etc.
TCR, BRC
Some cytokines (interferons), sometimes GFs
DNA damage
Hyper- or hypoosmolarity,
UV, pro- or antioxidants, heat shock
Some GPCR ligands
Kinase inhibitors
Pro-apoptotic pathways
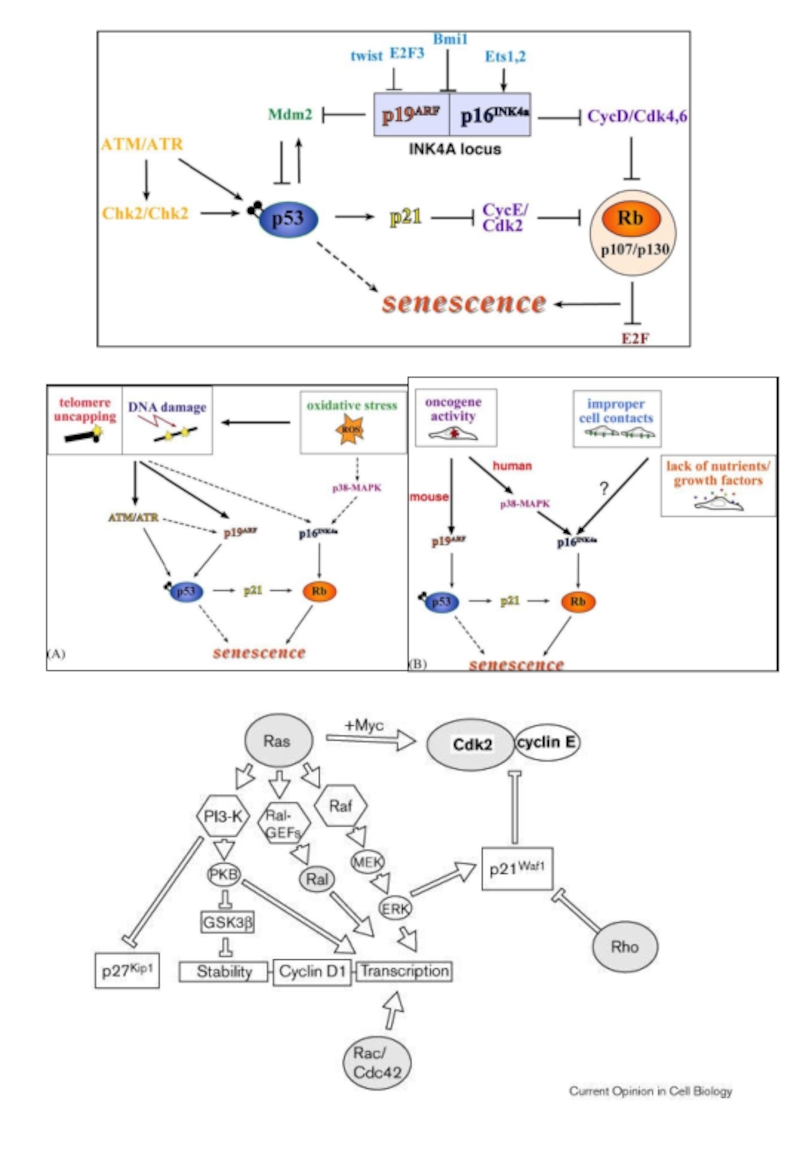
p53
p38, JNK (not always), upstream kinases (MEKK)
Crk
Ras (not always)
GSK3β
FoxO
STAT1, STAT2
PKCδ
Ceramide
Anti-apoptotic stimuli
Serum
Growth factors (especially IGF-1 and insulin),
some cytokines
Cell-matrix adhesion
TNF-family (all DD(-) receptors + some DD(+) )
CD19, CD28 etc. ligands
Some GPCR ligands
Caspase inhibitors
Anti-apoptotic pathways
PI-3 kinase, Akt-PKB
NFkB (not always)
ERK (not always), Raf, JNK (sometimes); AP-1
Ras (not always)
Most PKC isoforms
PKA
STAT3, STAT5
hsp70, hsp90, hsp27
p21waf1
Proliferative stimuli
Serum
Growth factors, some cytokines
Some GPCR ligands (especially LPA)
Cell-matrix adhesion
Steroid hormones
Proliferative pathways
GF receptors
Non-receptor tyrosine kinases
Ras
ERK, sometimes JNK
TCF, SRF, AP-1 (c-jun, c-fos) transcription factors
PI-3 kinase
Moderate ROS
PKC (various isoforms), often Ca
PKA (not always)
Integrins
Stimulators of actin membrane targeting and polymerisation
Rho family GTPases
c-myc, E2F
β-catenin, STAT3, STAT5
Anti-proliferative stimuli
Proliferative signals (serum, GF, adhesion etc) withdrawal
Cell-cell adhesion
TGFβ (not always)
Some cytokines (interferons), sometimes GFs
DNA damage, telomere shortening
Hyperosmolarity, UV, pro- or antioxidants, heat shock
Some GPCR ligands
Inhibitors of DNA or dNTP synthesis
Tubulin-reactive drugs
Oncogene activation (not always)
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Anti-proliferative pathways
p53
High and prolonged Ras or ERK
STAT1, STAT2
Smad 2, 3, 4
GSK3β
PKA (sometimes), PKC δ
JNK, p38
Telomere shortening
Bcl-2