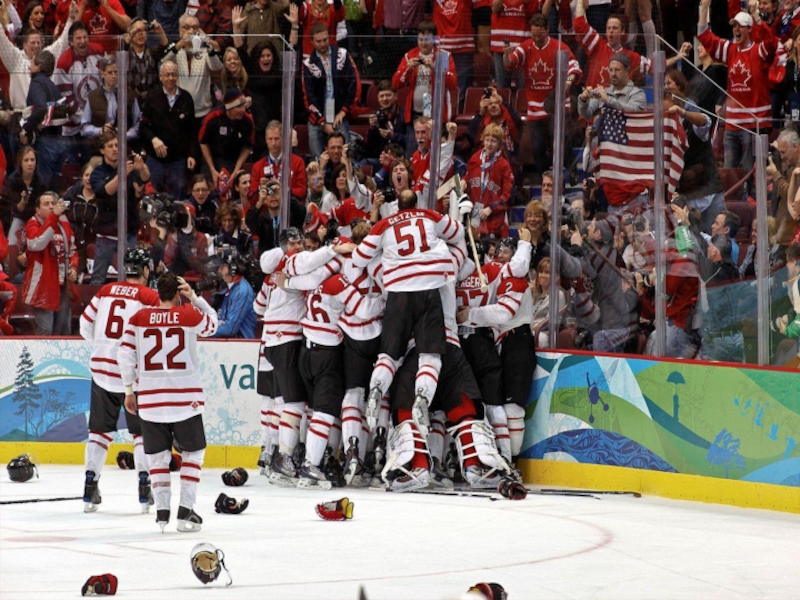
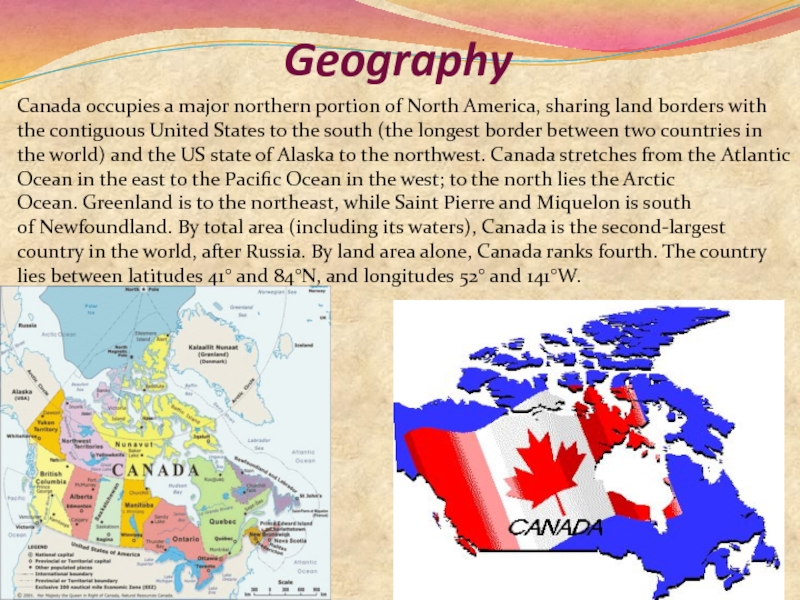
and three territories. Located in the northern part of the
continent, it extends from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean. At 9.98 million square kilometres in total, Canada is the world's second-largest country by total area and the fourth-largest country by land area. Its common border with the United States forms the world's longest land border.The land that is now Canada has been inhabited for millennia by various Aboriginal peoples. Beginning in the late 15th century, British and French colonies were established on the region's Atlantic coast. As a consequence ofvarious conflicts, the United Kingdom gained and lost North American territories until left, in the late 18th century, with what mostly comprises Canada today. Pursuant to the British North America Act, on July 1, 1867, three coloniesjoined to form the autonomous federal Dominion of Canada. This began an accretion of provinces and territories to the new self-governing Dominion. In 1931, Britain granted Canada near total independence with the Statute of Westminster 1931 and full sovereignty was attained when the Canada Act 1982 severed the vestiges of legal dependence on the British parliament.