Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Венерина мухоловка ( Dionaea muscipula ) — миксотроф: в её вегетативных органах
Содержание
- 1. Венерина мухоловка ( Dionaea muscipula ) — миксотроф: в её вегетативных органах
- 2. Заразиха люцерновая Orobanche lutea
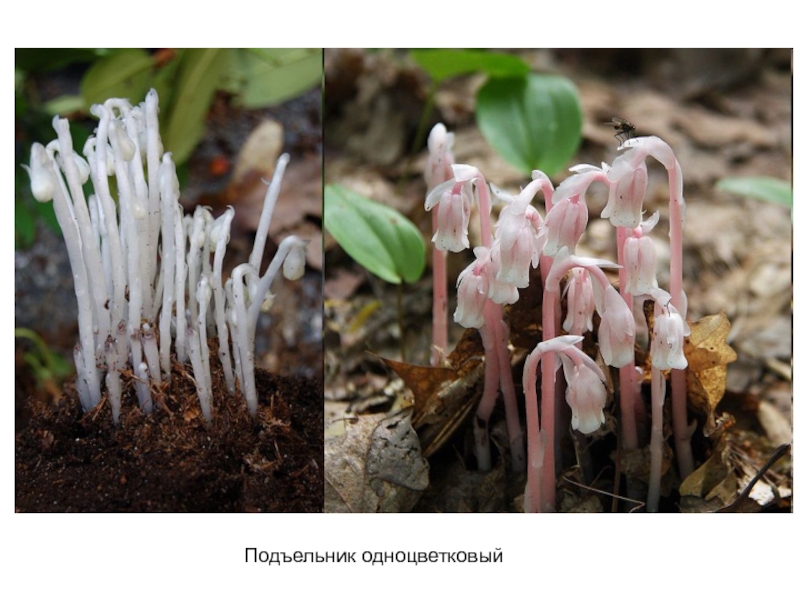
- 3. Подъельник одноцветковый
- 4. Слайд 4
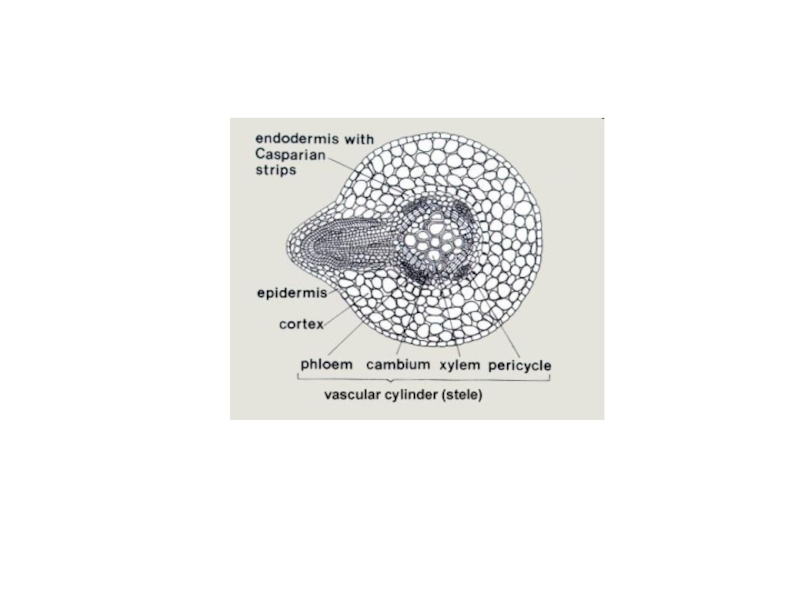
- 5. Слайд 5
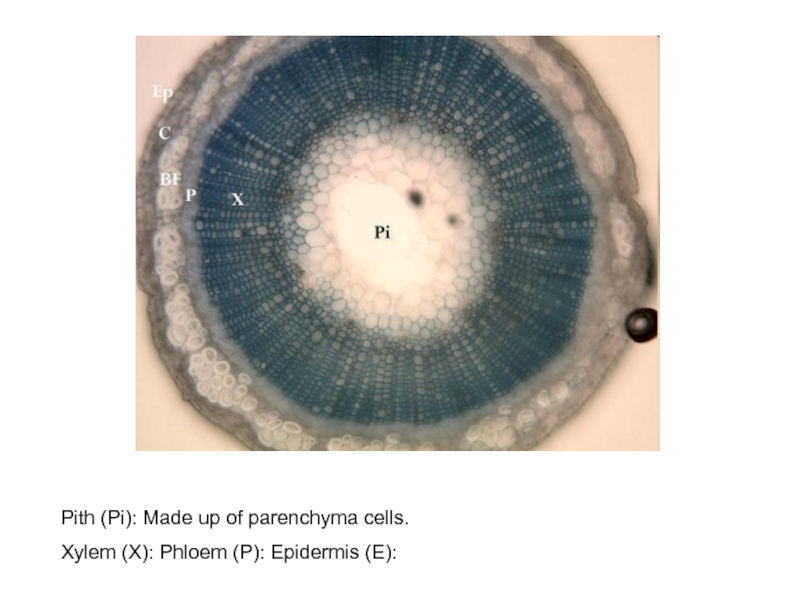
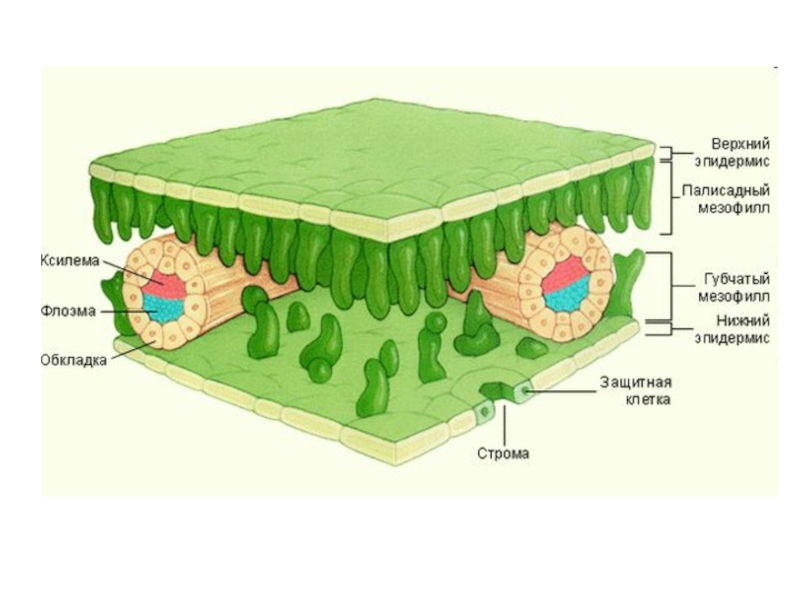
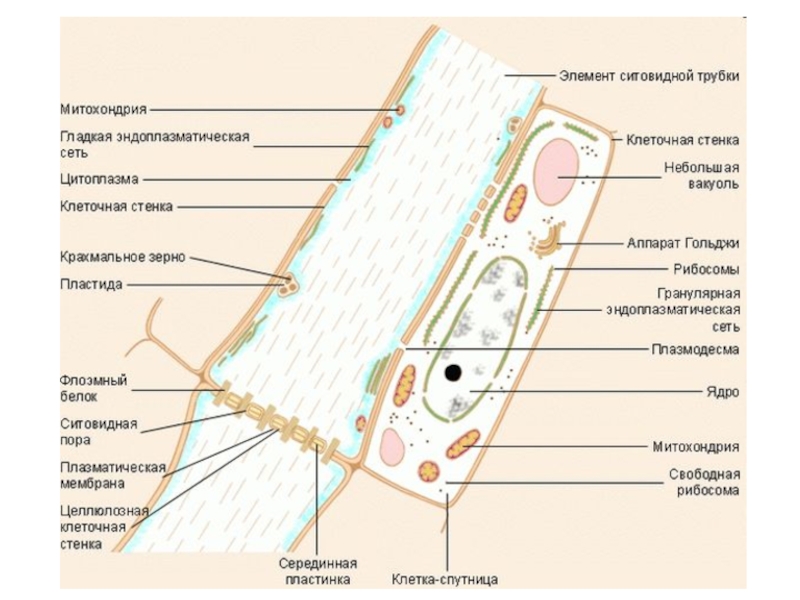
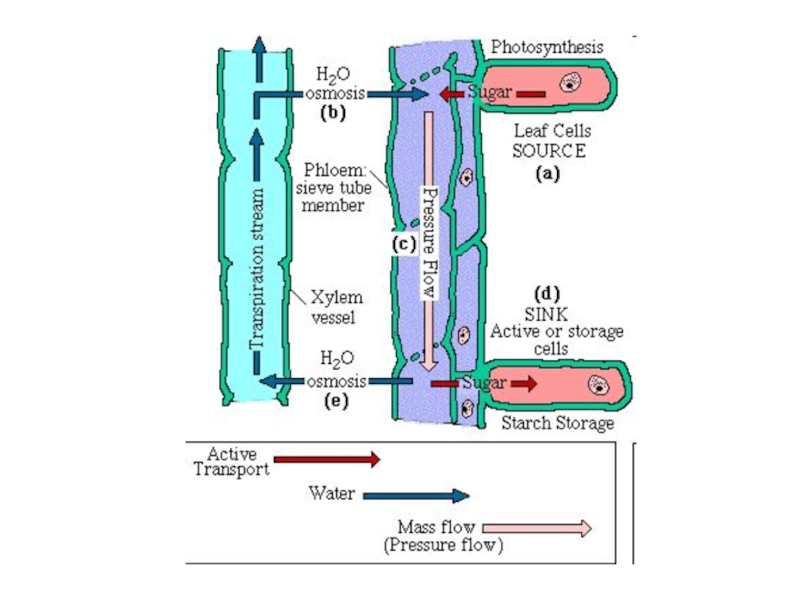
- 6. Pith (Pi): Made up of parenchyma cells.Xylem (X): Phloem (P): Epidermis (E):
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Слайд 11
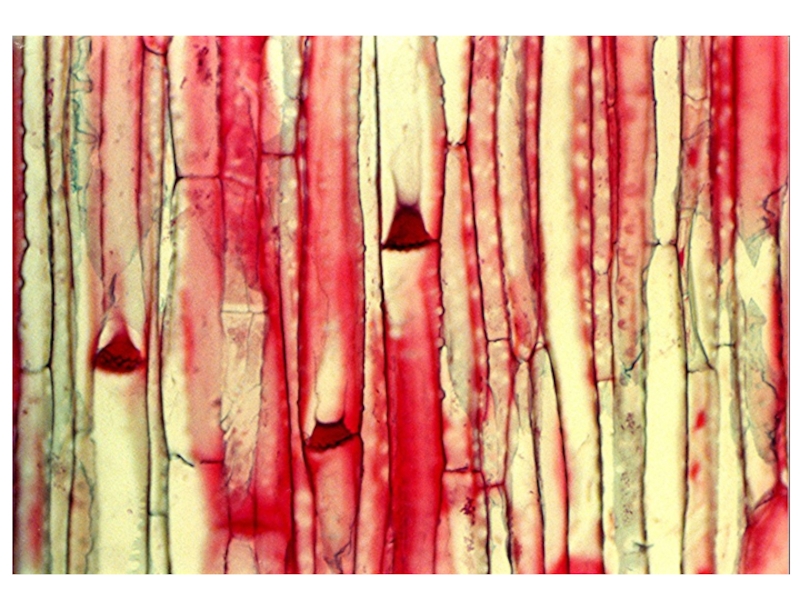
- 12. Rhubarb stem. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM)
- 13. False colour scanning electron micrograph of a
- 14. Xylem and phloem plant tissue. Coloured scanning
- 15. Xylem tissue. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM)
- 16. Color enhanced scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of
- 17. Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of xylem tubes
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Plant stem sieve plates. Coloured scanning electron
- 20. Sieve plates of 4 different plant species shown at
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Слайд 22
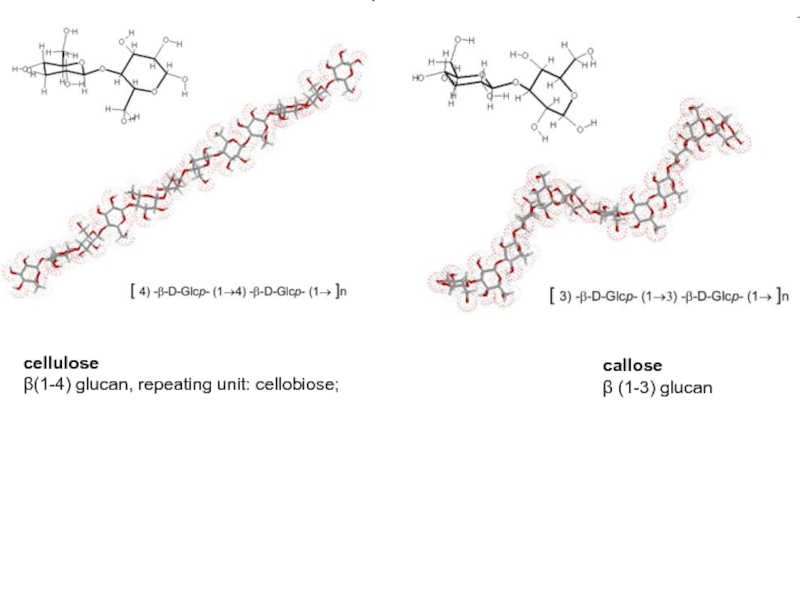
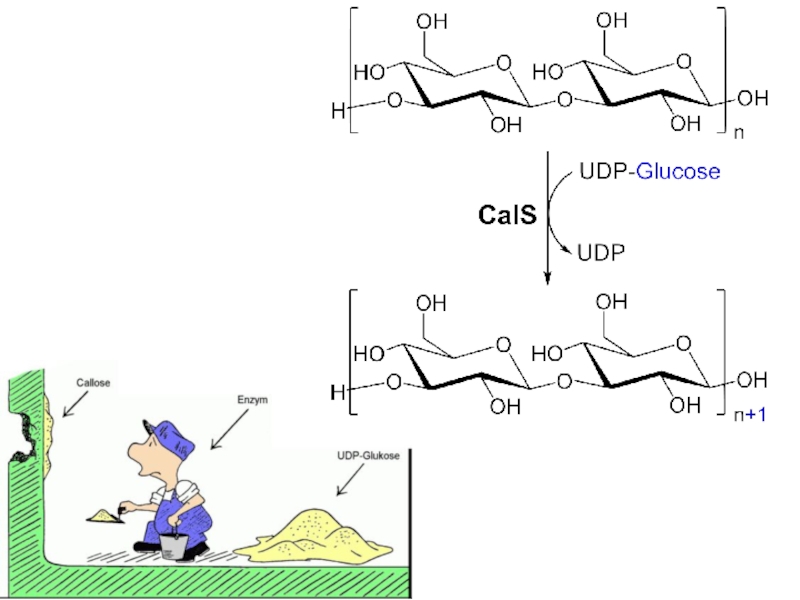
- 23. celluloseβ(1-4) glucan, repeating unit: cellobiose; callose β (1-3) glucan
- 24. Слайд 24
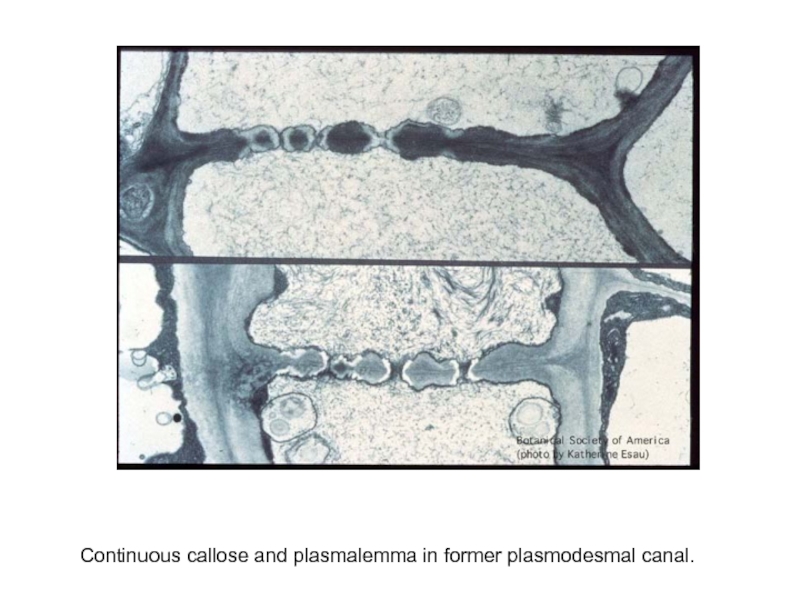
- 25. Continuous callose and plasmalemma in former plasmodesmal canal.
- 26. Overall view of a longitudinal section of
- 27. Callose formation in bamboo. Sieve plate in
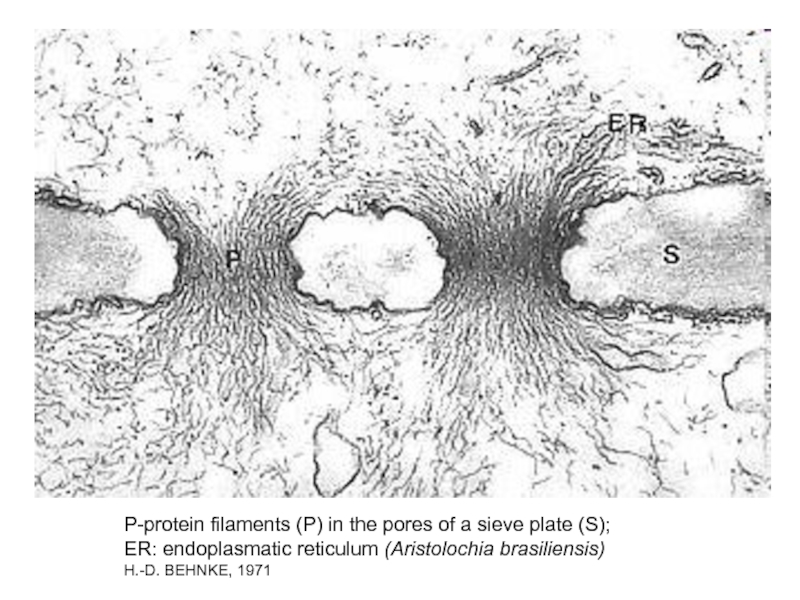
- 28. P-protein filaments (P) in the pores of
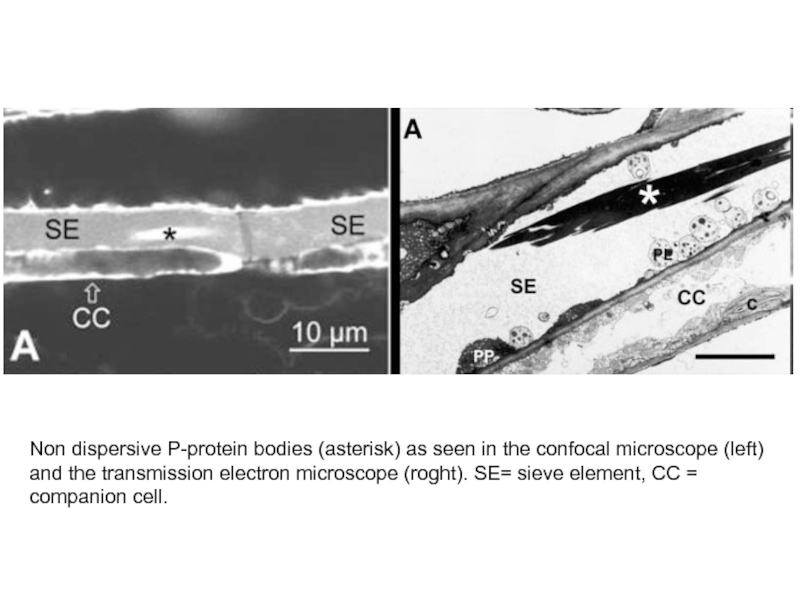
- 29. Non dispersive P-protein bodies (asterisk) as seen
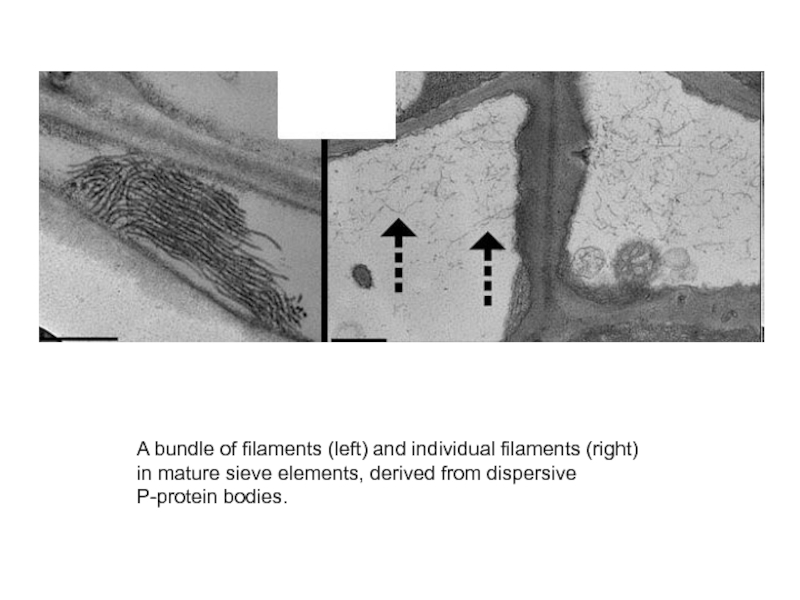
- 30. A bundle of filaments (left) and individual filaments (right) in mature sieve elements, derived from dispersive P-protein bodies.
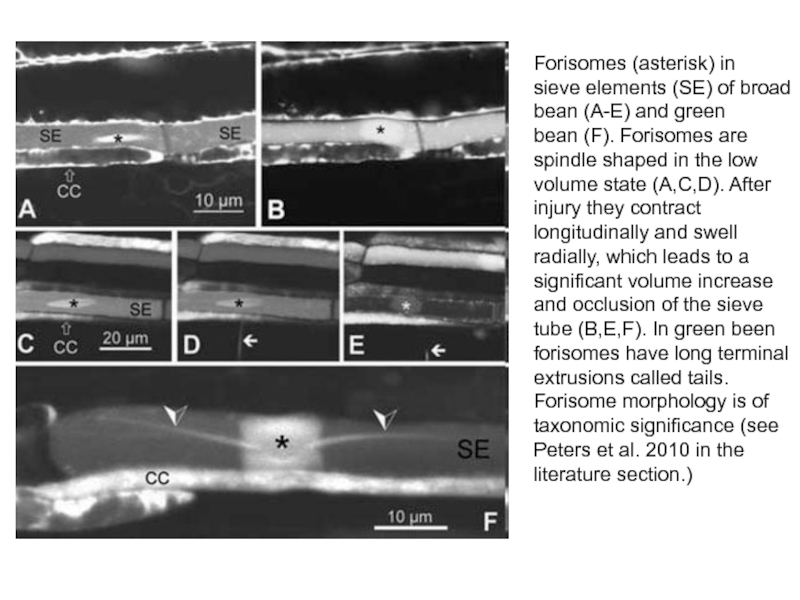
- 31. Forisomes (asterisk) in sieve elements (SE) of broad bean (A-E) and green
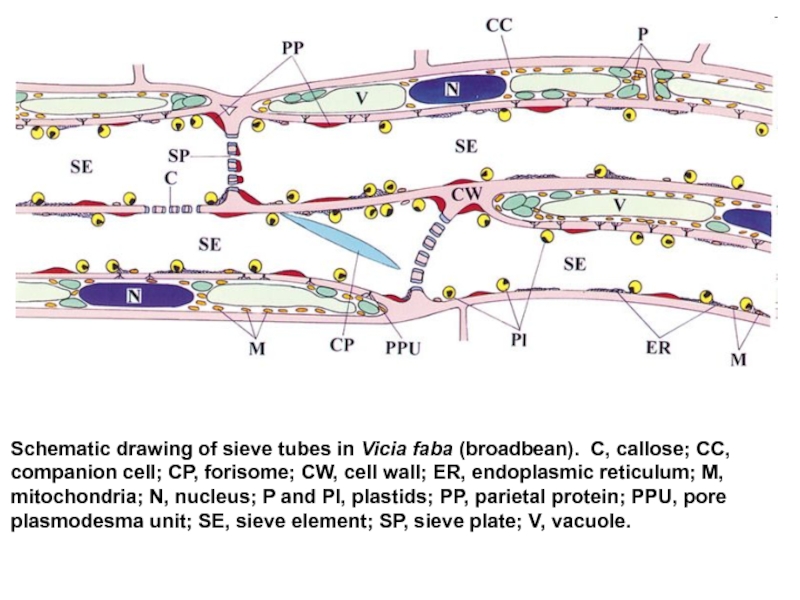
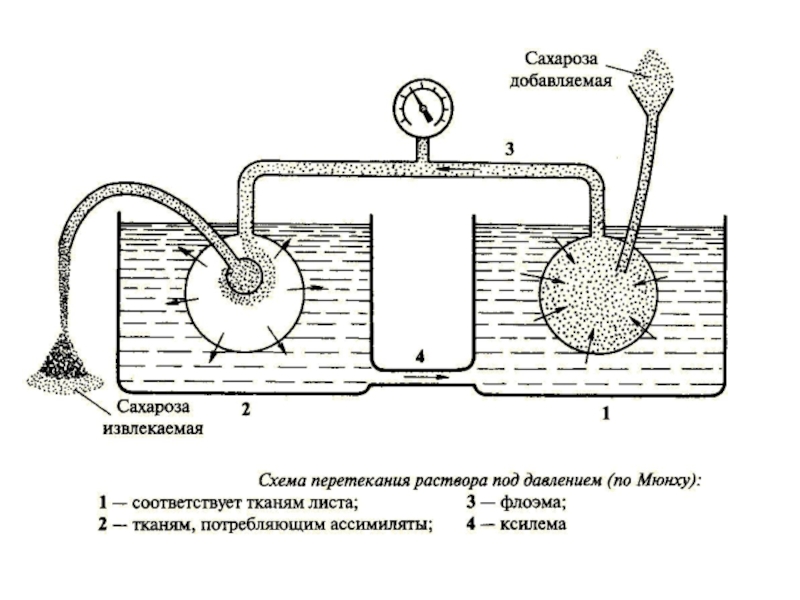
- 32. Schematic drawing of sieve tubes in Vicia faba
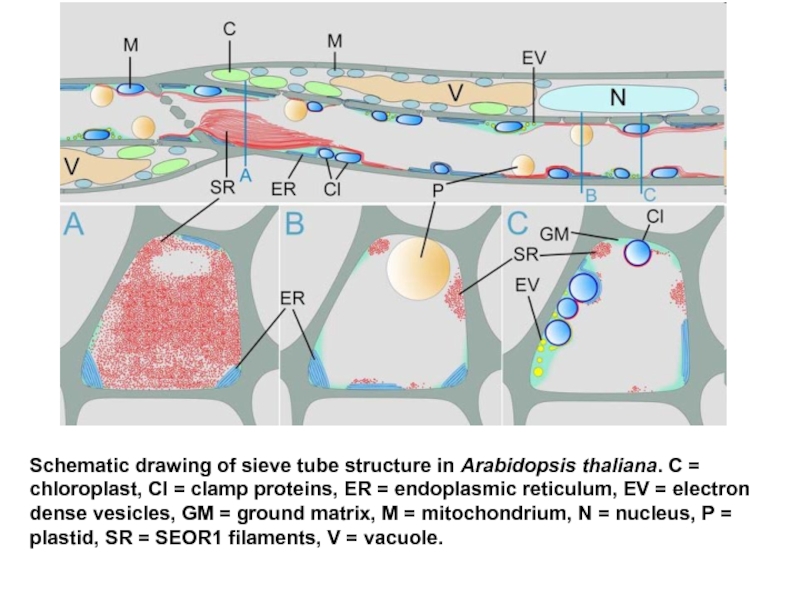
- 33. Schematic drawing of sieve tube structure in
- 34. Слайд 34
- 35. Слайд 35
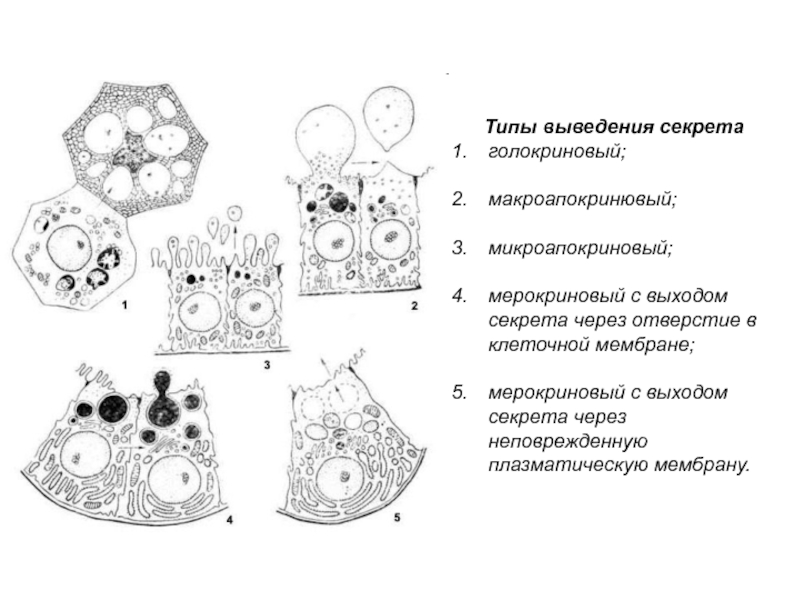
- 36. Типы выведения секретаголокриновый; макроапокринювый; микроапокриновый;
- 37. Скачать презентанцию
Заразиха люцерновая Orobanche lutea
Слайды и текст этой презентации
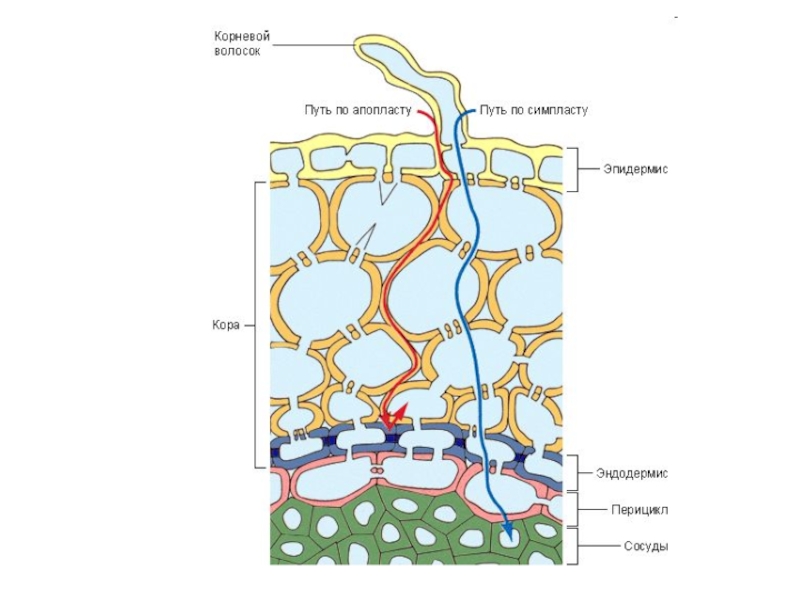
Слайд 1Венерина мухоловка (Dionaea muscipula)
— миксотроф: в её вегетативных органах
идёт процесс фотосинтеза, но растение также ловит и переваривает насекомых
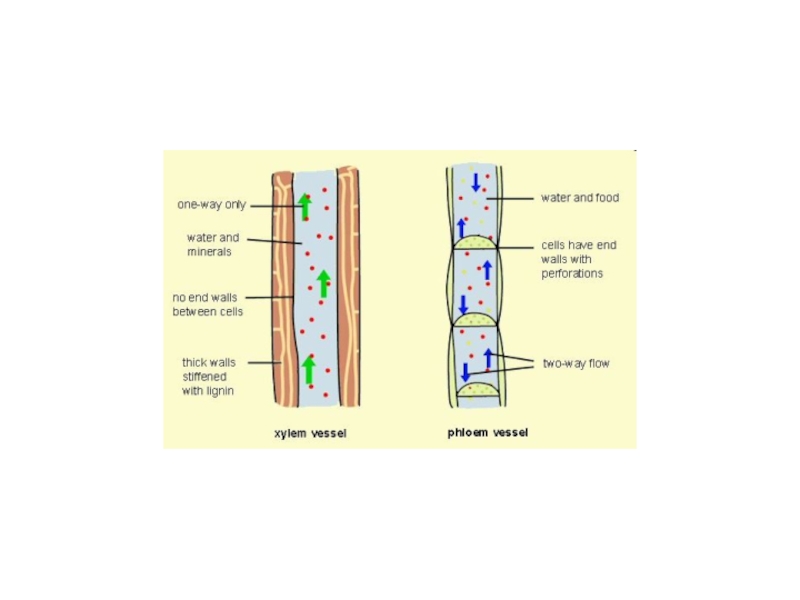
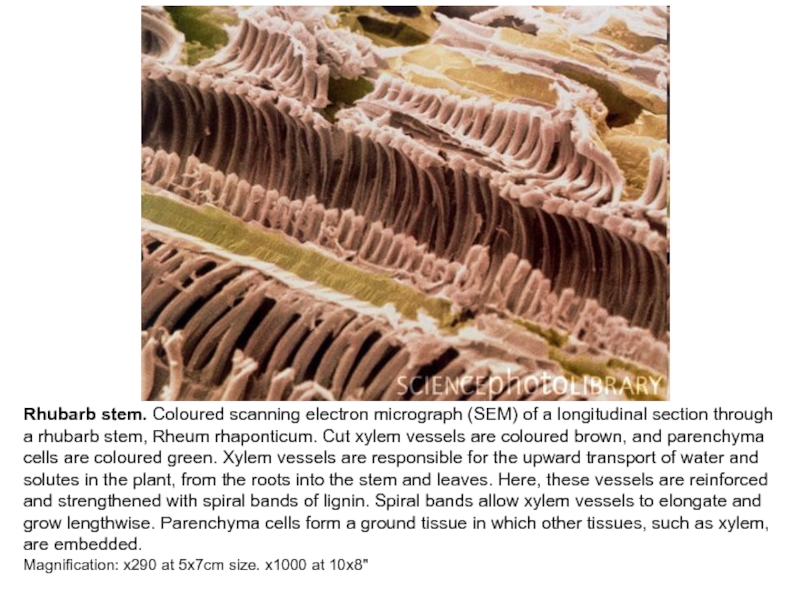
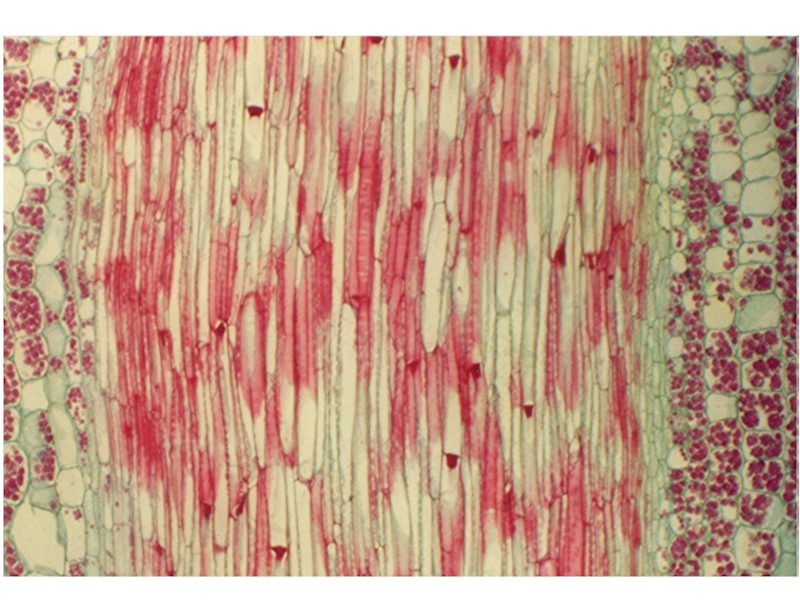
Слайд 12Rhubarb stem. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a longitudinal
section through a rhubarb stem, Rheum rhaponticum. Cut xylem vessels
are coloured brown, and parenchyma cells are coloured green. Xylem vessels are responsible for the upward transport of water and solutes in the plant, from the roots into the stem and leaves. Here, these vessels are reinforced and strengthened with spiral bands of lignin. Spiral bands allow xylem vessels to elongate and grow lengthwise. Parenchyma cells form a ground tissue in which other tissues, such as xylem, are embedded.Magnification: x290 at 5x7cm size. x1000 at 10x8"
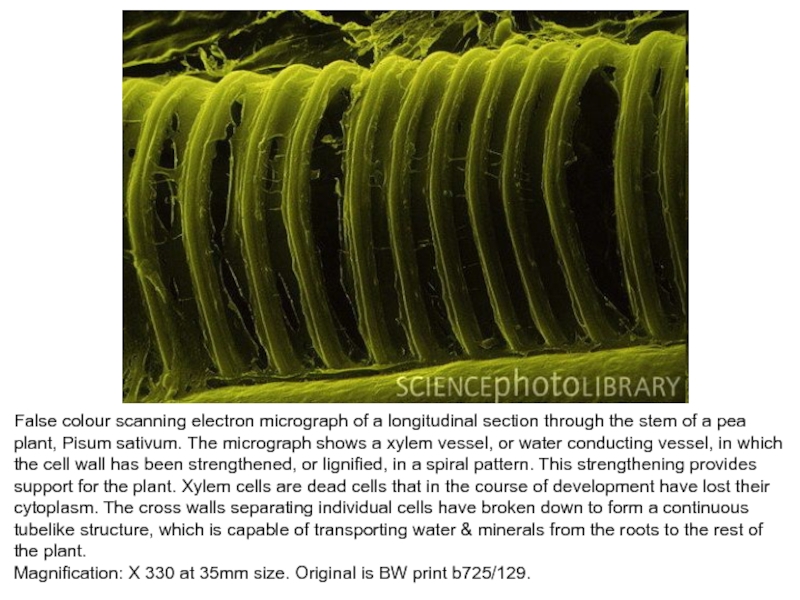
Слайд 13False colour scanning electron micrograph of a longitudinal section through
the stem of a pea plant, Pisum sativum. The micrograph
shows a xylem vessel, or water conducting vessel, in which the cell wall has been strengthened, or lignified, in a spiral pattern. This strengthening provides support for the plant. Xylem cells are dead cells that in the course of development have lost their cytoplasm. The cross walls separating individual cells have broken down to form a continuous tubelike structure, which is capable of transporting water & minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant.Magnification: X 330 at 35mm size. Original is BW print b725/129.
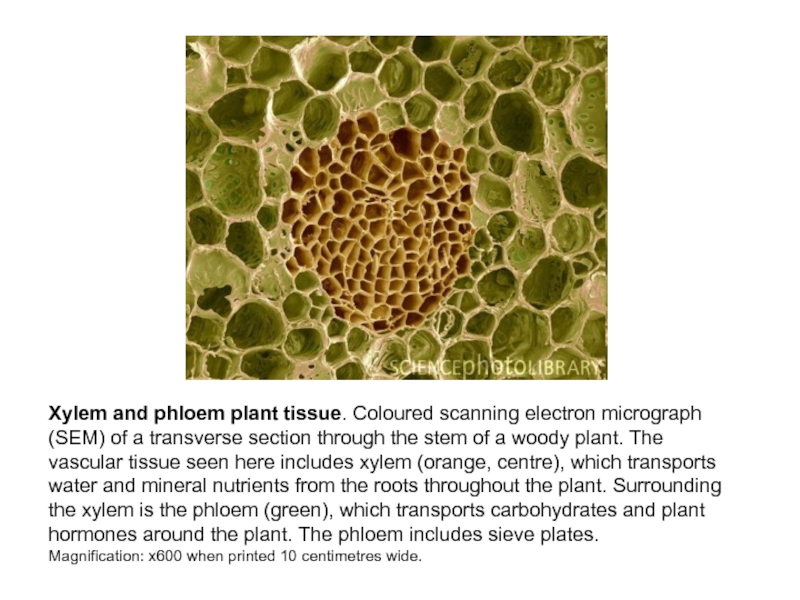
Слайд 14Xylem and phloem plant tissue. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM)
of a transverse section through the stem of a woody
plant. The vascular tissue seen here includes xylem (orange, centre), which transports water and mineral nutrients from the roots throughout the plant. Surrounding the xylem is the phloem (green), which transports carbohydrates and plant hormones around the plant. The phloem includes sieve plates.Magnification: x600 when printed 10 centimetres wide.
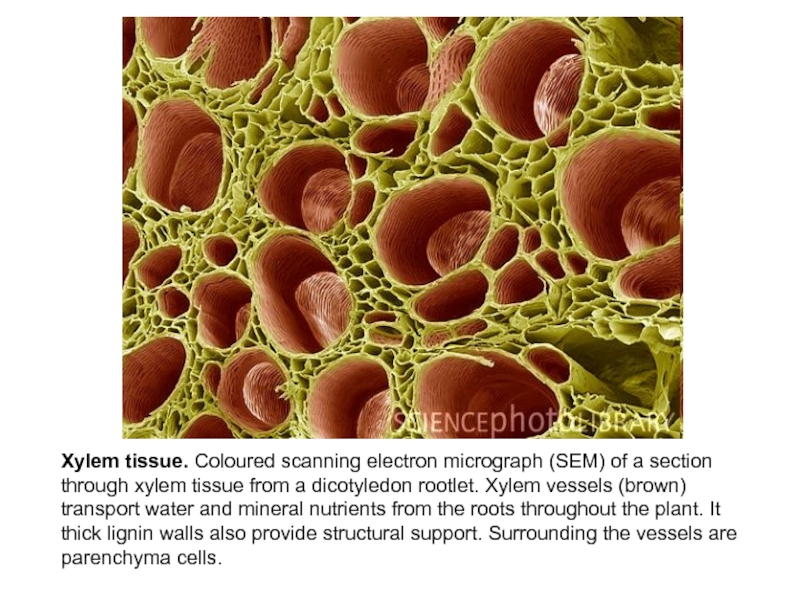
Слайд 15Xylem tissue. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a section
through xylem tissue from a dicotyledon rootlet. Xylem vessels (brown)
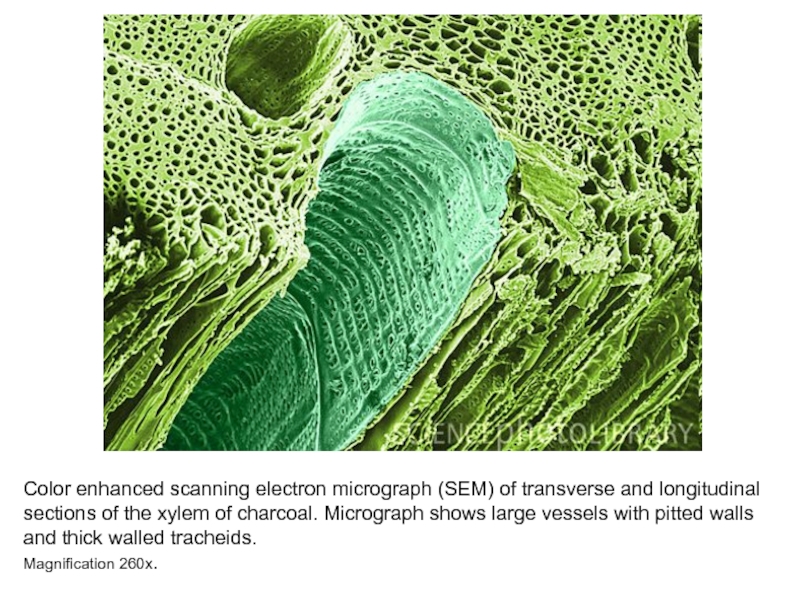
transport water and mineral nutrients from the roots throughout the plant. It thick lignin walls also provide structural support. Surrounding the vessels are parenchyma cells.Слайд 16Color enhanced scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of transverse and longitudinal
sections of the xylem of charcoal. Micrograph shows large vessels
with pitted walls and thick walled tracheids.Magnification 260x.
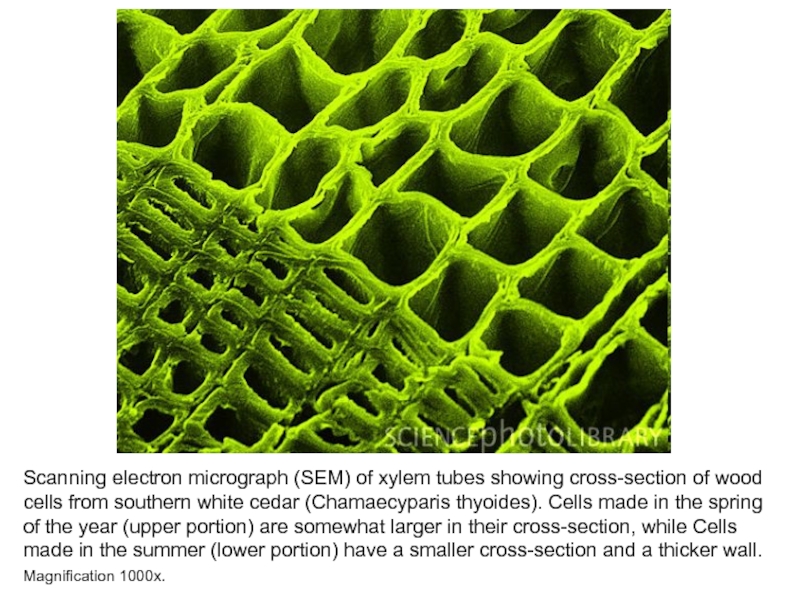
Слайд 17Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of xylem tubes showing cross-section of
wood cells from southern white cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides). Cells made
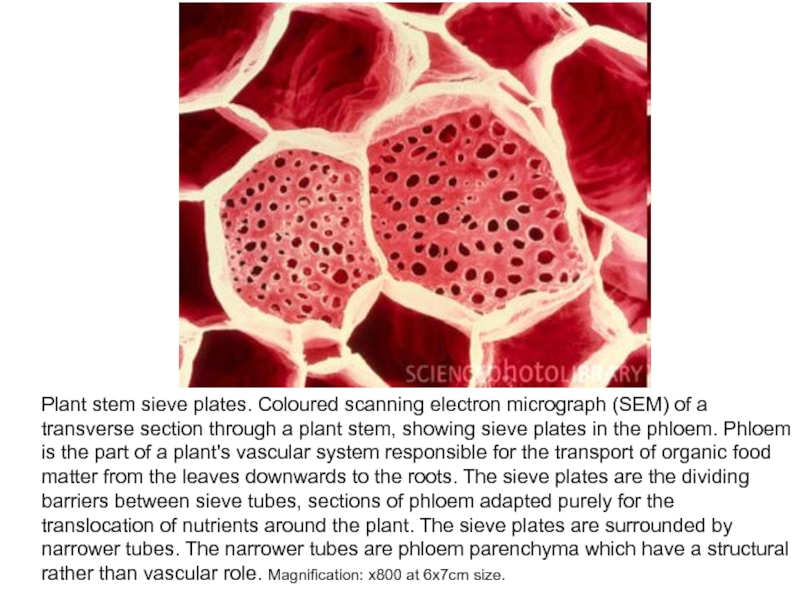
in the spring of the year (upper portion) are somewhat larger in their cross-section, while Cells made in the summer (lower portion) have a smaller cross-section and a thicker wall. Magnification 1000x.Слайд 19Plant stem sieve plates. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of
a transverse section through a plant stem, showing sieve plates
in the phloem. Phloem is the part of a plant's vascular system responsible for the transport of organic food matter from the leaves downwards to the roots. The sieve plates are the dividing barriers between sieve tubes, sections of phloem adapted purely for the translocation of nutrients around the plant. The sieve plates are surrounded by narrower tubes. The narrower tubes are phloem parenchyma which have a structural rather than vascular role. Magnification: x800 at 6x7cm size.Слайд 20Sieve plates of 4 different plant species shown at the same scale.
From left to right: pumpkin, green bean, castor bean, tomato.
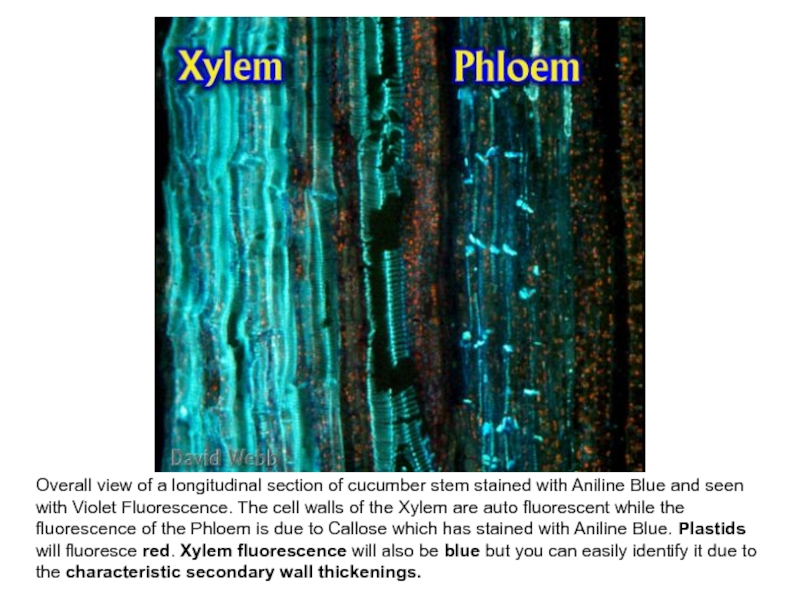
Слайд 26Overall view of a longitudinal section of cucumber stem stained
with Aniline Blue and seen with Violet Fluorescence. The cell
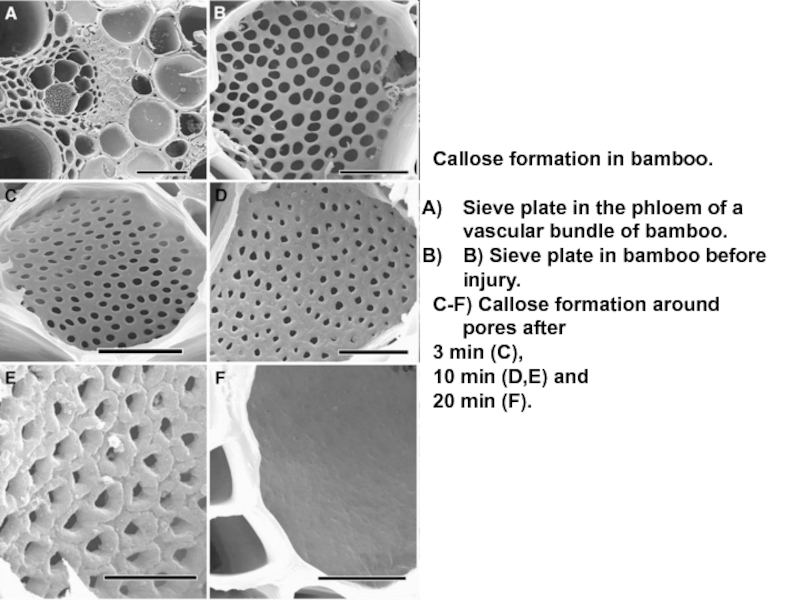
walls of the Xylem are auto fluorescent while the fluorescence of the Phloem is due to Callose which has stained with Aniline Blue. Plastids will fluoresce red. Xylem fluorescence will also be blue but you can easily identify it due to the characteristic secondary wall thickenings.Слайд 27Callose formation in bamboo.
Sieve plate in the phloem of
a vascular bundle of bamboo.
B) Sieve plate in bamboo
before injury. C-F) Callose formation around pores after
3 min (C),
10 min (D,E) and
20 min (F).