Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Well Logging
Содержание
- 1. Well Logging
- 2. What is well logging?Well logging, also known
- 3. How is well logging done?Wireline logging is
- 4. Слайд 4
- 5. History of Well LoggingConrad and Marcel Schlumberger,
- 6. History of Well LoggingOil-based mud (OBM) was
- 7. History of Well LoggingThe gamma ray log,
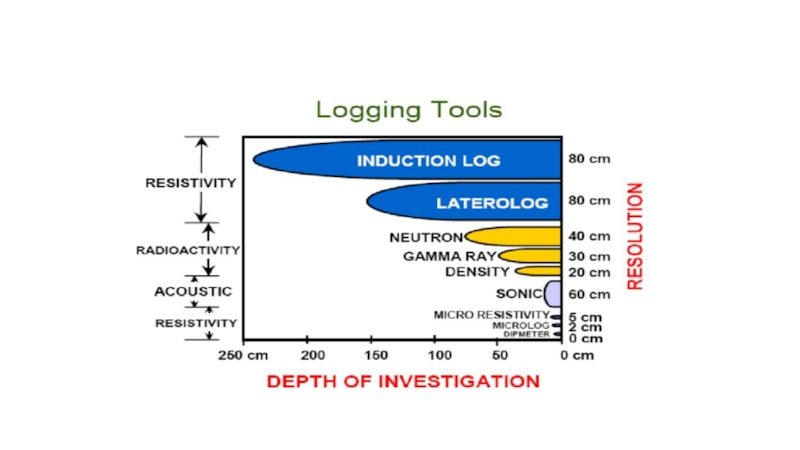
- 8. Classification of Well LoggingLogs can be classified
- 9. Permeability and Lithology Logs
- 10. Gamma Ray Logging (GR)Gamma Rays are high-energy
- 11. Spontaneous Potential LoggingThe spontaneous potential (SP) curve
- 12. Caliper LogThe logging system provides a continuous
- 13. Porosity Logs
- 14. Density LoggingThe formation density log is a
- 15. Sonic (Acoustic) LogAcoustic tools measure the speed
- 16. Neutron LoggingThe Neutron Log is primarily used
- 17. Electrical Logs
- 18. Resistivity LoggingResistivity logging measures the subsurface electrical
- 19. During logging, a current is produced within
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Caliper Logging Tool
- 22. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
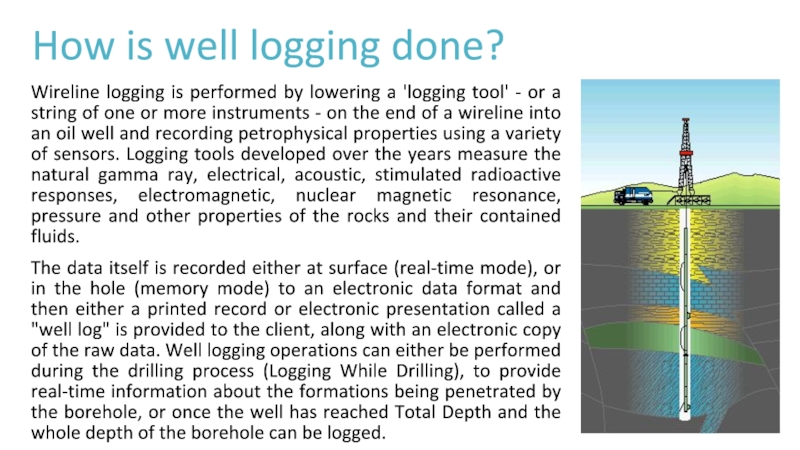
Слайд 3How is well logging done?
Wireline logging is performed by lowering
a 'logging tool' - or a string of one or
more instruments - on the end of a wireline into an oil well and recording petrophysical properties using a variety of sensors. Logging tools developed over the years measure the natural gamma ray, electrical, acoustic, stimulated radioactive responses, electromagnetic, nuclear magnetic resonance, pressure and other properties of the rocks and their contained fluids.The data itself is recorded either at surface (real-time mode), or in the hole (memory mode) to an electronic data format and then either a printed record or electronic presentation called a "well log" is provided to the client, along with an electronic copy of the raw data. Well logging operations can either be performed during the drilling process (Logging While Drilling), to provide real-time information about the formations being penetrated by the borehole, or once the well has reached Total Depth and the whole depth of the borehole can be logged.
Слайд 5History of Well Logging
Conrad and Marcel Schlumberger, who founded Schlumberger
Limited in 1926, are considered the inventors of electric well
logging. Conrad developed the Schlumberger array. On September 5, 1927, a crew working for Schlumberger lowered an electric sonde or tool down a well in Pechelbronn, France creating the first well log (resistivity log).In 1931, Henri George Doll and G. Dechatre, working for Schlumberger, discovered that the galvanometer wiggled even when no current was being passed through the logging cables down in the well. This led to the discovery of the spontaneous potential (SP) which was as important as the ability to measure resistivity.
In 1940, Schlumberger invented the dipmeter; this instrument allowed the calculation of the dip and direction of the dip of a layer.
Слайд 6History of Well Logging
Oil-based mud (OBM) was first used in
Colorado in 1948. Normal electric logs require a conductive or
water-based mud, but OBMs are nonconductive. The solution to this problem was the induction log, developed in the late 1940s.The introduction of the transistor and integrated circuits in the 1960s made electric logs vastly more reliable. Computerization allowed much faster log processing, and expanded log data-gathering capacity. The 1970s brought more logs and computers. These included combo type logs where resistivity logs and porosity logs were recorded in one pass in the borehole.
The two types of porosity logs (acoustic logs and nuclear logs) date originally from the 1940s. Sonic logs grew out of technology developed during World War II. Nuclear logging has supplemented acoustic logging, but acoustic or sonic logs are still run on some combination logging tools.
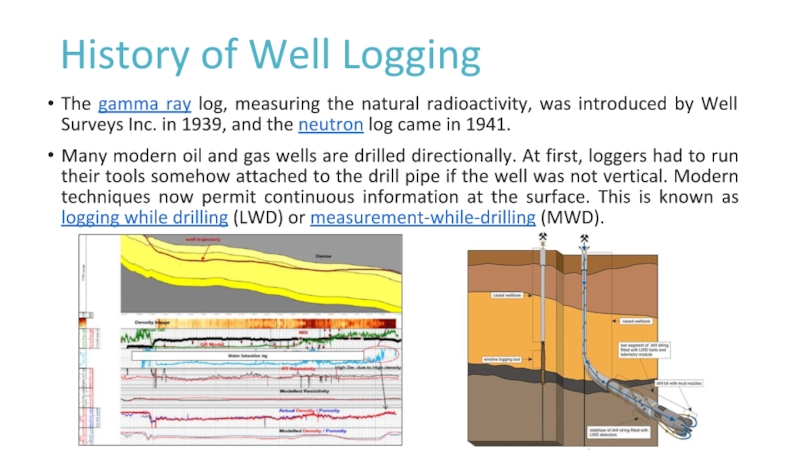
Слайд 7History of Well Logging
The gamma ray log, measuring the natural
radioactivity, was introduced by Well Surveys Inc. in 1939, and
the neutron log came in 1941.Many modern oil and gas wells are drilled directionally. At first, loggers had to run their tools somehow attached to the drill pipe if the well was not vertical. Modern techniques now permit continuous information at the surface. This is known as logging while drilling (LWD) or measurement-while-drilling (MWD).
Слайд 8Classification of Well Logging
Logs can be classified into several types
under different category
Permeability and lithology Logs
Gamma Ray Logging
Spontaneous Potential
LoggingCaliper Log
Porosity Logs
Density Logging
Sonic (Acoustic) Logging
Neutron Logging
Electrical Logs
Resistivity Logging
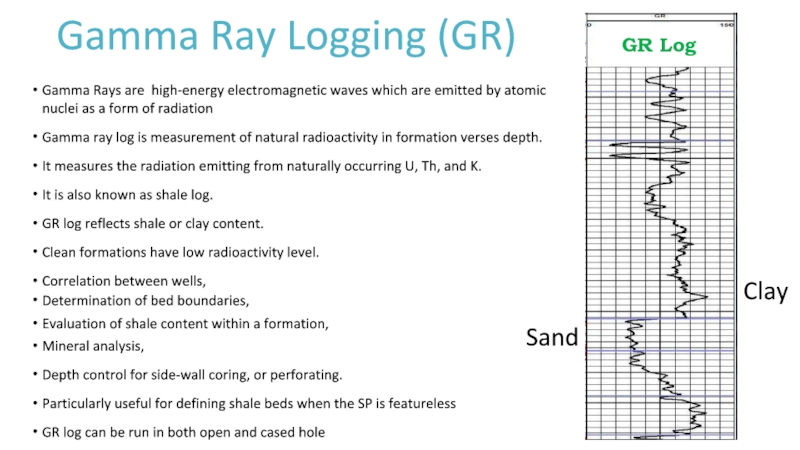
Слайд 10Gamma Ray Logging (GR)
Gamma Rays are high-energy electromagnetic waves which
are emitted by atomic nuclei as a form of radiation
Gamma
ray log is measurement of natural radioactivity in formation verses depth.It measures the radiation emitting from naturally occurring U, Th, and K.
It is also known as shale log.
GR log reflects shale or clay content.
Clean formations have low radioactivity level.
Correlation between wells,
Determination of bed boundaries,
Evaluation of shale content within a formation,
Mineral analysis,
Depth control for side-wall coring, or perforating.
Particularly useful for defining shale beds when the SP is featureless
GR log can be run in both open and cased hole
GR Log
Sand
Clay
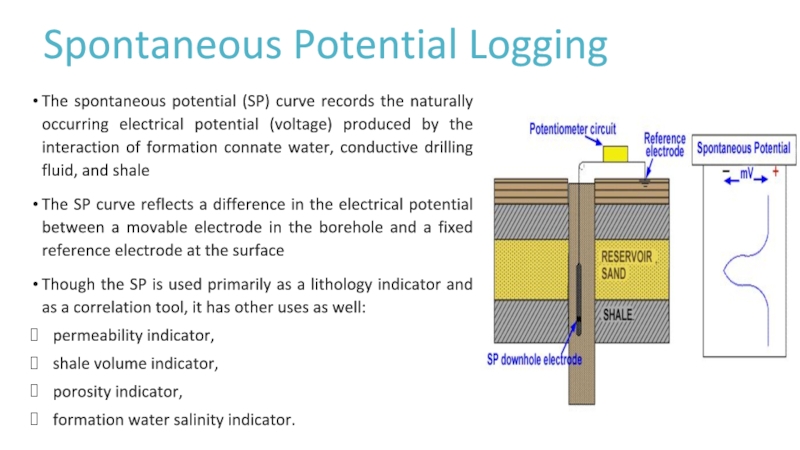
Слайд 11Spontaneous Potential Logging
The spontaneous potential (SP) curve records the naturally
occurring electrical potential (voltage) produced by the interaction of formation
connate water, conductive drilling fluid, and shaleThe SP curve reflects a difference in the electrical potential between a movable electrode in the borehole and a fixed reference electrode at the surface
Though the SP is used primarily as a lithology indicator and as a correlation tool, it has other uses as well:
permeability indicator,
shale volume indicator,
porosity indicator,
formation water salinity indicator.
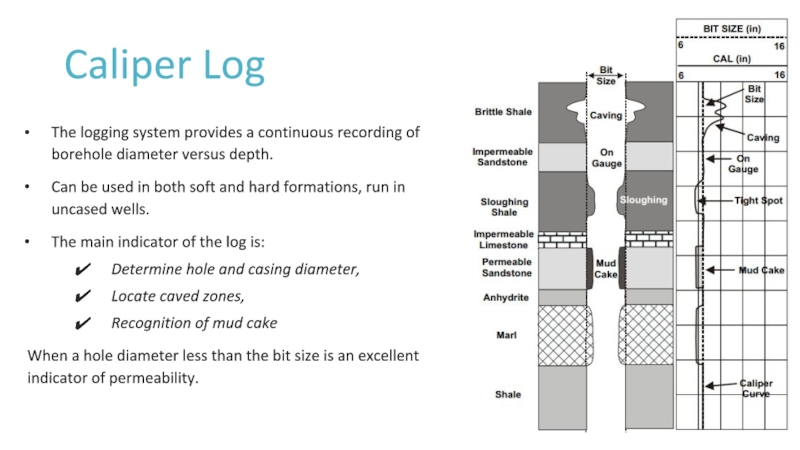
Слайд 12Caliper Log
The logging system provides a continuous recording of borehole
diameter versus depth.
Can be used in both soft and hard
formations, run in uncased wells.The main indicator of the log is:
Determine hole and casing diameter,
Locate caved zones,
Recognition of mud cake
When a hole diameter less than the bit size is an excellent indicator of permeability.
Слайд 14Density Logging
The formation density log is a porosity log that
measures electron density of a formation
Dense formations absorb many gamma
rays, while low-density formations absorb fewer. Thus, high-count rates at the detectors indicate low-density formations, whereas low count rates at the detectors indicate high-density formations.Therefore, scattered gamma rays reaching the detector is an indication of formation density.
A density derived porosity curve is sometimes present in tracks #2 and #3 along with the bulk density (rb) and correction (Dr) curves. Track #1 contains a gamma ray log and caliper.
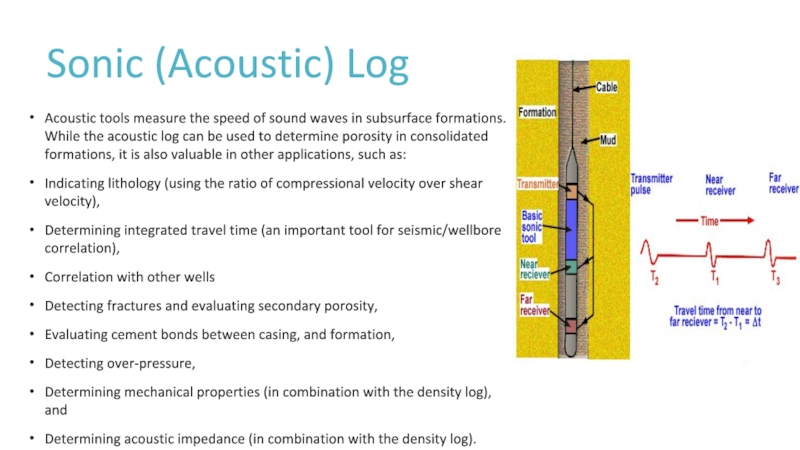
Слайд 15Sonic (Acoustic) Log
Acoustic tools measure the speed of sound waves
in subsurface formations. While the acoustic log can be used
to determine porosity in consolidated formations, it is also valuable in other applications, such as:Indicating lithology (using the ratio of compressional velocity over shear velocity),
Determining integrated travel time (an important tool for seismic/wellbore correlation),
Correlation with other wells
Detecting fractures and evaluating secondary porosity,
Evaluating cement bonds between casing, and formation,
Detecting over-pressure,
Determining mechanical properties (in combination with the density log), and
Determining acoustic impedance (in combination with the density log).
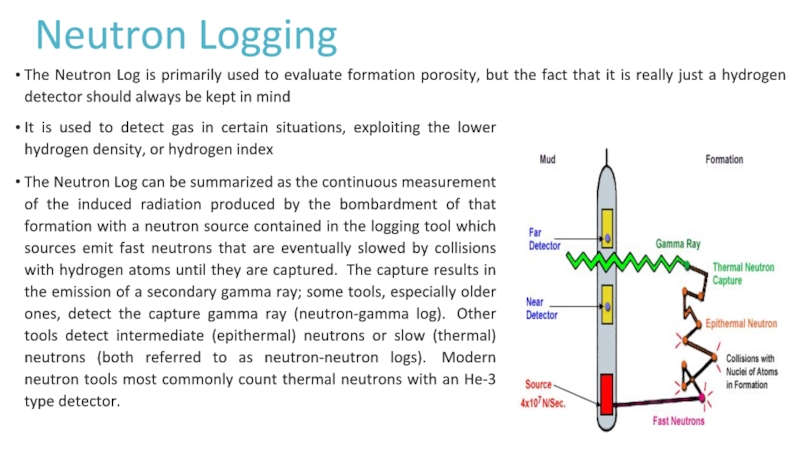
Слайд 16Neutron Logging
The Neutron Log is primarily used to evaluate formation
porosity, but the fact that it is really just a
hydrogen detector should always be kept in mindIt is used to detect gas in certain situations, exploiting the lower hydrogen density, or hydrogen index
The Neutron Log can be summarized as the continuous measurement of the induced radiation produced by the bombardment of that formation with a neutron source contained in the logging tool which sources emit fast neutrons that are eventually slowed by collisions with hydrogen atoms until they are captured. The capture results in the emission of a secondary gamma ray; some tools, especially older ones, detect the capture gamma ray (neutron-gamma log). Other tools detect intermediate (epithermal) neutrons or slow (thermal) neutrons (both referred to as neutron-neutron logs). Modern neutron tools most commonly count thermal neutrons with an He-3 type detector.
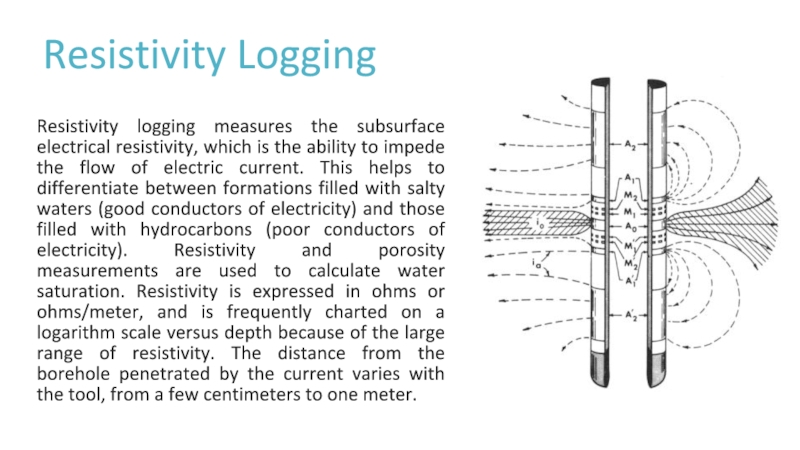
Слайд 18Resistivity Logging
Resistivity logging measures the subsurface electrical resistivity, which is
the ability to impede the flow of electric current. This
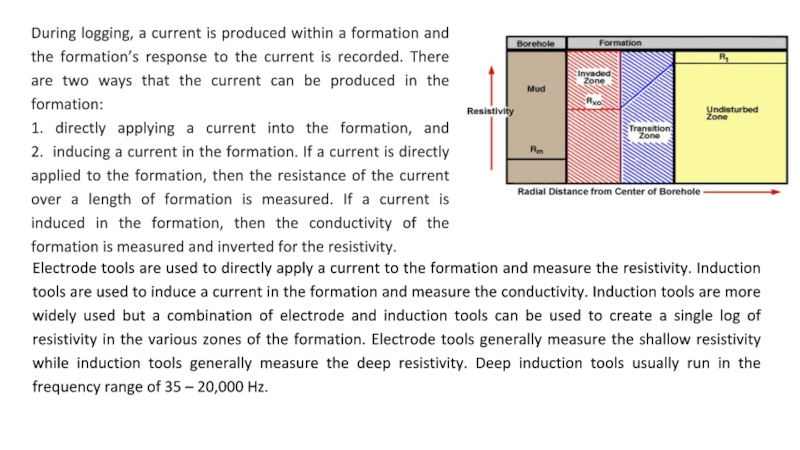
helps to differentiate between formations filled with salty waters (good conductors of electricity) and those filled with hydrocarbons (poor conductors of electricity). Resistivity and porosity measurements are used to calculate water saturation. Resistivity is expressed in ohms or ohms/meter, and is frequently charted on a logarithm scale versus depth because of the large range of resistivity. The distance from the borehole penetrated by the current varies with the tool, from a few centimeters to one meter.Слайд 19During logging, a current is produced within a formation and
the formation’s response to the current is recorded. There are
two ways that the current can be produced in the formation: 1. directly applying a current into the formation, and 2. inducing a current in the formation. If a current is directly applied to the formation, then the resistance of the current over a length of formation is measured. If a current is induced in the formation, then the conductivity of the formation is measured and inverted for the resistivity.Electrode tools are used to directly apply a current to the formation and measure the resistivity. Induction tools are used to induce a current in the formation and measure the conductivity. Induction tools are more widely used but a combination of electrode and induction tools can be used to create a single log of resistivity in the various zones of the formation. Electrode tools generally measure the shallow resistivity while induction tools generally measure the deep resistivity. Deep induction tools usually run in the frequency range of 35 – 20,000 Hz.
Слайд 21Caliper Logging Tool
Gamma Ray
Logging ToolVIKIZ (Induction Logging Tool) Acoustic Logging Tool