Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Urogenital infection
Содержание
- 1. Urogenital infection
- 2. SYPHILISSyphilis is true human infection Syphilis is
- 3. TreponemaT.pallidum consists of 3 sub/species:pallidum – syphilisendemicum – bejelpertenue – yawsT.carateum - pinta
- 4. T.pallidum/pallidumMicroaerophilic bacteriaIt cannot be cultivated in vitroDrying
- 5. T.pallidum/pallidumBiochemical properties are investigated badVirulence: lipoproteins propously
- 6. Syphilis is true human infection
- 7. SyphilisTreponema multiplies locally at the site of
- 8. SyphilisIn 2-10 weeks later the secondary lesions
- 9. SyphilisTerriary stage is characterized by: 1/ development
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. ImmunityPROTECTIVE IMMUNITY IS NOT FORMED !!!Antibodies are
- 13. DiagnosticMicroscopy, serology and PCRMicroscopy is used during
- 14. Diagnostic Positive VDRL and RPR develop after
- 15. Слайд 15
- 16. Congenital syphilisA pregnant syphilitic woman can transmit
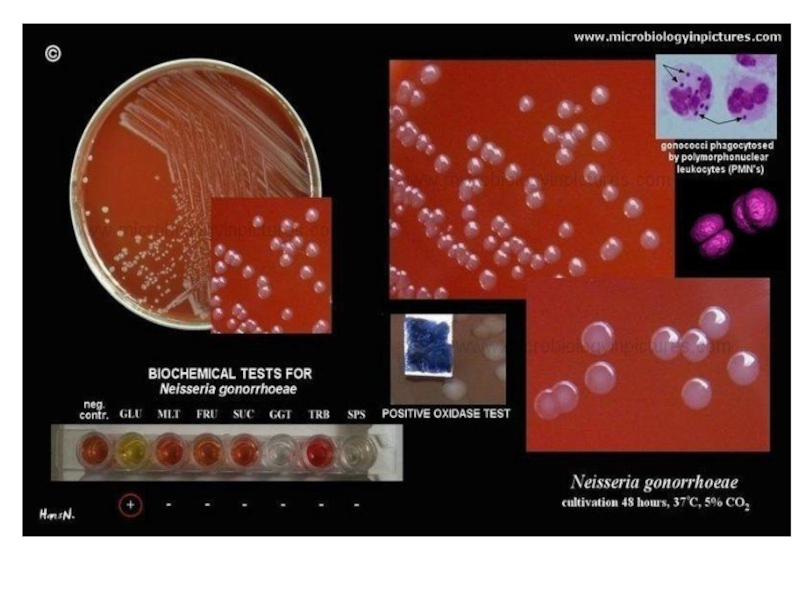
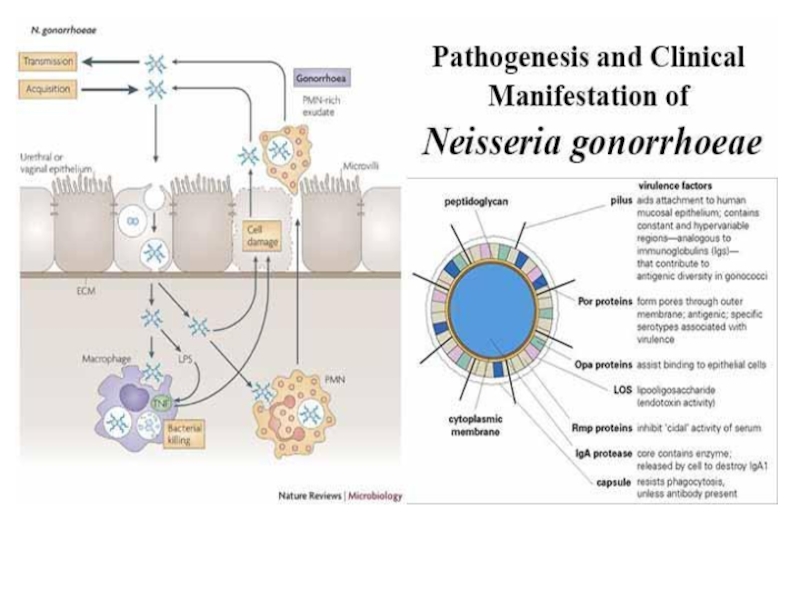
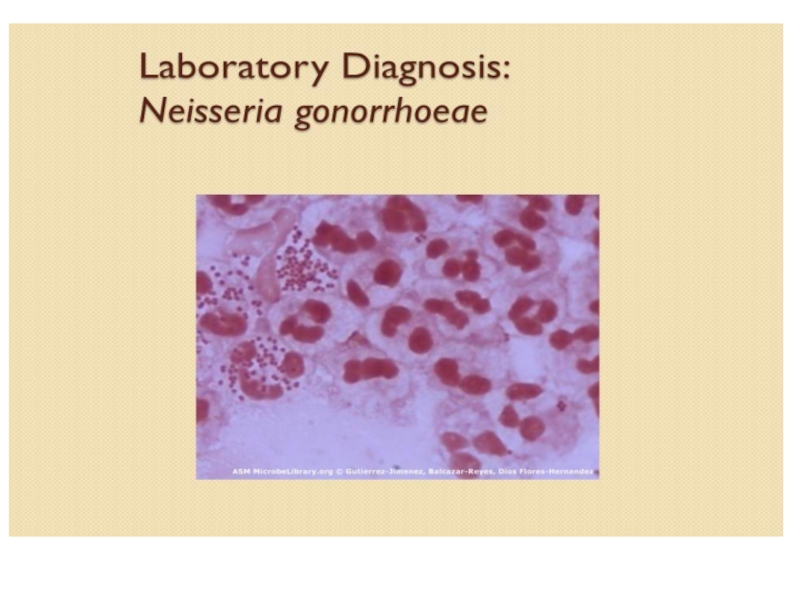
- 17. GonorrhoeaeCausative agent – Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Слайд 22
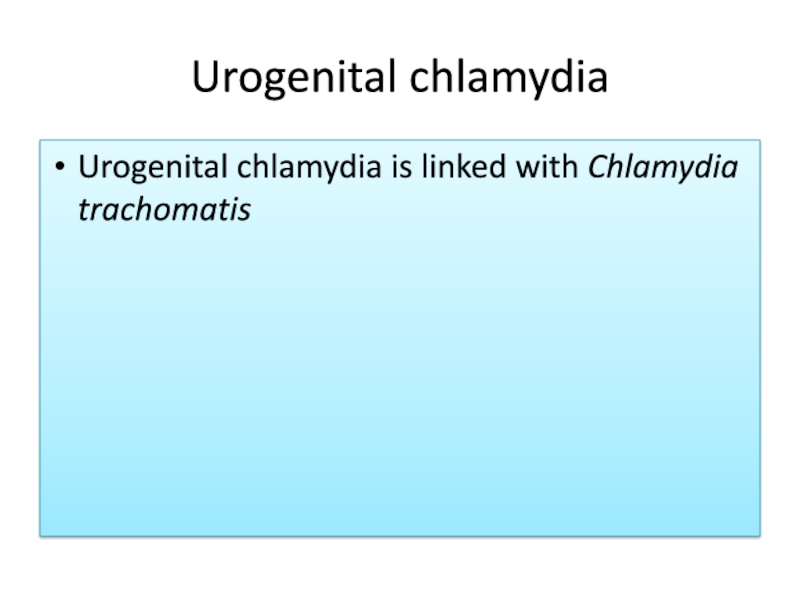
- 23. Urogenital chlamydiaUrogenital chlamydia is linked with Chlamydia trachomatis
- 24. ChlamydiaBacteria belonging to genus Chlamydia are: 1.
- 25. ChlamydiaAll chlamydia posses a common reproductive cycle.
- 26. ChlamydiaIn contras to RB, EB posses highly
- 27. ChlamydiaIntra inclusion EB convert into RB. RB
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. ChlamydiaChlamydia posses shared group specific heat stable
- 33. Chlamydia trachomatisChlamydia trachomatis consists of 18 serovarsSerovars
- 34. Слайд 34
- 35. Chlamydia trachomatisChlamydia trachomatis D - K above
- 36. Слайд 36
- 37. Chlamydia trachomatis Diagnosis Specimen: swab or cytology
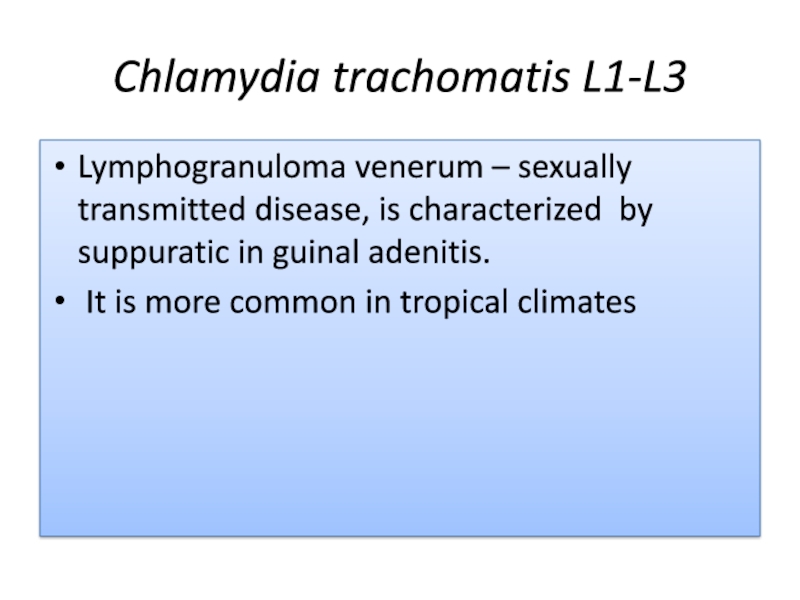
- 38. Chlamydia trachomatis L1-L3Lymphogranuloma venerum – sexually transmitted
- 39. Скачать презентанцию
SYPHILISSyphilis is true human infection Syphilis is caused by spiral form bacteria belonging to genera Treponema sp. T.pallidum
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2SYPHILIS
Syphilis is true human infection
Syphilis is caused by spiral form
bacteria belonging to genera Treponema
Слайд 3Treponema
T.pallidum consists of 3 sub/species:
pallidum – syphilis
endemicum – bejel
pertenue –
yaws
T.carateum - pinta
Слайд 4T.pallidum/pallidum
Microaerophilic bacteria
It cannot be cultivated in vitro
Drying kills microbe
In blood
stored at 4 C microbe remains viable for at least
24 h., which is a potential importance in blood transfusionMicrobe is sensitive to penicillin, is rapidly immobilized and killed by arsenical, mercury, bismuth
Слайд 5T.pallidum/pallidum
Biochemical properties are investigated bad
Virulence: lipoproteins propously can take part
in immunopathological properties
Antigenic
structure 1. Specific termosensitive antigen
2. Non specific lipid’s antigen composition of which is similar to cardiolipin extracted from bovin’s heart
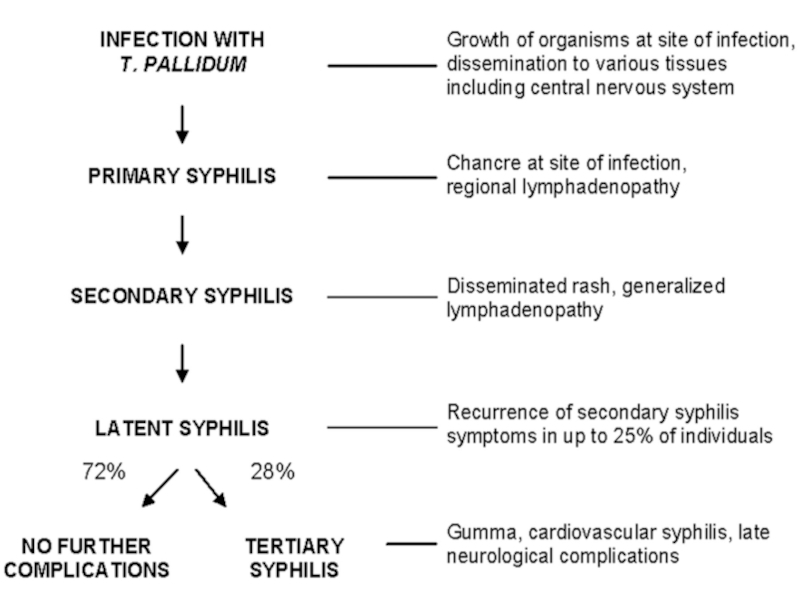
Слайд 7Syphilis
Treponema multiplies locally at the site of entry and spread
to nearly lymph nodes and then reach the blood stream
In
2-10 weeks after infection a papula develops at the site of infection and breaks down to form an ulcer with a clean hard base hard chancreThis is primery lesions
Слайд 8Syphilis
In 2-10 weeks later the secondary lesions appears.
They consists
of mascular papular rash anywhere on the body which contains
microbThe untreated infection remains latent. The disease progresses to the terriary stage
Слайд 9Syphilis
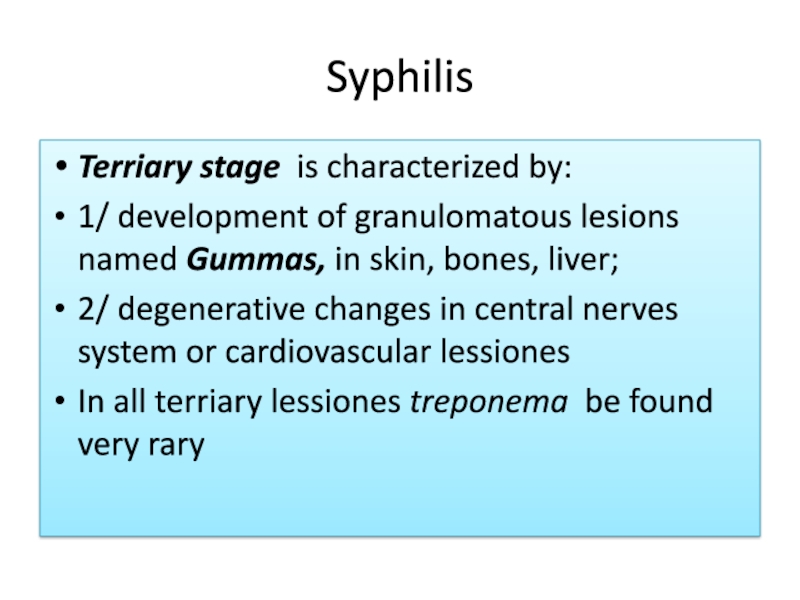
Terriary stage is characterized by:
1/ development of granulomatous lesions
named Gummas, in skin, bones, liver;
2/ degenerative changes in central
nerves system or cardiovascular lessionesIn all terriary lessiones treponema be found very rary
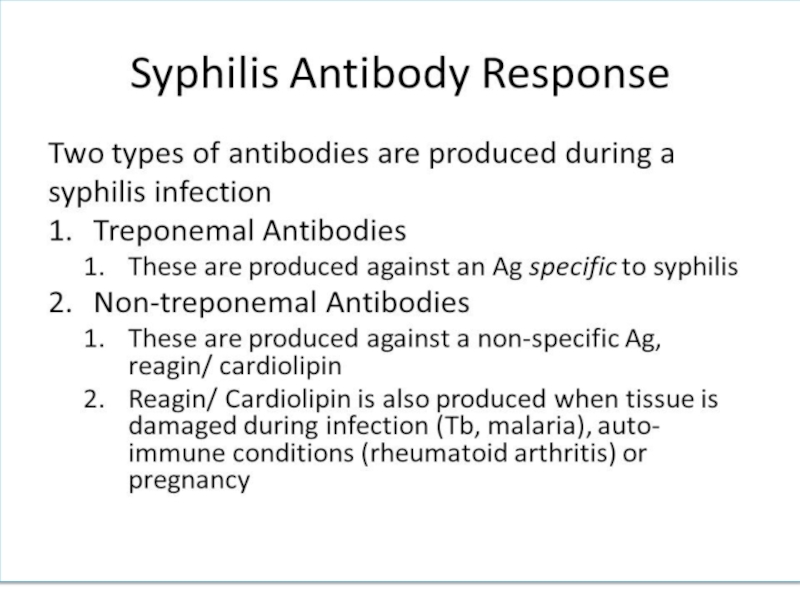
Слайд 12Immunity
PROTECTIVE IMMUNITY IS NOT FORMED !!!
Antibodies are evidence of infection
Antibodies
against non specific cardiolipin antigen appear first. They can persist
during presence of microbe in organismAntibodies against specific antigen appear later and they can be found long time after disease
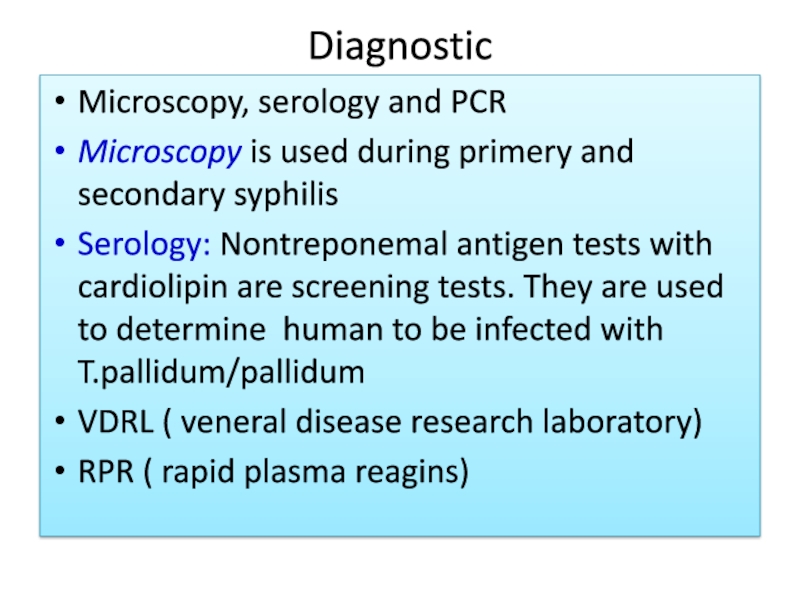
Слайд 13Diagnostic
Microscopy, serology and PCR
Microscopy is used during primery and secondary
syphilis
Serology: Nontreponemal antigen tests with cardiolipin are screening tests. They
are used to determine human to be infected with T.pallidum/pallidumVDRL ( veneral disease research laboratory)
RPR ( rapid plasma reagins)
Слайд 14Diagnostic
Positive VDRL and RPR develop after 2-3 weeks after
untreated syphilis and they are positive in high titer in
secondary syphilisNontreponemal tests may be false positive during some diseases: reumatism, malaria..
Treponemal antibodies test , containig specific antigen are used to confirm disease. IFA, indirect IF, IHA
Слайд 16Congenital syphilis
A pregnant syphilitic woman can transmit T. pallidum/pallidum to
the fetus through placenta beginning in the 10th – 15th
week of gestation. Some of infected fetus die. Others are born with symptoms of congenital syphilis:Keratitis, periostitis, central nerve system anomalies. Child shows IgM anti treponemal antibodies
Слайд 24Chlamydia
Bacteria belonging to genus Chlamydia are:
1. obligate intracellular parasites,
because they lack mechanism for production metabolic energy and cannot
synthesize ATP2. gramnegative bacteria which do not contain a typical peptidoglycan, because muramic acid appears to be absent from chlamydia cell wall
Слайд 25Chlamydia
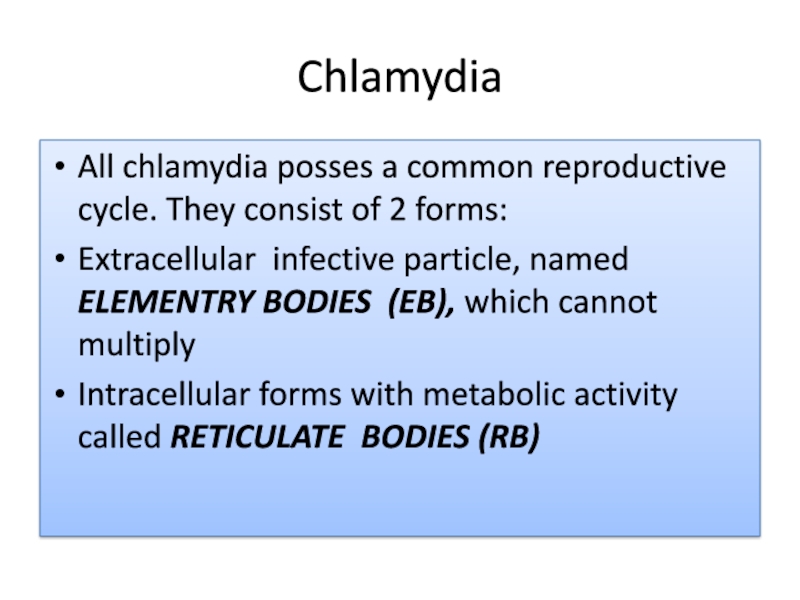
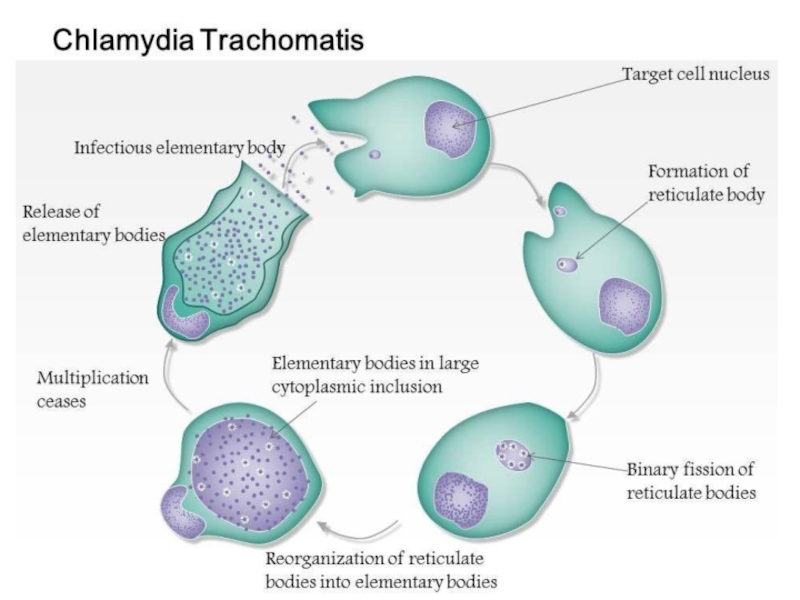
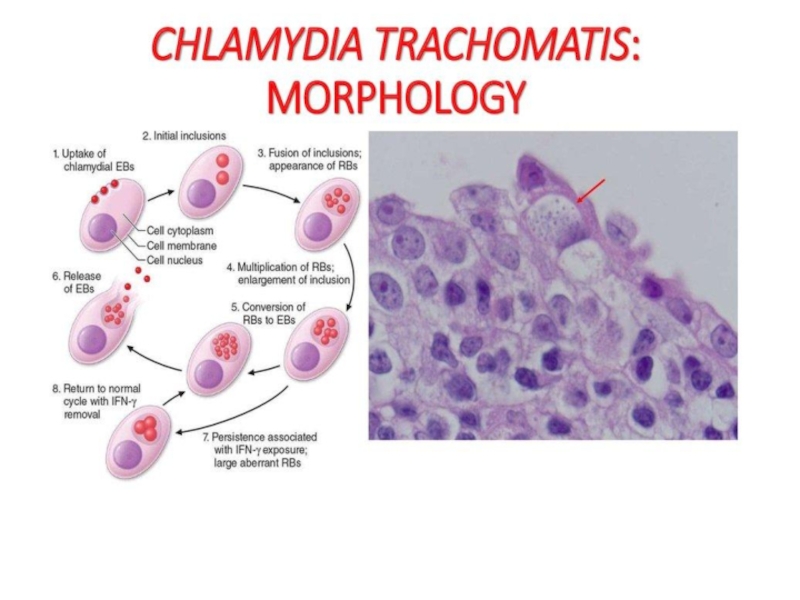
All chlamydia posses a common reproductive cycle. They consist of
2 forms:
Extracellular infective particle, named ELEMENTRY BODIES (EB), which cannot
multiplyIntracellular forms with metabolic activity called RETICULATE BODIES (RB)
Слайд 26Chlamydia
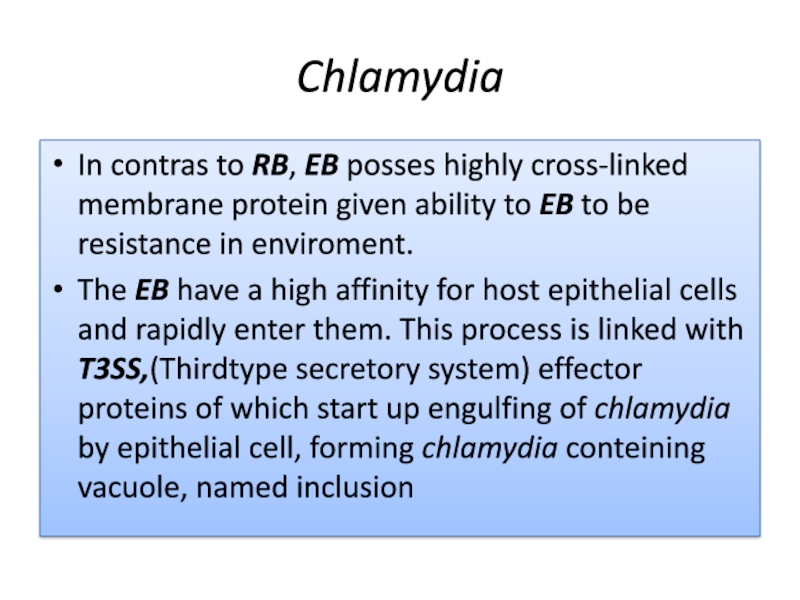
In contras to RB, EB posses highly cross-linked membrane protein
given ability to EB to be resistance in enviroment.
The EB
have a high affinity for host epithelial cells and rapidly enter them. This process is linked with T3SS,(Thirdtype secretory system) effector proteins of which start up engulfing of chlamydia by epithelial cell, forming chlamydia conteining vacuole, named inclusionСлайд 27Chlamydia
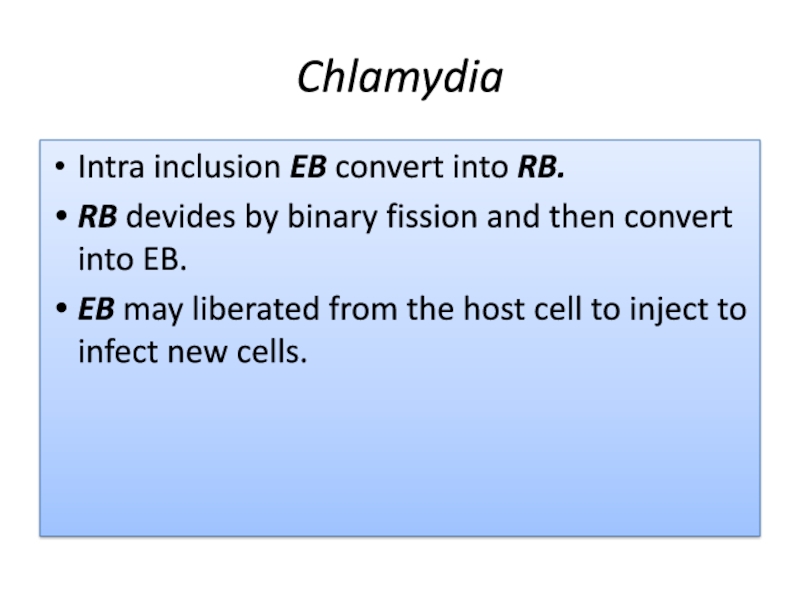
Intra inclusion EB convert into RB.
RB devides by binary
fission and then convert into EB.
EB may liberated from the
host cell to inject to infect new cells.Слайд 32Chlamydia
Chlamydia posses shared group specific heat stable antigen, antibody to
which cav be detected by CFT and IF
Species-specific, serovar-specific protein
antigenСлайд 33Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia trachomatis consists of 18 serovars
Serovars A,B,Ba,C –are linked
with trachoma -eye disease, beginning as kerato conjunctivitis progressing to
blindness.Serovars D-K –nongonococcal urethritis
Serovars L1- L3 –lymphogranuloma venerum
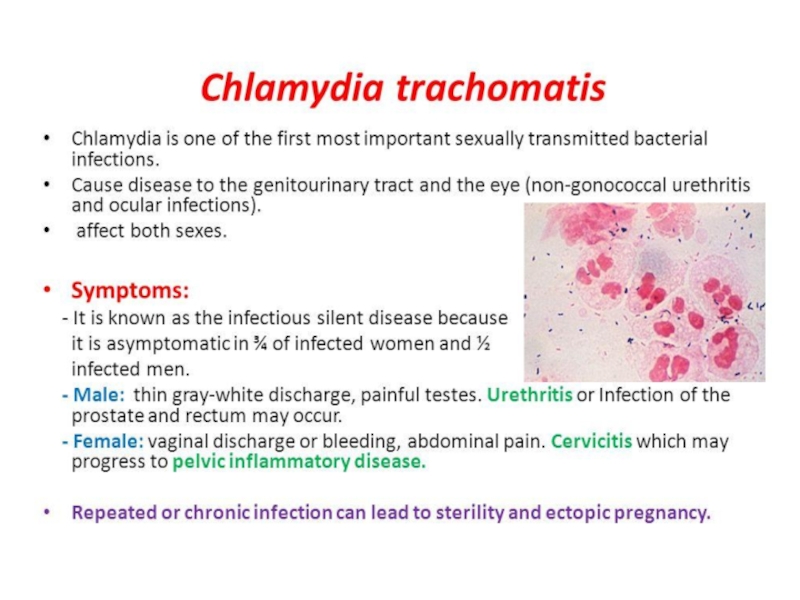
Слайд 35Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia trachomatis D - K above nongonococcal urethritis can
cause cervicitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, which can led to sterility
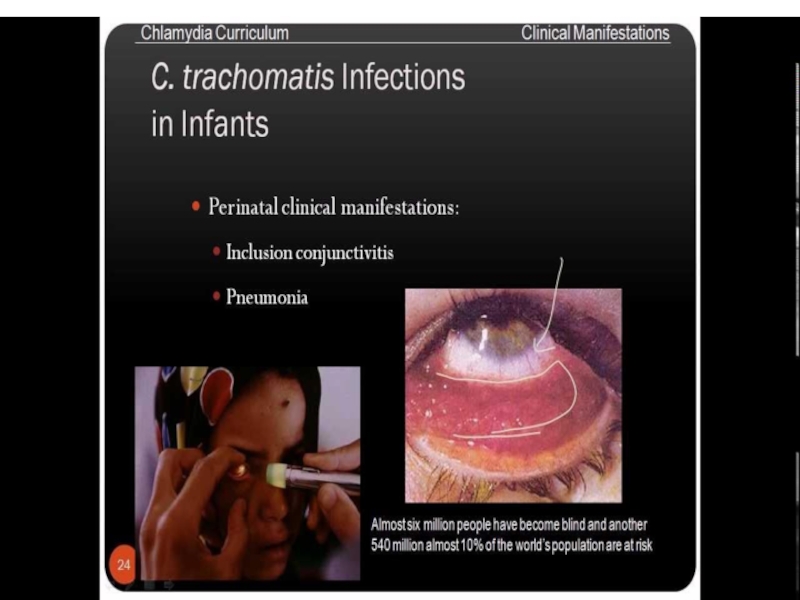
and predispose ectopic pregnancyThe newborn acquires the infection during passage through an infected birth canal. This infection is appeared as conjunctivitis
Слайд 37Chlamydia trachomatis
Diagnosis
Specimen: swab or cytology brush are used to scrape
epithelial cells from 1-2 cm deep into endocervix, vagine, urethra
or conjunctive.IF or Enzyme linked Immunoassay (EIA) are used to determine antigen, Such specimen may be used for PCR (urine) also may be used for PCR
Serology may be used for determination of the duration of infection and observation of effect of treatment