Слайд 1Computation and Problem Solving
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
Korzhumbayev Azamat
Слайд 2Values - Colors
Colors
is either a keyword (e.g. white, red),
or a numerical RGB notation.
A numerical RGB notation can be:
An
RGB value in hexadecimal notation, which is a ‘#’ immediately followed by a 6 digit or 3 digit hexadecimal number
E.g. #ff0000, #f00
An RGB value in functional notation
E.g. rgb(255,0,0), rgb(100%,0%,0%)
Слайд 3Values - Lenghts
Lengths can be
Relative
em (font size of the relevant
font),
ex (x-height of the relevant font),
% etc.
Absolute
px *(pixels),
in (inches), cm, mm,
pt (points, =1/72 in), pc (picas, 1 pc = 12 pt)
Note: no space between number and length notation
Слайд 4CSS Background
Background-color : color;
Background-image : url (‘URL’);
Background-repeat : repeat-x,repeat-y, no-repeat;
Background-attachment
: fixed, local
Background-position : left top, left bottom, etc.
Background: red
url(‘smiley.jpg’) no-repeat fixed 50% 50%;
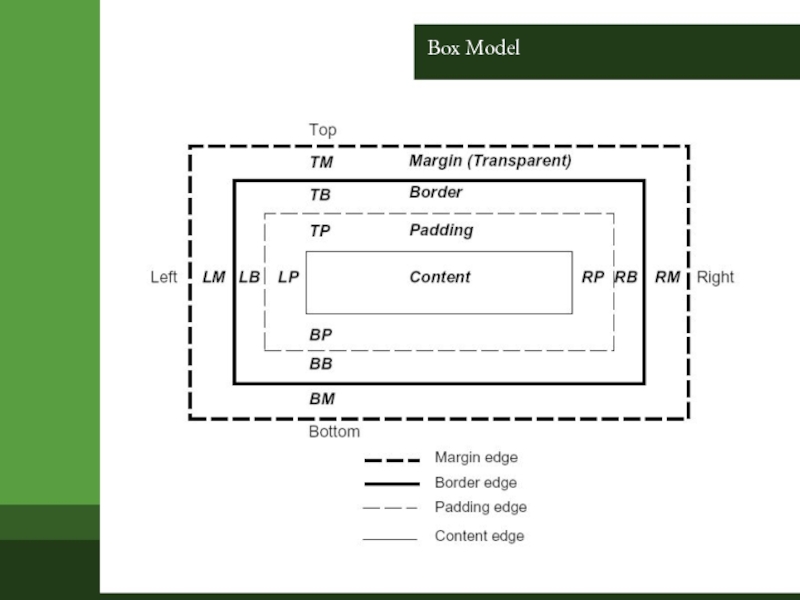
Слайд 5Box Properties
margin :
border :
padding :
content
width & height :
Example:
p{
margin: 50px;
padding: 30px;
float: right;
height: 200px;
width: 400px;
border:
5px solid #006633;
}
Слайд 7Border property
Border-style : dotted ,dashed, solid, double, groove, ridge, inset, outset,
none, hidden
Border-width : thin, medium, thick/px, etc.
Border-color : transparent/colors
Border :
dashed 10px red;
Border-radius : cm, px, etc.
Слайд 8Margin property
Margin-top : auto, length, %, inherit
Margin-right : auto, length,
%, inherit
Margin-bottom : auto, length, %, inherit
Margin-left : auto, length,
%, inherit
Margin :
Слайд 9Padding property
Padding-top : auto, length, %, inherit
Padding-right : auto, length,
%, inherit
Padding-bottom : auto, length, %, inherit
Padding-left : auto, length,
%, inherit
Padding :
Слайд 10Outline property
Outline-style : dotted ,dashed, solid, double, groove, ridge, inset, outset,
none, hidden
Outline-width : thin, medium, thick/px, etc.
Outline-color : invert, colors
Outline
: dashed 10px red;
Слайд 11Text Properties
font-family : , |
font-size :
| | inherit
font-weight : normal | bold | lighter
| 100 | 200
normal = 400, bold = 700, lighter is relative
font-style : normal | italic | oblique | inherit
line-height : normal |
| | inherit
text-transform : capitalize | uppercase | lowercase | none | inherit
text-decoration : overline | underline | line-through
color :
text-indent : | | inherit
text-align : left | right | center | justify | inherit
Слайд 12CSS Links
Links can be styled with any css property (color,
background-color, font-family etc.) and have 4 states which can also
be styled:
a:link : normal unvisited link
a:visited : visited link
a:hover : link when user mouses over it. MUST come after :link and :visited
a:active : link at the moment when it’s clicked. MUST come after :hover
Слайд 13List Properties
list-style: [disc | circle | square | decimal |
lower-roman | upper-roman | lower-alpha | upper-alpha | none] ||
[inside | outside] || [ | none]
Example
li { list-style: disc inside url(‘bullet2.gif’); }
Can use the list-style-type, list-style-position, list-style-image separately.
Слайд 14List Properties
Difference between inside and outside
Outside
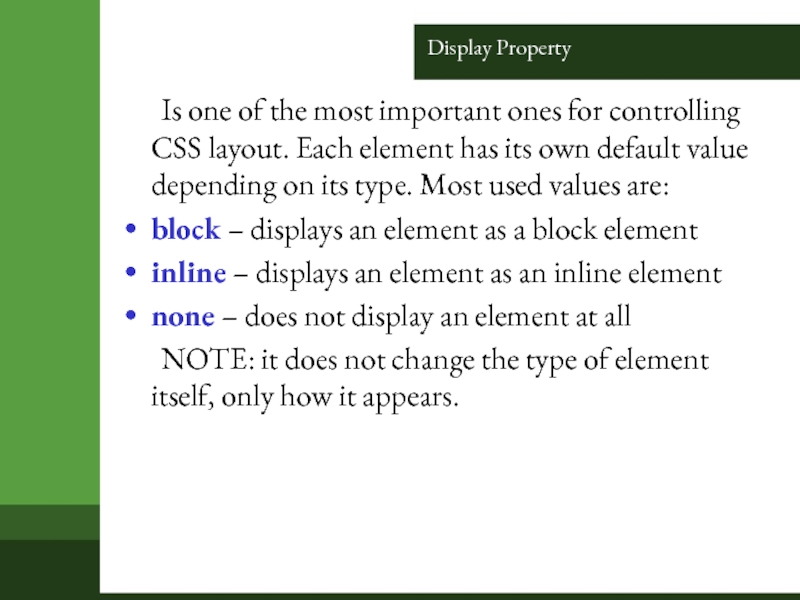
Слайд 15Display Property
Is one of the most important ones for controlling
CSS layout. Each element has its own default value depending
on its type. Most used values are:
block – displays an element as a block element
inline – displays an element as an inline element
none – does not display an element at all
NOTE: it does not change the type of element itself, only how it appears.
Слайд 16Positioning Properties
height : | % | inherit
width :
| % | inherit
max-width : | % |
inherit
left : | % | auto | inherit
top : | % | auto | inherit
right : | % | auto | inherit
bottom : | % | auto | inherit
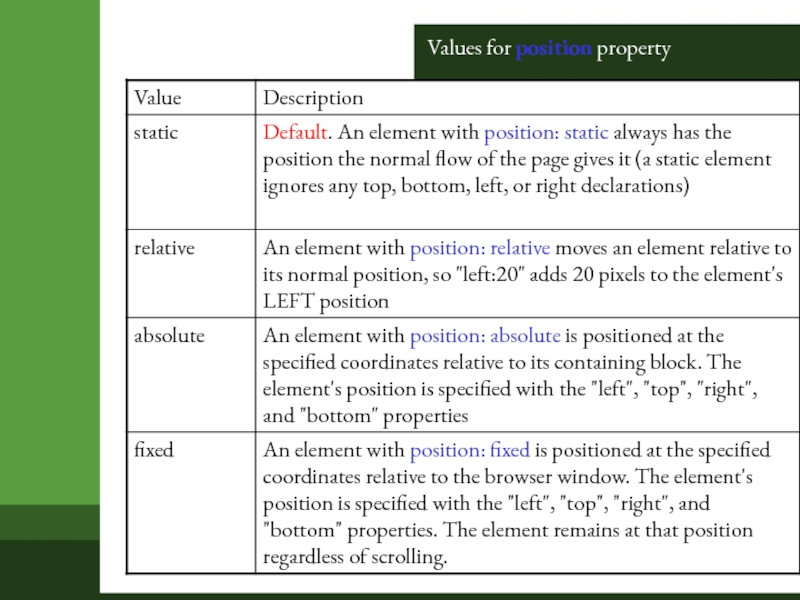
position : static | relative | absolute | fixed | inherit
left/top/right/bottom usually used when position is specified as absolute.
Слайд 18Z-index Property
When elements are positioned they can become overlapped. Z-index
property is used to specify the stack order.
Example
NOTE. If
two elements overlap without a z-index specified, the element positioned last in the HTML will be shown on top.
img {
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
z-index: -1;
}