Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Презентация3.ppt
Содержание
- 1. Презентация3.ppt
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. STP (Spanning Tree)802.1D
- 4. STP Overview STP is a Layer 2 link
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Для того чтобы определить какие порты заблокировать,
- 8. ROOT- только Root может генерировать BPDU Остальные
- 9. BRIDGE-IDКорневым становится коммутатор с наименьшим идентификатором моста
- 10. Когда новый свитч включается в топологию, он объявляет себя Root и начинает рассылать BPDU
- 11. Выборы Root:1. Все свитчи в топологии обмениваются
- 12. Root Bridge:все его порты будут переведены forwarding-designated состояние.
- 13. Состояния портов:Blocking — блокированиеListening — прослушиваниеLearning — обучениеForwarding — пересылка
- 14. Роли портов:Root Port — корневой порт коммутатора
- 15. COSTSpeed Cost 4 Мбит/с 25010 Мбит/с
- 16. Свитчи всегда передают cost до Root Bridge соседям, так как они его видят
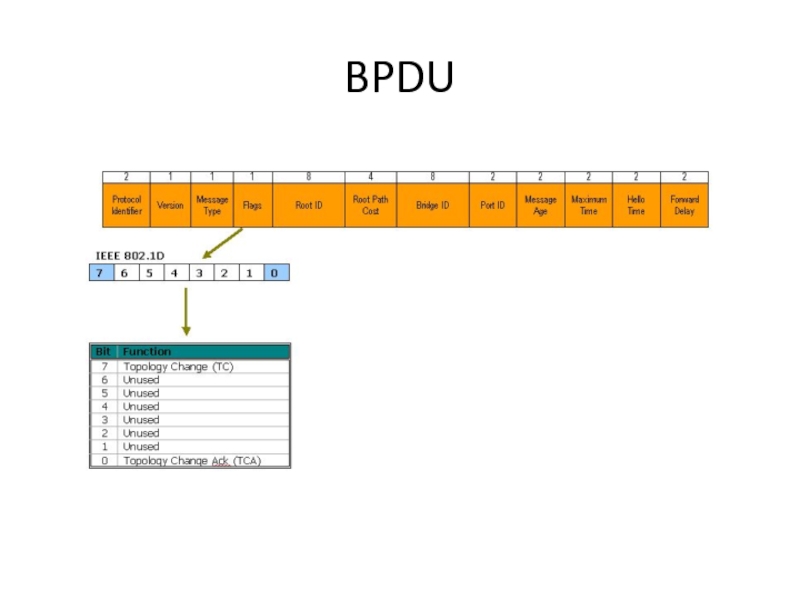
- 17. BPDU
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Spanning Tree Layer 2 Interface StatesWhen you
- 20. When the spanning tree algorithm places a
- 21. Blocking State A Layer 2 interface in
- 22. Listening StateA Layer 2 interface in the
- 23. Learning State A Layer 2 interface in
- 24. Forwarding State A Layer 2 interface in
- 25. Disabled State A disabled Layer 2 interface
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. DEFAULTS
- 28. Enabling STP By default, spanning tree is
- 29. Switch# show spanning-tree vlan 200 VLAN200
- 30. Configuring the Port Priority
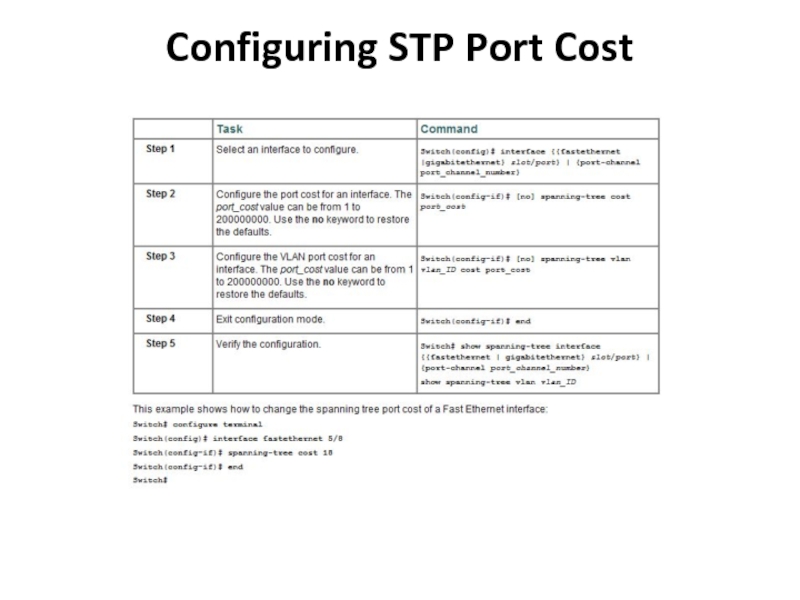
- 31. Configuring STP Port Cost
- 32. Switch(config)# [no] spanning-tree vlan vlan_ID priority bridge_priority Switch(config)# [no] spanning-tree vlan vlan_ID hello-time hello_time
- 33. STP features
- 34. PortFast Portfast — функция, которая позволяет порту пропустить
- 35. PortFast BPDU filteringПо умолчанию STP отсылает BPDU
- 36. Configuring PortFastСинтаксис команды для настройки Port Fast
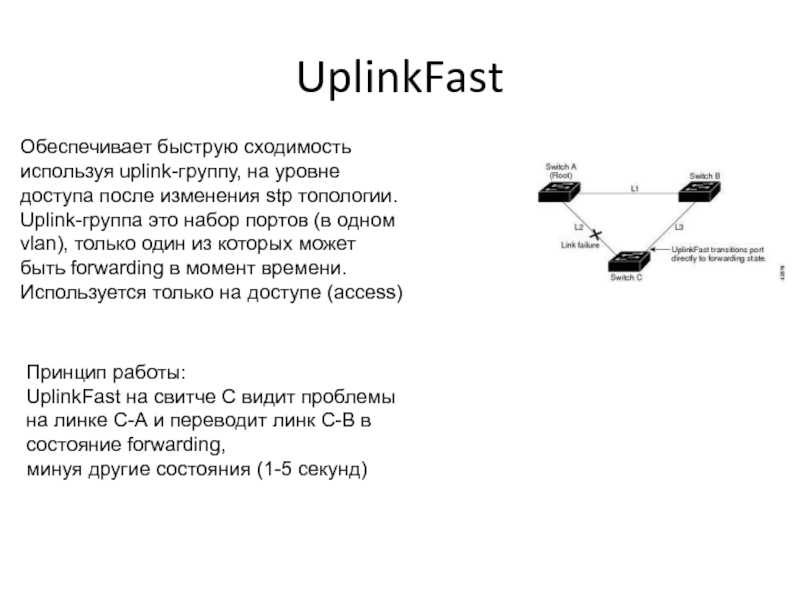
- 37. UplinkFastОбеспечивает быструю сходимость используя uplink-группу, на уровне
- 38. Как только свитч переключается на альтернативный линк,
- 39. BackboneFast Позволяет быстрее найти альтернативный путь, после
- 40. Loop Guard Одна из проблем с STP,
- 41. Loop Guard - обеспечивает дополнительную защиту на 2
- 42. conf t spanning-tree guard
- 43. show spanning-tree summary Router#show spanning-tree summary Switch
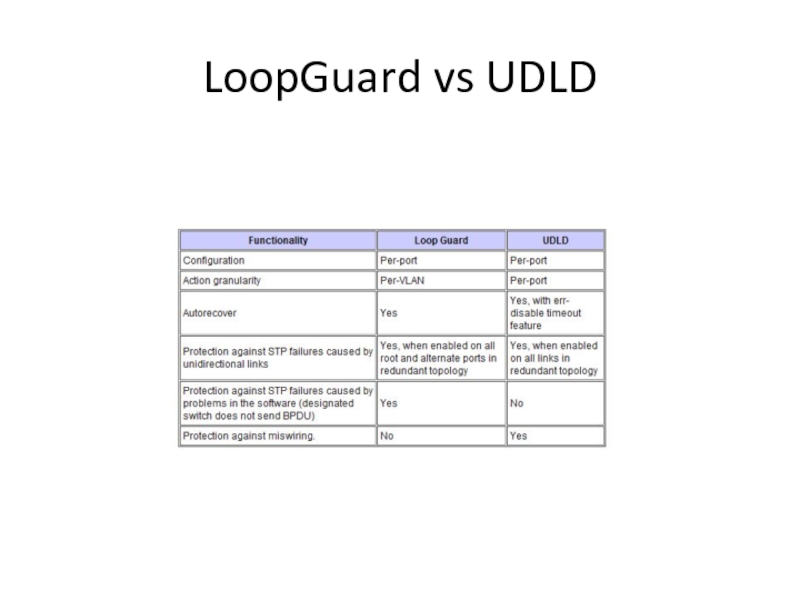
- 44. UDLDUDLD — использует сообщения канального уровня для того
- 45. LoopGuard vs UDLD
- 46. Скачать презентанцию
STP (Spanning Tree)802.1D
Слайды и текст этой презентации
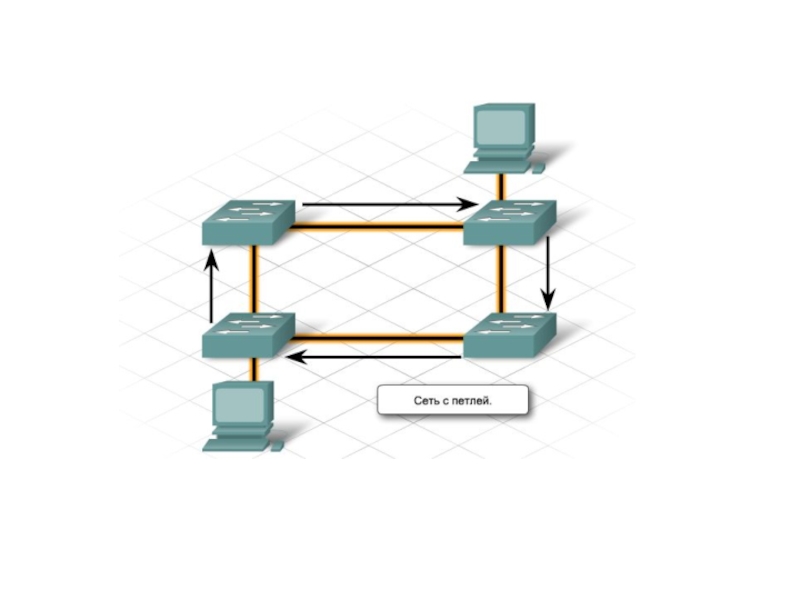
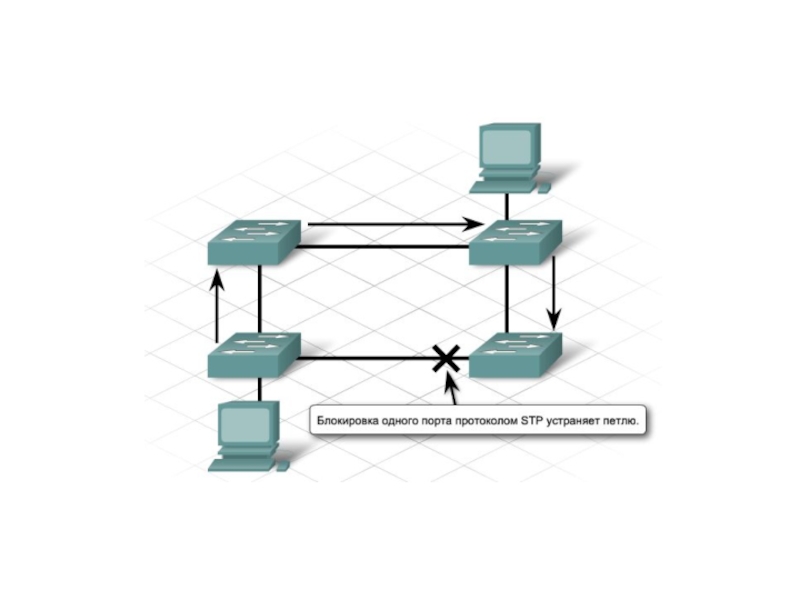
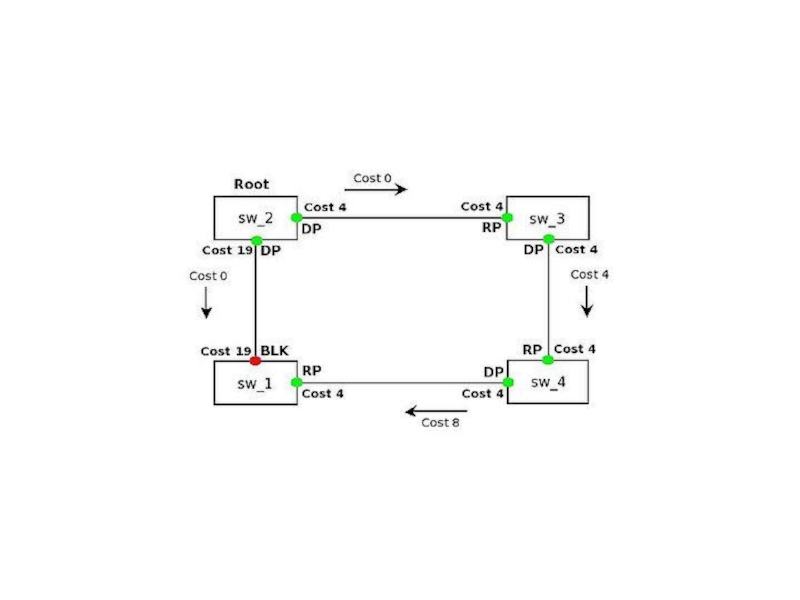
Слайд 7Для того чтобы определить какие порты заблокировать, а какие будут
forward, STP выполняет следующее:
Выбор корневого моста (Root Bridge)
Определение корневых портов
(Root Port)Определение выделенных портов (Designated Port)
Слайд 8ROOT
- только Root может генерировать BPDU Остальные свичи в топологии
могут только обмениваться ими. Если по каким-то причинам root перестает
отсылать BPDU (high cpu..), остальные будут молчать.- Root контролирует различные таймеры STP
- Root информирует L2-топологию об изменениях ("Topology Changed")
Слайд 9BRIDGE-ID
Корневым становится коммутатор с наименьшим идентификатором моста (Bridge ID).
Bridge-ID -
комбинация из Bridge priority и mac
default priority 32768 ( bridge
priority in increments of 4096)Bridge ID: 32768-00-11-22-33-44-55
Слайд 11Выборы Root:
1. Все свитчи в топологии обмениваются BPDU
2. Bridge Priority
сравнивается первой
3. Если находится свитч c наименьшей Priority, то процесс
выборов останавливается и он назначается Root4. Если все Priority одинаковы, то свитчи сравнивают свои mac-адреса. Т.к все они имеют уникальные mac-адреса, то один из них окажется численно наименьшим, и свитч с этим mac будет Root
Слайд 13Состояния портов:
Blocking — блокирование
Listening — прослушивание
Learning — обучение
Forwarding — пересылка
Слайд 14Роли портов:
Root Port — корневой порт коммутатора (порт, который имеет
наиболее быстрый путь к Root Bridge)
Designated Port — назначенный порт
сегмента (каждый коллизионный домен имеет один такой порт)Non-designated Port — неназначенный порт сегмента (Blocked)
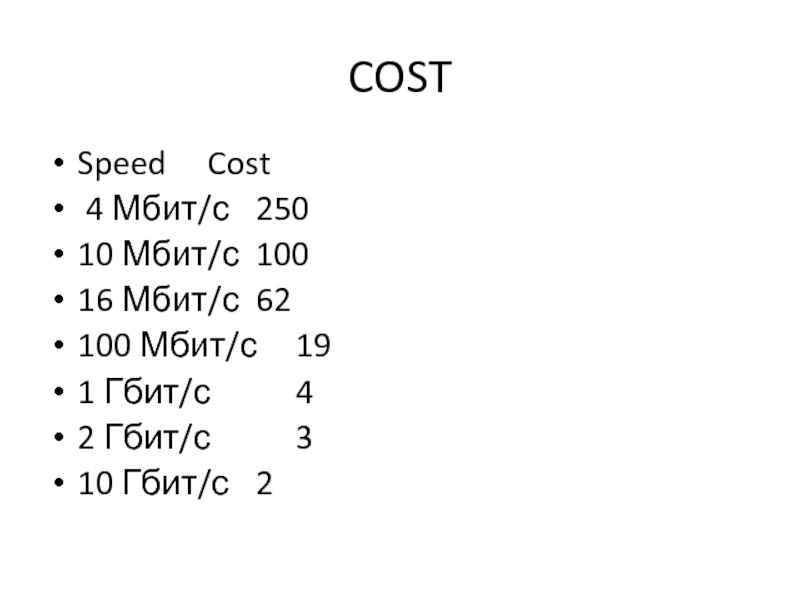
Слайд 15COST
Speed Cost
4 Мбит/с 250
10 Мбит/с 100
16 Мбит/с 62
100
Мбит/с 19
1 Гбит/с 4
2 Гбит/с 3
10 Гбит/с 2
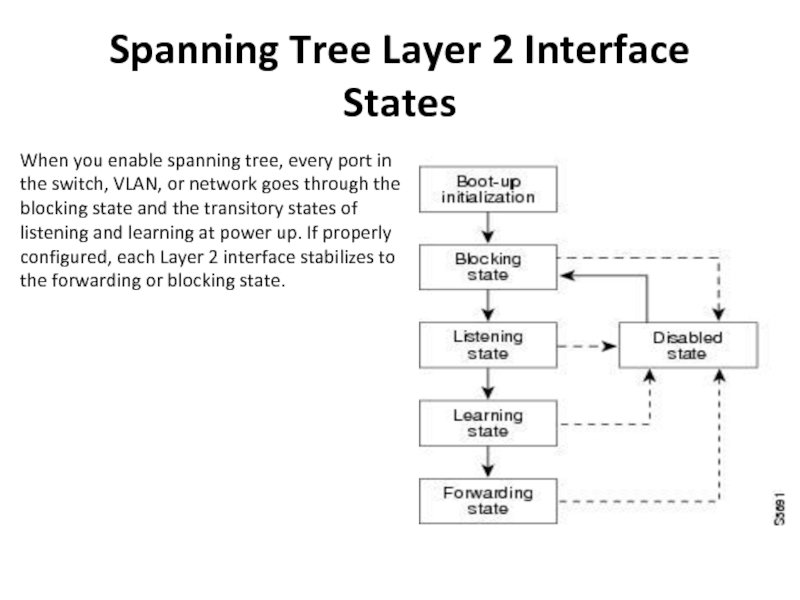
Слайд 19Spanning Tree Layer 2 Interface States
When you enable spanning tree,
every port in the switch, VLAN, or network goes through
the blocking state and the transitory states of listening and learning at power up. If properly configured, each Layer 2 interface stabilizes to the forwarding or blocking state.Слайд 20When the spanning tree algorithm places a Layer 2 interface
in the forwarding state, the following process occurs:
1. The Layer 2
interface is put into the listening state while it waits for protocol information that suggests it should go to the blocking state.2. The Layer 2 interface waits for the forward delay timer to expire, moves the Layer 2 interface to the learning state, and resets the forward delay timer.
3. In the learning state, the Layer 2 interface continues to block frame forwarding as it learns end station location information for the forwarding database.
4. The Layer 2 interface waits for the forward delay timer to expire and then moves the Layer 2 interface to the forwarding state, where both learning and frame forwarding are enabled.
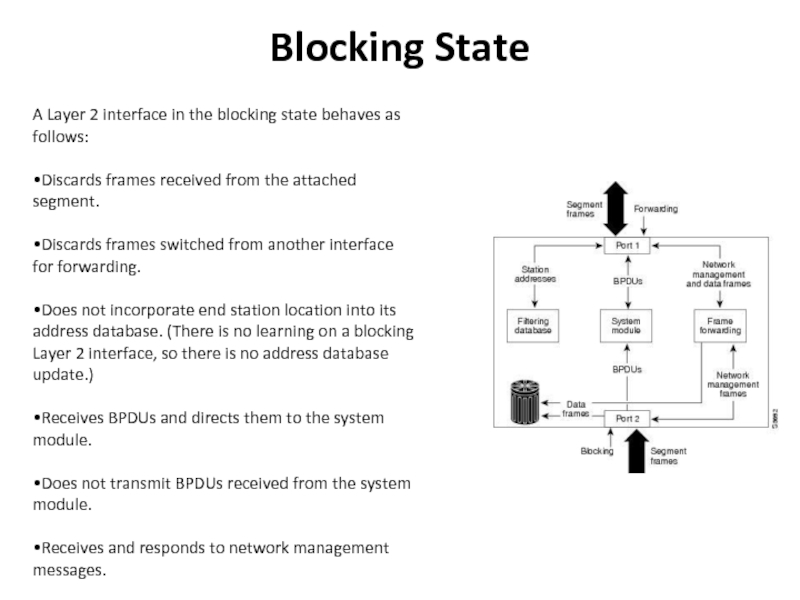
Слайд 21Blocking State
A Layer 2 interface in the blocking state behaves
as follows:
•Discards frames received from the attached segment.
•Discards frames switched
from another interface for forwarding.•Does not incorporate end station location into its address database. (There is no learning on a blocking Layer 2 interface, so there is no address database update.)
•Receives BPDUs and directs them to the system module.
•Does not transmit BPDUs received from the system module.
•Receives and responds to network management messages.
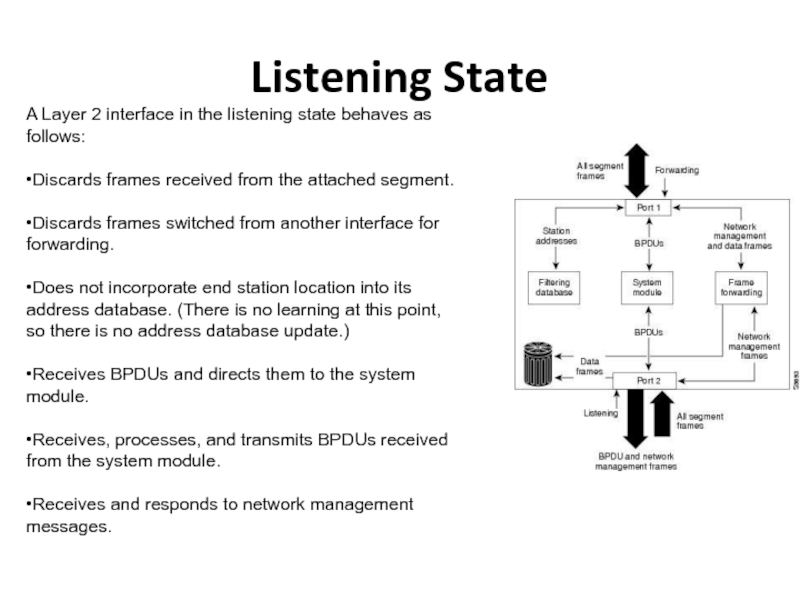
Слайд 22Listening State
A Layer 2 interface in the listening state behaves
as follows:
•Discards frames received from the attached segment.
•Discards frames switched
from another interface for forwarding.•Does not incorporate end station location into its address database. (There is no learning at this point, so there is no address database update.)
•Receives BPDUs and directs them to the system module.
•Receives, processes, and transmits BPDUs received from the system module.
•Receives and responds to network management messages.
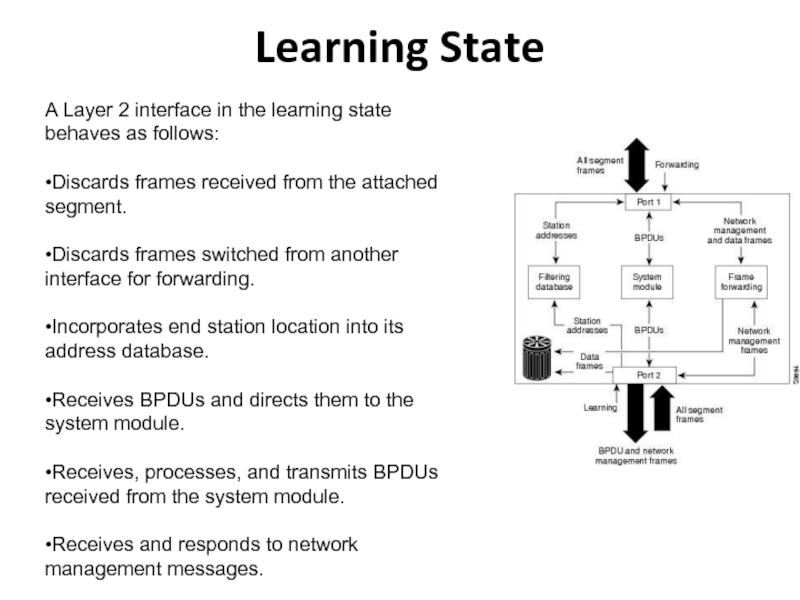
Слайд 23Learning State
A Layer 2 interface in the learning state behaves
as follows:
•Discards frames received from the attached segment.
•Discards frames switched
from another interface for forwarding.•Incorporates end station location into its address database.
•Receives BPDUs and directs them to the system module.
•Receives, processes, and transmits BPDUs received from the system module.
•Receives and responds to network management messages.
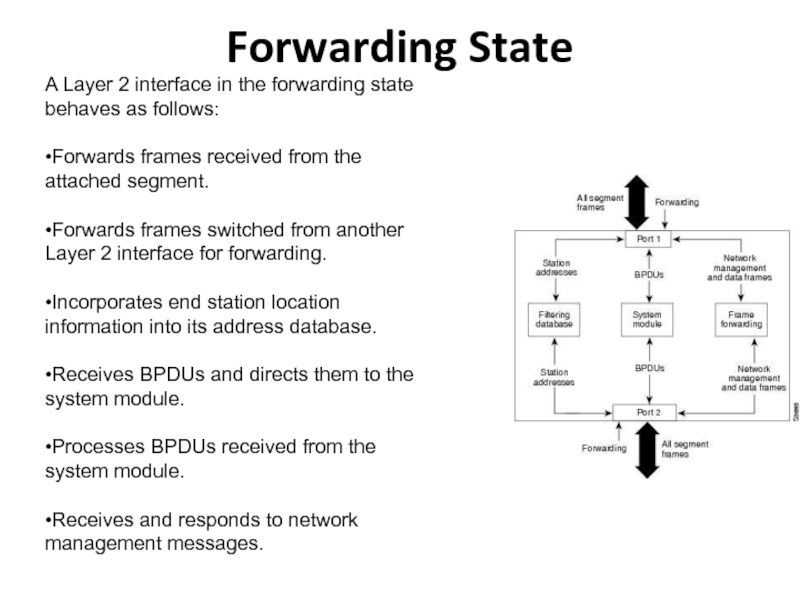
Слайд 24Forwarding State
A Layer 2 interface in the forwarding state behaves
as follows:
•Forwards frames received from the attached segment.
•Forwards frames switched
from another Layer 2 interface for forwarding.•Incorporates end station location information into its address database.
•Receives BPDUs and directs them to the system module.
•Processes BPDUs received from the system module.
•Receives and responds to network management messages.
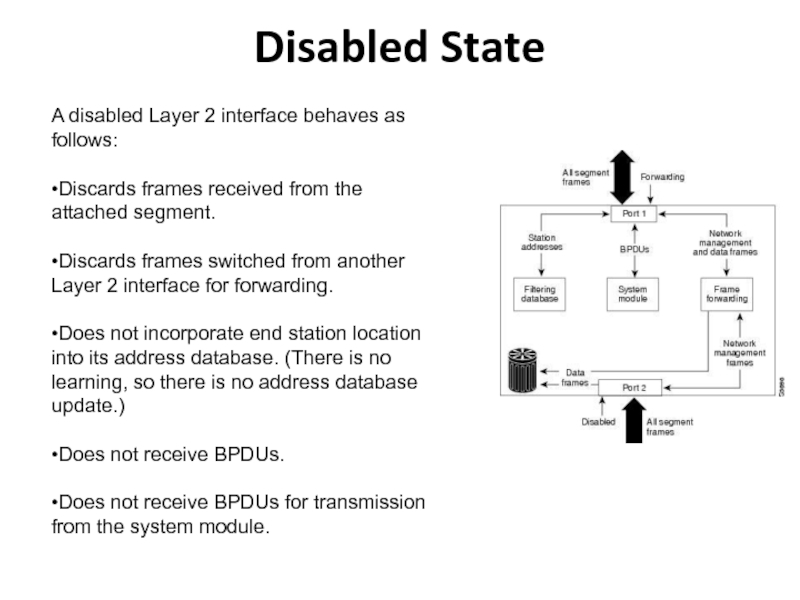
Слайд 25Disabled State
A disabled Layer 2 interface behaves as follows:
•Discards frames
received from the attached segment.
•Discards frames switched from another Layer
2 interface for forwarding.•Does not incorporate end station location into its address database. (There is no learning, so there is no address database update.)
•Does not receive BPDUs.
•Does not receive BPDUs for transmission from the system module.
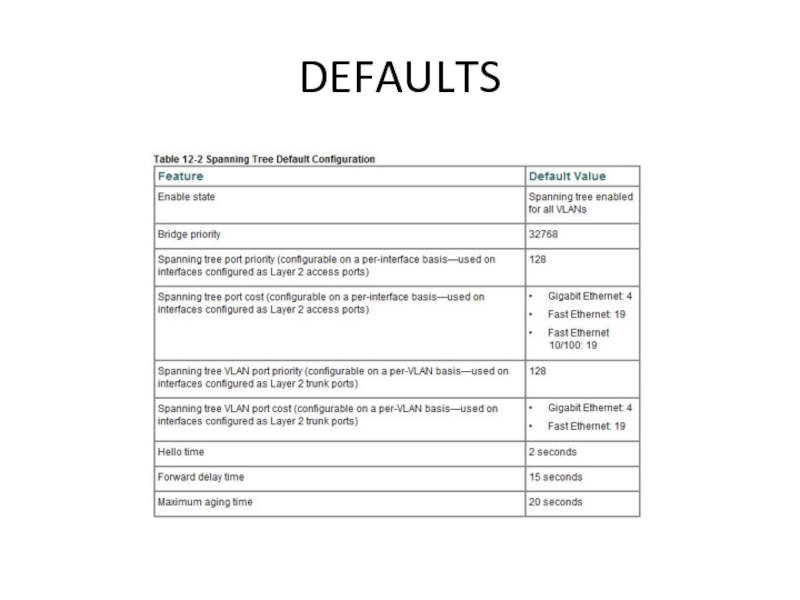
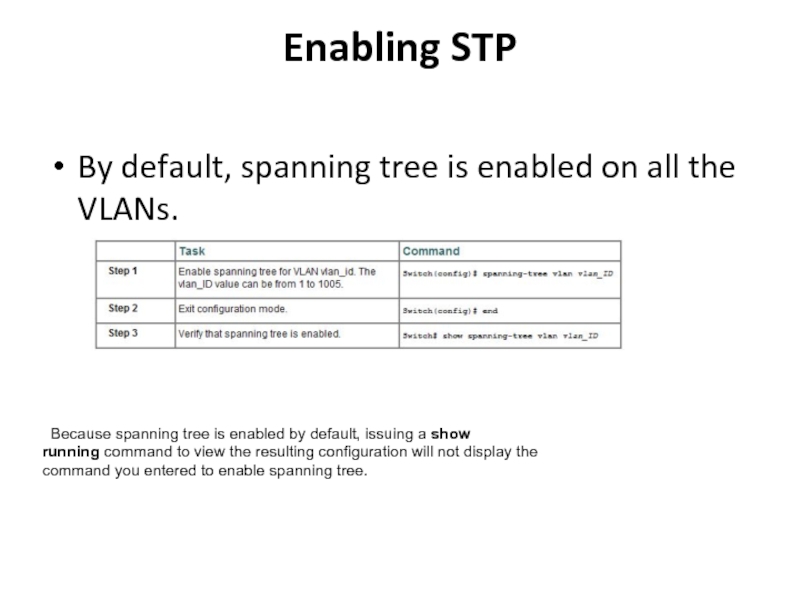
Слайд 28Enabling STP
By default, spanning tree is enabled on all the
VLANs.
Because spanning tree is enabled by default, issuing
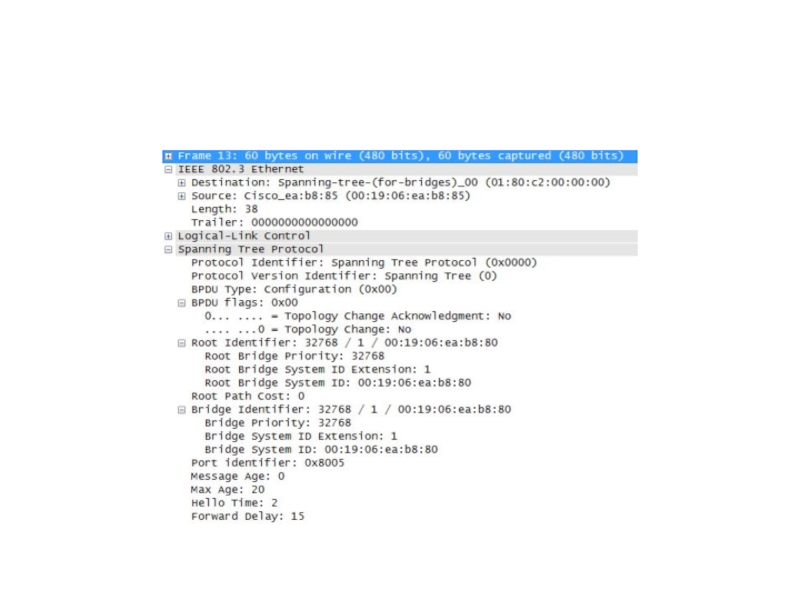
a show running command to view the resulting configuration will not display the command you entered to enable spanning tree. Слайд 29Switch# show spanning-tree vlan 200
VLAN200 is executing the ieee
compatible Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, address
0050.3e8d.6401 Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Current root has priority 16384, address 0060.704c.7000
Root port is 264 (FastEthernet5/8), cost of root path is 38
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 01:53:48 ago
Times: hold 1, topology change 24, notification 2
hello 2, max age 14, forward delay 10
Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0
Port 264 (FastEthernet5/8) of VLAN200 is forwarding
Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 129.9.
Designated root has priority 16384, address 0060.704c.7000
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 00e0.4fac.b000
Designated port id is 128.2, designated path cost 19
Timers: message age 3, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
BPDU: sent 3, received 3417
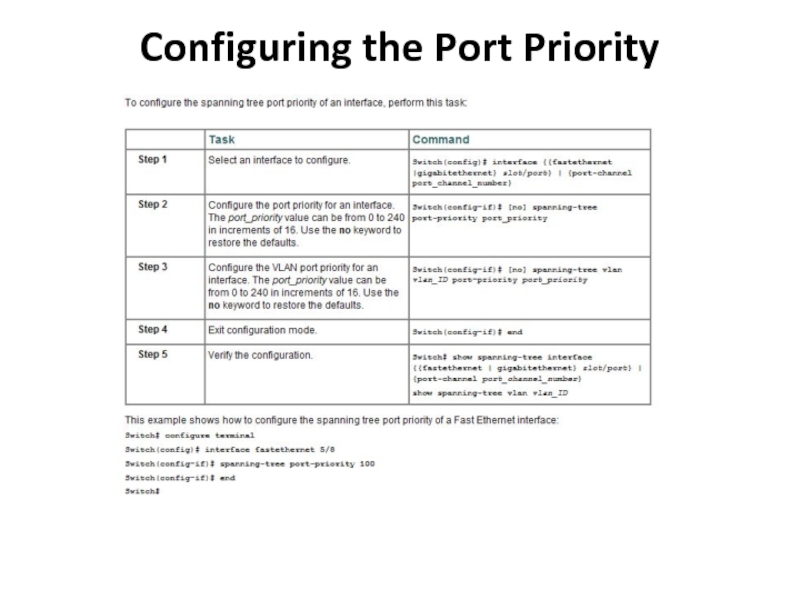
Слайд 32Switch(config)# [no] spanning-tree vlan vlan_ID priority bridge_priority
Switch(config)# [no] spanning-tree
vlan vlan_ID hello-time hello_time
Слайд 34PortFast
Portfast — функция, которая позволяет порту пропустить состояния listening и learning
и сразу же перейти в состояние forwarding. Настраивается на портах
уровня доступа, к которым подключены пользователи или сервера.Цель функции PortFast минимизировать время, которое необходимо для того чтобы порт перешел в состояние forward. Поэтому она эффективна только когда применена к портам, к которым подключены хосты. Если включить PortFast на портах, которые соединены с другими коммутаторами, то есть риск создания петли. Включение этой функции, так же препятствует возникновению сообщений о изменении состояния порта TCN BPDU (topology change notification Bridge Protocol Data Unit)
Слайд 35PortFast BPDU filtering
По умолчанию STP отсылает BPDU со всех портов
в независимости включен ли portfast или нет.
Filtering позволяет избежать передачи
BPDU на порты с включенным portfast режимом.Применяется на все portfast порты, включается глобально.
Слайд 36Configuring PortFast
Синтаксис команды для настройки Port Fast на интерфейсе:
sw(config-if)# spanning-tree
portfast [disable | trunk]
Настройка Port Fast на access-интерфейсе:
sw(config)#interface fa0/1
sw(config-if)# spanning-tree portfastНастройка Port Fast на интерфейсе, который работает в режиме trunk (тегированый порт):
sw(config)#interface fa0/1 sw(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast trunk
Если на интерфейсе, который работает в режиме транка выполнить команду без параметра trunk, то функция Port Fast не будет применена.
Функцию Port Fast можно настроить глобально на всех интерфейсах в режиме access:
sw(config)#spanning-tree portfast default
Отключить Port Fast на интерфейсе:
sw(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast disable
Слайд 37UplinkFast
Обеспечивает быструю сходимость используя uplink-группу, на уровне доступа после изменения
stp топологии.
Uplink-группа это набор портов (в одном vlan), только один
из которых может быть forwarding в момент времени.Используется только на доступе (access)
Принцип работы:
UplinkFast на свитче C видит проблемы на линке С-А и переводит линк С-В в состояние forwarding,
минуя другие состояния (1-5 секунд)
Слайд 38Как только свитч переключается на альтернативный линк, он начинает отправлять
пакет в mcast группу, один для каждой записи из EARL-таблицы.
EARL-таблица.
EARL-asic создает и обновляет таблицу соответствия mac-port в CAMСвитчи апдейтят EARL-таблицу и это позволяет использовать новый путь почти мгновенно.
Когда коннект с root-портом восстанавливается, свитч ждет период равный 2 задеркам пересылки + 5 секунд до того
как перевести этот линк в forwarding
Слайд 39BackboneFast
Позволяет быстрее найти альтернативный путь, после изменения топологии. Для того
чтобы функция работала, необходимо включить её на всех коммутаторах в
сети.Настройка BackboneFast:
sw(config)# spanning-tree backbonefast
Слайд 40Loop Guard
Одна из проблем с STP, это то что само
оборудование которое его использует может быть причиной сбоя и быть
причиной создание петли. Для предотвращения подобных сбоев и был создана команда Loop GuardСлайд 41Loop Guard - обеспечивает дополнительную защиту на 2 уровне от возникновения
петель. STP петля возникает когда блокированный порт в избыточной топологии
ошибочно переводится в состояние forwarding(передачи). Это может возникнуть например когда блокированный STP порт перестаёт получать BPDU. Так как работа протокола STP полагается на постоянное присутствие BPDU пакетов в сети.(Designated (назначенный) порт постоянно должен передавать BPDU пакеты а non-designated должен их получать). Как только на порт перестают поступать BPDU STP понимает это как изменение топологии и исчезновение петли и переводит порт в состояние forwarding. В случае использования Loop Guard порт после прекращения получения пакетов BPDU переводится в состояние loop-inconsistent и остаются по прежнему блокированным. А в логах появится следующее сообщение:• %SPANTREE-2-LOOPGUARD_BLOCK: Loop guard blocking port FastEthernet0/15 on VLAN0037.
Слайд 42 conf t
spanning-tree guard loop Router(config)#interface gigabitEthernet
1/1 Router(config-if)#spanning-tree guard loop
Чтобы включить Loop guard глобально:
Router(config)#spanning-tree loopguard default
Слайд 43show spanning-tree summary
Router#show spanning-tree summary
Switch is in pvst
mode
Root bridge for: none
EtherChannel misconfig guard is enabled
Extended system ID is disabledPortfast Default is disabled
PortFast BPDU Guard Default is disabled
Portfast BPDU Filter Default is disabled
Loopguard Default is enabled
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Pathcost method used is short












![Презентация3.ppt Switch(config)# [no] spanning-tree vlan vlan_ID priority bridge_priority Switch(config)# [no] spanning-tree vlan vlan_ID hello-time hello_time Switch(config)# [no] spanning-tree vlan vlan_ID priority bridge_priority Switch(config)# [no] spanning-tree vlan vlan_ID hello-time hello_time](/img/thumbs/7b8b08b5d91e6a525aa40601a0ecbf7e-800x.jpg)



![Презентация3.ppt Configuring PortFastСинтаксис команды для настройки Port Fast на интерфейсе:sw(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast Configuring PortFastСинтаксис команды для настройки Port Fast на интерфейсе:sw(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast [disable | trunk] Настройка Port Fast](/img/thumbs/ffb65df580df43bebf8c96180d1cecb6-800x.jpg)