Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Phrasal verbs are a really important part of the English language, especially for spoken English
Содержание
- 1. Phrasal verbs are a really important part of the English language, especially for spoken English
- 2. Phrasal verbs are usually two-word phrases consisting
- 3. English phrasal verbs come in many shapes and sizes.
- 4. Sometimes we call them two part verbs,
- 5. Difficulties sometimes occur when deciding if a
- 6. Example: The sewer gave off a horrible smell.NOT: The sewer gave a horrible
- 7. Example: Turn it on.NOT: Turn on it.If the above
- 8. back away move backwards, in fear
- 9. beef up improve, make more substantial He beefed up his presentation
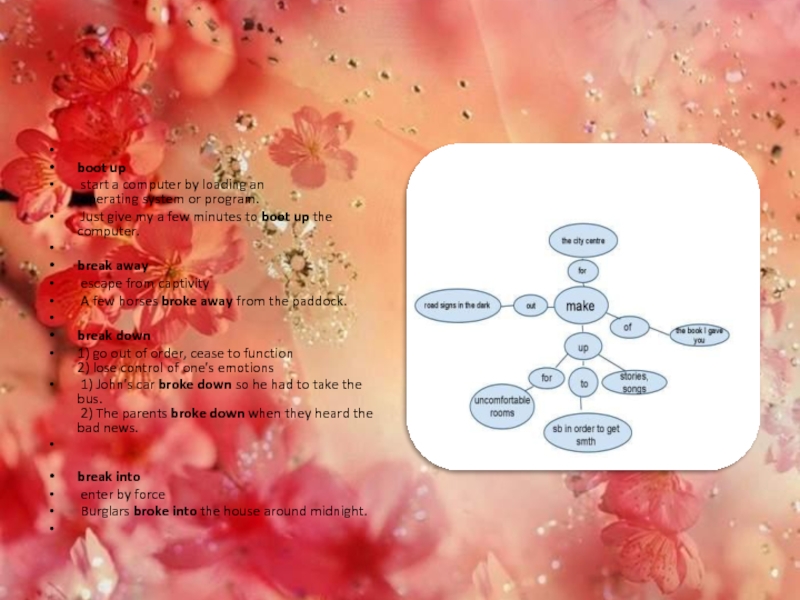
- 10. boot up start a computer by loading an
- 11. call on/upon sby formally invite or request I now call upon the
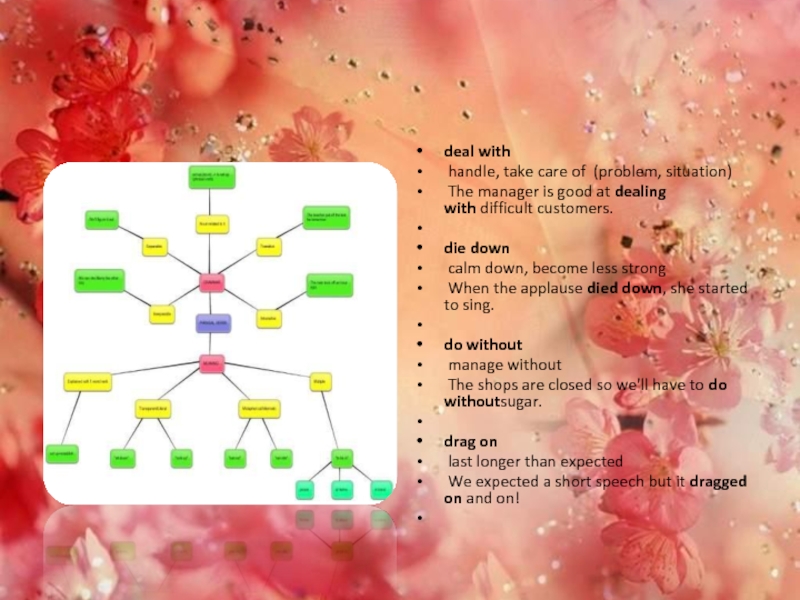
- 12. deal with handle, take care of (problem, situation) The
- 13. ease off reduce, become less severe or slow
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. Презентацию Подготовила ученица 7 «А» МБОУСОШ№11Алиева Амина
- 16. Скачать презентанцию
Phrasal verbs are usually two-word phrases consisting of verb + adverb or verb + preposition. Think of them as you would any other English vocabulary. Study them as you come across them, rather than
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Phrasal verbs are a really important part of the English
language, especially for spoken English.
section you can find hundreds of the most commonly used phrasal verbs clearly explained with example sentences and fun quiz questions to test your understanding.Слайд 2Phrasal verbs are usually two-word phrases consisting of verb + adverb or verb
+ preposition. Think of them as you would any other
English vocabulary. Study them as you come across them, rather than trying to memorize many at once. Use the list below as a reference guide when you find an expression that you don't recognize. The examples will help you understand the meanings. If you think of each phrasal verb as a separate verb with a specific meaning, you will be able to remember it more easily. Like many other verbs, phrasal verbs often have more than one meaningСлайд 3English phrasal verbs come in many shapes and sizes. Typically, they're a verb
and preposition combination which, when combined, changes the meaning of
the main verb into something else. Most students of English find them difficult because sometimes the idiomatic uses either make no sense at all, or the meaning change is so drastic that even a good guesser has no idea what they mean.Слайд 4Sometimes we call them two part verbs, three part verbs,
or multi-word verbs.
Whatever you call them, you should know some
basic truths regarding phrasal verb usage.
First of all, they are often used in a literal sense. That is, the combination of the verb with the preposition leads to a logical understanding. There are times when the meaning is far removed from the original verb and takes on a completely idiomatic usage.
Слайд 5Difficulties sometimes occur when deciding if a verb can be
'separated' from the preposition that forms the phrasal verb. The
following examples illustrate the problem.Example: Turn off the TV.
Example: Turn the TV off.
As seen above, some phrasal verbs can be separated with the object of the verb coming between the main verb and the preposition. It's important to know and remember, however, that some phrasal verbs can NOT be separated, and the verb and preposition must remain together.
Слайд 6
Example: The sewer gave off a horrible smell.
NOT: The sewer gave a horrible smell off.
Some verbs require
that the object comes before the adverb.
Example: They allowed the boy through.
NOT: They allowed through the boy.
When dealing with
transitive verbs and the object is a pronoun, then the pronoun comes before the adverb.
Слайд 7
Example: Turn it on.
NOT: Turn on it.
If the above seems to be
a little too much to take in at one time,
then I suggest coming back and doing a page or two at a time. My intentions are to include exercises along with some timely theory lessons to help you solidify your knowledge of phrasal verbs. For more information regarding prepositions and phrasal verbs, click on the preceding link.Слайд 8 back away
move backwards, in fear or dislike
When he
saw the dog, he backed away.
back down
withdraw, concede defeat
Local authorities backed down on
their plans to demolish the building.back up
1) give support or encouragement 2) make a copy of (file, program, etc.)
1) If I tell the boss we've got too much work, will youback me up? 2) It is recommended to back up all files in a secure location.
bank on
base your hopes on someone/something
Don't forget the date. I'm banking on your help.
Слайд 9beef up
improve, make more substantial
He beefed up his presentation with diagrams and
statistics.
black out
faint, lose consciousness
When he fell off the horse he blacked
out.block off
Separate using a barrier.
The area was blocked off during the demonstration.
blow up
1) explode; 2) be destroyed by an explosion
1) The terrorists said the bomb would blow up at 9 o'clock. 2) The car blew up but luckily there was nobody in it.
boil down to
be summarized as
The problem boils down to a lack of money.
Слайд 10
boot up
start a computer by loading an
operating system or program.
Just
give my a few minutes to boot up the computer.
break away
escape from
captivityA few horses broke away from the paddock.
break down
1) go out of order, cease to function 2) lose control of one's emotions
1) John's car broke down so he had to take the bus. 2) The parents broke down when they heard the bad news.
break into
enter by force
Burglars broke into the house around midnight.
Слайд 11call on/upon sby
formally invite or request
I now call upon the President to address
the assembly.
calm down
become more relaxed, less angry or upset
He was
angry at first but he eventually calmed down.carry on
continue
He carried on gardening in spite of the rain.
carry out
1) do something as specified (a plan, an order, a threat) 2) perform or conduct (test, experiment)
1) The plan was carried out to perfection. 2) Tests are carried out to determine the efficiency of a new drug.
carry over
postpone until later
As regards holidays, can you carry over any days from one year to the next?
Слайд 12deal with
handle, take care of (problem, situation)
The manager is good
at dealing with difficult customers.
die down
calm down, become less strong
When the applause died
down, she started to sing.do without
manage without
The shops are closed so we'll have to do withoutsugar.
drag on
last longer than expected
We expected a short speech but it dragged on and on!
Слайд 13ease off
reduce, become less severe or slow down
(pain, traffic, work)
After
Christmas the workload generally eases off.
end in
finish in a certain way;
result inTheir marriage ended in divorce.
end up
finally reach a state, place or action
If he continues his misconduct he'll end up in prison.
even out
1) eliminate differences of opinion. 2) become level or regular
1) After a long discussion they managed to even outtheir differences. 2) The road was evened out to make it safer.