Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Сын есім та?ырыбында?ы ашы? саба?
Содержание
- 1. Сын есім та?ырыбында?ы ашы? саба?
- 2. Adverb Clauses PretestAdverb Clauses modify _______, _______, and ________.
- 3. Adverb Clauses PretestAdverb Clauses modify _______, _______, and ________.Adverb Clauses are introduced by _________ ________.
- 4. Adverb Clauses PretestAdverb Clauses modify _______, _______,
- 5. Adverb Clauses PretestAdverb Clauses modify _______, _______,
- 6. Adverb Clauses PretestAdverb Clauses modify _______, _______,
- 7. Adverb Clauses Pretest5. The words than and
- 8. Adverb Clauses PretestAdverb Clauses modify _verbs_, _adjectives___, and _other adverbs___.
- 9. Adverb Clauses Pretest2. Adverb Clauses are introduced by __subordinating__ _conjunctions_.
- 10. Adverb Clauses Pretest3. T/F : The words
- 11. Adverb Clauses Pretest4. A comma always
- 12. Adverb Clauses Pretest5. The words than and
- 13. Adverb Clauses Pretest6. Adverb Clauses that have
- 14. How did you do?Let’s learn more about adverb clauses.
- 15. Let’s start by comparing independent and dependent
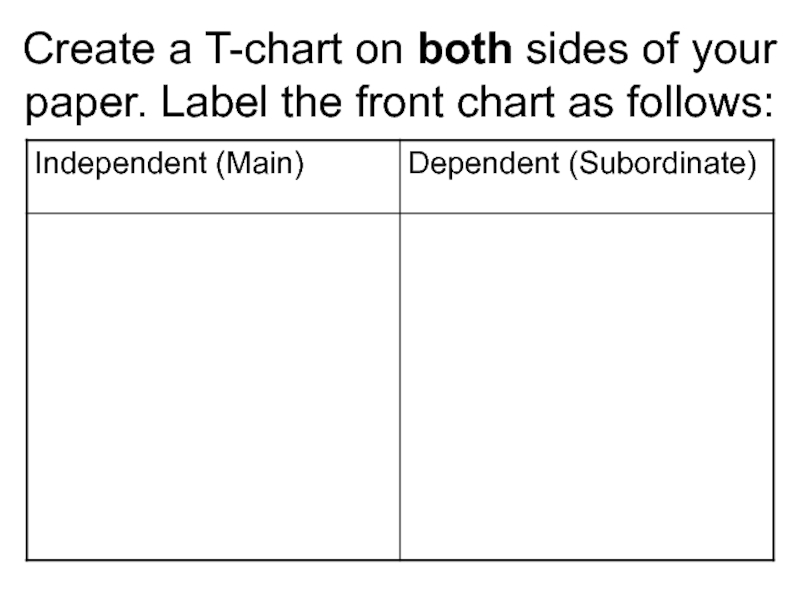
- 16. Create a T-chart on both sides of your paper. Label the front chart as follows:
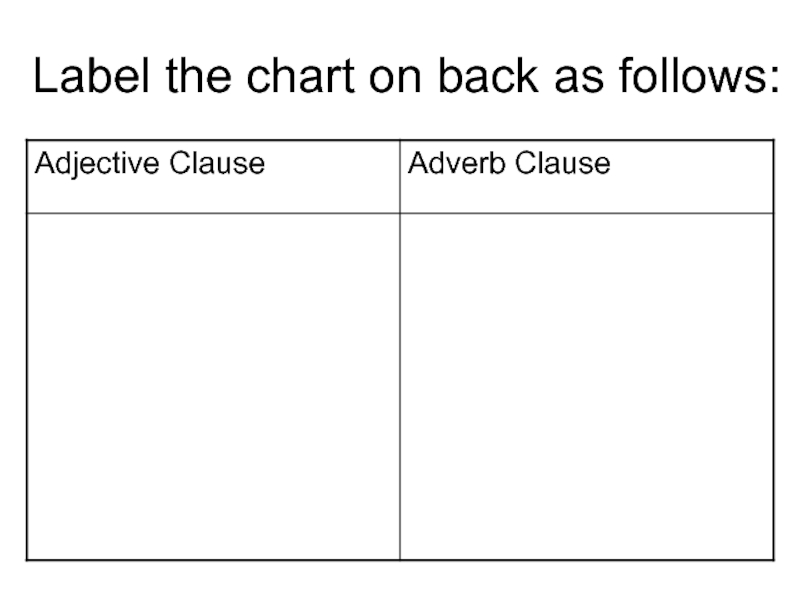
- 17. Label the chart on back as follows:
- 18. Take notes over the following comparisons between
- 19. Comparing ClausesIndependent (Main)Has a subjectDependent (Subordinate)Has a subject
- 20. Comparing ClausesIndependent (Main)Has a subjectHas a verbDependent (Subordinate)Has a subjectHas a verb
- 21. Comparing ClausesIndependent (Main)Has a subjectHas a verbExpresses
- 22. Comparing ClausesIndependent (Main)Has a subjectHas a verbExpresses
- 23. Comparing Dependent ClausesAdjective ClauseModifies noun or pronounAdverb ClauseModifies verb, adjective, or adverb
- 24. Comparing Dependent ClausesAdjective ClauseModifies noun or pronounAnswers
- 25. Comparing Dependent ClausesAdjective ClauseModifies noun or pronounAnswers
- 26. A complex sentence is made up of an independent clause and a dependent clause.
- 27. Example: The television was playing (independent clause
- 28. There are three kinds of dependent clauses: adjective clause adverb clause noun clause
- 29. Adverb ClauseAn adverb clause is a dependent
- 30. Adverb clauses are introduced by subordinate conjunctions
- 31. Example:They arrived before the game had ended.
- 32. Write the adverb clauses from the following
- 33. Answers 1. while I clean the carpet
- 34. Sometimes the adverb clause is placed at
- 35. Example:Before the game had ended, they arrived.
- 36. Write the adverb clauses in the following
- 37. Answers 1. When you came from the
- 38. Elliptical ClausesThan and as introduce clauses that
- 39. Example:“You are smarter than I.” (am smart.) They always modify the comparative word (smarter).
- 40. Complete the elliptical adverb clauses in the
- 41. Answers 1. My dog is older than
- 42. Write the adverb clauses in the following
- 43. Answers 1. Although I became tired modifies
- 44. Write the adverb clauses from the following
- 45. Answers 1. than Becky (can read music
- 46. Find the adverb clauses in the following
- 47. Answers 1. than I thought modifies the
- 48. Sentence Combining Adverb clauses can give variety
- 49. Combine the following sentences using adverb clauses
- 50. Answers Several different subordinate conjunctions can be
- 51. Combine the following sentences using adverb clauses
- 52. Answers Several different subordinate conjunctions can be
- 53. Reduced Adverb Clauses.Adverb clauses like adjective clauses
- 54. Reduce the adverb clauses in these sentences.
- 55. Answers1. While watching the geese, he saw
- 56. Rewrite the following reduced adverb clauses adding
- 57. Answers1. After they had heard the terrible
- 58. Write the adverb clauses in these sentences
- 59. Answers 1. as if I enjoy punishing
- 60. SELF QUIZ: Write the adverb clauses in
- 61. Quiz Answers 1. when you help other
- 62. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3Adverb Clauses Pretest
Adverb Clauses modify _______, _______, and ________.
Adverb Clauses
are introduced by _________ ________.
Слайд 4Adverb Clauses Pretest
Adverb Clauses modify _______, _______, and ________.
Adverb Clauses
are introduced by _________ ________.
T/F : The words and and
but are two examples of these signal words.Слайд 5Adverb Clauses Pretest
Adverb Clauses modify _______, _______, and ________.
Adverb Clauses
are introduced by _________ ________.
T/F : The words and and
but are two examples of these signal words.A comma always follows an Adverb Clause when it is placed at the ________ of the sentence.
Слайд 6Adverb Clauses Pretest
Adverb Clauses modify _______, _______, and ________.
Adverb Clauses
are introduced by _________ ________.
T/F : The words and and
but are two examples of these signal words.A comma always follows an Adverb Clause when it is placed at the ________ of the sentence.
The words than and as introduce a type of Adverb Clause called an ________ _______.
Слайд 7Adverb Clauses Pretest
5. The words than and as introduce a
type of Adverb Clause called an ________ _______.
6. Adverb Clauses
that have words left out in the middle are called _________ __________ _________. Слайд 10Adverb Clauses Pretest
3. T/F : The words and and but
are two examples of these signal words.
F
Слайд 11Adverb Clauses Pretest
4. A comma always follows an Adverb
Clause when it is placed at the __beginning__ of the
sentence.Слайд 12Adverb Clauses Pretest
5. The words than and as introduce a
type of Adverb Clause called an _ elliptical__ __clause__.
Слайд 13Adverb Clauses Pretest
6. Adverb Clauses that have words left out
in the middle are called _reduced___ ___adverb _
__clauses ___.Слайд 15
Let’s start by comparing independent and dependent clauses, then adjective
clauses and adverb clauses.
Use your T-Charts to take notes.
Слайд 18
Take notes over the following comparisons between Independent and Dependent
Clauses on the front T-Chart.
Take notes over the following comparisons
between Adjective and Adverb Clauses on the back T-Chart.The notes will be helpful as you study for the upcoming test over the Conventions Standard Elements.
Слайд 20Comparing Clauses
Independent (Main)
Has a subject
Has a verb
Dependent (Subordinate)
Has a subject
Has
a verb
Слайд 21Comparing Clauses
Independent (Main)
Has a subject
Has a verb
Expresses a complete thought
Dependent
(Subordinate)
Has a subject
Has a verb
Begins with a relative pronoun or
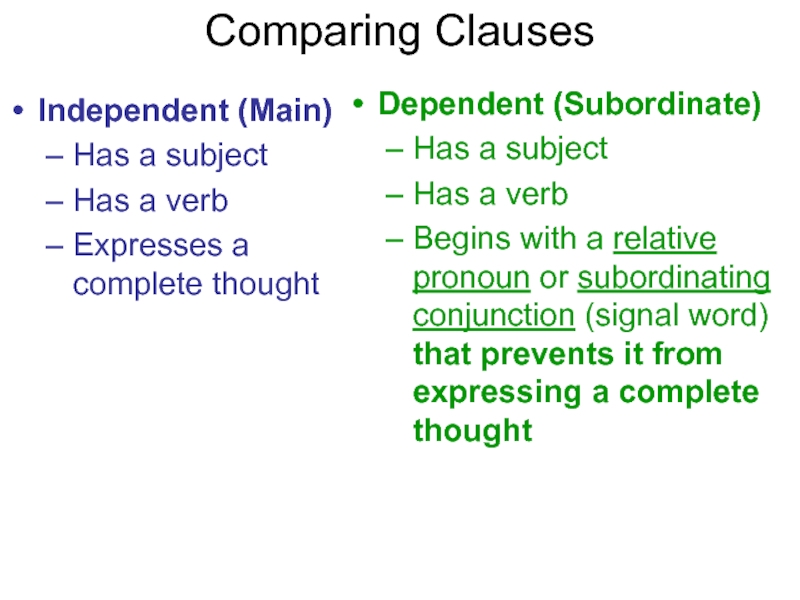
subordinating conjunction (signal word) that prevents it from expressing a complete thoughtСлайд 22Comparing Clauses
Independent (Main)
Has a subject
Has a verb
Expresses a complete thought
Can
be a sentence by itself
Dependent (Subordinate)
Has a subject
Has a verb
Begins
with a relative pronoun or subordinating conjunction (signal word) that prevents it from expressing a complete thoughtMust be attached to an Independent Clause to make a sentence
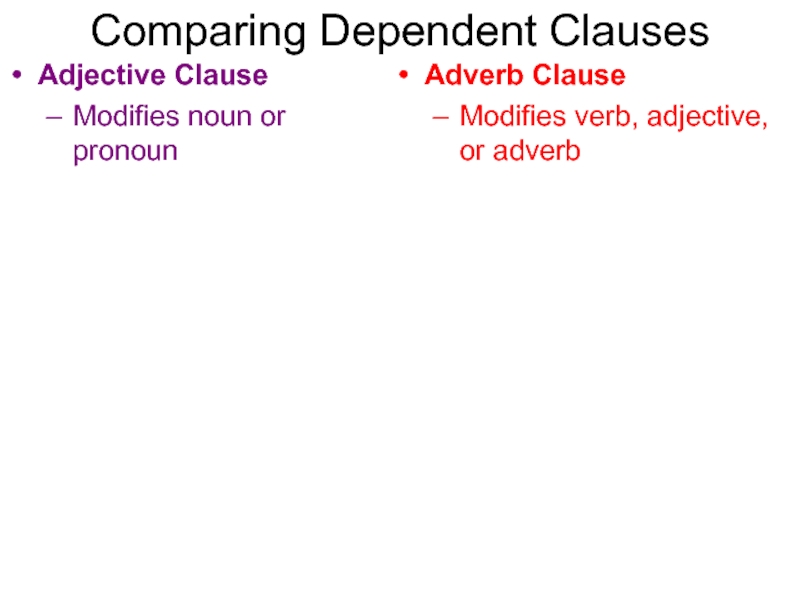
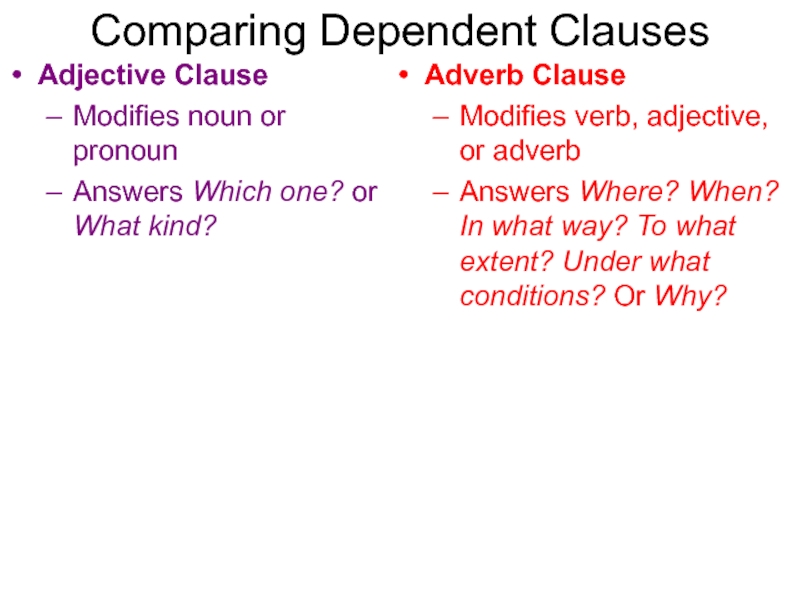
Слайд 23Comparing Dependent Clauses
Adjective Clause
Modifies noun or pronoun
Adverb Clause
Modifies verb, adjective,
or adverb
Слайд 24Comparing Dependent Clauses
Adjective Clause
Modifies noun or pronoun
Answers Which one? or
What kind?
Adverb Clause
Modifies verb, adjective, or adverb
Answers Where? When? In
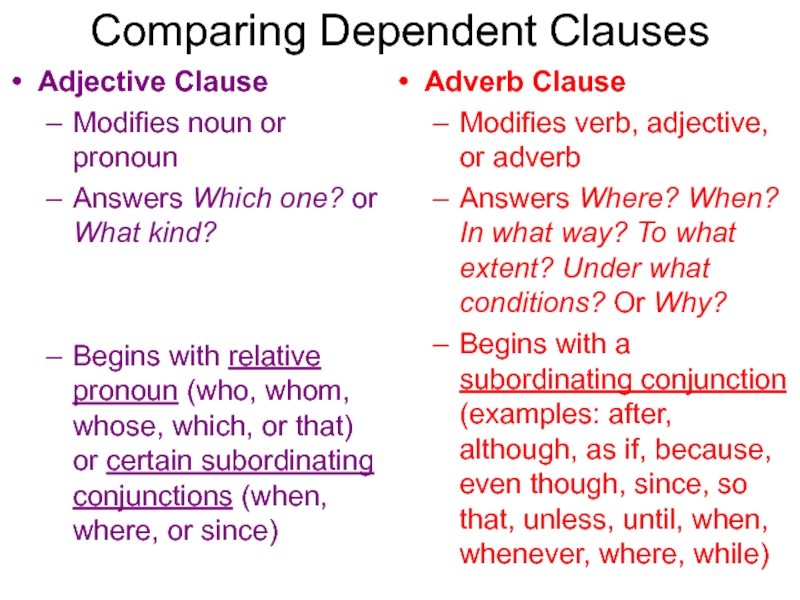
what way? To what extent? Under what conditions? Or Why?Слайд 25Comparing Dependent Clauses
Adjective Clause
Modifies noun or pronoun
Answers Which one? or
What kind?
Begins with relative pronoun (who, whom, whose, which, or
that) or certain subordinating conjunctions (when, where, or since)Adverb Clause
Modifies verb, adjective, or adverb
Answers Where? When? In what way? To what extent? Under what conditions? Or Why?
Begins with a subordinating conjunction (examples: after, although, as if, because, even though, since, so that, unless, until, when, whenever, where, while)
Слайд 27
Example:
The television was playing (independent clause which can stand
alone and make sense) as I left the room (dependent
clause which must be attached to the independent clause to make sense).Слайд 29Adverb Clause
An adverb clause is a dependent clause that modifies
a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It usually modifies the
verb.Слайд 30
Adverb clauses are introduced by subordinate conjunctions including after, although,
as, as if, before, because, if, since, so that, than,
though, unless, until, when, where, and while.These are just some of the more common ones.
Слайд 31Example:
They arrived before the game had ended.
"before the game
had ended" is the adverb clause modifying the verb arrived
telling when.Слайд 32Write the adverb clauses from the following sentences and the
word they modify.
1. You clean the bathroom while I clean
the carpet.2. Ann was confident that she would play the best.
3. Bring in the toys before they get destroyed.
4. I stood on the box so that I could see the top of the shelf.
5. Your face becomes red when you are angry.
Слайд 33Answers
1. while I clean the carpet modifies the verb clean
2.
that she would play the best modifies the predicate adjective
confident3. before they get destroyed modifies the verb bring
4. so that I could see the top of the shelf modifies the verb stood
5. when you are angry modifies the verb becomes
Слайд 34
Sometimes the adverb clause is placed at the beginning of
the sentence.
When it introduces the sentence, it is always
set off with a comma. Слайд 36Write the adverb clauses in the following sentences and the
word they modify.
1. When you came from the garage, did
you see the mower there?2. Because the field was muddy, the game had to be cancelled.
3. Although you should return to class, just wait here for me.
4. As I sat motionless, the two squirrels came closer and closer.
5. Since I can spare only a few minutes, please be brief with your presentation.
Слайд 37Answers
1. When you came from the garage modifies the verb
did see
2. Because the field was muddy modifies the verbal
to be cancelled3. Although you should return to class modifies the verb wait
4. As I sat motionless modifies the verb came
5. Since I can spare only a few minutes modifies the predicate adjective brief
Слайд 38Elliptical Clauses
Than and as introduce clauses that are called elliptical
clauses.
That is, they have some of their parts understood
but not stated. Слайд 39Example:
“You are smarter than I.” (am smart.)
They always modify
the comparative word (smarter).
Слайд 40Complete the elliptical adverb clauses in the following sentences and
write the words they modify.
1. My dog is older than
I.2. Jim can run faster than Jeff.
3. Pam spells more accurately than she keyboards.
4. He is trying harder than James.
5. Barbara is a better tennis player than Jeanne.
Слайд 41Answers
1. My dog is older than I am old. than
I am old modifies the predicate adjective older
2. Jim can
run faster than Jeff can run fast. than Jeff can run fast modifies the adverb faster3. Pam spells more accurately than she keyboards accurately. than she keyboards accurately modifies the adverb more accurately
4. He is trying harder than James is trying hard. as James is trying hard modifies the adverb harder
5. Barbara is a better tennis player than Jeanne is a tennis player. than Jeanne is a good tennis player modifies the adjective better
Слайд 42Write the adverb clauses in the following sentences and the
words they modify.
1. Although I became tired, I enjoyed the
hike.2. You cannot become an expert driver until you drive for several years.
3. Buy that coat now because it might be sold tomorrow.
4. I cannot reach the top window unless I have a ladder.
5. After you have eaten lunch, we will leave for New York.
Слайд 43Answers
1. Although I became tired modifies the verb enjoyed
2. until
you drive for several years modifies the verb can become
3.
because it might be sold tomorrow modifies the verb buy4. unless I have a ladder modifies the verb can reach
5. After you have eaten lunch modifies the verb will leave
Слайд 44Write the adverb clauses from the following sentences and the
words they modify.
1. Ila reads music better than Becky.
2. The
dog whined sadly as I walked into the house.3. If you have time, finish doing the dishes for me.
4. Many operations are unsuccessful because the patient is not careful afterwards.
5. Whenever I go out the door, the dog barks to go also.
Слайд 45Answers
1. than Becky (can read music well) modifies the adverb
better
2. as I walked into the house modifies the verb
whined3. If you have time modifies the verb finish
4. because the patient in not careful afterwards modifies the predicate adjective unsuccessful
5. Whenever I go out the door modifies the verb barks
Слайд 46Find the adverb clauses in the following sentences and the
words they modify.
1. I am hungrier than I thought.
2. We
left before the game was over.3. Lee is older than Bill.
4. While I waited for the phone call, I read a book.
5. If you don't believe me, ask my wife.
6. Are you upset because I didn't call?
7. The alarm rang while I was in the shower.
8. Open the window so that we can have fresh air.
9. Paul will take you home when you are ready.
10. You shouldn't say those things unless you are certain about their validity.
Слайд 47Answers
1. than I thought modifies the predicate adjective hungrier
2. before
the game was over modifies the verb left
3. than Bill
(is old) modifies the predicate adjective older4. While I waited for the phone call modifies the verb read
5. If you don't believe me modifies the verb ask
6. because I didn't call modifies the predicate adjective upset
7. while I was in the shower modifies the verb rang
8. so that we can have fresh air modifies the verb open
9. when you are ready modifies the verb will take
10. unless you are certain about their validity modifies the verb should say
Слайд 48Sentence Combining
Adverb clauses can give variety to your sentences.
The
resulting sentences will be either complex or compound-complex.
Слайд 49Combine the following sentences using adverb clauses at the end
of the sentence.
1. We watched the robins. They raised their
young in our apple tree.2. Becky read the book. It was recommended by a friend.
3. Dad donates his suits to charity. He has worn them a year.
4. The policemen delayed the drivers. The wrecks were cleared.
5. Ann ate an apple. She studied her vocabulary.
Слайд 50Answers
Several different subordinate conjunctions can be used to combine adverb
clauses with independent clauses. These answers show only one possibility.
1.
We watched the robins while they raised their young in our apple tree.2. Becky read the book since it was recommended by a friend.
3. Dad donates his suits to charity after he has worn them a year.
4. The policemen delayed the drivers until the wrecks were cleared.
5. Ann ate an apple as she studied her vocabulary.
Слайд 51Combine the following sentences using adverb clauses at the beginning
of the sentence.
1. Frank started medical training. He drove a
forklift for a living.2. The rains had started the mud slides. The homes were not safe to live in.
3. Older people love to sit in the park. They feed the birds and visit.
4. I enjoyed camping out. I was much younger.
5. Joe recognized the man. The man had stopped his car to help.
Слайд 52Answers
Several different subordinate conjunctions can be used to combine adverb
clauses with independent clauses, but I will only show one
possibility.1. Before Frank started medical training, he drove a forklift for a living.
2. Because the rains had started the mud slides, the homes were not safe to live in.
3. While they feed the birds and visit, older people love to sit in the park.
4. When I was much younger, I enjoyed camping out.
5. After the man had stopped his car to help, Joe recognized him.
Слайд 53Reduced Adverb Clauses.
Adverb clauses like adjective clauses can give variety
to your sentences.
Sometimes we find adverb clauses that have
left some words out. They are called reduced adverb clauses.
Example: While (she was) speaking to the timid student, the teacher spoke slowly.
Слайд 54Reduce the adverb clauses in these sentences.
1. While he was
watching the geese, he saw the fox.
2. Richard got a
thorn in his finger when he was pruning the roses.3. The cat meowed loudly after it searched for a way into the house.
4. Although the man feared being ostracized, he continued helping everyone.
5. Will measured the board again before he made his final cut.
Слайд 55Answers
1. While watching the geese, he saw the fox.
2. Richard
got a thorn in his finger when pruning the roses.
3.
The cat meowed loudly after searching for a way into the house.4. Although fearing being ostracized, the man continued helping everyone.
5. Will measured the board again before making his final cut.
Слайд 56Rewrite the following reduced adverb clauses adding the missing words.
1.
After hearing the terrible noise, they ran for their lives.
2.
The customer paid for his groceries when passing through the check out stand.3. Allen is only happy while participating in an argument.
4. Before leaving for the hike, the boy scouts were warned about snakes.
5. Until watering the lawn in the morning, he didn't see the dandelions in it.
Слайд 57Answers
1. After they had heard the terrible noise, they ran
for their lives.
2. The customer paid for his groceries when
he passed through the check out stand.3. Allen is only happy while he is participating in an argument.
4. Before they left for the hike, the boy scouts were warned about snakes.
5. Until he had watered the lawn in the morning, he didn't see the dandelions in it.
Слайд 58Write the adverb clauses in these sentences and tell what
word they modify. If it is a reduced adverb clause
or elliptical adverb clause add the missing words.1. You act as if I enjoy punishing you.
2. The contractor roughened the concrete while it was still wet.
3. My sister is smarter than I.
4. The manager talked with the workers after listening to their suggestions.
5. Before returning to work, he ate his lunch.
Слайд 59Answers
1. as if I enjoy punishing you modifies the verb
act
2. while it was still wet modifies the verb roughened
3.
than I (am smart) modifies the predicate adjective smarter4. after (he had listened) to their suggestions modifies the verb talked
5. Before (he returned) to work modifies the verb ate
Слайд 60SELF QUIZ: Write the adverb clauses in these sentences and
tell what word they modify. If it is a reduced
adverb clause or elliptical adverb clause add the missing words.1. You seem very happy when you help other people.
2. While you wait, we will detail your car.
3. That horse is more obstinate than a mule.
4. As the lions approached the carcass, the cheetahs retreated once more.
5. While eating, I choked on a bone.
Слайд 61Quiz Answers
1. when you help other people modifies the predicate
adjective happy
2. While you wait modifies the verb will detail
3.
than a mule (is obstinate) modifies the predicate adjective more obstinate4. As the lions approached the carcass modifies the verb retreated
5. While (I was) eating modifies the verb choked