Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Types of Chemical Reactions
Содержание
- 1. Types of Chemical Reactions
- 2. TopicsNaming chemical compoundsRevision (Periodic Law)Types of chemical reactionsClasses of inorganic compounds and their properties
- 3. Compoundssubstances composed of more than one element,
- 4. Which of the following shows how the
- 5. The atomic number of magnesium is 12.
- 6. The alkali metals all react with water.a
- 7. Which one of the following is NOT
- 8. Organic and Inorganic Compounds Chemical compounds can
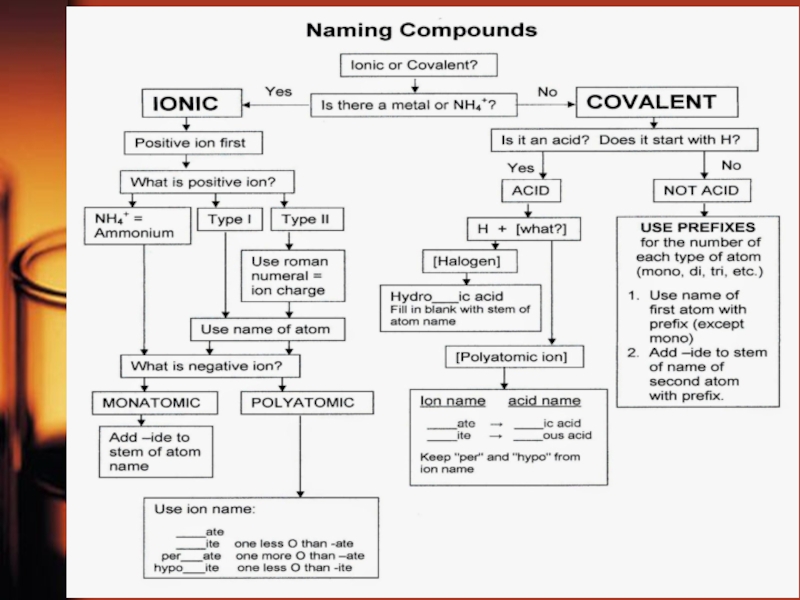
- 9. Naming of Chemical CompoundsChemical nomenclature is the
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Inorganic Compounds
- 12. It’s your turn…Name the compoundsSO2 Fe(OH)2
- 13. How many of the following compounds are
- 14. Indicators of chemical reactionsEmission of light or
- 15. Describing Chemical ReactionsAtoms aren’t created or destroyed.
- 16. 1. Synthesis Reactions Реакция соединенияoccurs when two
- 17. 2. Decomposition Reactions Реакция разложенияoccurs when a
- 18. 3. Single Displacements Реакция замещенияoccurs when a
- 19. Using the Activity SeriesThe activity series (электрохимический
- 20. Using the Activity SeriesYou can use the
- 21. 4. Double Displacements Реакция обменаalways involves two
- 22. Indicators of occurring reactionsPrecipitate – solid formed
- 23. 5. Combustion Reaction Реакция горенияoccurs when a
- 24. Incomplete Combustion If a combustion occurs at
- 25. It’s your turn…C2H5OH + O2 CO2
- 26. OxidesCompounds of oxygen with other elements are
- 27. Classification of Oxides 1. Acidic Oxides
- 28. BasesCompounds dissolving in water by producing OH-
- 29. Classification of Bases According
- 30. AcidsCompounds dissolving in water by producing H+
- 31. Classification of Acids According to
- 32. Chemical Properties of Acids• Acids
- 33. Amphoteric Compounds Most of the compounds of
- 34. pHpH is a numeric scale used to
- 35. SaltsSalts are ionic compounds of anions and
- 36. Classification of SaltsA. Neutral Salts are formed
- 37. Chemical Properties of SaltsSalts can react with
- 38. The end
- 39. Скачать презентанцию
TopicsNaming chemical compoundsRevision (Periodic Law)Types of chemical reactionsClasses of inorganic compounds and their properties
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Topics
Naming chemical compounds
Revision (Periodic Law)
Types of chemical reactions
Classes of inorganic
compounds and their properties
Слайд 3Compounds
substances composed of more than one element, chemically combined. A
compound is represented by its chemical formula, a notation that
uses atomic symbols with numerical subscripts to convey the relative proportion of atoms of different elements in the substance.E. g. HCl, H2O, NH3
There are three fundamental kinds of chemical bonds between atoms - covalent bonds, ionic bonds and metallic bonds.
Слайд 4Which of the following shows how the atomic radius of
the elements changes on crossing from left to right in
the row of the Periodic Table from potassium to bromine?K to Ca Sc to Zn Ga to Br
A decrease increase decrease
B decrease decrease increase
C decrease decrease decrease
D increase decrease increase
E increase increase increase
Слайд 5The atomic number of magnesium is 12. Which electron configuration
given below corresponds to the Mg2+ ion (in its ground
state)?A. Is22s22p63s23p2
B. Is22s22p63s2
C. Is22s22p6
D. Is22s22p63s1
E. Is22s22p53s1
Слайд 6The alkali metals all react with water.
a Describe what happens
as each of lithium, sodium and potassium reacts with water.
b
State the difference in the reactivity of these alkali metals with water.с Describe what you could do experimentally to show what the product(s) are.
Слайд 7Which one of the following is NOT the correct formula
for a lithium compound?
A Li2S
B LiCO3
C CH3CO2Li
D LiHSO4
E Li3N
Слайд 8Organic and Inorganic Compounds
Chemical compounds can be classified as organic
or inorganic. Organic compounds are those formed by carbon and
hydrogen (hydrocarbon) or carbon and hydrogen together with oxygen, nitrogen, and a few other elements.Inorganic compounds are compounds composed of elements other than carbon. Except a few simple compounds of carbon, including carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbonates and cyanides are generally considered to be inorganic.
Слайд 9Naming of Chemical Compounds
Chemical nomenclature is the system of names
that chemists use to identify compounds. Two classes of names
exist: common names and systematic names. Common names: ammonia, water, baking soda, laughing gas, muriatic acid, table saltSystematic names precisely identify the chemical composition of the compound. The present system of inorganic chemical nomenclature was devised by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
Слайд 12It’s your turn…
Name the compounds
SO2 Fe(OH)2 HCl
HCl(aq) CuCl2, HNO3 Cl2O7 BaSO4 KNO3
H2SiO3 NH4Cl H2SO4 NaHCO3 (CuOH)2CO32. Write the formulas
diphosphorus trioxide, iron dichloride, hydrogen sulfide, phosphoric acid, ammonia, sodium nitrite, phosphine, sulfurous acid, aluminium hydroxide, potassium dihydrocarbonate, sodium dichromate, sodium hexahydroxogermanate
Слайд 13How many of the following compounds are acidic, alkaline or
amphoteric (react with both acids and alkalis)?
Al2O3 Cl2O7 CO2
HCl H3PO4 K2O KOH MgO Na2O NO2 P4O10 SiO2 SO2
A. Acidic = 10; Amphoteric = 2; Alkaline = 4
B. Acidic = 7; Amphoteric = 1; Alkaline = 5
C. Acidic = 9; Amphoteric = 2; Alkaline = 2
D. Acidic = 6; Amphoteric = 1; Alkaline = 6
E. Acidic = 8; Amphoteric = 1; Alkaline = 4
Слайд 14Indicators of chemical reactions
Emission of light or heat
Formation of a
gas
Formation of a precipitate
Color change
Emission of odor
Слайд 15Describing Chemical Reactions
Atoms aren’t created or destroyed. A chemical equation
should be balanced.
Sulfur reacts with oxygen to form/to give sulfur
dioxide.One mole of sulfur reacts with one mole of oxygen forming/giving one mole of sulfur dioxide.
Sulfur, a yellow solid, burns forming a colorless gas with an irritating smell.
sulfur + oxygen sulfur dioxide
S(s) + O2(g) SO2(g)
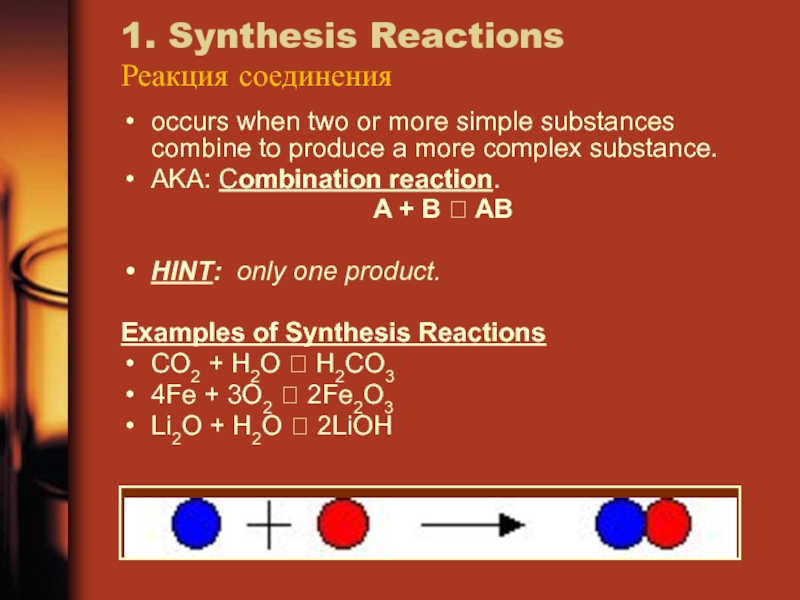
Слайд 161. Synthesis Reactions
Реакция соединения
occurs when two or more simple substances
combine to produce a more complex substance.
AKA: Combination reaction.
A +
B ABHINT: only one product.
Examples of Synthesis Reactions
CO2 + H2O H2CO3
4Fe + 3O2 2Fe2O3
Li2O + H2O 2LiOH
Слайд 172. Decomposition Reactions
Реакция разложения
occurs when a complex substance is broken
down into two or more simpler substances.
Heat is often used
to aid in decomposition reactions – these reactions that employ heat are called thermal decompositions.Decompositions and synthesis reactions are opposites.
AB A + B
HINT: only one reactant, two or more products.
Examples of Decomposition Reactions:
NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O
Ca(OH)2 CaO + H2O
2H2O2 2H2O + O2
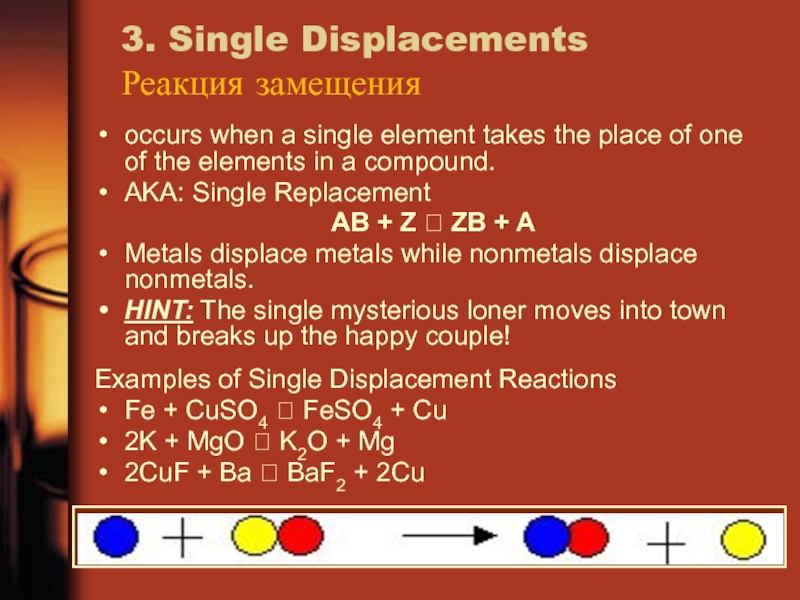
Слайд 183. Single Displacements
Реакция замещения
occurs when a single element takes the
place of one of the elements in a compound.
AKA: Single
ReplacementAB + Z ZB + A
Metals displace metals while nonmetals displace nonmetals.
HINT: The single mysterious loner moves into town and breaks up the happy couple!
Examples of Single Displacement Reactions
Fe + CuSO4 FeSO4 + Cu
2K + MgO K2O + Mg
2CuF + Ba BaF2 + 2Cu
Слайд 19Using the Activity Series
The activity series (электрохимический ряд напряжений металлов)
is a list of metals and hydrogen that are arranged
in order of reactivity.Li K Ba Ca Na Mg Al Zn Fe Ni Sn Pb H Cu Hg Ag Au
The rule is that the element can only be displaced by another element that is to the left of it. This makes Lithium the strongest and Gold the weakest.
There is also a halogen activity series – it is used to predict reactions with halides.
F Cl Br I
Слайд 20Using the Activity Series
You can use the activity series in
three ways:
Straight forward Single Displacements
Reactions with Acids
Reactions with Water
Straight Forward
Single DisplacementsUse the rule of “whoever is more to the left wins” to see if there is a reaction or not.
Reactions with Acids
Acids contain hydrogen (positive like the metals). If you are to the left of hydrogen – you react and take its place – if you are to the right – there is no reaction.
Reactions with Water
Only the first five elements (Li K Ba Ca Na) will react with water. It will form a hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
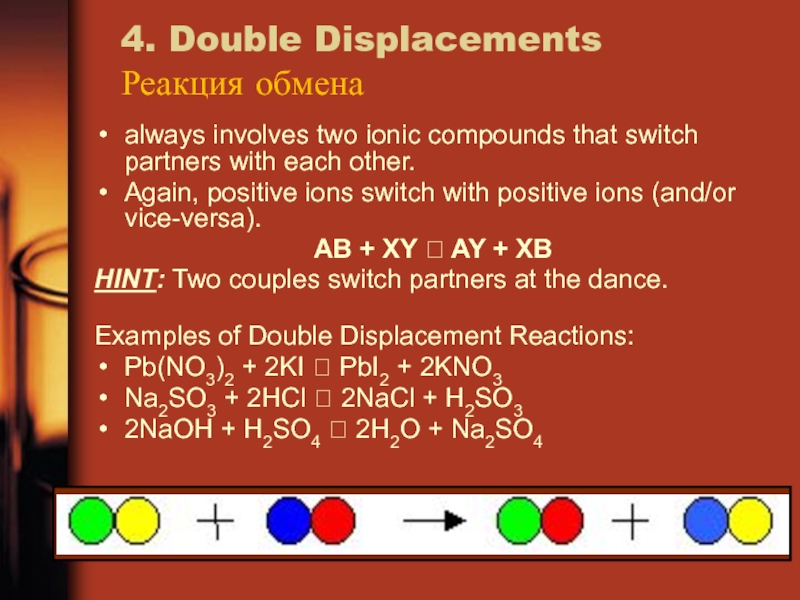
Слайд 214. Double Displacements
Реакция обмена
always involves two ionic compounds that switch
partners with each other.
Again, positive ions switch with positive ions
(and/or vice-versa).AB + XY AY + XB
HINT: Two couples switch partners at the dance.
Examples of Double Displacement Reactions:
Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI PbI2 + 2KNO3
Na2SO3 + 2HCl 2NaCl + H2SO3
2NaOH + H2SO4 2H2O + Na2SO4
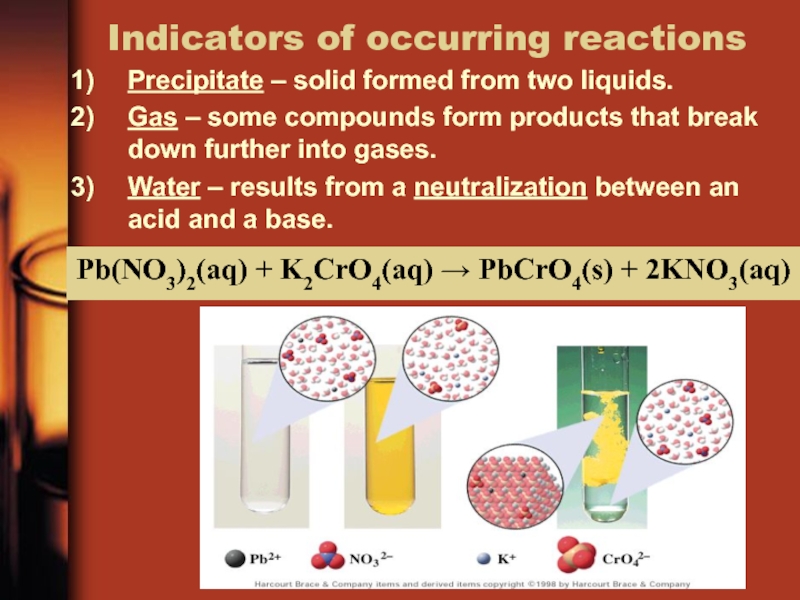
Слайд 22Indicators of occurring reactions
Precipitate – solid formed from two liquids.
Gas
– some compounds form products that break down further into
gases.Water – results from a neutralization between an acid and a base.
Pb(NO3)2(aq) + K2CrO4(aq) PbCrO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
Слайд 235. Combustion Reaction
Реакция горения
occurs when a substance (the “fuel”) reacts
very rapidly with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water.
Combustion
reactions release a good deal of energy in a very short period of time.Fuel + O2 CO2 + H2O
HINT: Something combines with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
C10H8(s) + 12O2 (g) 10CO2 (g) + 4H2O(g)
Слайд 24Incomplete Combustion
If a combustion occurs at a lower temperature, it
may result in an incomplete combustion.
The products of an incomplete
combustion are water, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and carbon (a solid residue).The general equation is:
Fuel + O2 H2O + CO2 + CO + C
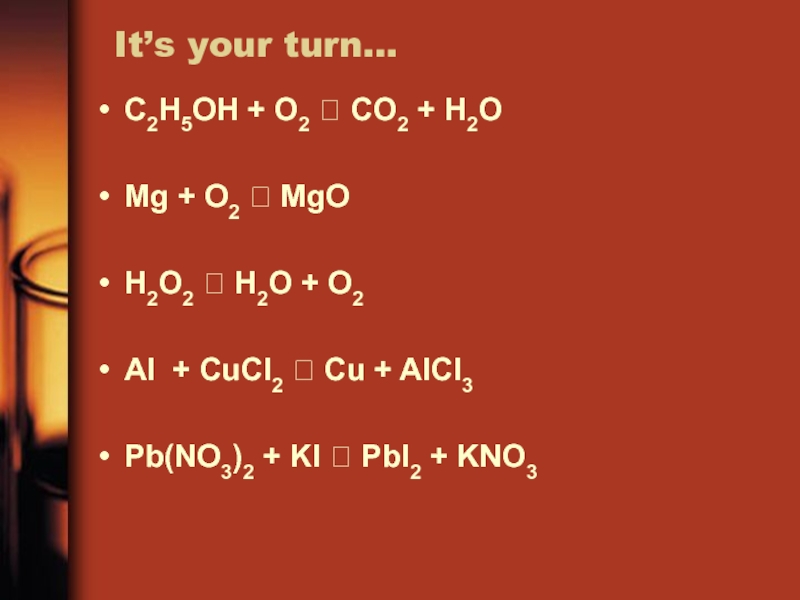
Слайд 25It’s your turn…
C2H5OH + O2 CO2 + H2O
Mg +
O2 MgO
H2O2 H2O + O2
Al + CuCl2
Cu + AlCl3Pb(NO3)2 + KI PbI2 + KNO3
Слайд 26Oxides
Compounds of oxygen with other elements are called oxides.
NO2,
SO2, H2O, CO2, N2O5, NO, N2O are common non metal
oxides, they have covalent bond structure.Na2O, FeO, Al2O3, CaO, SiO2, MgO, CuO, PbO are some common metal oxides they have ionic structure.
Naming of Oxides
They are named like binary compounds.
MgO : Magnesium oxide
SO2 : Sulfur dioxide
P2O5 : Diphosphorus pentoxide
SnO2 : Tin(IV) oxide
Слайд 27Classification of Oxides
1. Acidic Oxides
Oxygen rich compounds of
non metals are called acidic oxides. SO2, NO2, P2O5, Cl2O
are examples.Their solutions are acidic. They are known as acidic anhydrides.
Acidic oxide + water → Acid P2O5 + 3H2O → 2H3PO4
2. Basic Oxides
Generally metal oxides are called basic oxides. Na2O, CaO, MgO are examples.
Their solutions are basic. They are known as basic anhydrides.
Basic oxide + water → Base MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2
3. Mixed Oxides
Compounds that contain two oxides of the same metal are called mixed oxides. Fe3O4, Mn3O4, Pb3O4 are examples. They behave as if they are two separate oxides in chemical reactions.
Fe3O4 : FeO*Fe2O3 : Iron (II, III) oxide
Слайд 28Bases
Compounds dissolving in water by producing OH- ion are called
bases.
They have slippery feeling. Many cleaning products contain bases.
NaOH(s) → Na+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Naming of Bases
The word “hydroxide” is added after the name of metal ion in the naming of bases.
Mg(OH)2 : Magnesium hydroxide
KOH : Potassium hydroxide
NaOH : Sodium hydroxide
Ba(OH)2 : Barium hydroxide
Слайд 29Classification of Bases
According to Strength
Bases that ionize
in water completely are said to be strong base. NaOH,
KOH and LiOH are strong bases (alkalis).Bases that ionize in water partially are called weak bases. Fe(OH)2, Al(OH)3 are example for weak bases.
Chemical Properties of Bases
According to solubility bases conduct electricity.
change the color of litmus paper to blue.
react with acids and produce salt and water.
Water insoluble bases decompose on heating to give metal oxides and water.
2KOH(s) + H2SO4(l) → K2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Mg(OH)2 → MgO + H2O
Слайд 30Acids
Compounds dissolving in water by producing H+ ion are called
acids.
HCl(g) → H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
H2SO4 → 2H+(aq) + SO4-2(aq) • They have sour taste.
They change the color of litmus paper to red.
Their aqueous solutions conduct electricity.
They are corrosive substances.
Most of them are soluble in water.
Naming of Acids
Acids containing two types of atoms are called binary acids. Their names follow the form hydro + nonmetal name + –ic + acid.
HCl : Hydrochloric acid
Acids containing oxygen atoms are called oxy acids. Their names follow the form –ic + acid, or –ous + acid.
HNO3 : Nitric acid HNO2 : Nitrous acid
Слайд 31
Classification of Acids
According to Strength
If an acid
ionizes completely, it is an strong acid, and if it
ionizes partially it is a weak acid.Strong acids HCl, H2SO4, HNO3
Weak acids H2SO3, HNO2, H2S, HCN
According to Number of Hydrogen Atoms
According to number of H+ ion produced acids are classified as monoprotic, diprotic or triprotic.
Monoprotic acids HCl, HNO3, HI, HBr, HClO4
Diprotic acids H2SO3, H2S, H2CO3, H2SO4
Triprotic acids H3PO4
Слайд 32
Chemical Properties of Acids
• Acids ionize in water and
conduct electricity, during the ionization heat is released.
• They
change the color of indicators. • They react with bases and produce salt and water, it is called neutralization reaction.
They react with basic oxides and some salts.
• They react with some metals and produce hydrogen gas.
HNO3(l) + KOH(s) → KNO3(aq) + H2O(l)
2HCl(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Слайд 33Amphoteric Compounds
Most of the compounds of Zn, Al, Cr,
Sn, Pb, and Be are amphoteric compounds. Oxides and hydroxides
of these metals have both acidic and basic characters.They are insoluble in water and do not react with it.
ZnO, Al2O3 are oxides, and Zn(OH)2, Al(OH)3 are hydroxides.
ZnO + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2O
ZnO + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + 2H2O
Слайд 34pH
pH is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity
or basicity of an aqueous solution. It is approximately the
negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the molar concentration, measured in units of moles per liter, of hydrogen ions. More precisely it is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion.pH = - lg [H+]
Слайд 35Salts
Salts are ionic compounds of anions and cations: NaCl, CaCO3,
ZnBr2, FeSO4…etc
• They are all crystalline solids.
• They have
high melting and boiling points. • Many of them are soluble in water and their aqueous solutions conduct electricity.
Naming of Salts
In the naming of salts first metal ion (positive ion) then name of negative ion is read.
KMnO4 Potassium permanganate
Слайд 36Classification of Salts
A. Neutral Salts
are formed from the reactions
of strong acids with strong bases.
NaCl, LiNO3, KNO3, Li2SO4
. B. Acidic Salts
are formed from the reactions of strong acids with weak bases. Their solutions are acidic.
FeCl2, Zn(NO3)2
C. Basic Salts
are formed from the reactions of weak acids with strong bases. Their solutions are basic.
NaCN, LiF, K2CO3, K2C2O4
Слайд 37Chemical Properties of Salts
Salts can react with metals according to
activity strength.
Zn(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq)
Water soluble salts undergo displacement reaction. KCI(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → 2AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq)
They may also react with acids under certain conditions.
2HCI + CaCO3 → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2