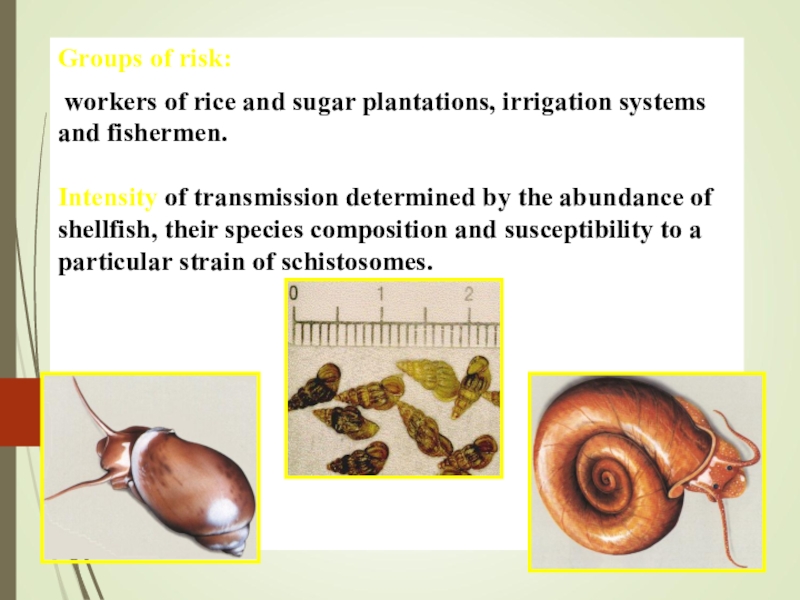
Слайд 16Groups of risk:
workers of rice and sugar plantations, irrigation
systems and fishermen. Intensity of transmission determined by the abundance of
shellfish, their species composition and susceptibility to a particular strain of schistosomes.Слайд 17
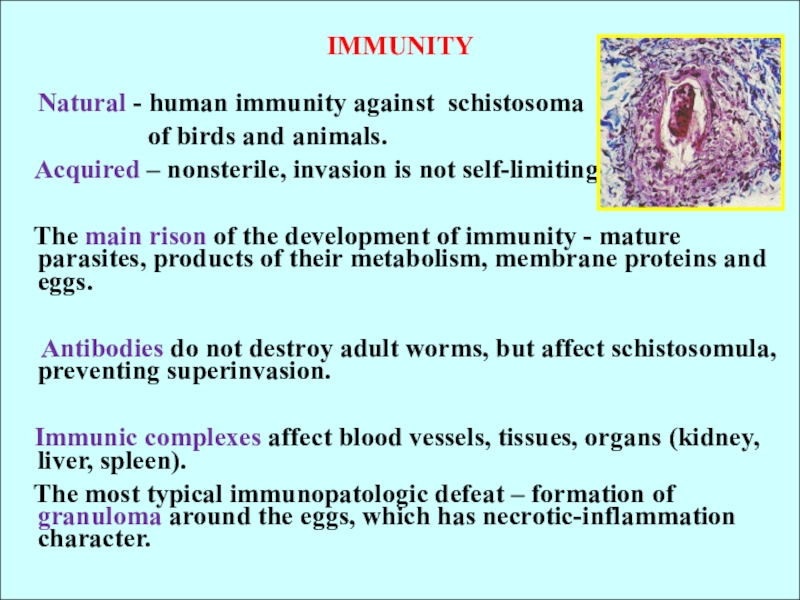
IMMUNITY
Natural - human immunity against schistosoma
of birds and
animals.Acquired – nonsterile, invasion is not self-limiting.
The main rison of the development of immunity - mature parasites, products of their metabolism, membrane proteins and eggs.
Antibodies do not destroy adult worms, but affect schistosomula, preventing superinvasion.
Immunic complexes affect blood vessels, tissues, organs (kidney, liver, spleen).
The most typical immunopatologic defeat – formation of granuloma around the eggs, which has necrotic-inflammation character.
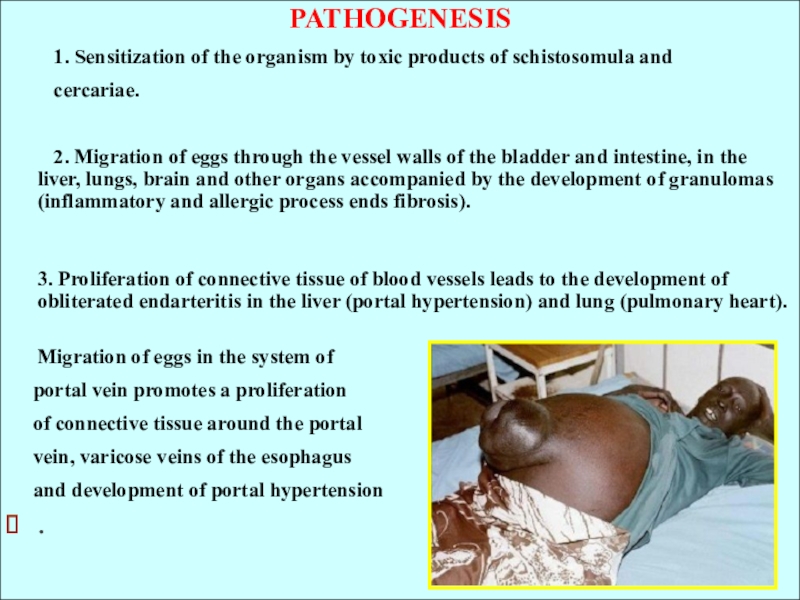
Слайд 18PATHOGENESIS
1. Sensitization of the organism
by toxic products of schistosomula and
cercariae.2. Migration of eggs through the vessel walls of the bladder and intestine, in the liver, lungs, brain and other organs accompanied by the development of granulomas (inflammatory and allergic process ends fibrosis).
3. Proliferation of connective tissue of blood vessels leads to the development of obliterated endarteritis in the liver (portal hypertension) and lung (pulmonary heart).
Migration of eggs in the system of
portal vein promotes a proliferation
of connective tissue around the portal
vein, varicose veins of the esophagus
and development of portal hypertension
.
Слайд 19
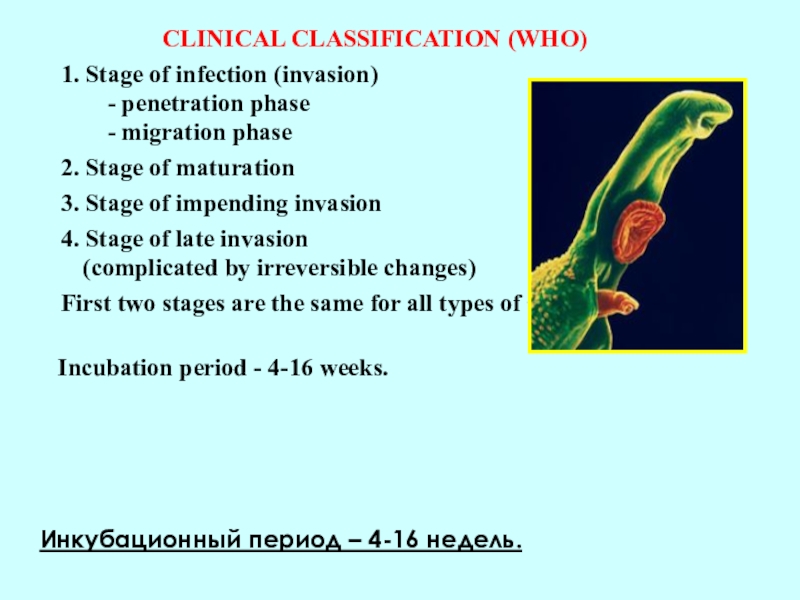
CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION (WHO)
1. Stage of infection (invasion)
- penetration phase- migration phase 2. Stage of maturation 3. Stage of impending invasion 4. Stage of late invasion
(complicated by irreversible changes) First two stages are the same for all types of schistosoma
Incubation period - 4-16 weeks.
Инкубационный период – 4-16 недель.
Слайд 20
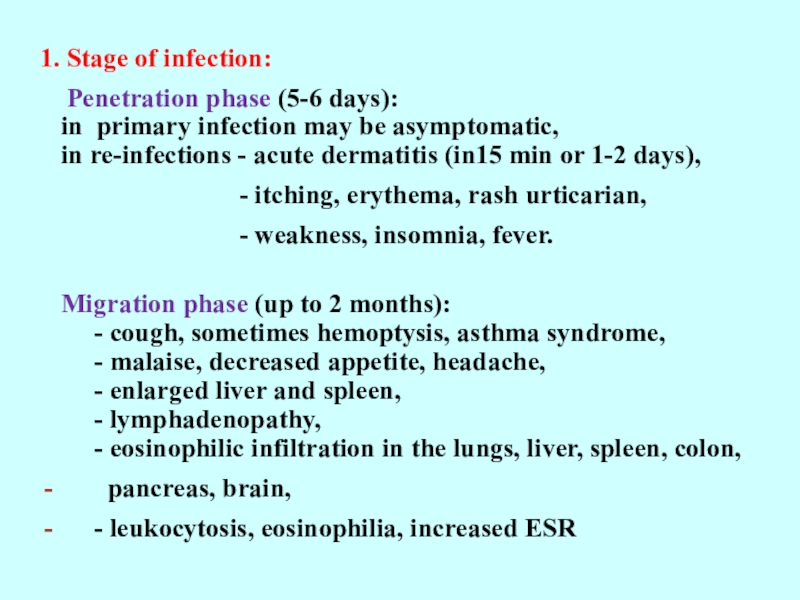
1. Stage of infection:
Penetration phase (5-6
days): in primary infection may be asymptomatic, in re-infections - acute dermatitis
(in15 min or 1-2 days),- itching, erythema, rash urticarian,
- weakness, insomnia, fever.
Migration phase (up to 2 months): - cough, sometimes hemoptysis, asthma syndrome, - malaise, decreased appetite, headache, - enlarged liver and spleen, - lymphadenopathy, - eosinophilic infiltration in the lungs, liver, spleen, colon,
pancreas, brain,
- leukocytosis, eosinophilia, increased ESR
Слайд 212. Stage of maturation
(Japanese sch. - 4 weeks, Mansony
sch.-5 weeks,
urogenital sch. -8-10 weeks):
- parasites complet there maturation,
lay eggs and reach their habitatsClinically: - high temperature with eosinophilia, headache,
weakness,
- loss of appetite, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea,
- rash,
- increased alpha-, gamma-globulin,
- «syndrome Katayama» (in Japanese sch. in europeans)
eosinophilia, splenomegaly, urticaria-rash at the
absence of eggs in the stool.
Слайд 22
3.Stage of impending invasion (3-7 years):
Common to all types of
schistosomiasis:
- intensive production of eggs in the place of parasitizing
and discharge with urine and feces,
-development of destructive reactions (necrosis, exudation, eosinofilia) around the egg with subsequent proliferation,
- thrombosis and inflammation of blood vessels,
Слайд 23Intestinal schistosomiasis:
characterized by lesions of large intestine (eggs pass through
the wall), the liver and spleen.
Stage of impending invasion:
- pain
in the abdomen, frequent stool with admixes of blood and mucus, tenesmus, meteorism,- polyps of the colon - pain, partial or total obstruction of the bowel, weight loss,
- affection of the liver and spleen (associated with drift eggs and granulemas) – heaviness in epigastrium, hepatosplenomegaly, hypoproteinemia, increased ALT, anemia,
- the defeat of the spinal cord (paraplegia, pain),
- glomerulonephritis, pneumonia, bronchitis, asthma, emphysema
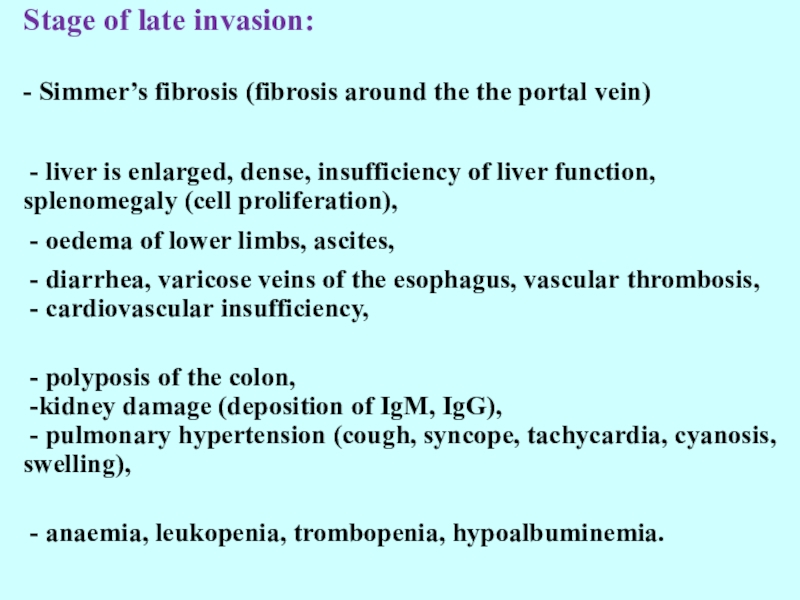
Слайд 24Stage of late invasion:
- Simmer’s fibrosis (fibrosis around the the
portal vein)
- liver is enlarged, dense, insufficiency of liver
function, splenomegaly (cell proliferation), - oedema of lower limbs, ascites,
- diarrhea, varicose veins of the esophagus, vascular thrombosis, - cardiovascular insufficiency,
- polyposis of the colon, -kidney damage (deposition of IgM, IgG), - pulmonary hypertension (cough, syncope, tachycardia, cyanosis, swelling),
- anaemia, leukopenia, trombopenia, hypoalbuminemia.
Слайд 25
Japanese schistosomiasis:
1. The worms produce the maximum number of eggs
(up to 3,000),
2. Necrosis followed by fibrosis prevails in granulemas,
3.
Fibrosis of the liver is often developed,4. Drift of eggs in the nervous system activates development of gepatocerebral encephalopathy, acute and chronic cerebral form of psychosis, Schistosomiasis Mekongi (like the Japanese):
often bacteremia caused by Salmonella, which are localized on the surface
or in the intestine of schistosomes.
Слайд 26
LABORATORY DIAGNOSTICS:
1. Microscopy detection of eggs in the urine (after
physical exertion), faeces (method of thick smear by Kato),
less - in sputum, semen, liquor with a certain amount of eggs.
2. Larva-scopy – after the incubation of sediment urine or faeces with a water detect moving miracidium.
3. Cystoscopy (determination of changes in the mucosa - atrophy, pallor, thickening of the blood vessels, hyperemia, accumulation of eggs, polyps, ulcers) with intravesical biopsy (identification eggs) – in urogenital schistosomiasis.4. RR-scopy (hyperemia, erosion, ulcer, papillomas) with biopsy - in the case of intestinal schistosomiasis.
Слайд 27
5. Clinical methods – X-ray examination of the
bladder, lungs, esophagus, stomach, angiography, biochemical, and laparoscopy. 6. Immunological methods
(on early and late stages) - CBR, RP, ELISA and other. 5. Material of autopsy - swab-prints.Слайд 30
PREVENTION
1. Straggle with the intermediate hosts - mollusks (chemical method
and biological methods - bacteria, fish, crabs; ecological method -
environmental change).2. Improvement of the source of the invasion: therapy of sick people and infected animals. At high infestation - chemotherapy for all children.
3. Sanitary-hygienic measures on improvement of settlements (water, sewerage, shower and other).
4. Individual prevention - protective clothing at risk groups.
5. Health education of the population (not pollute the water with feces, not to swim and others).
6. Sanitary supervision over natural reservoirs