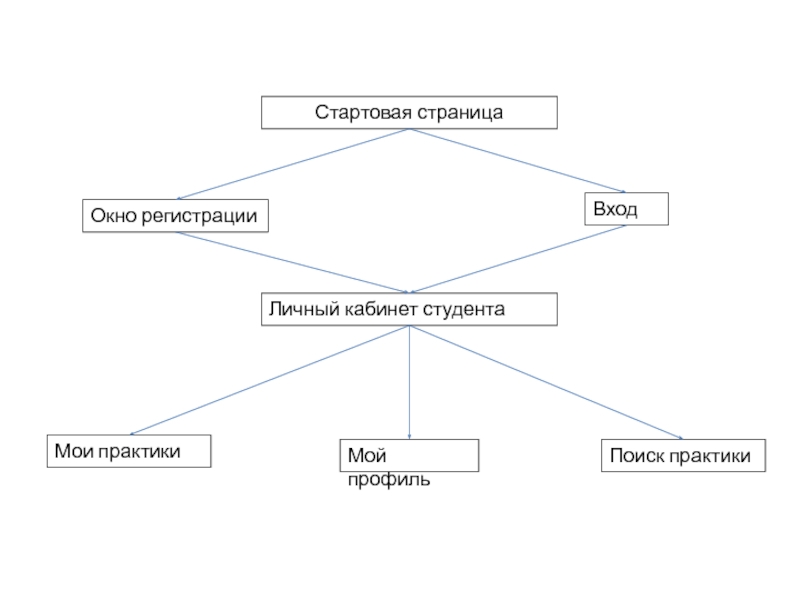
Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The presentation was made by Lomakina D. 21-KA The BANK of Canada
Содержание
- 1. The presentation was made by Lomakina D. 21-KA The BANK of Canada
- 2. The presentation was made by Lomakina
- 3. The Bank of Canada issues its bank
- 4. In response to the Bank of Canada's
- 5. During the period that John Crow was Governor of
- 6. On July 15, 2015, the Bank of Canada announced
- 7. The Bank's main
- 8. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2The presentation was made
by Lomakina D. 21-KA
The mandate of
the central bank—the Bank of Canada is to conduct monetary policy that
"preserves the value of money by keeping inflation low and stable"Слайд 3The Bank of Canada issues its bank rate announcement through
its Monetary Policy Report which is released eight times a year. The Bank of
Canada, a federal crown corporation, has the responsibility of Canada's monetary system.Under the inflation-targeting monetary policy that has been the cornerstone of Canada's monetary and fiscal policy since the early 1990s, the Bank of Canada sets an inflation target. The inflation target was set at 2 per cent, which is the midpoint of an inflation range of 1 to 3 per cent.Слайд 4In response to the Bank of Canada's July 15, 2015
rate adjustment, Prime Minister Stephen Harper explained that the economy was "being
dragged down by forces beyond Canadian borders such as global oil prices, the European debt crisis, and China's economic slowdown" which has made the global economy "fragile".The Chinese stock market had lost about US$3 trillion of wealth by July 2015 when panicked investors sold stocks, which created declines in the commodities markets, which in turn negatively impacted resource-producing countries like Canada.Слайд 5During the period that John Crow was Governor of the Bank of
Canada—1987 to 1994— there was a worldwide recession and the bank rate
rose to around 14% and unemployment topped 11%. Although since that time inflation-targeting has been adopted by "most advanced-world central banks", in 1991 it was innovative and Canada was an early adopter when the then-Finance Minister Michael Wilson approved the Bank of Canada's first inflation-targeting in the 1991 federal budget. The inflation target was set at 2 per cent. Inflation is measured by the total consumer price index (CPI). In 2011 the Government of Canada and the Bank of Canada extended Canada's inflation-control target to December 31, 2016. The Bank of Canada uses three unconventional instruments to achieve the inflation target: "a conditional statement on the future path of the policy rate", quantitative easing, and credit easing.Слайд 6On July 15, 2015, the Bank of Canada announced that it was
lowering its target for the overnight rate by another one-quarter
percentage point, to 0.5 per cent[62] "to try to stimulate an economy that appears to have failed to rebound meaningfully from the oil shock woes that dragged it into decline in the first quarter".[63] According to the Bank of Canada announcement, in the first quarter of 2015, the total Consumer price index (CPI) inflation was about 1 per cent. This reflects "year-over-year price declines for consumer energy products". Core inflation in the first quarter of 2015 was about 2 per cent with an underlying trend in inflation at about 1.5 to 1.7 per cent.On July 15, 2015, the Bank of Canada announced that it was lowering its target for the overnight rate by another one-quarter percentage point, to 0.5 per cent "to try to stimulate an economy that appears to have failed to rebound meaningfully from the oil shock woes that dragged it into decline in the first quarter". According to the Bank of Canada announcement, in the first quarter of 2015, the total Consumer price index (CPI) inflation was about 1 per cent. This reflects "year-over-year price declines for consumer energy products". Core inflation in the first quarter of 2015 was about 2 per cent with an underlying trend in inflation at about 1.5 to 1.7 per cent.
Слайд 7 The Bank's main priority has been
to keep inflation at a moderate level. As part of
that strategy, interest rates were kept at a low level for almost seven years.Since September 2010, the key interest rate (overnight rate) was 0.5%. Since September 2010, the key interest rate (overnight rate) was 0.5%.
In mid 2017, inflation remained below the Bank's 2% target, (at 1.6%) mostly because of reductions in the cost of energy, food and automobiles; as well, the economy was in a continuing spurt with a predicted GDP growth of 2.8 percent by year end.
Early on 12 July 2017, the bank issued a statement that the benchmark rate would be increased to 0.75%.