Слайд 1Medical Academy Named after S. I. Georgievsky of Crimea Federal
University
Department of Dermatovenerology and Cosmetology
PhD. in Medical Sciences, Department of
Dermatovenerology and Cosmetology
Maraqa Мarwan Y.N
Мараках Марван Якин Нажи
Слайд 2Tertiary syphilis
Congenital syphilis.
Getting infection.
There are two routs of getting infection
through the placenta:
Treponema pallidum enters the foetus in the
form of an embole through the umbilical vein;
Treponema pallidum enters the foetus along the lymph slits of the umbilical cord.
Syphilitic infection as a rule causes definite changes in placenta: the increase in size, mass, changes in their correlation to 1:3-1:4, with normal 1:5-1:6.
Слайд 3Tertiary syphilis
Histopathotology
There are lesions of vessels and villi, especially
in the embryonal part of the placenta, mainly in its
central part. Proliferation of granulation tissue near the villi, the formation of micro-abscesses, and also endo-, meso- and perivasculitis of the vessels are characteristic for the congenital syphilis. It leads to the narrowing of vessels and complete obliteration, as the result of that the nutrition, trophic systems and metabolism are disturbed, what at the end becomes the reason of its death.
Слайд 4Tertiary syphilis
Classification of Congenital Syphilis
A. WHO classification:
1. Embryonal syphilis;
2.
Early congenital syphilis (up to 2 years);
-active;
-latent;
3. Late congenital syphilis
(after 2 years);
-active;
-latent;
Слайд 5Tertiary syphilis
Russian classification
1. Syphilis of the foetus;
2. Early congenital syphilis;
n
Congenital infantile syphilis(up to 1 year);
n Syphilis of early childhood
(1-4 years);
3. Late congenital syphilis (after 4 years).
Слайд 6Tertiary syphilis
Syphilis of the foetus
The affection of the foetus
by syphilis is revealed on the 5th month of intrauterine
life and is linked with the development of placenta blood circulation. Specific affections of the internal organs of the foetus are mainly of diffuse inflam-matory character. The liver, spleen, the lungs and kidneys are the first to be damaged because of their early development. The liver enlarges, mass correlation of liver and body becomes 1:15-1:14, normally 1:21, histologically: minor cell infiltration, desquamation of the alveolar epithelium, growth of fibrous tissues in the interalveolar spaces. Such changes in the lungs usually do not combine with life-pneumonia alba. A syphilitic child has a characte-ristic look: wrinkled and flabby - “A small old man”, the pallor of skin tissues with a grey hue is macerated, turgor of skin tissues is reduced, which leads to the formation of wrinkles, insufficient development of hypodermic cellulose, it looks like hypertrophia, usually the child is flabby, or extremely excited due to the increase of the blood skull pressure.

Слайд 7Tertiary syphilis
Congenital syphilis of the newborn
There are characteristics of
this or that period of syphlilis:
1. Syphilitic rhinitis;
2. Hochsinger’s
diffuse papular infiltration;
3. Syphilitic pemphigus of the newborn;
4. Veginer’s osteohondritis.
Слайд 8Tertiary syphilis
Three stages of syphilitic rhinitis
The 1st - there
is a mild swelling of the mucous membranes, nasal breathing
becomes difficult, the child is as if sniffing when he breathes through the nose;
The 2nd - more considerable swelling and more difficult nasal breathing, copious serous-purulent secretions from the nose cavity, what leads to the maceration of surrounding tissues;
The 3rd - the most difficult stage, when not only cartilaginous but also bony tissue of the nose, i.e. erosions, ulcers are formed on the mucous membrane, serous-purulent secretions become purulent haemorrhagic and sequestration is possible, discharging of cartilaginous and bony sequesters through the nose routs with further formation of one of the most evident features of late congenital syphilis-goat-like (saddle-black, opera-glass) nose.
Syphilitic rhinitis is a very often manifestation and a child can be born with it, or it may develop during the first days, weeks or months.
Слайд 9Tertiary syphilis
Hochsinger’s diffuse papular infiltration
Hochsinger’s diffuse papular infiltration appears on
the 8th or 9th week after birth, favourite localisation: palms,
soles, face and hairy part of the head. First diffuse erythema or several erythematous spots appear, which tend to coalesce. The skin here thickens, namely the skin on the palms and soles becomes smooth, infiltrated, dark-red, glittering, wrinkles smooth out ,elasticity is lost and the process ends in laminar scaling.
Слайд 10Tertiary syphilis
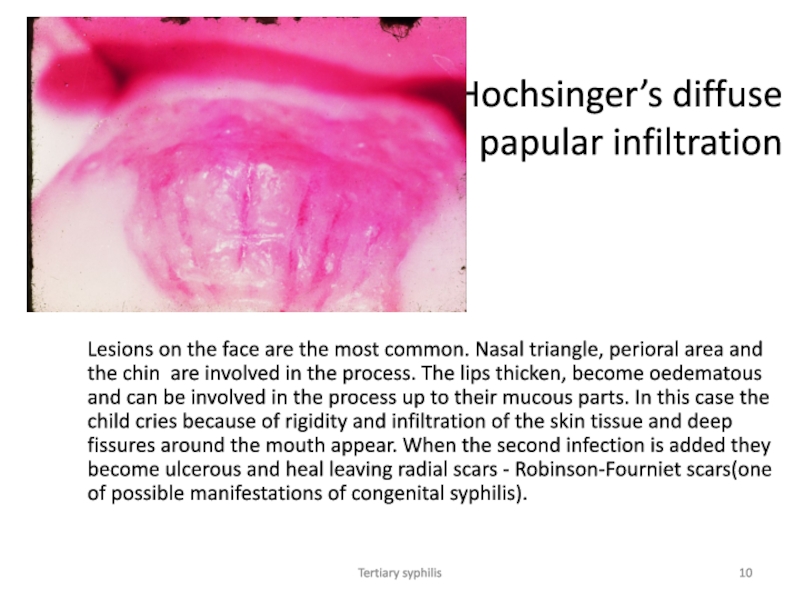
Hochsinger’s diffuse papular infiltration
Lesions on the face are the
most common. Nasal triangle, perioral area and the chin are
involved in the process. The lips thicken, become oedematous and can be involved in the process up to their mucous parts. In this case the child cries because of rigidity and infiltration of the skin tissue and deep fissures around the mouth appear. When the second infection is added they become ulcerous and heal leaving radial scars - Robinson-Fourniet scars(one of possible manifestations of congenital syphilis).
Слайд 11Tertiary syphilis
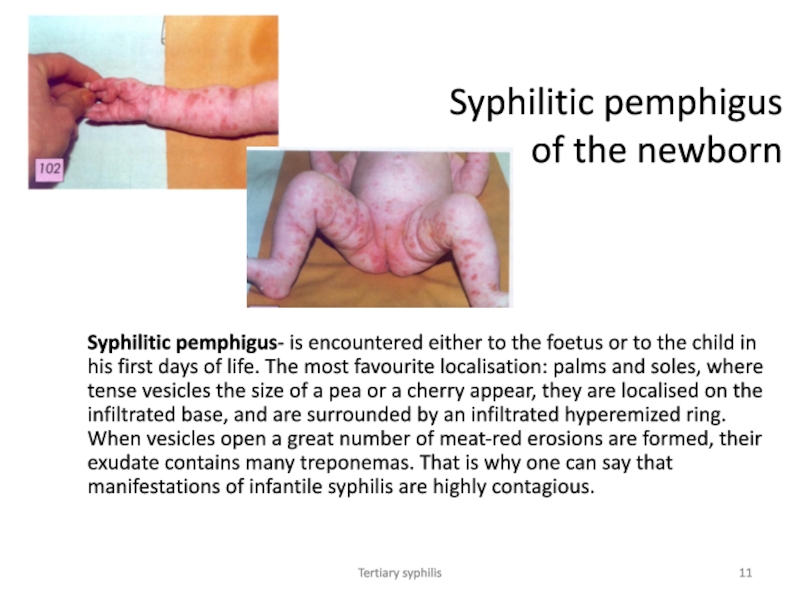
Syphilitic pemphigus of the newborn
Syphilitic pemphigus- is encountered either
to the foetus or to the child in his first
days of life. The most favourite localisation: palms and soles, where tense vesicles the size of a pea or a cherry appear, they are localised on the infiltrated base, and are surrounded by an infiltrated hyperemized ring. When vesicles open a great number of meat-red erosions are formed, their exudate contains many treponemas. That is why one can say that manifestations of infantile syphilis are highly contagious.
Слайд 13Tertiary syphilis
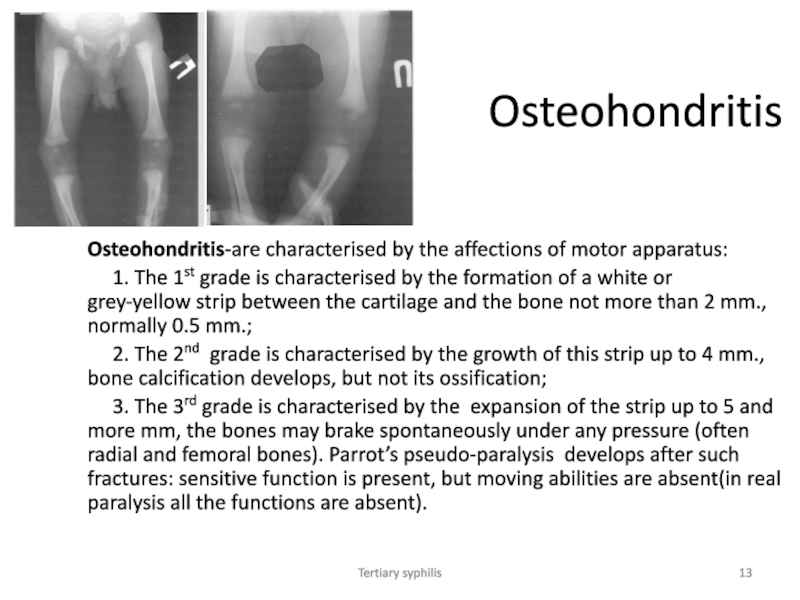
Osteohondritis
Osteohondritis-are characterised by the affections of motor apparatus:
1. The 1st grade is characterised by the formation
of a white or grey-yellow strip between the cartilage and the bone not more than 2 mm., normally 0.5 mm.;
2. The 2nd grade is characterised by the growth of this strip up to 4 mm., bone calcification develops, but not its ossification;
3. The 3rd grade is characterised by the expansion of the strip up to 5 and more mm, the bones may brake spontaneously under any pressure (often radial and femoral bones). Parrot’s pseudo-paralysis develops after such fractures: sensitive function is present, but moving abilities are absent(in real paralysis all the functions are absent).
Слайд 14Tertiary syphilis
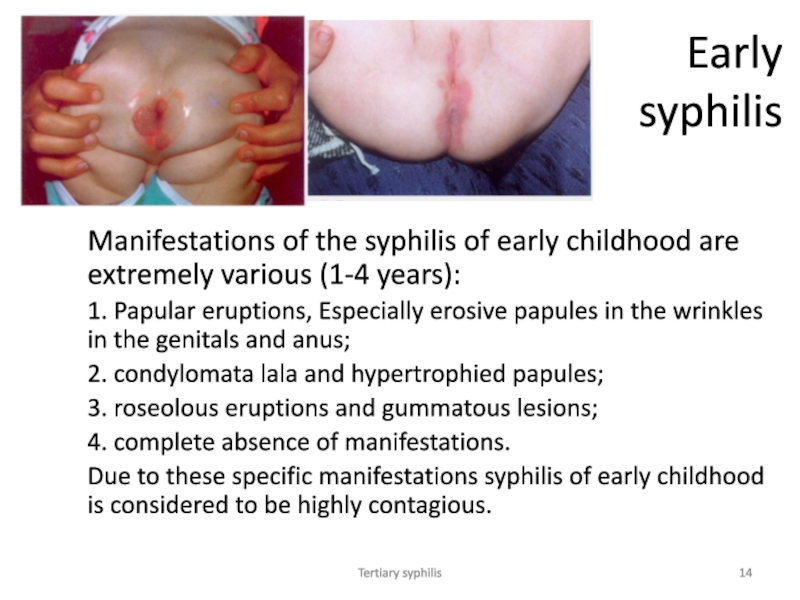
Early syphilis
Manifestations of the syphilis of early childhood are
extremely various (1-4 years):
1. Papular eruptions, Especially erosive papules
in the wrinkles in the genitals and anus;
2. condylomata lala and hypertrophied papules;
3. roseolous eruptions and gummatous lesions;
4. complete absence of manifestations.
Due to these specific manifestations syphilis of early childhood is considered to be highly contagious.
Слайд 15Tertiary syphilis
Late syphilis
Late congenital syphilis is diagnosed in children at
the age of 15-17 years, though it should be mentioned
that manifestations of late congenital syphilis can be traced much later(25-30 years). Symptoms of late congenital syphilis are various and they all are divided into different groups:
Слайд 16Tertiary syphilis
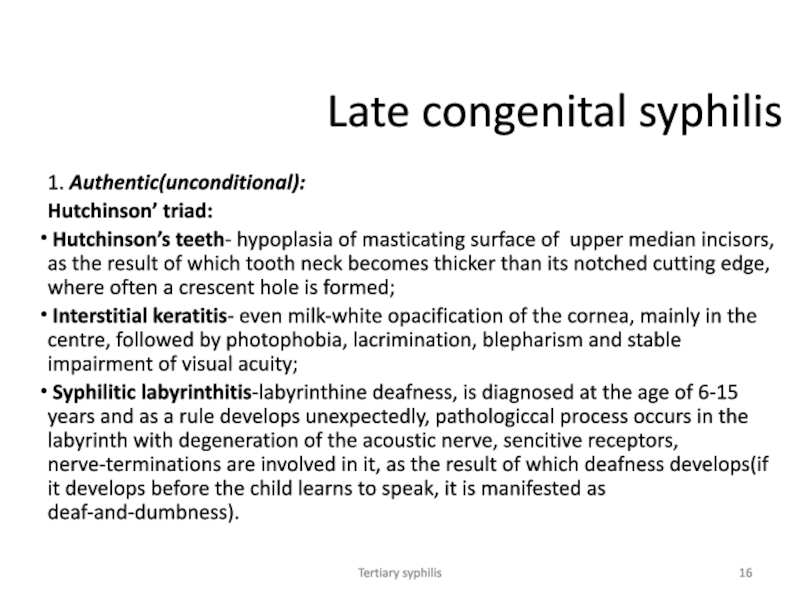
Late congenital syphilis
1. Authentic(unconditional):
Hutchinson’ triad:
Hutchinson’s teeth- hypoplasia of
masticating surface of upper median incisors, as the result of
which tooth neck becomes thicker than its notched cutting edge, where often a crescent hole is formed;
Interstitial keratitis- even milk-white opacification of the cornea, mainly in the centre, followed by photophobia, lacrimination, blepharism and stable impairment of visual acuity;
Syphilitic labyrinthitis-labyrinthine deafness, is diagnosed at the age of 6-15 years and as a rule develops unexpectedly, pathologiccal process occurs in the labyrinth with degeneration of the acoustic nerve, sencitive receptors, nerve-terminations are involved in it, as the result of which deafness develops(if it develops before the child learns to speak, it is manifested as deaf-and-dumbness).
Слайд 17Tertiary syphilis
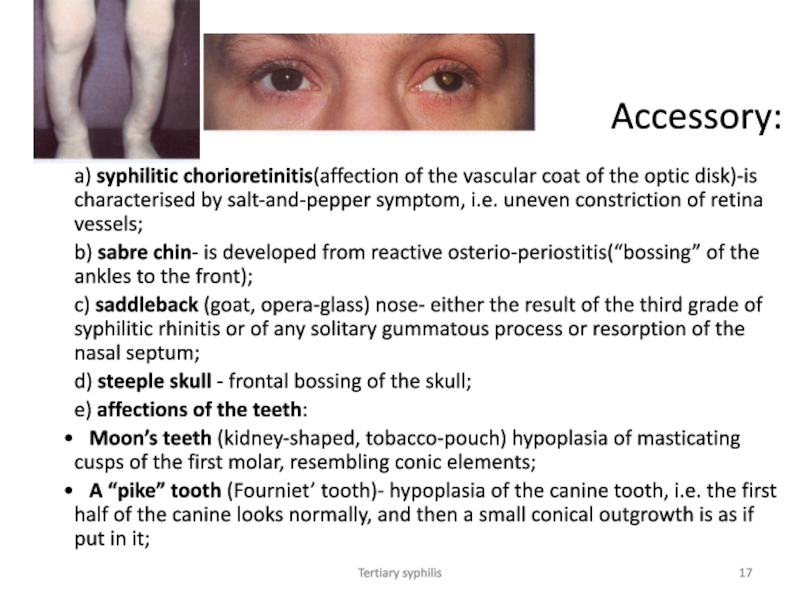
Accessory:
a) syphilitic chorioretinitis(affection of the vascular coat of the
optic disk)-is characterised by salt-and-pepper symptom, i.e. uneven constriction of
retina vessels;
b) sabre chin- is developed from reactive osterio-periostitis(“bossing” of the ankles to the front);
c) saddleback (goat, opera-glass) nose- either the result of the third grade of syphilitic rhinitis or of any solitary gummatous process or resorption of the nasal septum;
d) steeple skull - frontal bossing of the skull;
e) affections of the teeth:
Moon’s teeth (kidney-shaped, tobacco-pouch) hypoplasia of masticating cusps of the first molar, resembling conic elements;
A “pike” tooth (Fourniet’ tooth)- hypoplasia of the canine tooth, i.e. the first half of the canine looks normally, and then a small conical outgrowth is as if put in it;
Слайд 18Tertiary syphilis
Stigmata (dystrophies):
Avsitidiisky-Higoumenakia’s sign- thickening of the sternal
end of the clavicle at the place of crossing with
the first rib often on the right;
gothic(high, lancet-like) hard palate;
axiphoidia- absence of the sternal xiphoid outgrowth;
Goshe’s diastema- gaps between the upper incisors;
Dubois-Gissard’s sign(infantile little finger)- the crease of the distal joint of a little finger is below the crease of the middle joint of the middle finger and is a little turned inward;
racket-like nails(Vishnevsky’s sign)- the nails on the thumbs resemble a tennis rocket;
Carabelli’s cusps- the presence of the fifth aditional cusp on the masticatory surface of the first molar;
hypertrichosis- growth of the hair mainly encountered in females, a more characteristic symptom is bolding of the hair, the border of the hairy part of the head comes closer to the eye-brows in the form of a wedge.